Hair Alteration Methods
Meaning ❉ Hair Alteration Methods encompass intentional modifications to hair's structure or appearance, serving as a profound link to cultural heritage and identity for textured hair.

Black Aesthetic
Meaning ❉ The Black Aesthetic is a cultural framework of beauty and self-expression, deeply woven into the heritage of textured hair, signifying identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom.

What minerals in clay benefit hair heritage?
Clay minerals cleanse and nourish textured hair, reflecting ancient practices for strength and vitality across diverse heritage traditions.
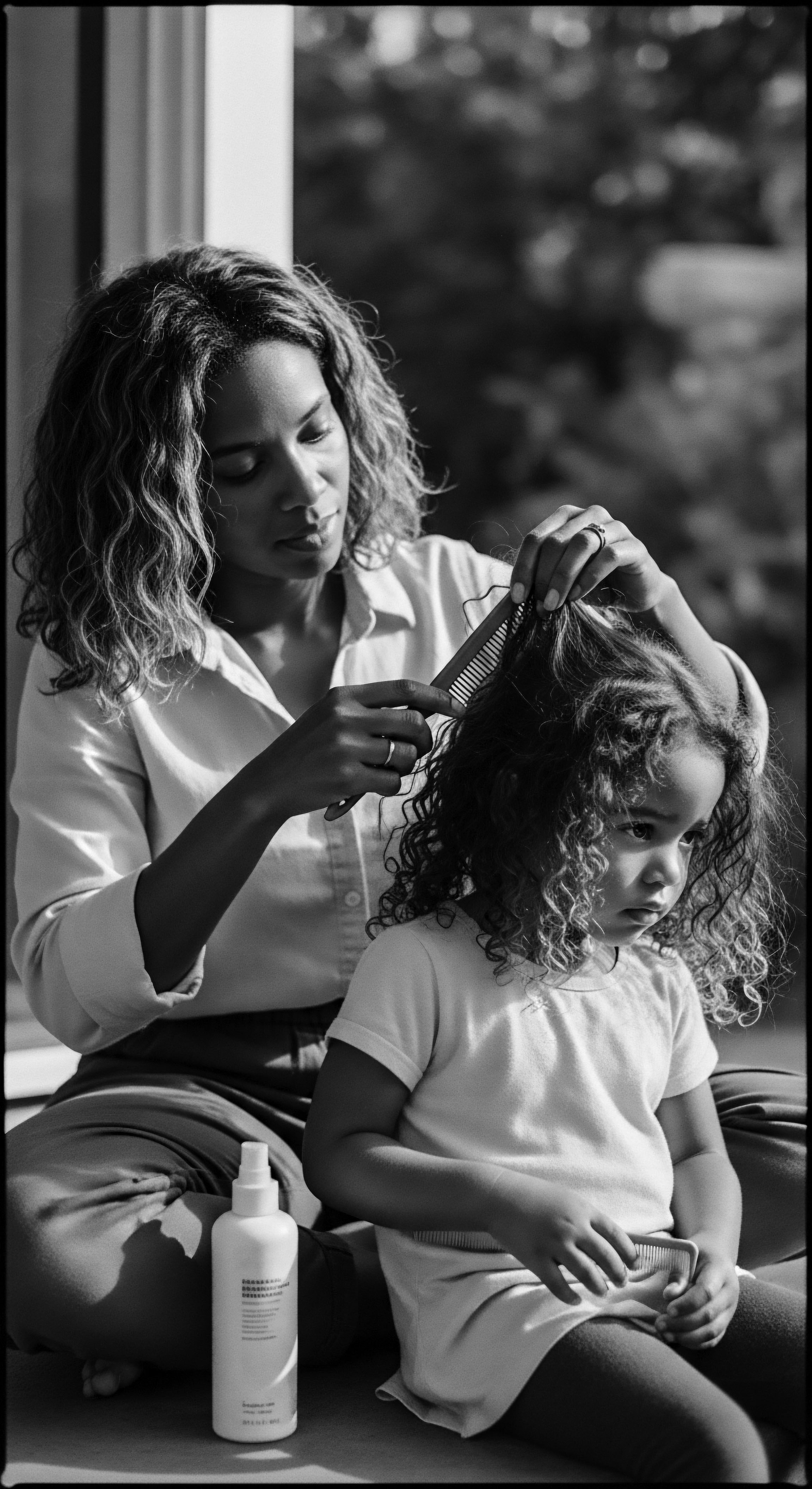

In what ways do historical West African hair cleansing practices connect to cultural identity today?
Historical West African hair cleansing practices remain deeply intertwined with modern cultural identity, offering a powerful ancestral connection for textured hair heritage.

Racial Pride Movement
Meaning ❉ The Racial Pride Movement signifies a collective reclamation and celebration of one's racial identity, profoundly expressed through textured hair heritage.
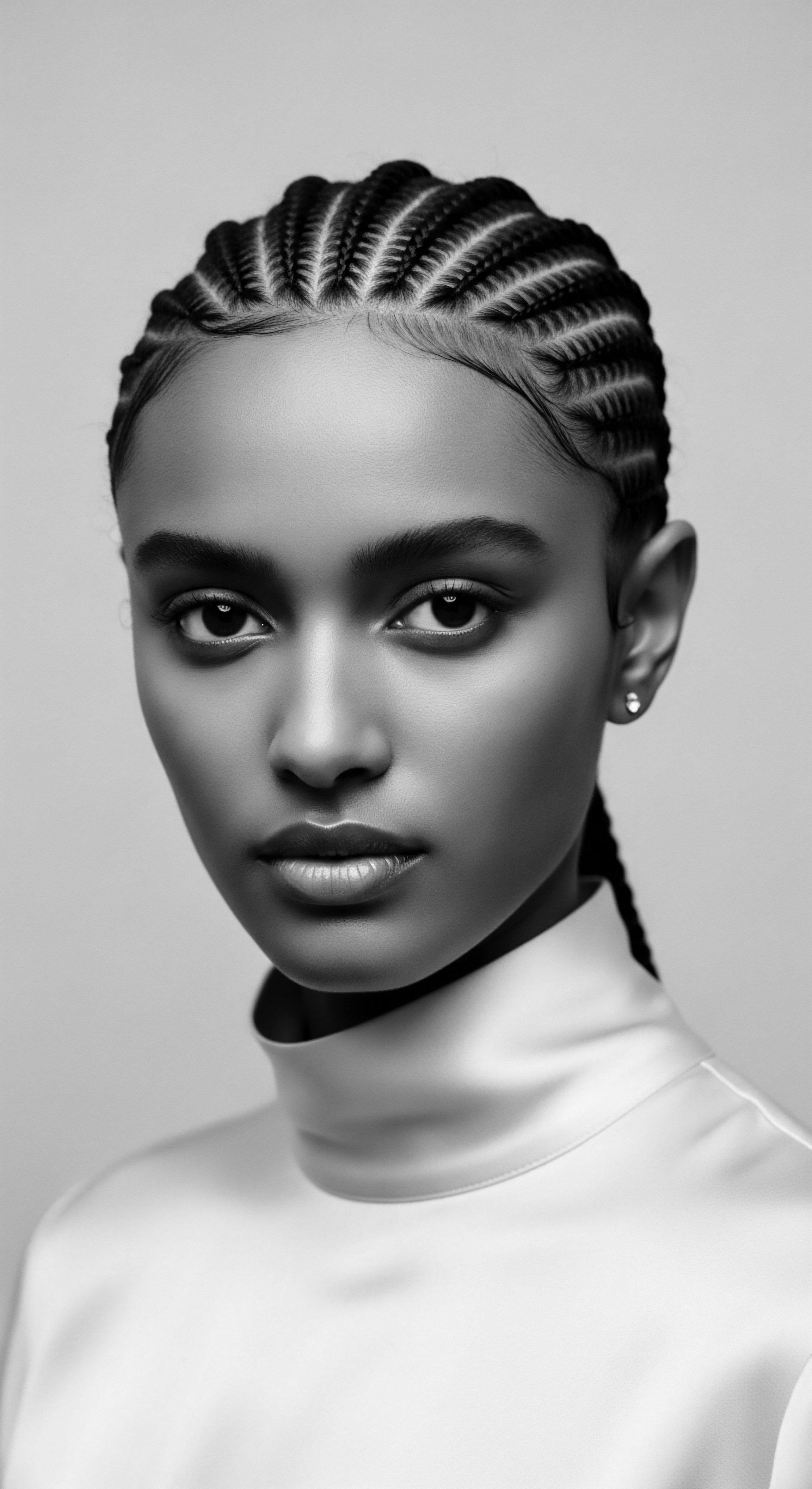

What ancestral ingredients enhance cornrow durability and hair health?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and Chebe powder enhance cornrow durability by providing deep moisture and protection, rooted in textured hair heritage.

Black Self-Reliance
Meaning ❉ Black Self-Reliance signifies the innate capacity of Black communities to define their reality and well-being through cultural ingenuity and collective strength.

How do communal rituals preserve shea butter’s hair care heritage?
Communal rituals safeguard shea butter's hair care heritage by transmitting ancestral knowledge and fostering collective identity for textured hair.

What historical West African cleansing plants are used today?
Historical West African cleansing plants like African Black Soap, Moringa, and Hibiscus are used today, connecting modern hair care to textured hair heritage.

In what ways did enslaved Africans preserve heritage through hair practices?
Enslaved Africans preserved heritage through hair practices by transforming styling into covert communication, a symbol of resistance, and a vessel for cultural memory.

How does hair heritage influence cleansing choices?
Hair heritage informs cleansing choices by guiding preferences for gentle, moisture-preserving methods and natural ingredients.

Which botanicals from African heritage support hair vitality and growth?
African heritage offers botanicals like Shea butter, Baobab oil, and Chebe powder, historically used to moisturize, strengthen, and protect textured hair.
How did historical African hair care practices preserve moisture?
Historical African hair care preserved moisture through occlusive ingredients, protective styling, and routine care.

What is the heritage of African hair practices?
African hair practices are a timeless legacy of identity, resilience, and care deeply embedded in textured hair heritage.

Which ancestral plants offer deep moisture for coily hair?
Ancestral plants such as shea butter, aloe vera, slippery elm, and okra offer deep moisture for coily hair, rooted in heritage.

How did heritage shape traditional textured hair care?
Heritage shaped traditional textured hair care by embedding practices in ancient cultural meaning, communal ritual, and protective necessity.

How does textured hair heritage shape modern care principles?
Textured hair heritage shapes modern care principles by grounding them in ancestral practices of moisture, protection, and identity preservation.

How do traditional African botanicals validate modern scientific understanding of hair?
Traditional African botanicals offer scientific validation for textured hair health, linking ancestral wisdom to modern understanding.
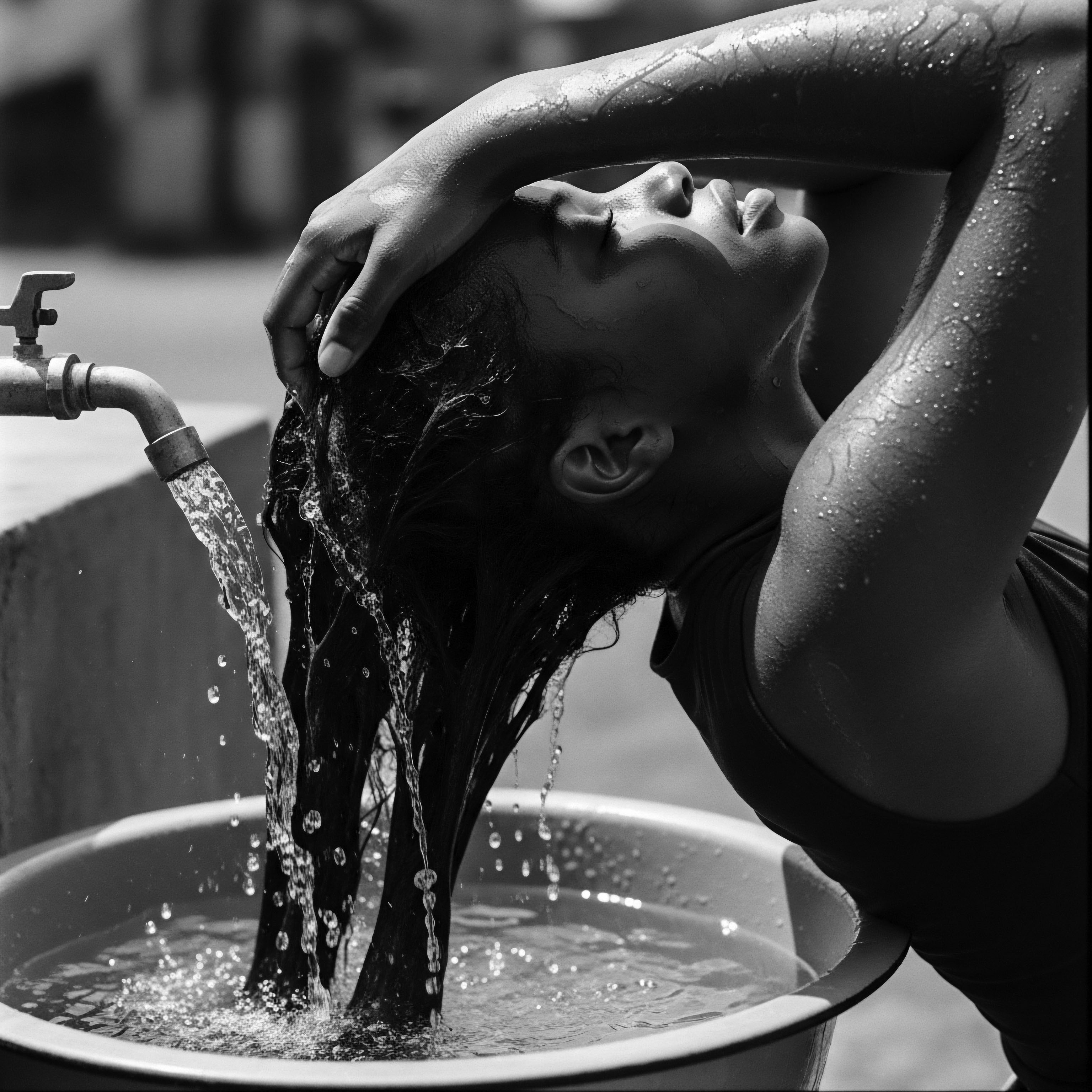

What natural ingredients did ancient cultures use for hair cleansing?
Ancient cultures utilized plant-based saponins, mineral clays, and acidic rinses for gentle hair cleansing, directly supporting textured hair heritage.

What is the spiritual meaning of hair in textured hair heritage?
Textured hair's spiritual meaning in heritage connects individuals to ancestry, identity, and cosmic order through sacred practices.

What oils did ancient Egyptians use for hair health?
Ancient Egyptians used oils like castor, moringa, and sesame to condition and protect textured hair, a practice echoing through Black and mixed-race hair heritage today.

What plant-based emollients were staples in traditional textured hair heritage?
Traditional textured hair heritage relied on plant-based emollients like shea butter, castor oil, and coconut oil for their deeply nourishing and protective qualities.

How did ancient Egyptian oils strengthen hair?
Ancient Egyptian oils strengthened hair by providing hydration and protection, a heritage of care particularly beneficial for textured strands.

Traditional African Braids
Meaning ❉ Traditional African Braids are ancient, culturally rich hairstyles signifying identity, social status, and spiritual connection for textured hair.

How have legal frameworks adapted to protect textured hair heritage today?
Legal frameworks are adapting to protect textured hair heritage by prohibiting discrimination based on natural hair and cultural styles.

In what ways do historical hair rituals connect to modern hair wellness?
Historical hair rituals for textured hair serve as the blueprint for modern wellness practices, deeply connecting contemporary care to ancestral knowing and cultural resilience.

How did slave diets impact hair?
Slave diets, critically deficient in vital nutrients, led to brittle, thin, and dull hair, impacting its appearance and growth, a legacy shaping textured hair heritage.

What is the cultural significance of hair porosity in Black communities?
Hair porosity holds profound cultural weight in Black communities, guiding traditional care and styling that honors textured hair heritage.

What ancestral ingredients support hair health today?
Ancestral ingredients, rooted in earth's wisdom, continue to nourish textured hair by offering natural solutions for strength and moisture.

