What historical oils help textured hair?
Historical oils like shea butter, castor oil, and coconut oil, used for millennia, represent foundational heritage for textured hair care.

Keratin Use
Meaning ❉ Keratin use encompasses understanding and applying treatments that interact with hair's protein structure, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

Can historical plant-based cleansing practices offer lessons for contemporary textured hair wellness?
Historical plant-based cleansing practices offer profound heritage-infused lessons for contemporary textured hair wellness.

Soil Enrichment
Meaning ❉ Soil Enrichment for textured hair is the deliberate replenishment of elements for scalp and hair fiber vitality, rooted in ancestral wisdom and scientific understanding.

How does genetics determine textured hair type?
Genetics primarily determines textured hair type through the inherited shape of the hair follicle and the expression of specific genes influencing protein structures, a legacy reflected in ancestral hair heritage.

Water Cleaning
Meaning ❉ Water Cleaning involves the purification and hydration of textured hair, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and the unique structural needs of curls, coils, and kinks.

Neolithic Hair
Meaning ❉ Neolithic Hair describes the intrinsic characteristics and early human interactions with hair during the ancient Neolithic period, deeply connected to ancestral hair practices.
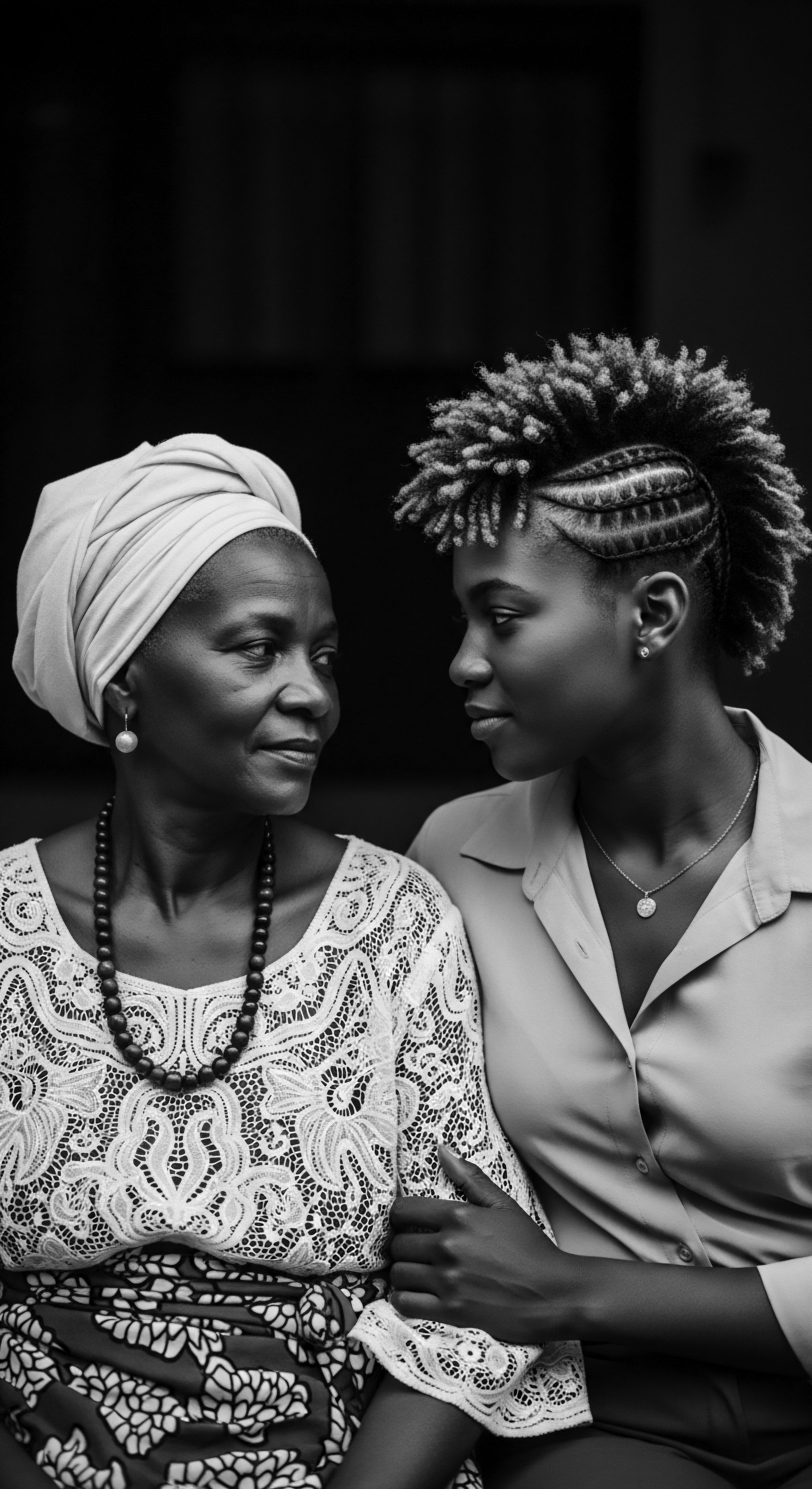
Can traditional hair practices offer solutions for modern textured hair care challenges?
Traditional hair practices offer powerful, heritage-rooted solutions for modern textured hair care challenges by emphasizing holistic wellness.

What historical botanical ingredients benefited textured hair?
Historical botanical ingredients, from oils to clays, offered moisture, strength, and cleansing, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

What traditional African practices guarded textured hair from sun exposure?
Traditional African practices guarded textured hair from sun through natural oils, specific hairstyles, and symbolic head coverings, embodying a rich heritage of environmental adaptation.
What is the cultural background of shea butter in textured hair care?
Shea butter’s cultural background in textured hair care is rooted in centuries of West African heritage, communal practices, and ancestral wisdom.

What historical cleansing agents respected textured hair’s moisture needs?
Historical cleansing agents for textured hair often included saponin-rich plants and mineral clays, which gently purified while preserving vital moisture and honoring ancestral wisdom.

Human Identity Definition
Meaning ❉ Human identity definition involves a complex interplay of genetic, cultural, historical, and psychological elements, profoundly shaped by textured hair heritage.

Can traditional Amazonian rituals benefit modern textured hair routines?
Traditional Amazonian rituals offer ancestral botanical wisdom that can nourish modern textured hair routines, deepening connection to heritage.

Do natural plant washes clarify textured hair?
Natural plant washes, rich in saponins, gently clarify textured hair by lifting buildup while preserving moisture, honoring centuries of ancestral heritage.

Olkaria Pigment
Meaning ❉ Olkaria Pigment represents an ancestral vital force imparting resilience and vibrancy to textured hair, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and natural elements.

How ancient grooming tools shaped textured hair care?
Ancient grooming tools profoundly shaped textured hair care by establishing ancestral practices of protection, styling, and cultural expression.

What scientific principles support traditional textured hair care practices?
Ancestral textured hair care methods align with modern scientific principles by prioritizing moisture, protection, and gentle manipulation, rooted in deep heritage knowledge.

Maasai Ochre Heritage
Meaning ❉ Maasai Ochre Heritage defines the cultural legacy of using red earth pigments and fats for traditional hair care and identity expression.
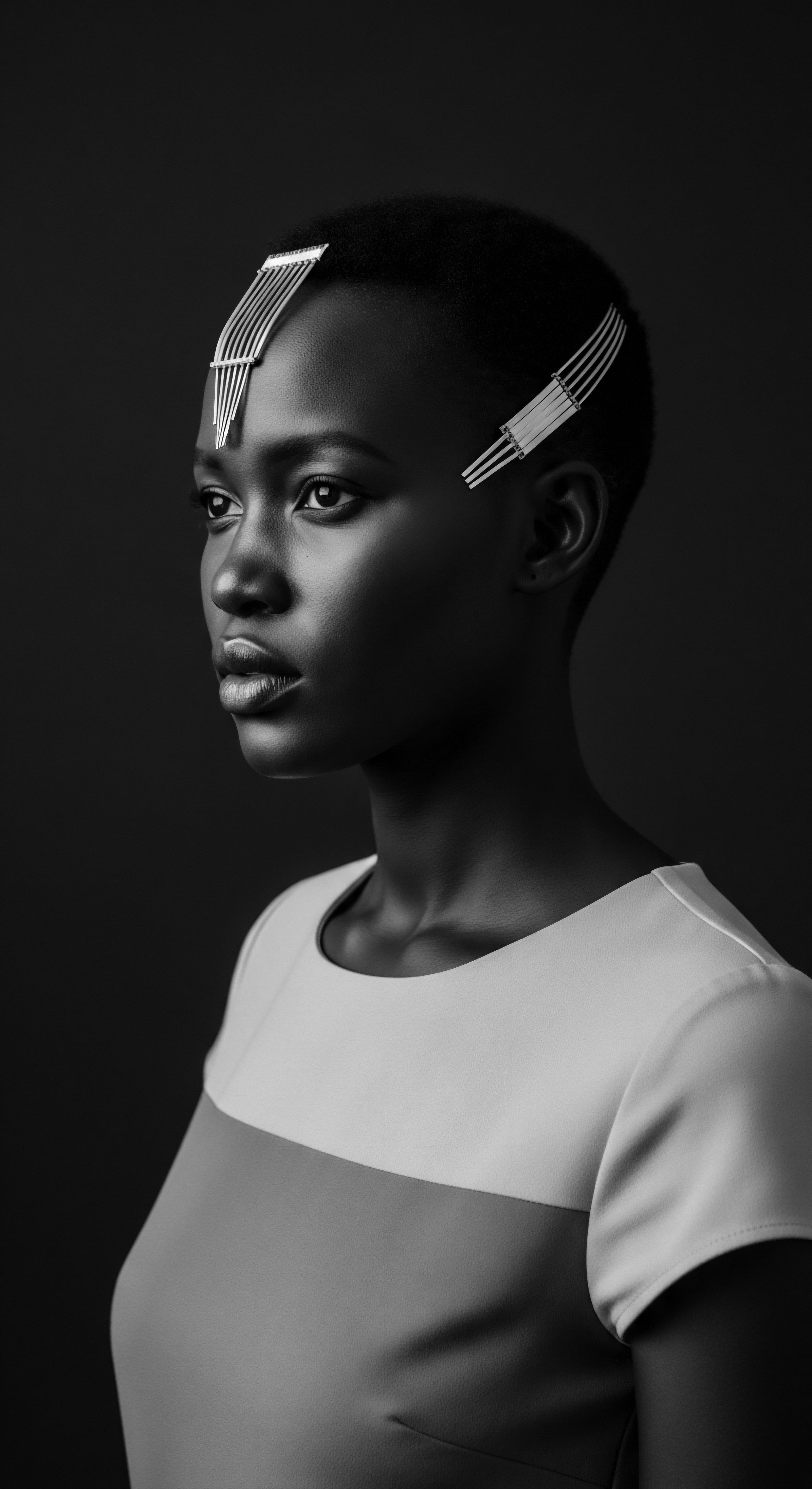

In what ways did textured hair symbolize status in pre-colonial societies?
Textured hair in pre-colonial societies was a sophisticated visual language, signifying social rank, marital status, age, and spiritual connection, deeply reflecting cultural heritage.
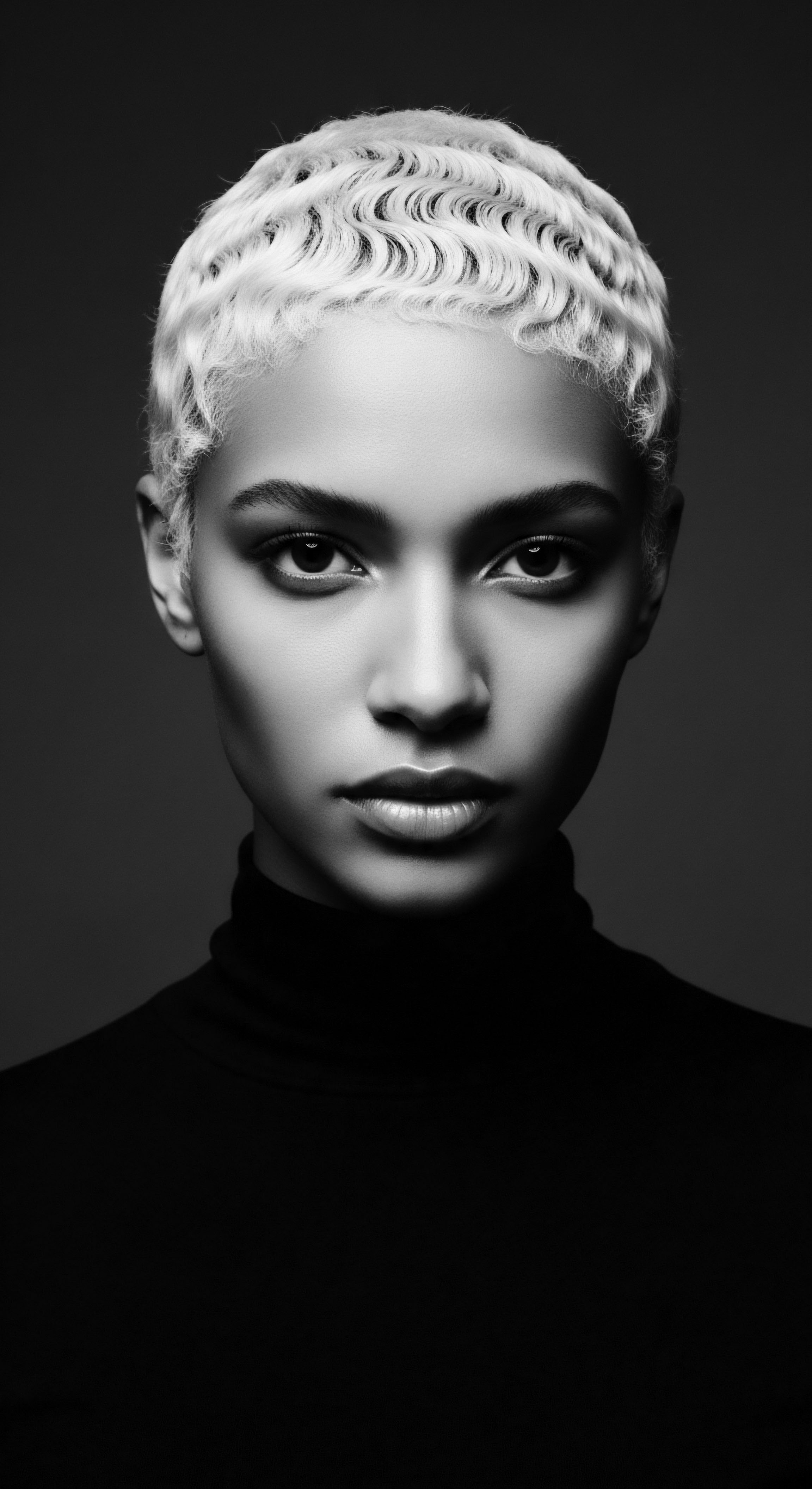

Native American Foodways
Meaning ❉ Native American Foodways represents a sophisticated system of practices and knowledge connecting Indigenous peoples to their sustenance and heritage.
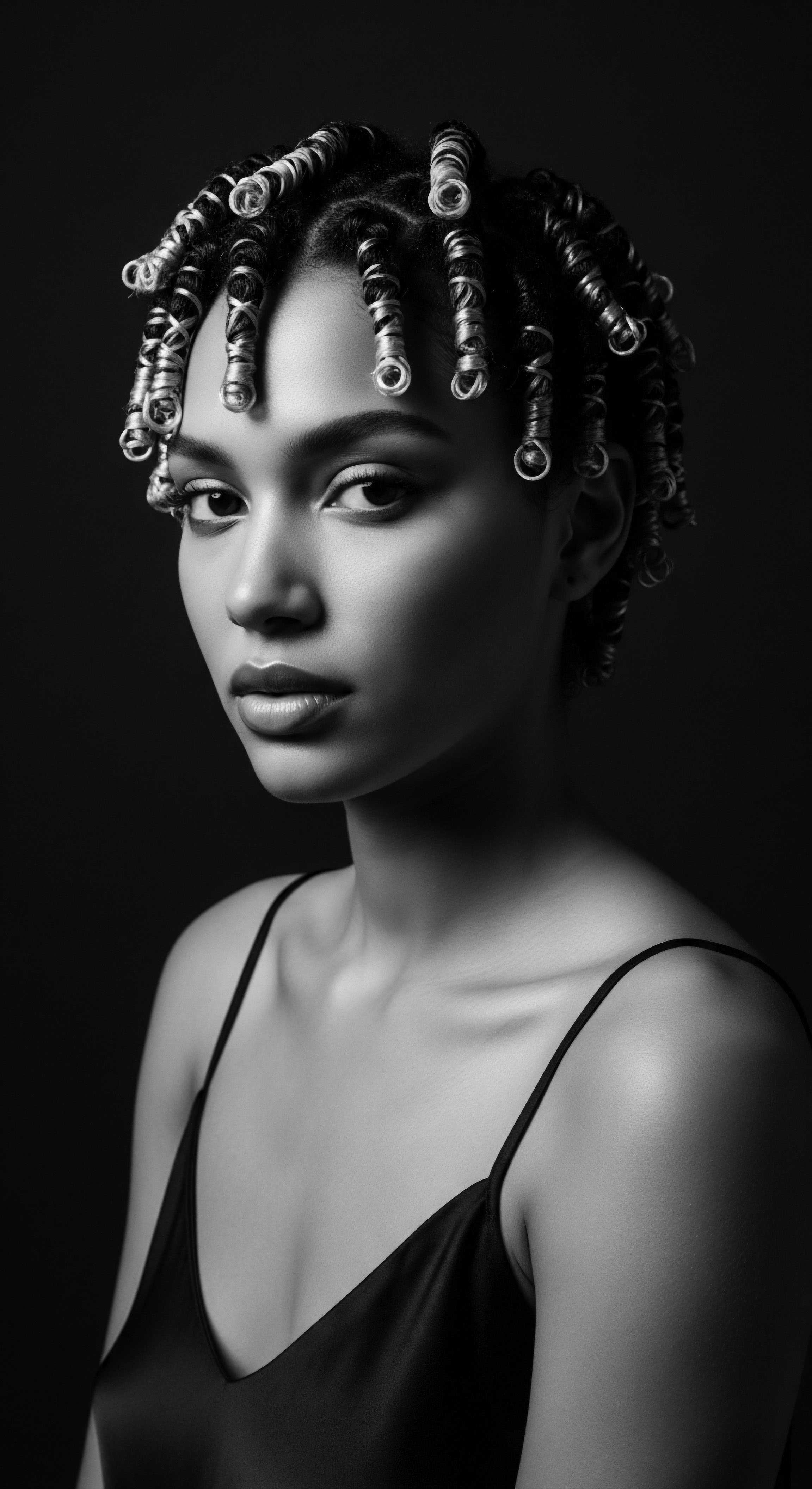

What historical significance do textured hairstyles hold in the diaspora?
Textured hairstyles in the diaspora represent a profound heritage of identity, resistance, communication, and self-expression, deeply rooted in ancestral African practices.

How did pre-colonial practices influence modern textured hair identity?
Pre-colonial hair practices, rooted in diverse African cultures, shaped modern textured hair identity through their profound emphasis on social symbolism, communal rituals, and natural ingredient-based care.

What ancient cultural practices shaped textured hair rituals?
Ancient cultural practices rooted hair rituals in identity, spirituality, and communal belonging, deeply shaping textured hair heritage.

How does modern understanding of textured hair validate ancestral care practices?
Modern hair science affirms ancestral textured hair care, recognizing its deep roots in heritage and the hair’s unique biological needs.

Can ancestral black soap traditions aid modern textured hair care?
Ancestral black soap traditions, rooted in West African heritage, aid modern textured hair care by offering gentle, nourishing cleansing.

What historical dietary shifts affected the mineral content of textured hair?
Historical dietary shifts profoundly altered the mineral content of textured hair, reflecting a tangible legacy of heritage and adaptation.
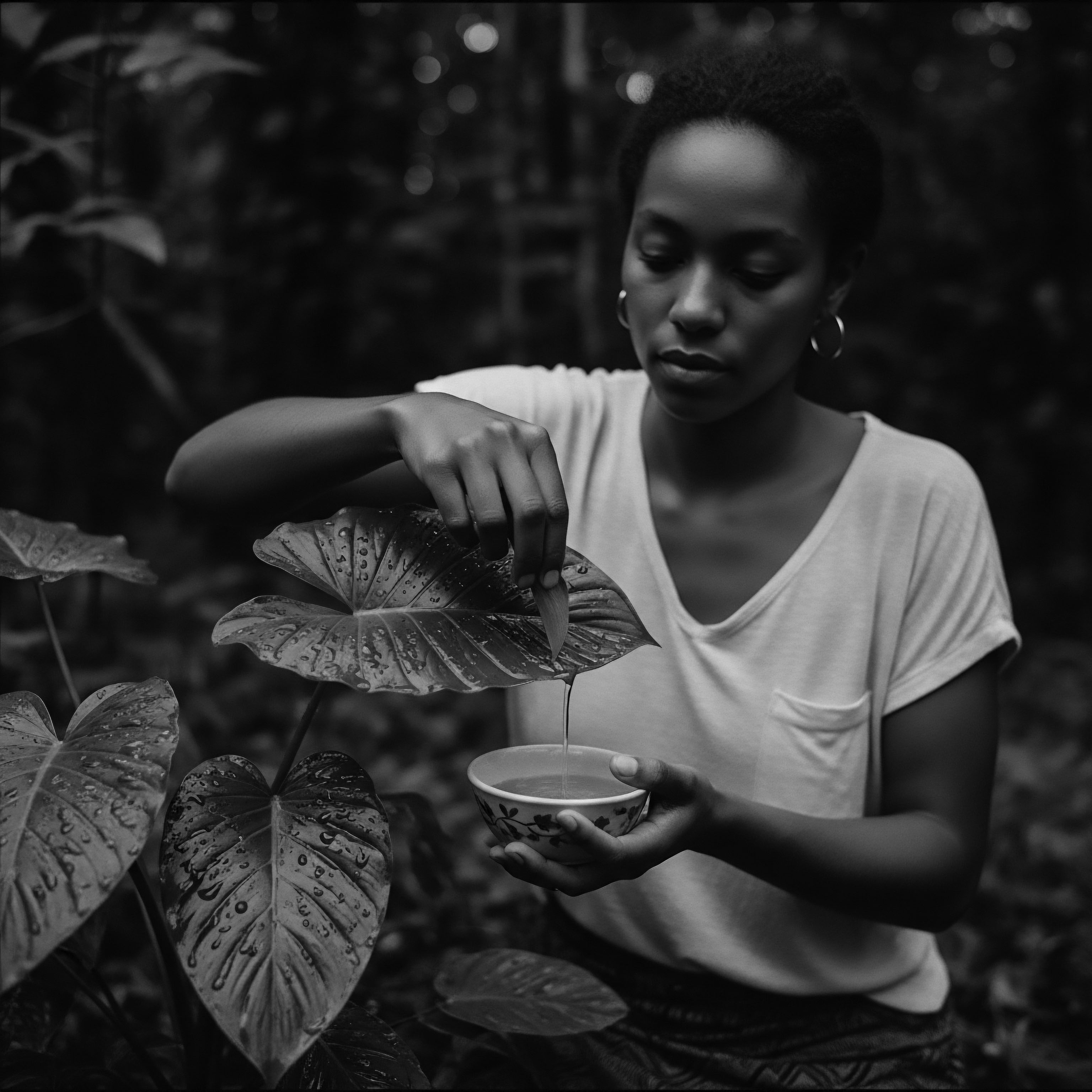

Which traditional ingredients best moisturize textured hair?
Ancestral wisdom reveals shea butter, coconut oil, and Jamaican Black Castor Oil as top moisturizers for textured hair.

Why did textured hair become a political symbol?
Textured hair gained political meaning as ancestral identity was challenged, forcing its public display to signify defiance and heritage.

