
Hair Breaking
Meaning ❉ Hair Breaking is the physical rupture of a hair shaft, deeply intertwined with the unique biology and rich ancestral care practices of textured hair.
What ancestral knowledge guides contemporary textured hair care practices?
Ancestral knowledge guides contemporary textured hair care by emphasizing natural ingredients, protective styling, and holistic well-being, rooted in deep heritage.

What historical coloring methods influenced modern textured hair care?
Historical coloring methods, rooted in ancestral plant and mineral wisdom, shaped modern textured hair care by emphasizing natural pigment interaction and holistic hair health.

Combs Cultural Significance
Meaning ❉ The Combs Cultural Significance defines the profound historical and social role of hair combs within diverse cultural contexts.

Why does textured hair need legal protection?
Legal protection for textured hair defends a vital part of Black and mixed-race heritage, combating historical biases and fostering equity.

What specific laws suppressed textured hair in colonial periods?
Colonial laws suppressed textured hair by mandating head coverings and regulating appearance, aiming to diminish status and erase visual heritage.

Himbe Hair
Meaning ❉ Himbe Hair describes traditional African hair care, epitomized by Himba practices, signifying cultural identity and ancestral wisdom.
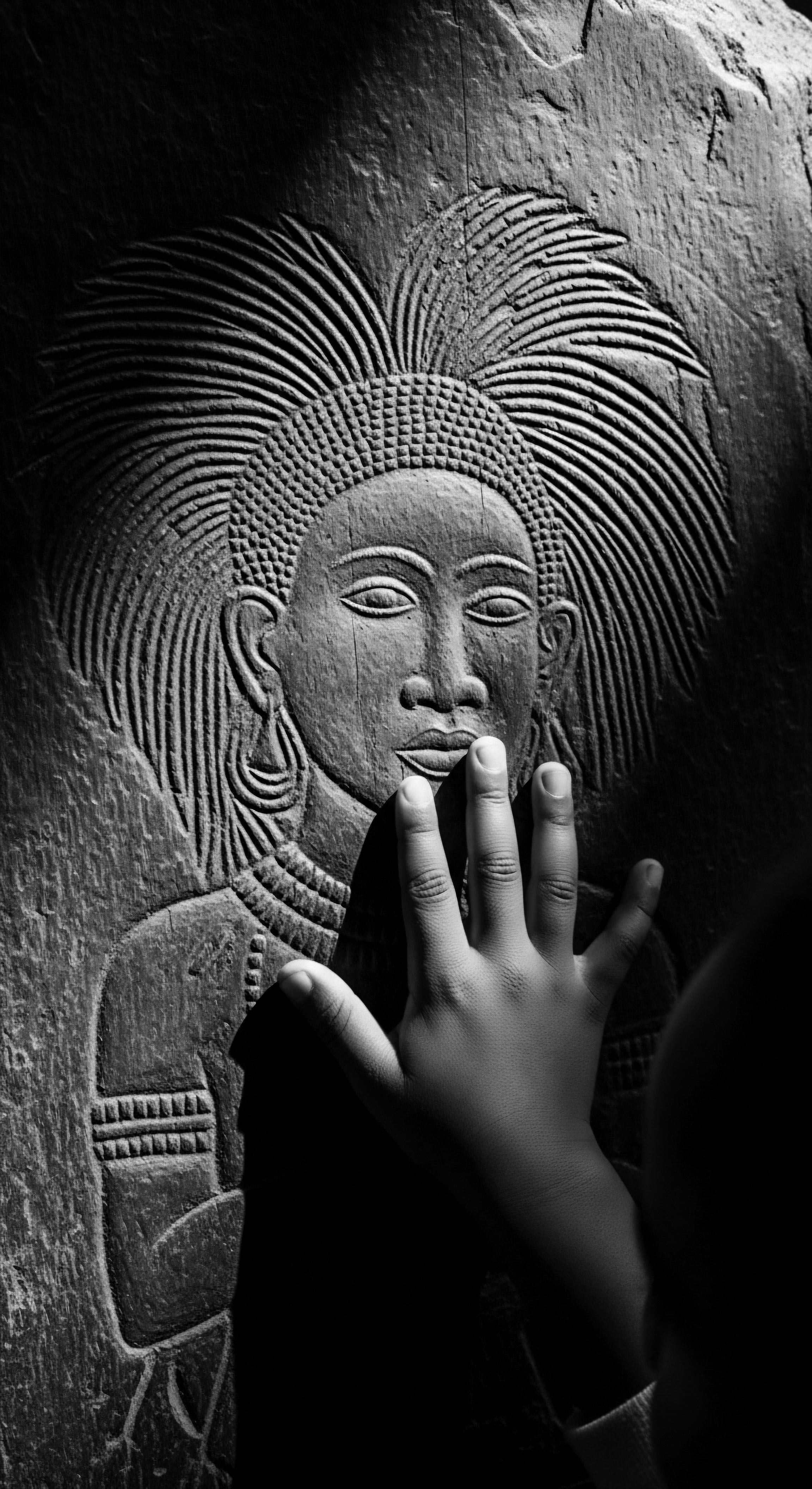

What is the ideal pH for afro-textured hair?
The ideal pH for afro-textured hair is slightly acidic, generally between 4.5 and 5.5, crucial for preserving its ancestral moisture and structural integrity.

What historical styling practices shaped textured hair identity?
Historical styling practices for textured hair deeply shaped identity through social communication, spiritual connection, and acts of heritage preservation.
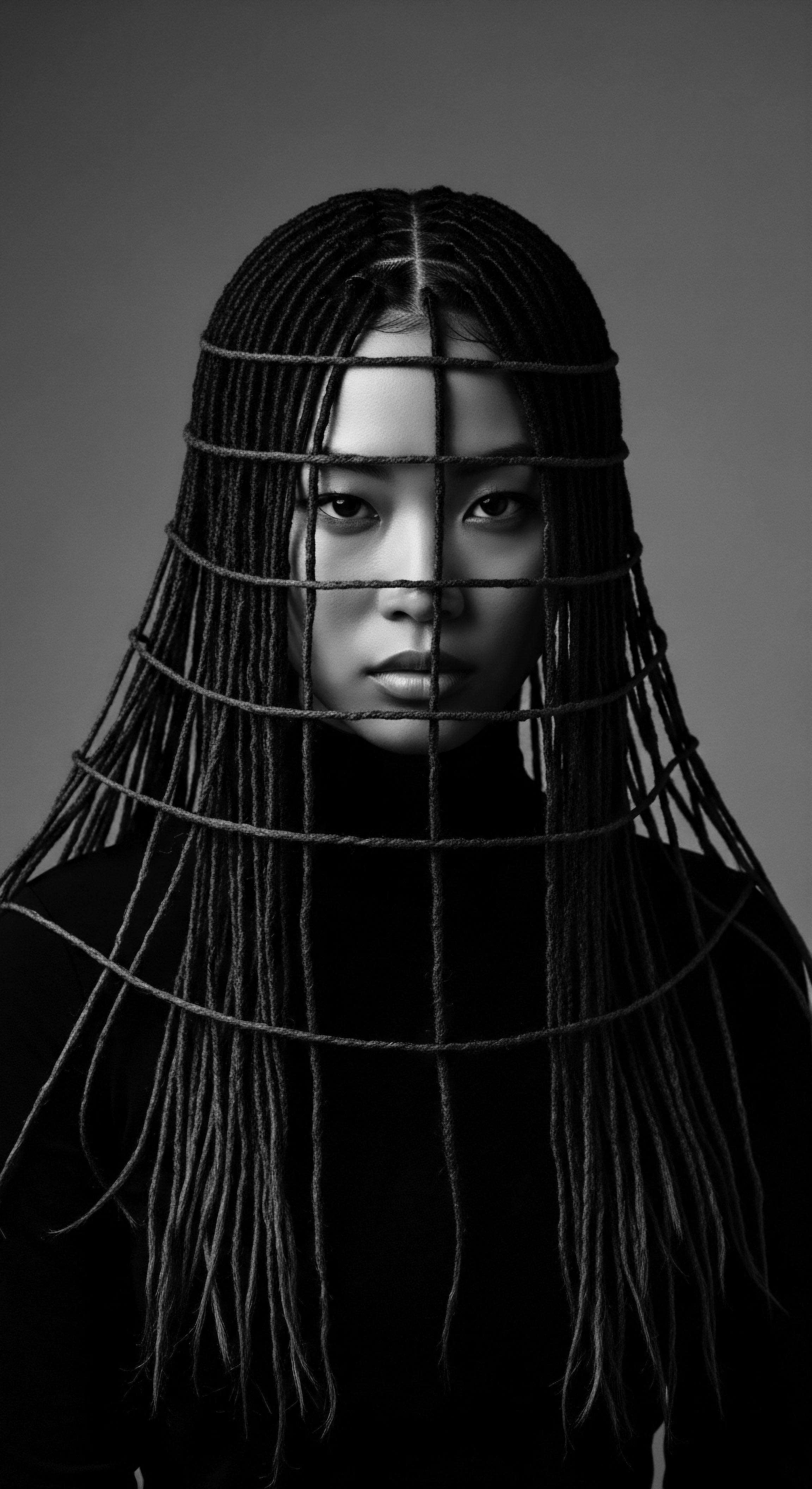

Why do textured hair traditions symbolize defiance?
Textured hair traditions symbolize defiance through enduring cultural heritage, reclaiming identity, and resisting imposed beauty norms.

How does HBCO’s preparation honor heritage?
HBCO's preparation honors heritage by weaving ancestral wisdom into its formulations, recognizing textured hair's profound cultural and historical identity.

What is the legacy of ancient hair oils in modern textured hair practices?
Ancient hair oils gifted textured hair practices a legacy of moisture, protection, and cultural identity, profoundly linking modern care to ancestral wisdom.
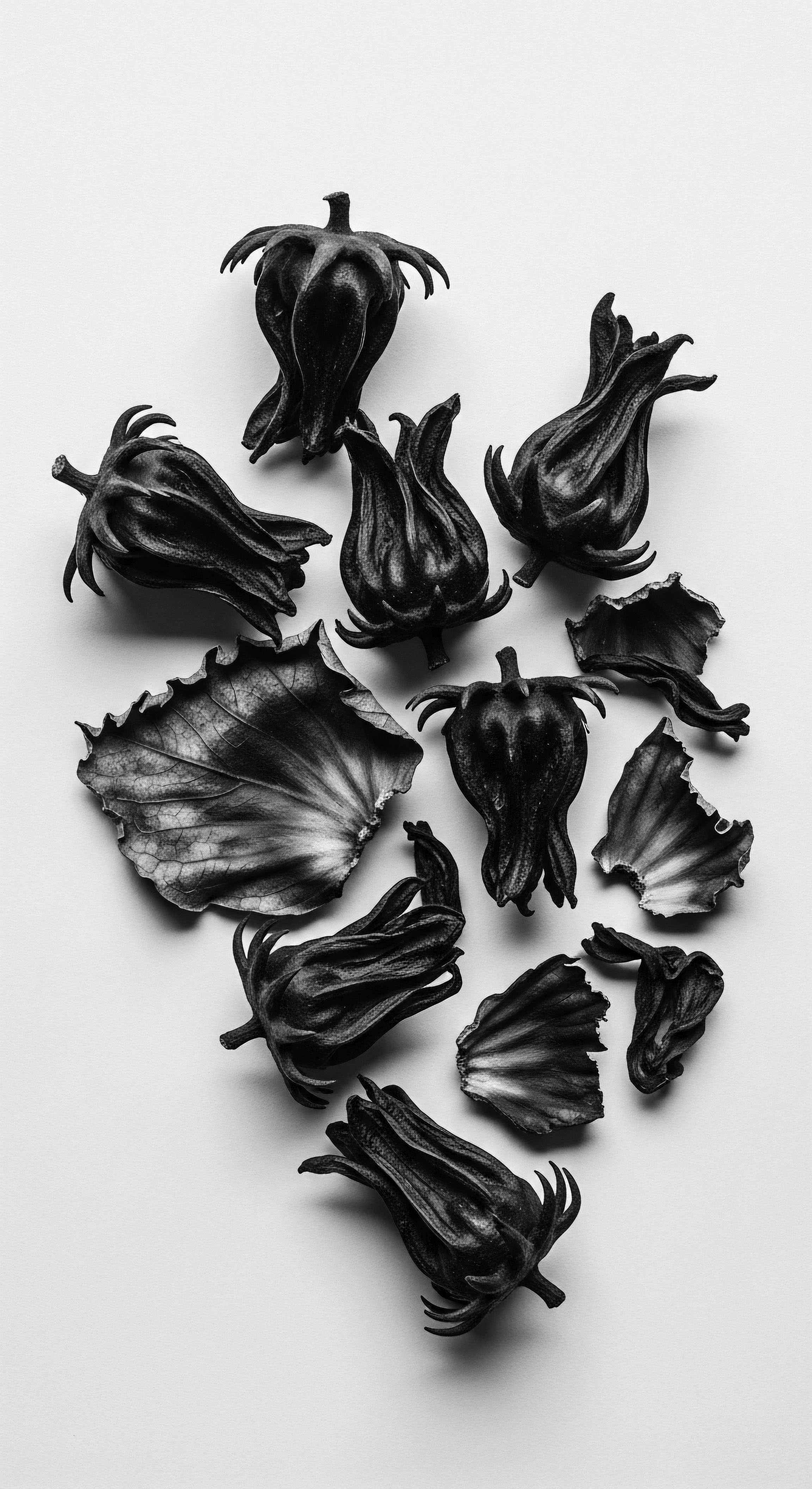

When did castor oil become crucial for textured hair?
Castor oil became vital for textured hair during the transatlantic slave trade, solidifying its role in preserving ancestral Black and mixed-race hair heritage.

What historical significance do natural hair practices hold for Black heritage?
Natural hair practices for Black heritage embody survival, resistance, and identity, rooted in ancestral wisdom and communal care.
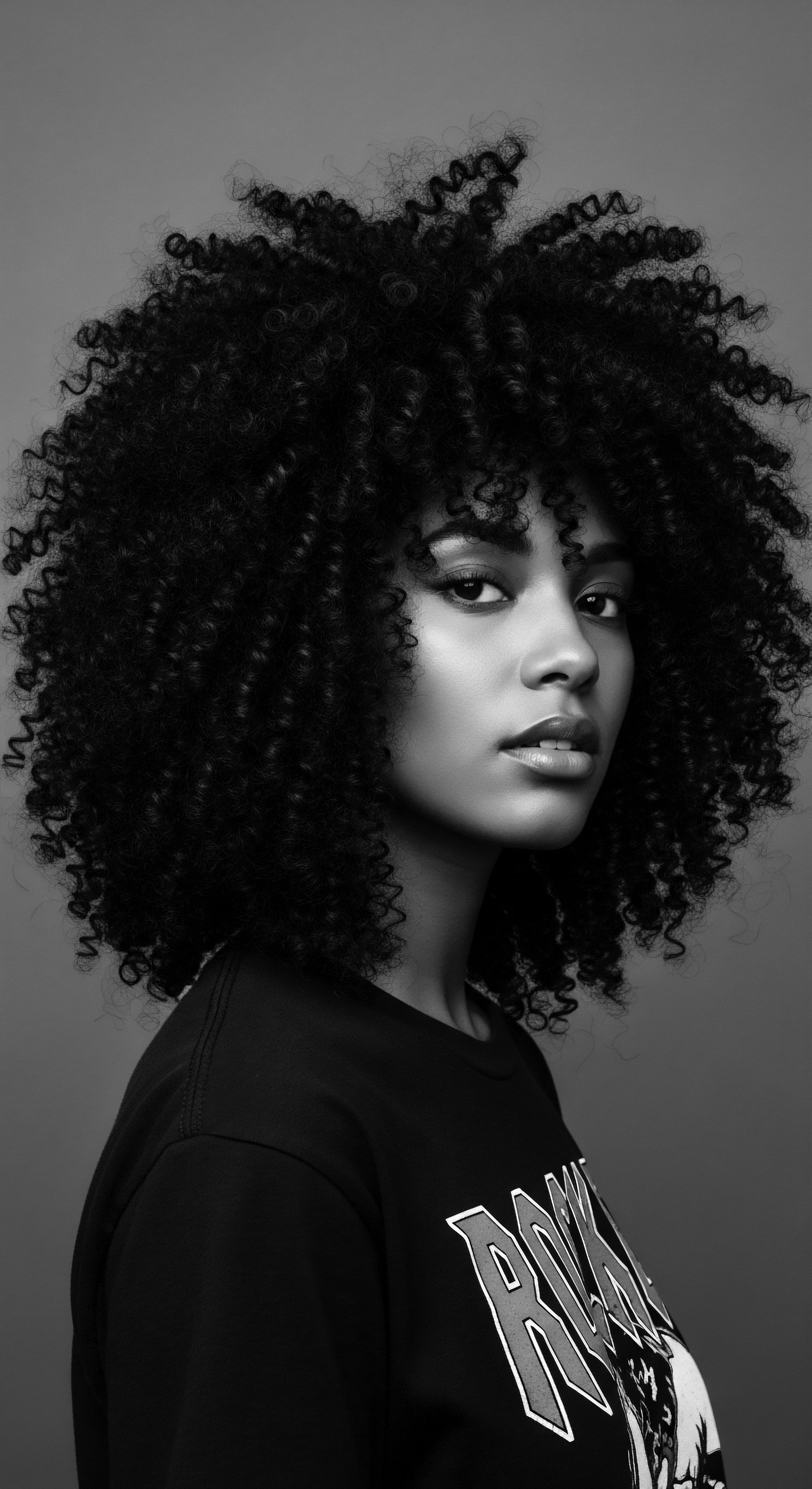

Which ancestral oils protected textured coils?
Ancestral oils, including shea butter, castor oil, and coconut oil, protected textured coils by deeply hydrating and strengthening strands, preserving a rich hair heritage.

How do traditional practices shape modern textured hair routines?
Traditional practices, rooted in ancestral wisdom and communal care, profoundly shape modern textured hair routines by providing foundational techniques and an enduring ethos of protection.
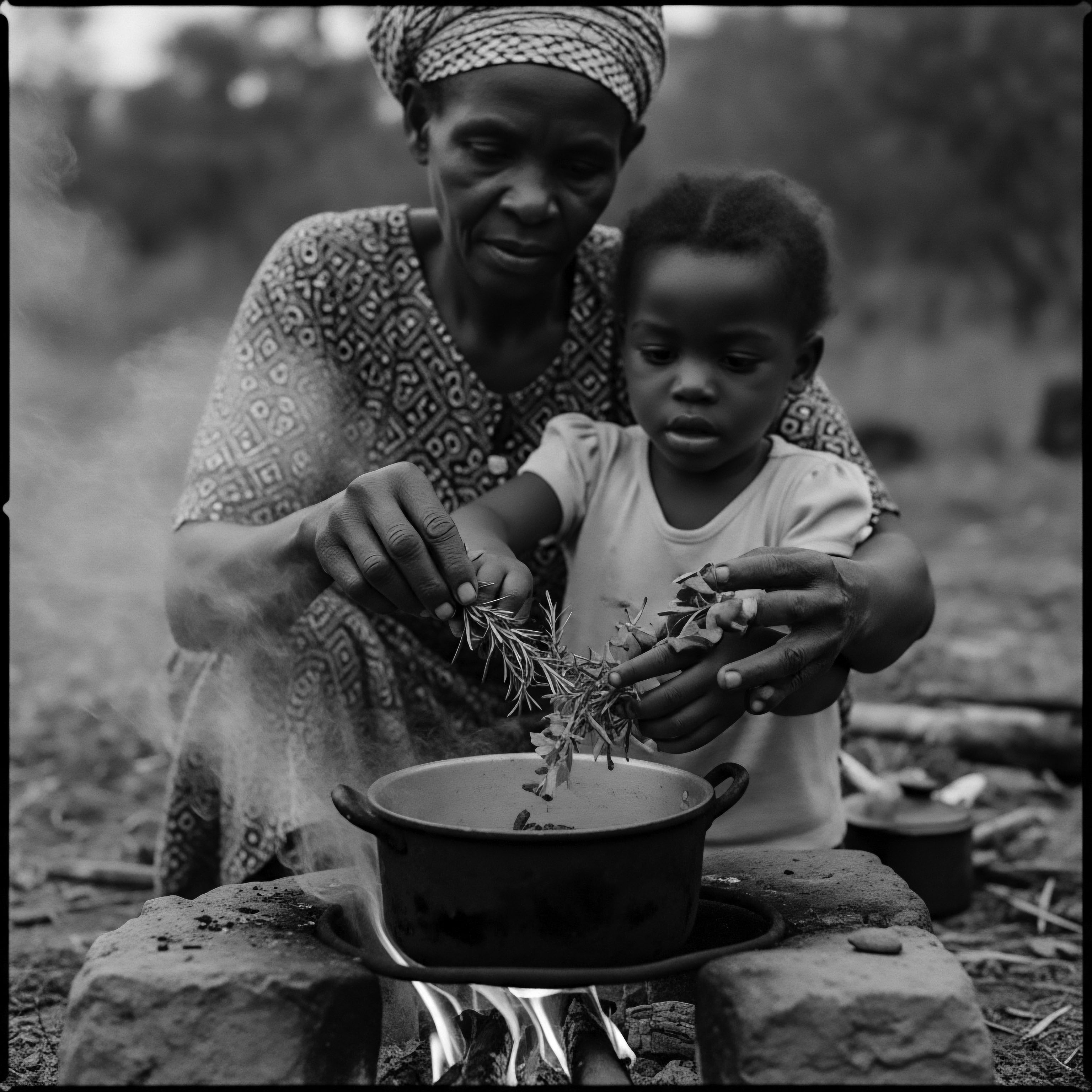

How does communal care reflect textured hair heritage and identity?
Communal hair care reflects textured hair heritage by preserving ancestral wisdom, fostering collective identity, and transmitting cultural resilience through shared rituals.

How have ancestral plant-based remedies influenced modern textured hair products?
Ancestral plant remedies deeply influence modern textured hair products, offering a heritage of natural ingredients and care principles.

Can ancient hair care ingredients benefit contemporary textured strands?
Ancient hair care ingredients provide profound benefits for textured strands by connecting modern routines to ancestral wisdom.
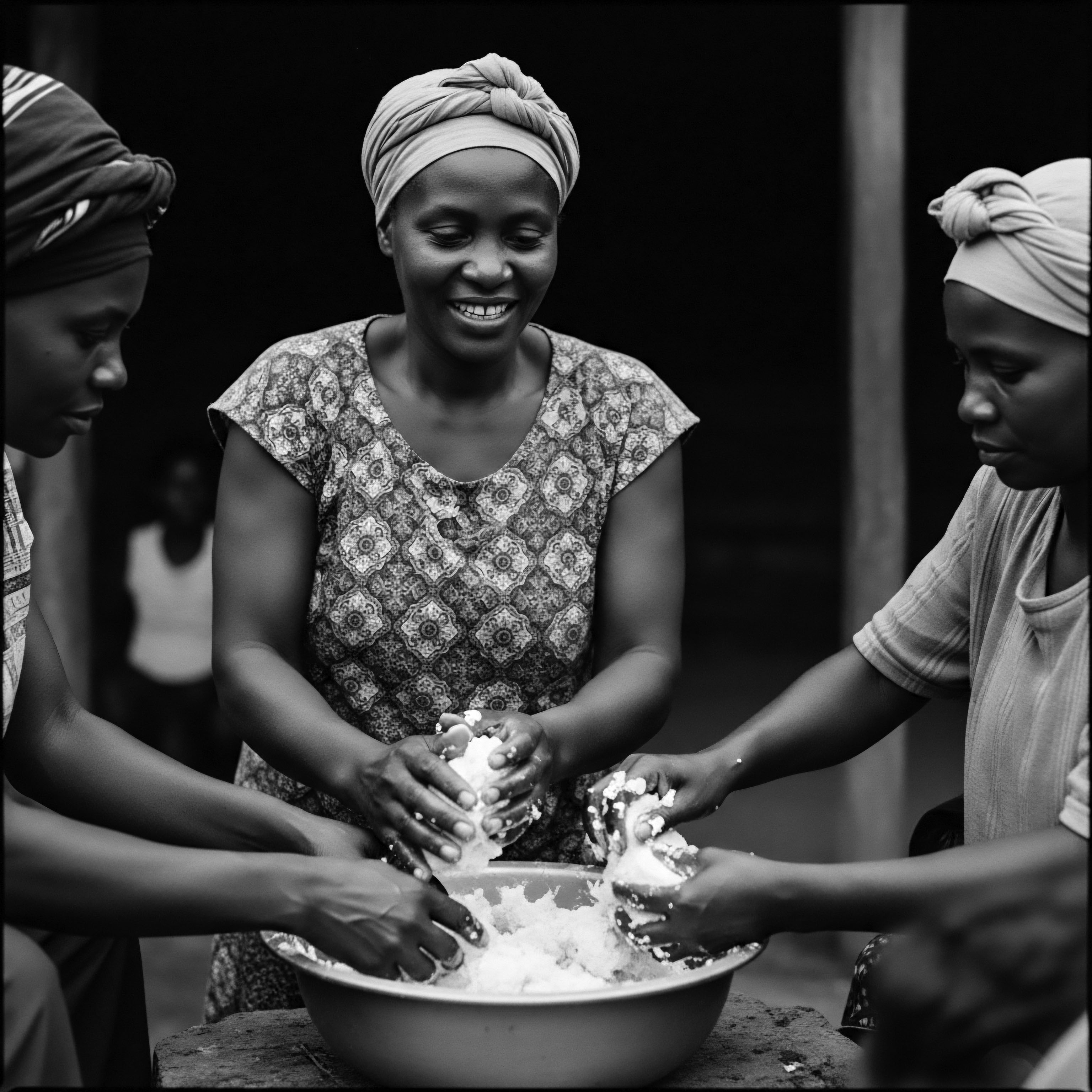

What enduring heritage practices prevent textured hair dryness?
Heritage practices prevent textured hair dryness through consistent oiling, protective styles, and thoughtful nighttime care, rooted in ancestral wisdom.

What ancestral techniques preserve textured hair?
Ancestral techniques preserve textured hair through protective styling, natural emollients, and communal care, rooted in deep cultural heritage.

Why does textured hair require more moisture?
Textured hair requires more moisture due to its unique coiled structure hindering natural oil distribution, and its ancestral heritage of adapting to arid climates.

How did historical cultural practices preserve textured hair heritage?
Historical cultural practices preserved textured hair heritage through spiritual reverence, coded styling, and natural care systems.

Can traditional African ingredients improve current textured hair practices?
Traditional African ingredients, steeped in heritage, can significantly enhance current textured hair practices through their restorative properties and alignment with ancestral care philosophies.

What is rhassoul clay’s historical role in textured hair care?
Rhassoul clay, an ancient Moroccan earth, served as a revered cleansing and nourishing agent for textured hair, deeply rooted in ancestral care rituals and cultural identity.

What traditional ingredients sustain textured hair heritage?
Traditional ingredients for textured hair heritage are earth's bounty, like shea butter and coconut oil, used for deep nourishment and protective styling.

How did ancient materials shape textured hair routines?
Ancient materials like plant oils, clays, and natural fibers profoundly shaped textured hair routines, anchoring them in cultural heritage and ancestral wisdom.

Can baobab protein genuinely strengthen diverse textured hair?
Baobab protein strengthens diverse textured hair by reinforcing its keratin structure, a practice echoing centuries of ancestral care.

Can textured hair be a symbol of historical resistance?
Textured hair stands as a powerful symbol of historical resistance, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race heritage, embodying cultural pride and defiance.

