What historical oils protected African textured hair?
Historical African oils, like shea butter and palm oil, deeply protected textured hair, connecting generations to a rich heritage of resilience and care.

What scientific aspects confirm shea butter’s historical benefits for textured hair?
Shea butter's fatty acids and anti-inflammatory compounds scientifically affirm its historical benefits for textured hair hydration and protection, echoing ancestral wisdom.

Hair Oiling Rituals
Meaning ❉ The Hair Oiling Rituals signify a heritage-rich practice of applying natural oils to textured hair for nourishment, protection, and cultural affirmation.

How does cultural identity shape textured hair oiling practices today?
Cultural identity profoundly shapes textured hair oiling practices by linking ancestral wisdom, resilience, and communal rituals to modern care.

What cultural significance do traditional oils hold for textured hair?
Traditional oils for textured hair signify a profound connection to ancestral practices, cultural identity, and a legacy of resilient beauty.

How does understanding textured hair’s biology honor its cultural lineage and traditional care?
Understanding textured hair's biology reveals its inherent strength, honoring a rich cultural lineage of care and resilience.

What ancestral oils are still used for textured hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, castor, coconut, olive, and jojoba continue to deeply nourish textured hair, connecting us to a rich heritage of care.

How did enslaved people care for their textured hair?
Enslaved people cared for textured hair through resourceful adaptation of available materials and ancestral practices, transforming grooming into a profound act of cultural heritage and resistance.

Hair Oiling History
Meaning ❉ Hair Oiling History is the ancient, culturally rich practice of nourishing hair with natural oils and butters, particularly significant for textured hair heritage.
What role does hair discrimination play in the ongoing conversation about textured hair heritage?
Hair discrimination challenges the deeply rooted heritage of textured hair, demanding a collective recognition of its cultural significance and inherent beauty.

Biocultural Hair
Meaning ❉ Biocultural Hair is the interwoven connection of hair's biology with its profound cultural, historical, and communal significance, especially for textured hair.

How did ancient oils protect textured hair?
Ancient oils protected textured hair by sealing moisture and creating a barrier against environmental stressors, a heritage of care.

Chadian Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Chadian Hair Traditions encompass ancient, community-centered practices using natural botanicals like Chébé and Ambunu for textured hair health and cultural expression.

Hair Follicle Structure
Meaning ❉ The hair follicle, a dermal organ, is the biological source of hair, profoundly shaping textured hair's unique qualities and its deep cultural heritage.

Can modern hair science validate traditional textured hair practices?
Modern hair science validates traditional textured hair practices by affirming their biological efficacy and cultural significance.

Can modern science explain why traditional oiling practices benefit textured hair?
Modern science confirms traditional oiling practices benefit textured hair by providing moisture, strengthening strands, and protecting against damage, validating ancestral wisdom.

Which ancient oils deeply nourish textured hair?
Ancient oils like shea, coconut, and castor deeply nourish textured hair, reflecting ancestral wisdom and cultural heritage.

How does historical hair care influence modern textured hair practices?
Historical hair care practices deeply influence modern textured hair routines by providing foundational knowledge, tools, and cultural significance.

How does hair oiling protect textured hair?
Hair oiling protects textured hair by sealing in moisture, reducing friction, and strengthening strands, a practice deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

How did communal hair practices preserve heritage during the transatlantic slave trade?
Communal hair practices served as vital, covert means to preserve identity and transmit critical knowledge for survival.

In what ways does cultural identity guide contemporary oil selection for textured hair?
Cultural identity profoundly guides contemporary oil selection for textured hair by honoring ancestral practices and inherited botanical wisdom.

Jojoba Oil
Meaning ❉ Jojoba Oil is a liquid wax ester derived from the Simmondsia chinensis plant, revered for its sebum-like properties and deep connection to textured hair heritage.

In what ways do cornrows continue to symbolize cultural defiance and textured hair heritage?
Cornrows symbolize cultural defiance and textured hair heritage by embodying ancestral knowledge, historical resistance, and contemporary identity.
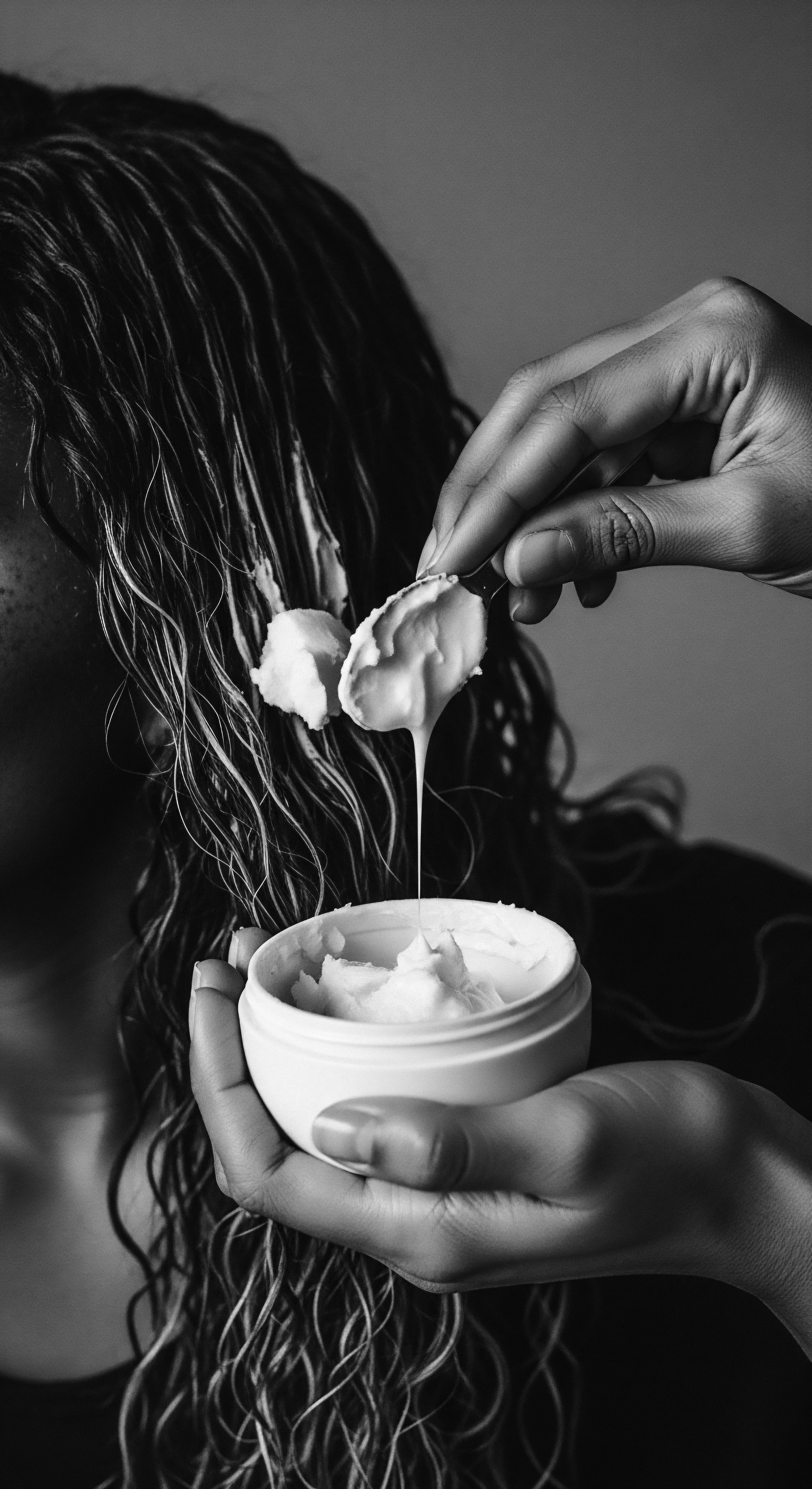

Can historical hair practices influence modern textured hair product formulation?
Historical hair practices deeply inform modern textured hair product formulation by providing a heritage of ingredients, techniques, and holistic care principles.

Botanical Ingredients
Meaning ❉ Botanical Ingredients are plant-derived components deeply rooted in ancestral practices, providing natural nourishment and cultural significance for textured hair.
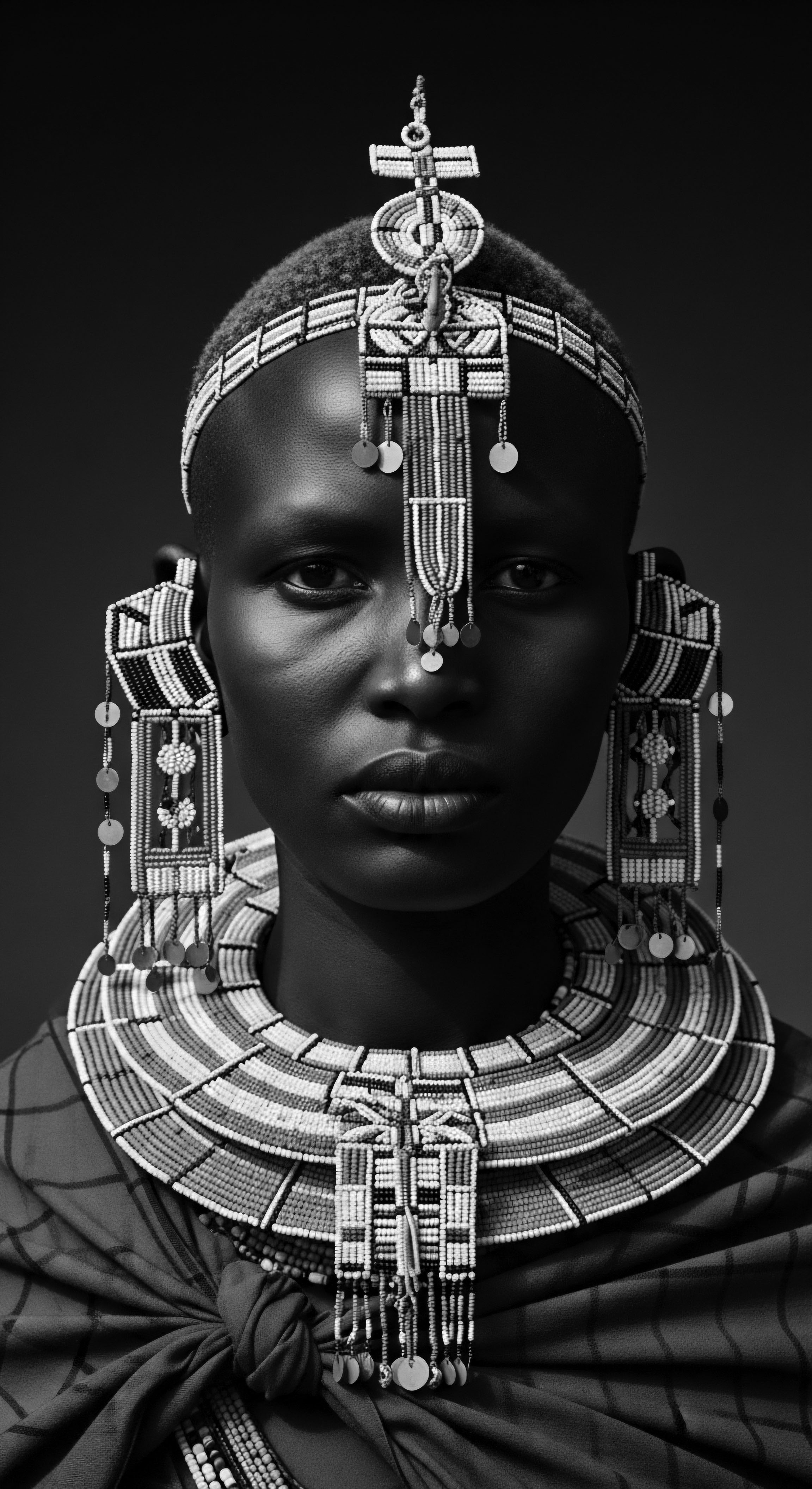

Can textured hair heritage illuminate ancestral African social hierarchies through styling?
Textured hair heritage powerfully reveals ancestral African social hierarchies through specific styling, adornments, and communal practices, each a silent language of status and identity.

Hair Oiling Benefits
Meaning ❉ Hair Oiling Benefits refers to the profound, historically rooted advantages of applying lipids to textured hair, preserving its vitality and cultural significance.


