
Ethnobotany Scalp
Meaning ❉ Ethnobotany Scalp defines the study of traditional plant knowledge and practices used for textured hair scalp health across diverse cultural heritages.

What historical care rituals preserved textured hair heritage?
Historical care rituals preserved textured hair heritage through protective styling, natural ingredients, and communal practices that embodied identity and resilience.

Which ancient oils were most common for textured hair?
Ancient textured hair care primarily used shea butter, castor oil, coconut oil, palm oil, olive oil, and baobab oil, reflecting regional flora and ancestral heritage.

Knowledge Transmission
Meaning ❉ Knowledge Transmission is the dynamic process by which understanding, practices, and cultural significance of textured hair are passed across generations.

What modern legislative efforts protect textured hair expression and heritage?
Modern legislative efforts, particularly the CROWN Act, protect textured hair expression by prohibiting discrimination rooted in racial bias, affirming its heritage.

In what ways did historical events impact textured hair care traditions?
Historical events profoundly shaped textured hair care, transforming ancient identity markers into symbols of both oppression and powerful heritage resistance.

African Hair Genetics
Meaning ❉ African Hair Genetics describes the inherited traits shaping diverse hair textures and patterns, deeply rooted in ancestral adaptation and cultural heritage.

Adornment Semiotics
Meaning ❉ Adornment Semiotics explores the cultural meanings and historical narratives communicated through the styling and ornamentation of textured hair.

How do braids safeguard textured hair from environmental elements?
Braids safeguard textured hair by physically shielding strands from environmental elements, reducing manipulation, and honoring centuries of ancestral protective practices.

How did ancient cleansers work on textured hair?
Ancient cleansers utilized natural ingredients like saponins, clays, and plant ash to gently purify textured hair, honoring its heritage and moisture.

Societal Pressure
Meaning ❉ Societal Pressure signifies the collective expectations and norms influencing how textured hair is perceived and presented, deeply tied to historical and cultural legacies.

Can traditional hair care methods strengthen textured hair’s ancestral bonds?
Traditional hair care methods strengthen textured hair's ancestral bonds by integrating historical practices, cultural identity, and natural ingredients.

What ancient oils benefited textured hair?
Ancient oils like castor, shea, and olive nourished textured hair, preserving its heritage through generations of traditional care and protective styling.

Botanical Sun Protection
Meaning ❉ Botanical Sun Protection involves using plant-derived elements to shield textured hair and scalp from solar radiation, deeply rooted in ancestral practices.

Can specific mineral compositions of clays impact diverse textured hair types?
Specific mineral compositions of clays cleanse, condition, and fortify diverse textured hair types, echoing ancestral wisdom in hair care heritage.

What ancestral practices of textured hair care now require legal recognition?
Ancestral textured hair practices require legal recognition to protect heritage, combat discrimination, and support cultural entrepreneurship.
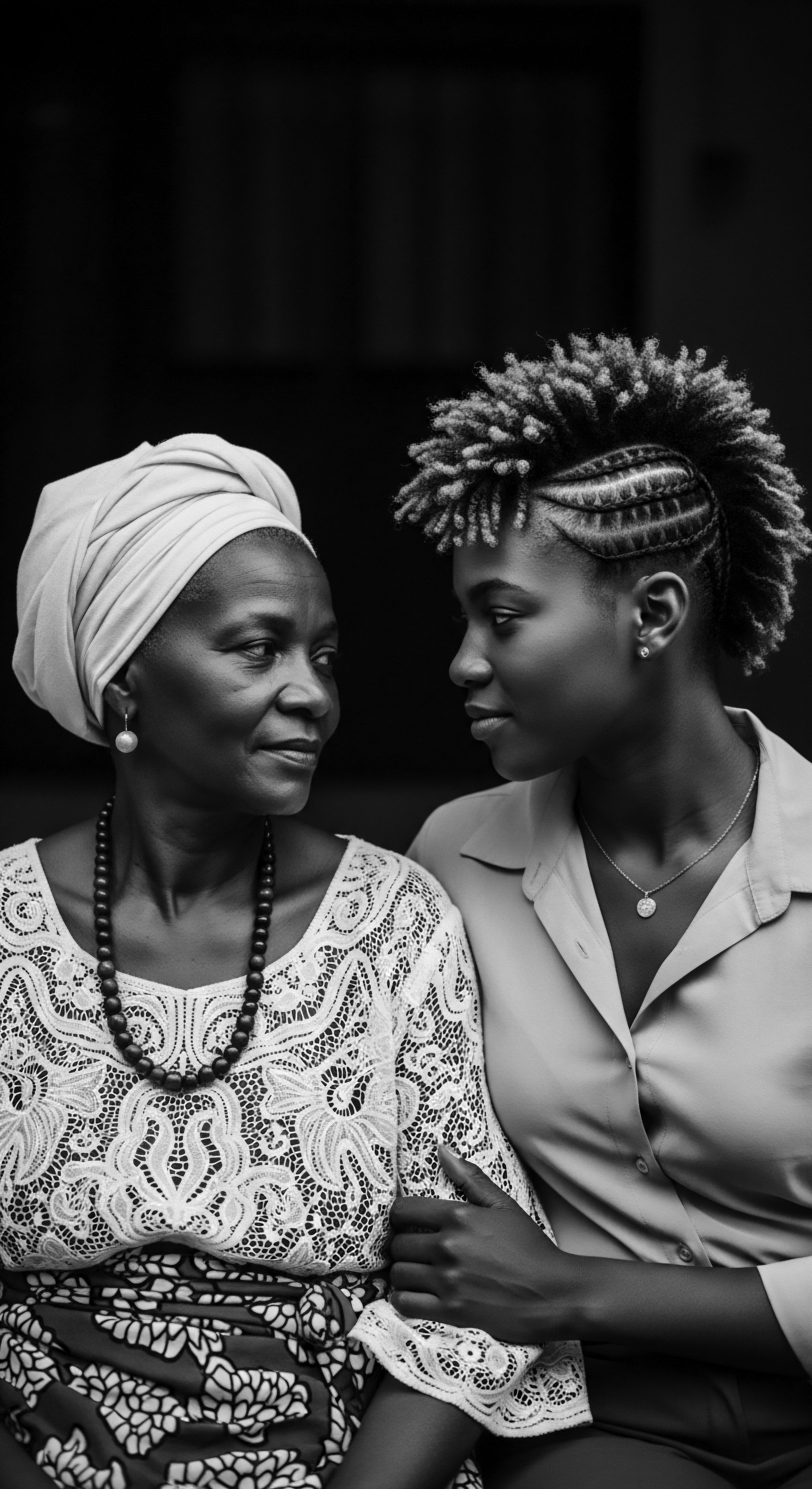
Shared Hair Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Shared Hair Wisdom is the profound, intergenerational knowledge of textured hair, its care, and its cultural significance as a legacy of resilience.

How did ancient communities define textured hair?
Ancient communities defined textured hair as a profound marker of heritage, status, and spiritual connection.

How do historical practices of hair care resonate with modern scientific understanding of textured hair?
Historical hair care practices, particularly for textured hair, align with modern science by intuitively addressing its unique structure and needs, preserving a rich heritage of wellness.

Himba Hair Culture
Meaning ❉ Himba Hair Culture defines the traditional hair care practices of the Himba people, emphasizing otjize use, protective styling, and social symbolism.

Natural Hair Emollients
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Emollients are botanical substances that soften, smooth, and shield textured hair, rooted deeply in ancestral care traditions and cultural heritage.

What historical laws impacted textured hair expression?
Historical laws impacted textured hair expression by imposing Eurocentric beauty standards, aiming to suppress cultural identity and ancestral practices.

What specific botanicals shielded textured hair in ancient communities?
Ancient communities shielded textured hair with botanicals like shea butter, Chebe powder, argan oil, aloe vera, hibiscus, fenugreek, and yucca root, honoring ancestral care.

Hair Coverings Symbolism
Meaning ❉ Hair Coverings Symbolism signifies the profound cultural, social, and spiritual meanings attributed to concealing or adorning hair, especially within textured hair heritage.

Can traditional ingredients truly offer modern solutions for textured hair wellness?
Traditional ingredients, rooted in ancestral wisdom and validated by science, offer holistic and effective solutions for modern textured hair wellness.

Ayurvedic Oils
Meaning ❉ Ayurvedic Oils are ancient botanical elixirs, deeply rooted in Indian wisdom, offering holistic nourishment for textured hair through ancestral practices.

Diaspora Ethnobotany
Meaning ❉ Diaspora Ethnobotany is the study of plant knowledge and cultural practices of the African diaspora, especially concerning textured hair heritage.

What ancestral ingredients nourished textured hair resilience?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and chebe powder, coupled with communal care rituals, built textured hair resilience.

What scientific principles validate traditional textured hair oiling practices?
Traditional textured hair oiling practices are validated by their ability to moisturize, protect, and strengthen hair, deeply rooted in ancestral knowledge of hair biology and cultural heritage.

