6-Gingerol
Meaning ❉ 6-Gingerol, a primary compound in ginger, offers anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits for scalp health, yet research indicates it may inhibit hair growth.

What is the role of natural butters in African hair heritage?
Natural butters serve as foundational emollients in African hair heritage, linking ancient care rituals to modern textured hair health and identity.

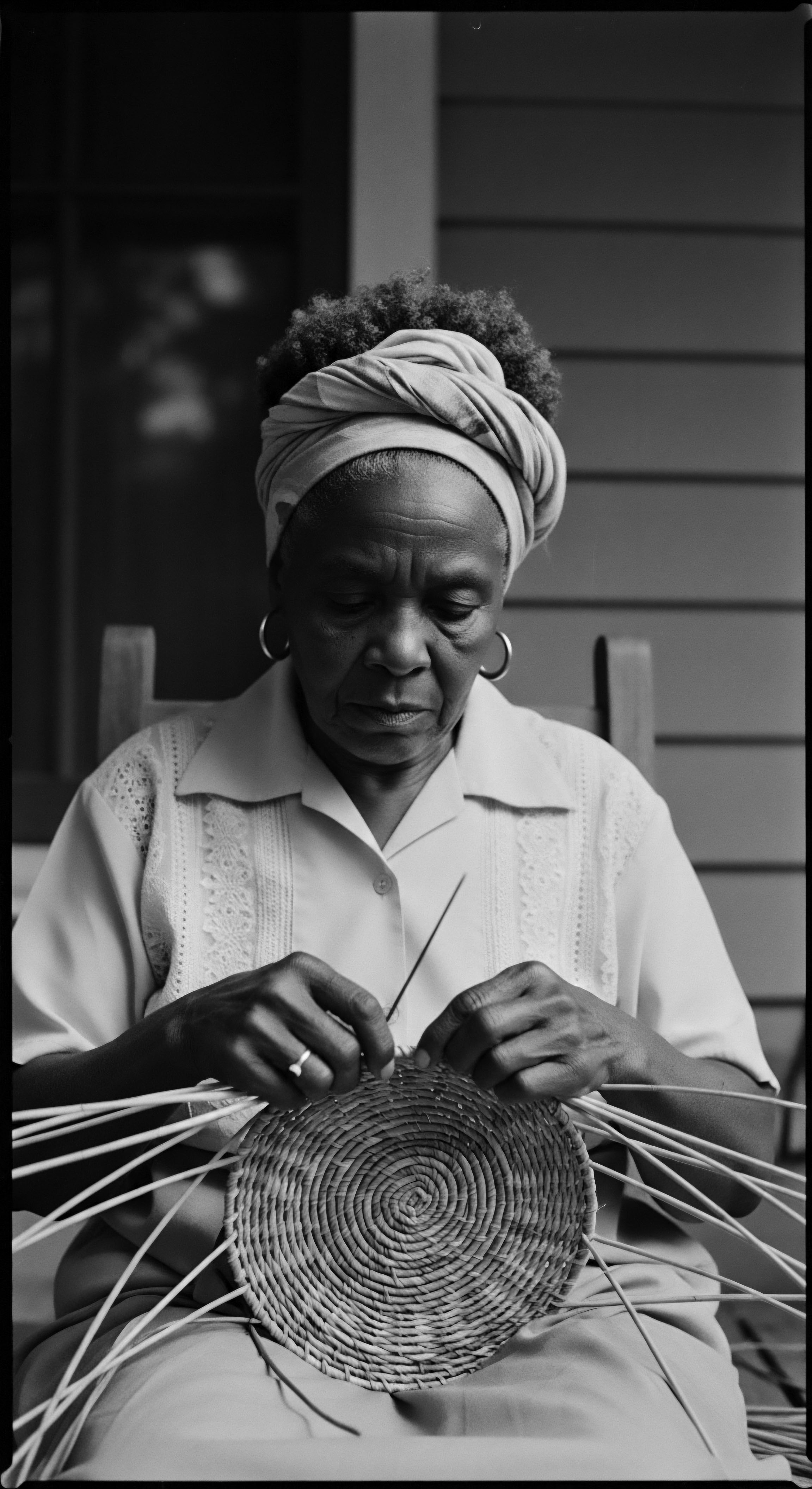
How did traditional Black hairstyles serve as acts of resistance during historical oppression?
Traditional Black hairstyles served as powerful acts of resistance by preserving cultural heritage, conveying hidden messages, and asserting identity amidst historical oppression.

Growth Patterns
Meaning ❉ Growth Patterns define the cyclical life of hair strands, deeply influencing appearance and care practices within textured hair heritage.

Mukanda Mask
Meaning ❉ The Mukanda Mask is a conceptual framework representing the protective, cultural, and ancestral layers of care inherent in textured hair heritage.
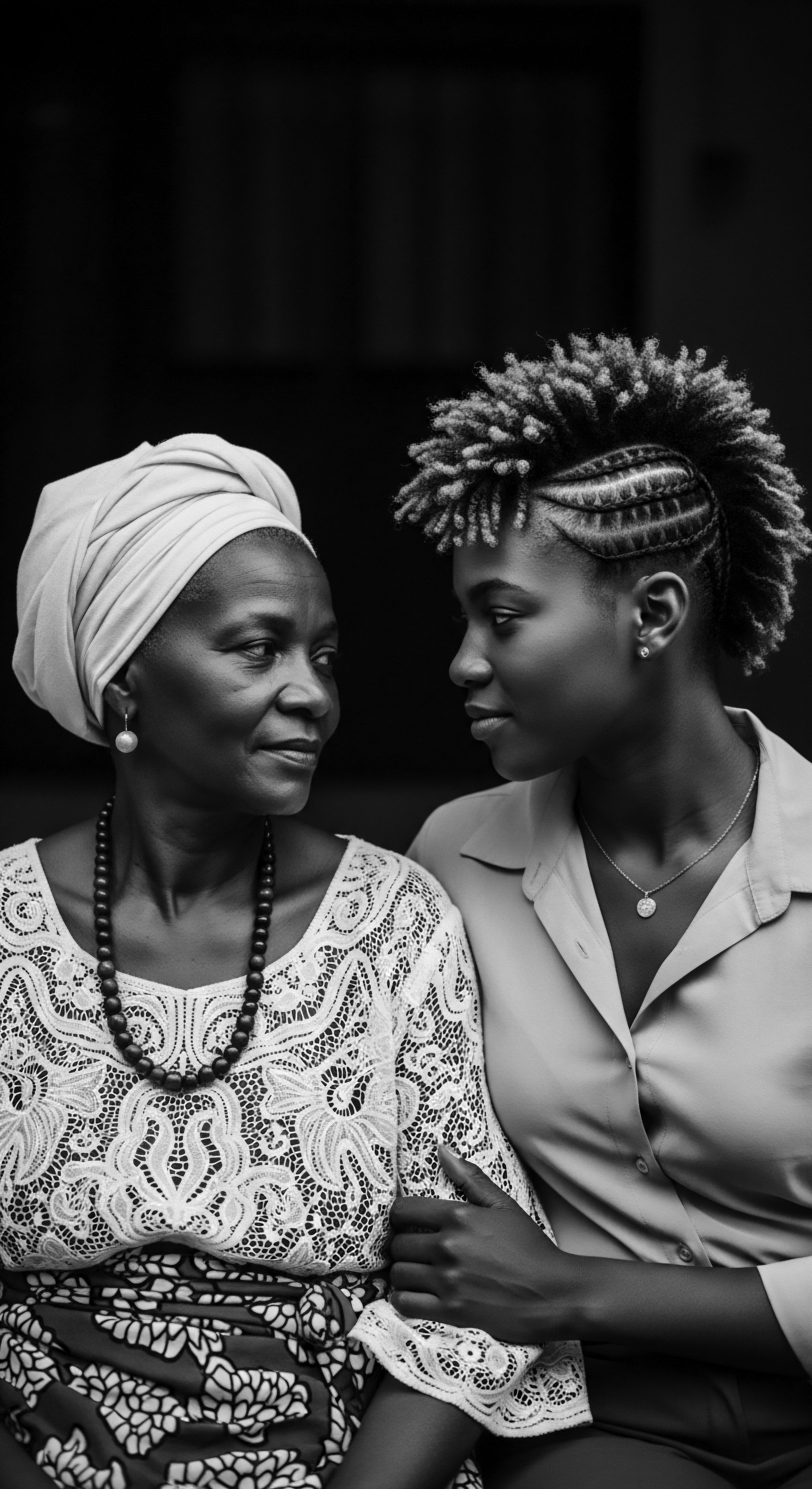
Can long-term use of plant remedies truly strengthen coily hair heritage?
Long-term plant remedy use strengthens coily hair by reinforcing its heritage of natural resilience and ancestral care.
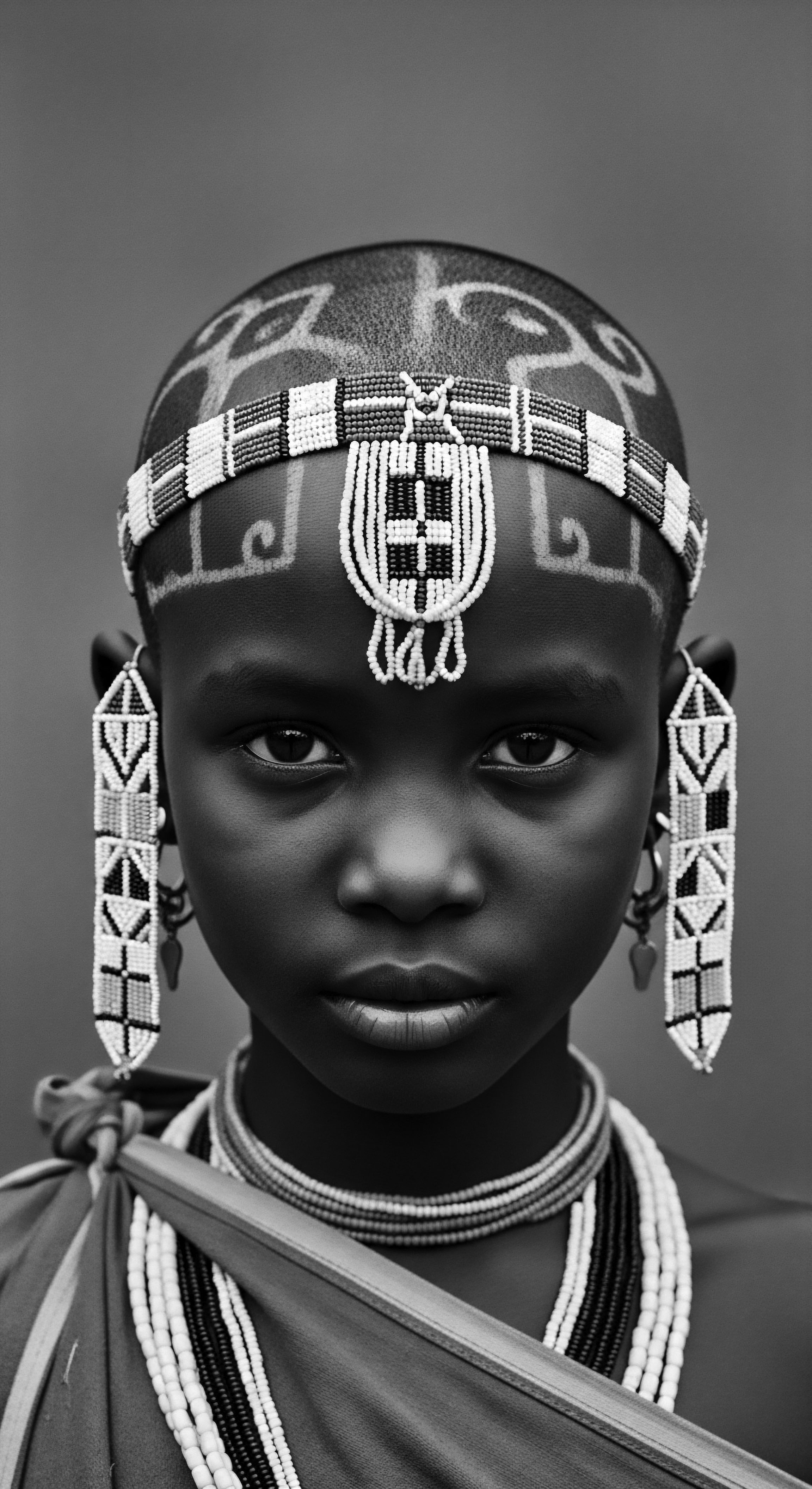

How do ancestral hair rituals shape modern identity?
Ancestral hair rituals shape modern identity by imbuing textured hair with deep cultural, social, and spiritual significance, linking individuals to their heritage.
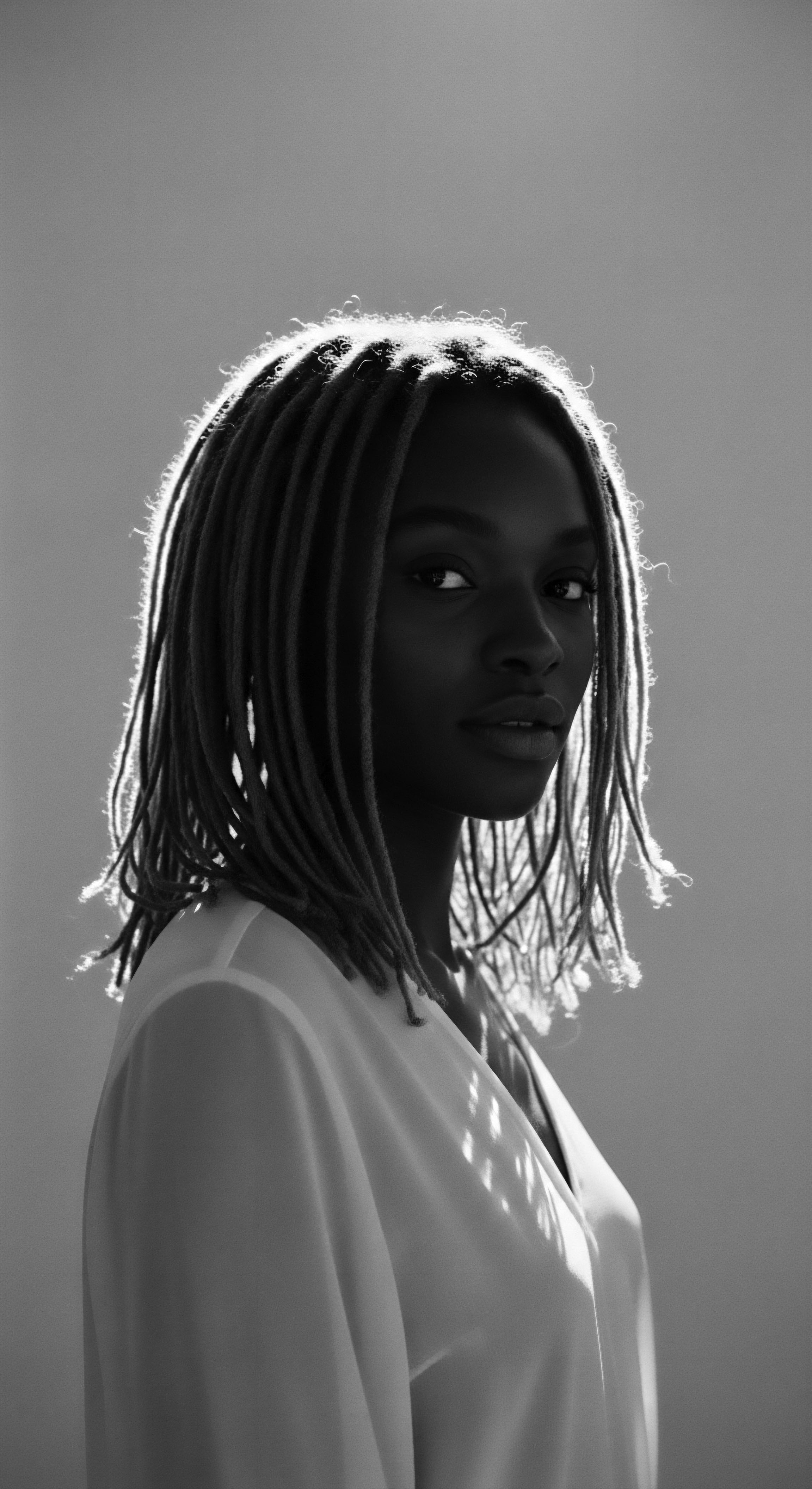

What specific oils offer protective qualities for hair?
Specific oils from ancestral traditions like coconut, shea, and jojoba offer protective qualities by penetrating, sealing, and strengthening textured hair.

How did palm oil support hair care heritage during transatlantic crossings?
Palm oil served as a vital, adaptable element in sustaining textured hair heritage amidst the challenges of transatlantic crossings.

How has textured hair care evolved with heritage?
Textured hair care evolved by adapting ancestral practices with new innovations, always rooted in cultural identity and historical resilience.

How did ancestral communities select hair oils?
Ancestral communities selected hair oils based on local plant availability and empirical observation of benefits for textured hair moisture and protection.
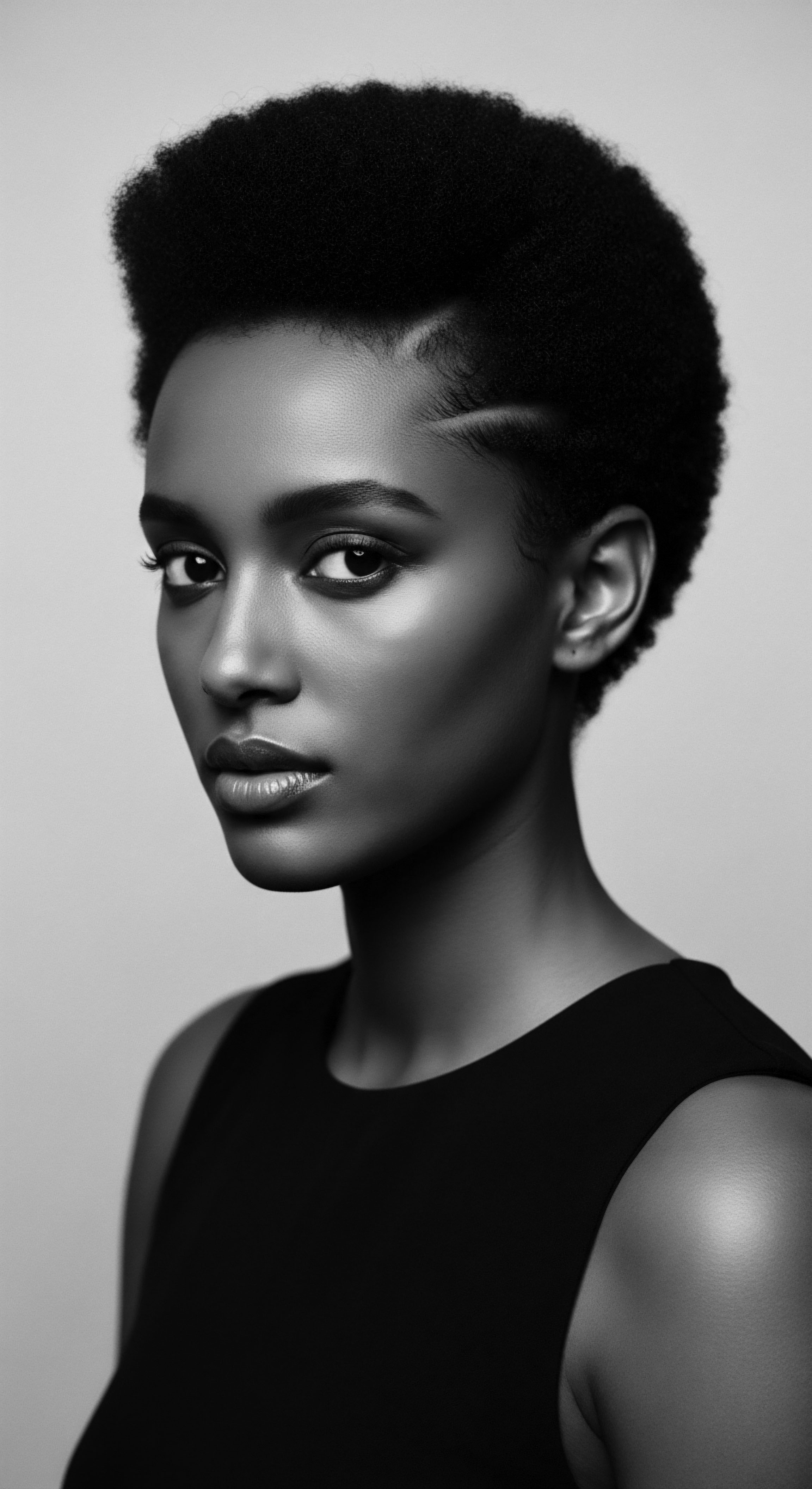

How does the CROWN Act protect textured hair as cultural heritage today?
The CROWN Act protects textured hair as cultural heritage by legally prohibiting discrimination against ancestral hairstyles and natural hair textures.
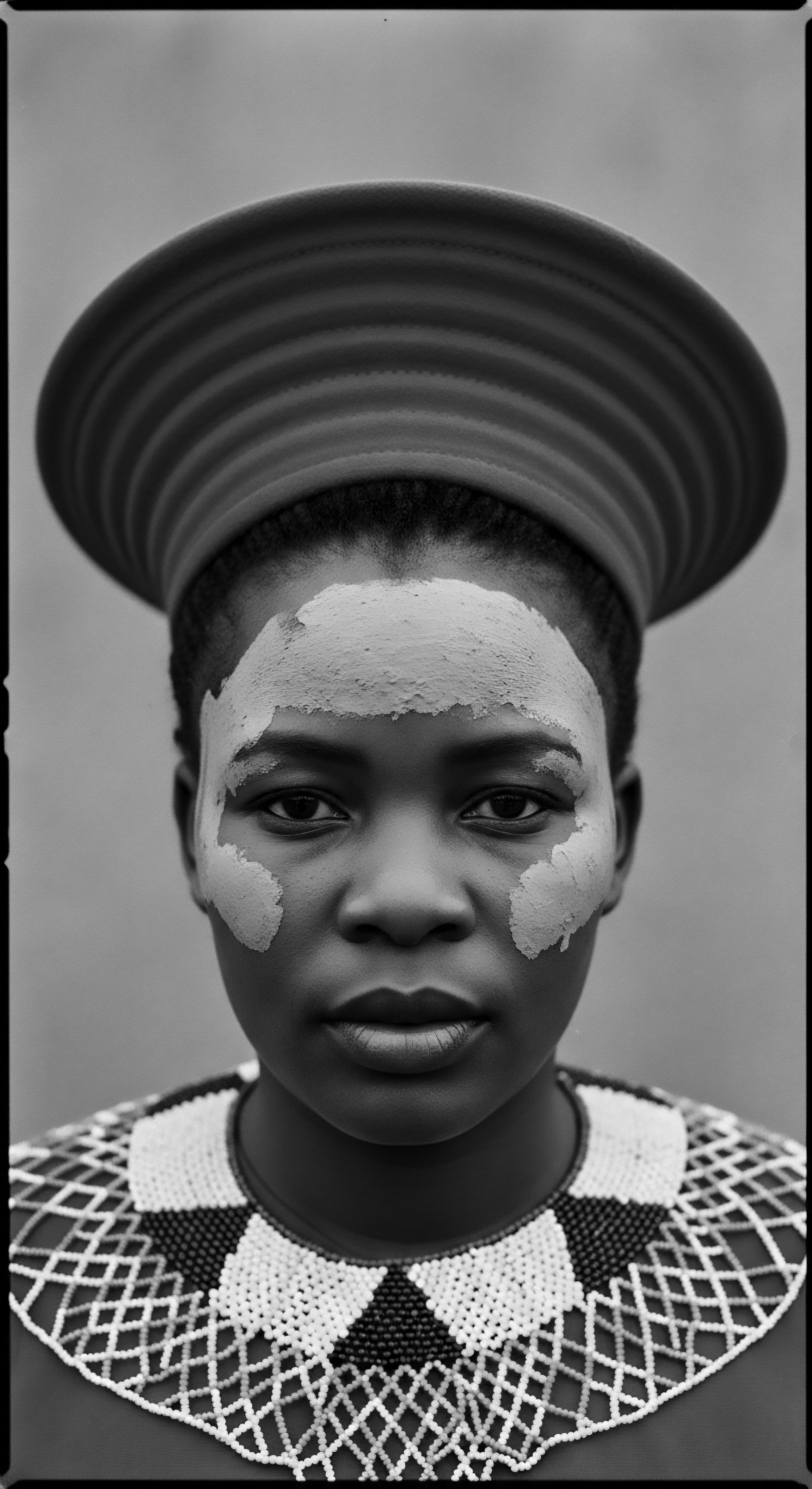

What ancestral practices influence head wrap use?
Ancestral practices influencing head wrap use center on protecting textured hair, communicating cultural identity, and preserving heritage across generations.
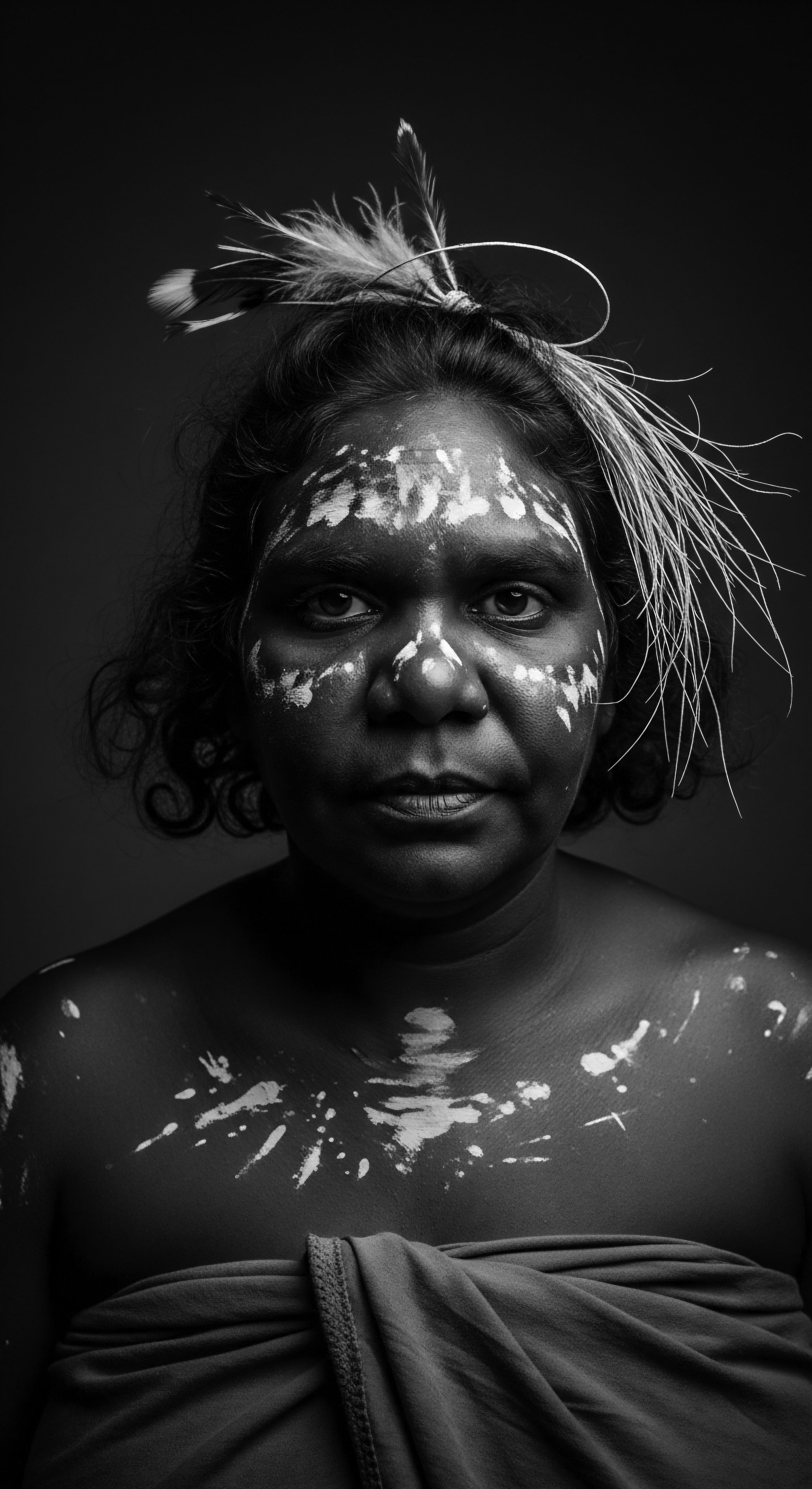

What is the historical significance of scalp rituals in textured hair heritage?
Scalp rituals in textured hair heritage embody an ancestral wisdom of care, communication, and resilience, linking physical health to profound cultural identity.

What cultural significance did hair oiling hold for Black communities?
Hair oiling holds deep significance for Black communities, rooted in ancestral practices, communal care, and identity preservation.
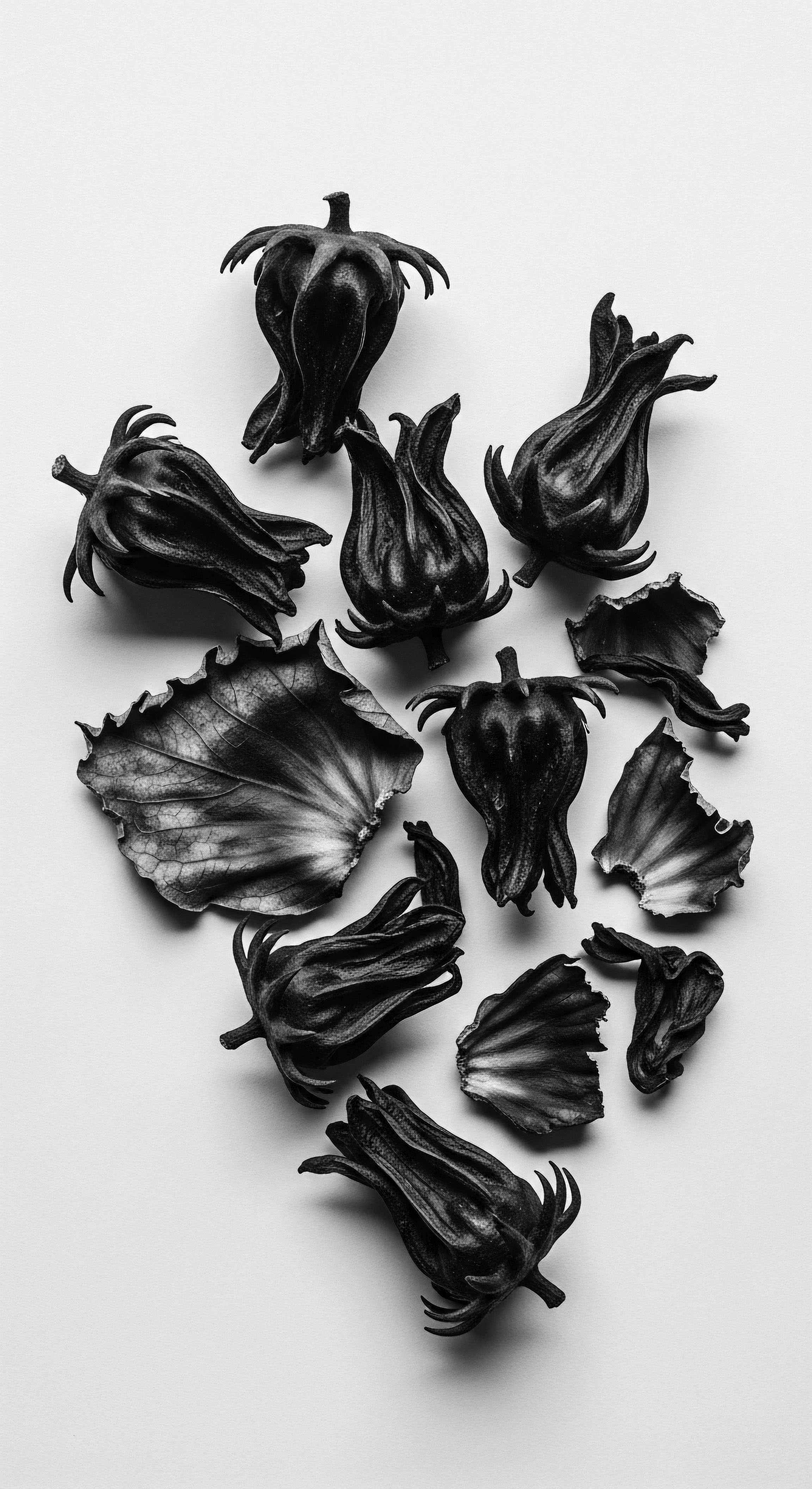

How do plant-based nighttime rituals connect to textured hair heritage?
Plant-based nighttime rituals deeply connect to textured hair heritage by preserving ancestral knowledge of botanical care and cultural identity.
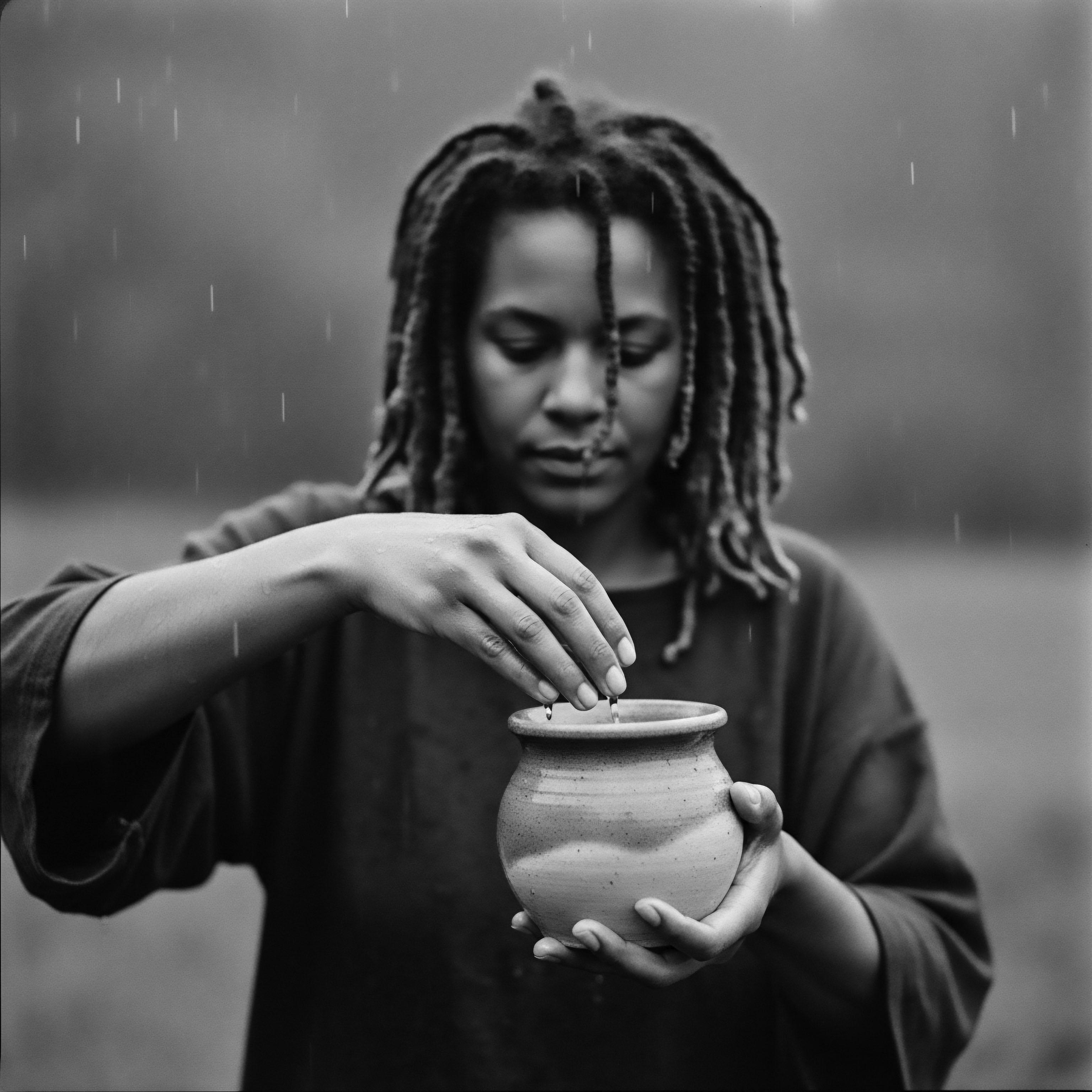

How did ancestral oils support hair growth?
Ancestral oils supported hair growth by nurturing scalp health and preserving strand integrity, rooted in textured hair heritage.

What is shea butter’s historical origin?
Shea butter's historical origin traces to ancient West Africa, deeply rooted in ancestral care for textured hair and community life.

How do ancestral plant traditions shape hair health?
Ancestral plant traditions shape textured hair health through time-honored botanical wisdom and deeply personal heritage practices.

What traditional materials were used for head coverings and hair care?
Traditional materials for head coverings and hair care centered on natural elements like plant fibers, oils, and minerals, embodying deep textured hair heritage.
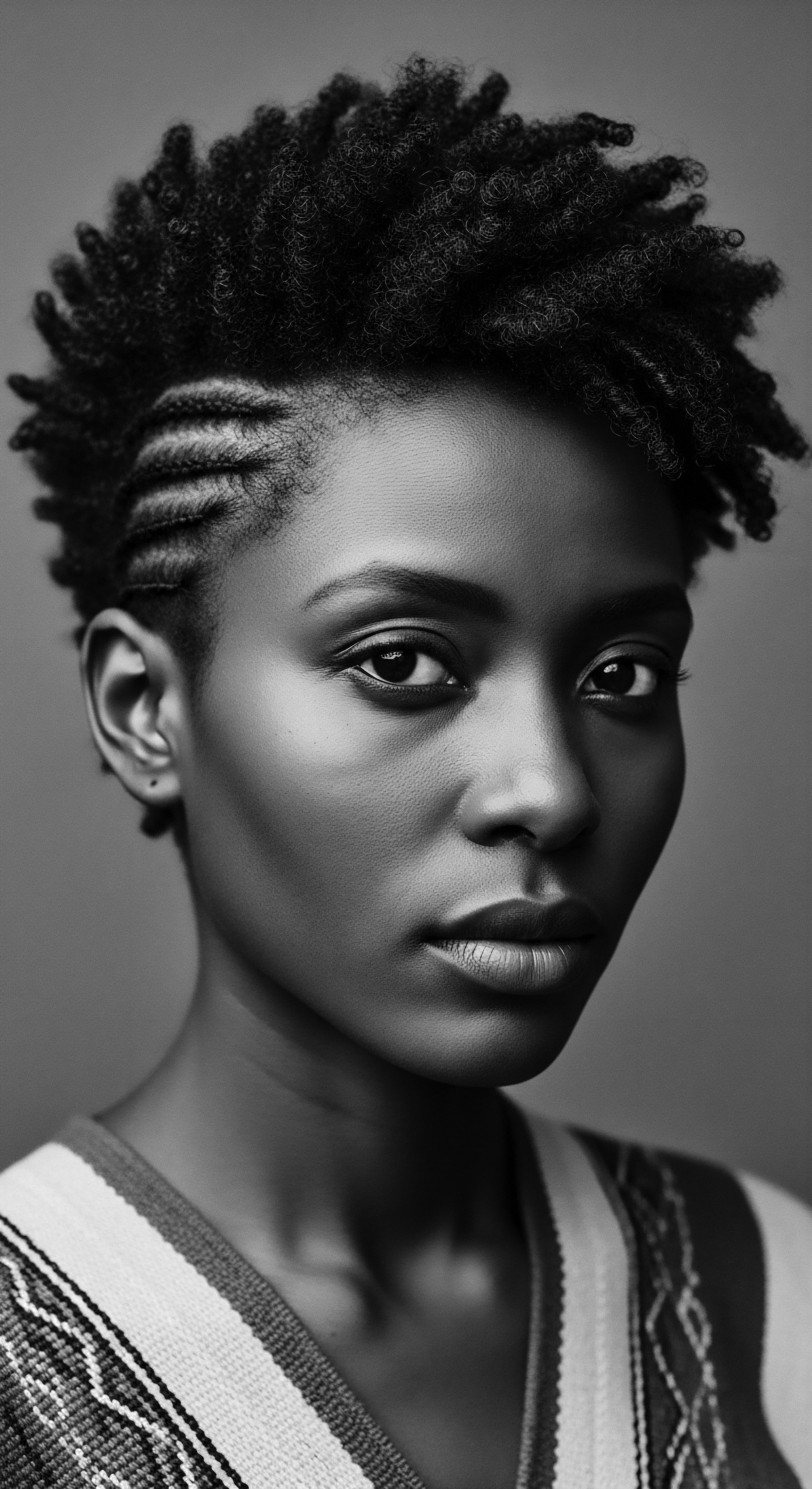

How did ancient African hair braiding communicate status?
Ancient African hair braiding communicated status by intricately mapping social standing, age, and lineage directly onto textured hair through diverse styles and adornments.
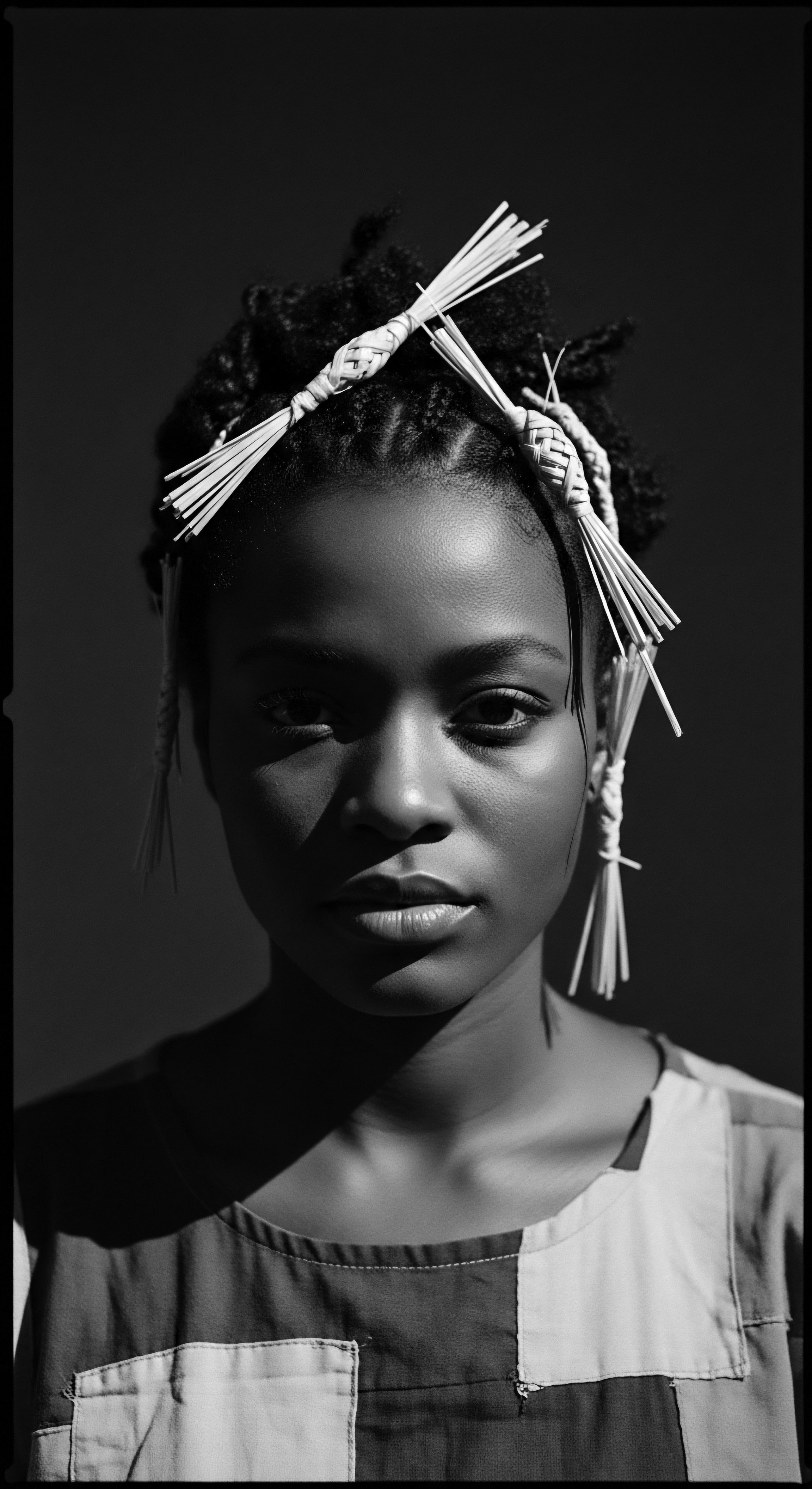

In what ways does shea butter uphold the heritage of African textured hair identity?
Shea butter upholds African textured hair heritage by linking ancestral practices, biological harmony, and cultural identity through its enduring care traditions.
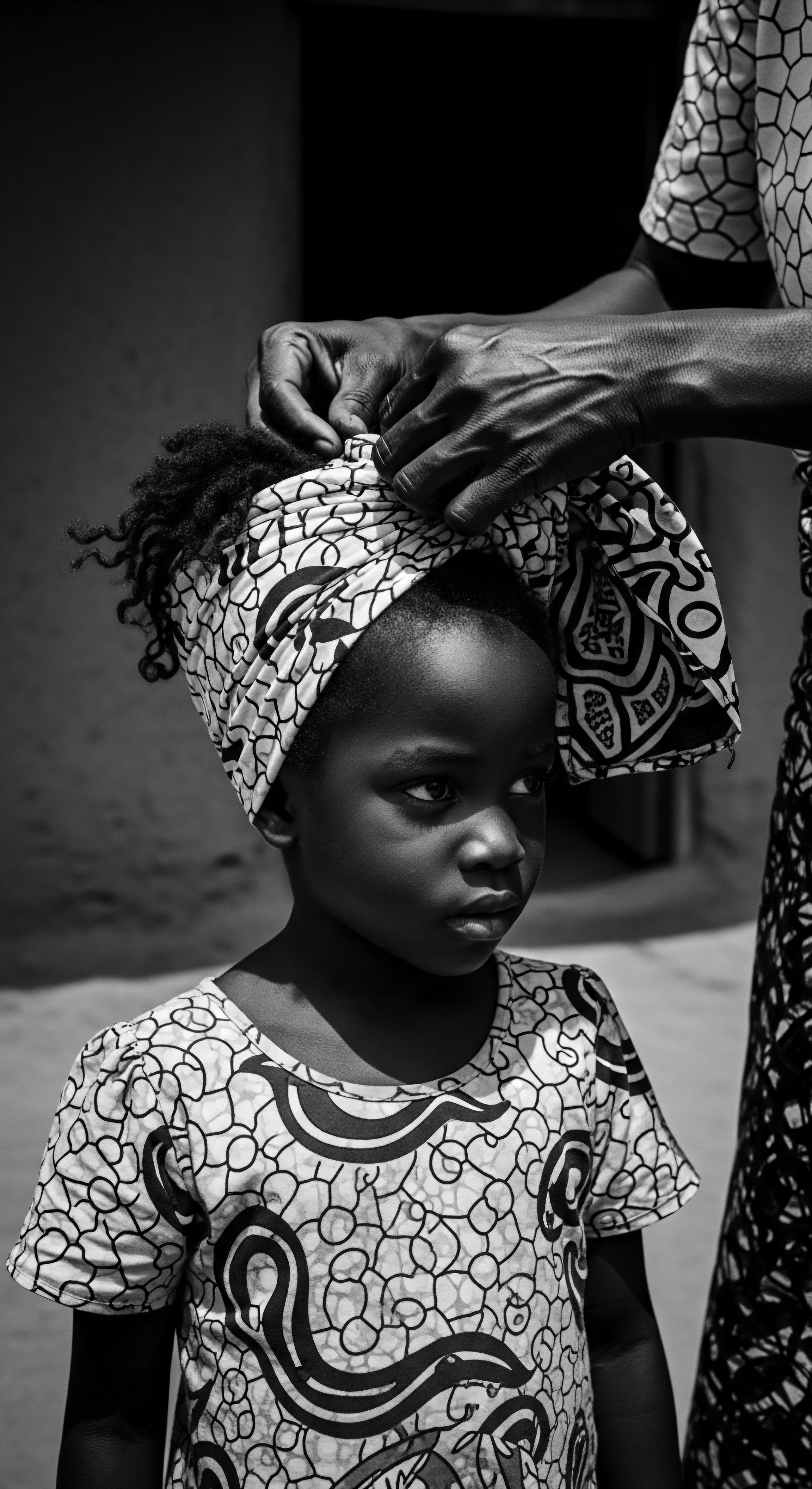

What historical evidence connects specific plant-based ingredients to ancient hair care practices?
Historical evidence shows plant-based ingredients like shea butter, castor oil, and Chebe powder deeply connected to ancient textured hair care practices.

How did shea butter become central to West African hair rituals?
Shea butter became central through ancestral wisdom recognizing its protective and moisturizing qualities, deeply connecting it to textured hair heritage and community rituals.

How does hair texture relate to collective memory and cultural resilience?
Hair texture serves as a living archive, embodying collective memory and cultural resilience within Black and mixed-race heritage.

What is the cultural history of Black hair adornments?
Black hair adornments are a living record of heritage, symbolizing identity, status, spirituality, and resilience across generations.
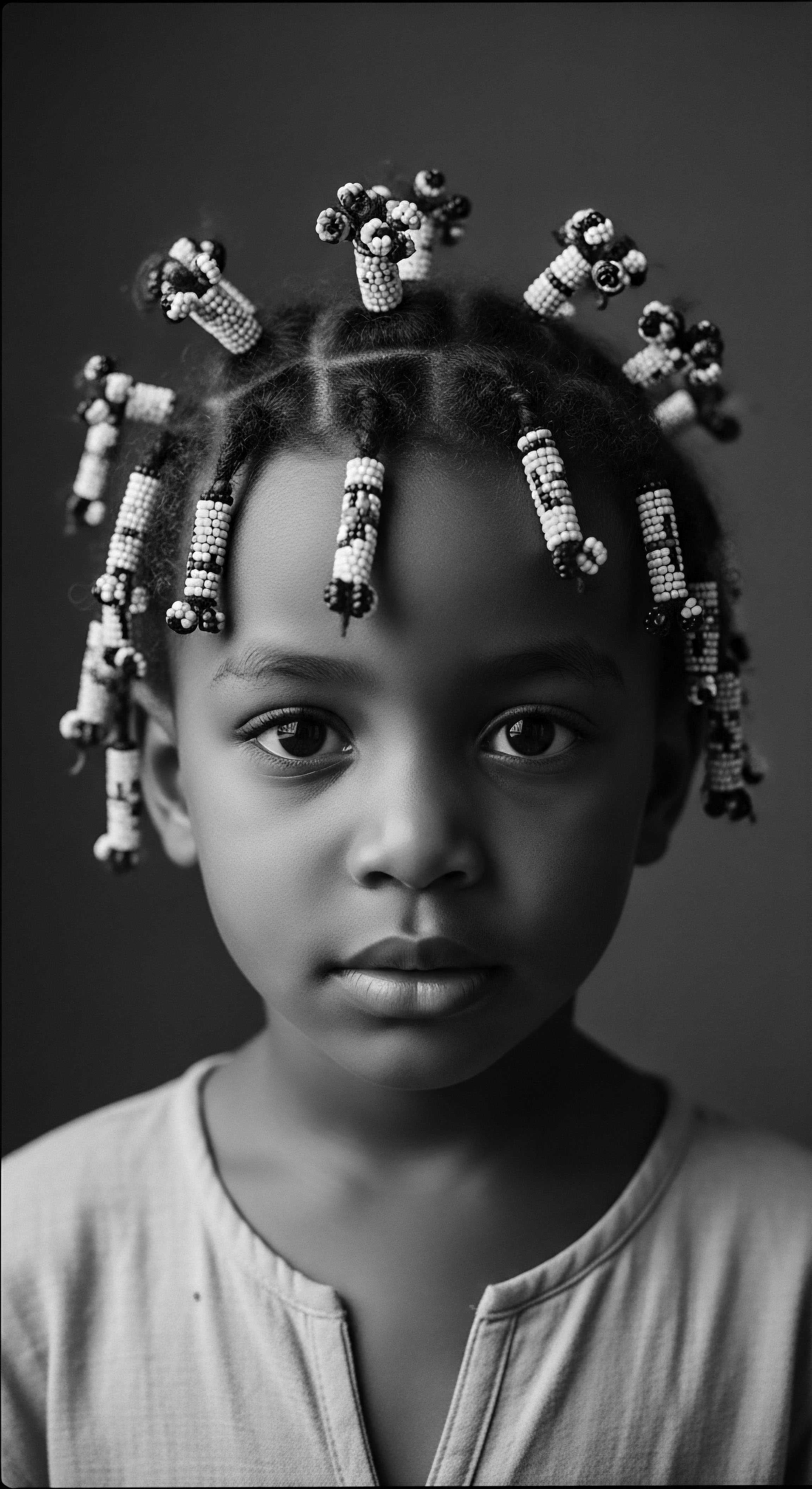

In what ways did braids serve as a tool for resistance during slavery?
Braids served as covert maps, hiding sustenance, and affirming cultural identity, powerfully linking survival to textured hair heritage.

How do braided patterns communicate social standing?
Braided patterns communicate social standing through visual codes reflecting heritage, identity, and societal roles.

In what ways did hair care rituals preserve cultural knowledge through generations?
Hair care rituals preserved cultural knowledge by embodying ancestral wisdom, historical narratives, and communal identity within textured hair heritage.

