
What Historical Significance Do Protective Styles Hold for Identity?
Protective styles for textured hair signify identity and resistance, rooted in ancient practices and deep cultural heritage.

How Do Ancestral Hair Rituals Continue to Affirm Identity and Community Bonds Today?
Ancestral hair rituals for textured hair affirm identity and community by preserving historical narratives, fostering communal bonds, and serving as symbols of cultural resilience.

How Do Modern Textured Hair Styles Echo Ancestral Practices of Communication?
Modern textured hair styles continue a lineage of silent, symbolic communication, profoundly rooted in ancestral heritage.

What Role Did Textured Hair Play in Resistance during Enslavement?
Textured hair during enslavement served as a profound tool for resistance, symbolizing cultural heritage, facilitating covert communication, and affirming identity.

What Materials Did Ancestors Use for Nighttime Hair Coverings?
Ancestors used natural fibers like silk, cotton, and various cloths for nighttime hair coverings to protect textured hair, a practice deeply rooted in heritage and care.

How Did Ancient Communities Perceive Hair’s Vitality?
Ancient communities perceived hair's vitality as a profound reflection of spirit, status, and heritage, deeply woven into their cultural fabric.

In What Ways Did Ancestral Hair Rituals Connect to Community Identity and Spiritual Well-Being?
Ancestral hair rituals deeply connected individuals to their communal identity and spiritual well-being, affirming textured hair heritage.

What Natural Ingredients Did Ancient Communities Use for Hair Health?
Ancient communities nurtured textured hair with natural ingredients like shea butter and clay, embodying deep heritage in every strand.

What Historical Influences Shaped Textured Hair Product Innovation?
Historical influences on textured hair products come from ancient remedies, resilience through oppression, and entrepreneurial ingenuity.

Can Modern Science Validate Traditional Hair Strengthening Ingredients?
Modern science affirms that traditional hair strengthening ingredients deeply rooted in textured hair heritage offer proven benefits for hair vitality.

How Did Enslavement Impact Traditional Black Hair Care?
Enslavement profoundly shifted Black hair care from communal ritual to a symbol of survival and resistance, deeply impacting textured hair heritage.

Do Traditional African Hair Oils Truly Protect Strands?
Traditional African hair oils shield strands by nurturing hair's unique structure and deepening its connection to ancestral care heritage.
Can Textured Hair’s Biological Makeup Explain Its Historical Resilience?
Textured hair’s biological design and inherited wisdom from ancestral care practices explain its enduring resilience.

Can Modern Science Explain the Benefits of Ancient African Hair Practices?
Modern science confirms many benefits of ancient African hair practices, validating their heritage and effectiveness for textured hair health.

How Did Diasporic Communities Adapt Hair Care?
Diasporic communities adapted hair care by blending ancestral practices with new resources, protecting textured hair heritage.

Why Do People Use Silk Bonnets for Textured Hair?
People use silk bonnets for textured hair to guard against friction, preserve moisture, and honor a deep ancestral tradition of hair protection.

What Historical Significance Do Traditional African Hair Ingredients Hold?
Traditional African hair ingredients hold profound historical significance, representing cultural identity, ancestral knowledge, and resilience in textured hair heritage.

What Specific Botanicals from Ancestral Traditions Support Hair Growth and Health?
Ancestral botanicals, like Chebe, Amla, and Black Seed Oil, offer profound support for textured hair by nourishing scalp and strands, reflecting centuries of heritage wisdom.

What Is the Historical Link between Head Coverings and Nighttime Hair Care?
Head coverings for nighttime hair care historically protected textured hair, preserving styles and moisture while acting as symbols of identity and resilience.

In What Ways Do Traditional African Hair Practices Connect to Cultural Identity and Resilience?
Traditional African hair practices are living expressions of cultural identity and resilience, intricately linking individuals to their heritage.

What Botanical Ingredients Were Essential for Historical African Hair Health?
Historical African hair health relied on botanicals like shea, baobab, and chebe, deeply connected to textured hair heritage and ancestral wisdom.
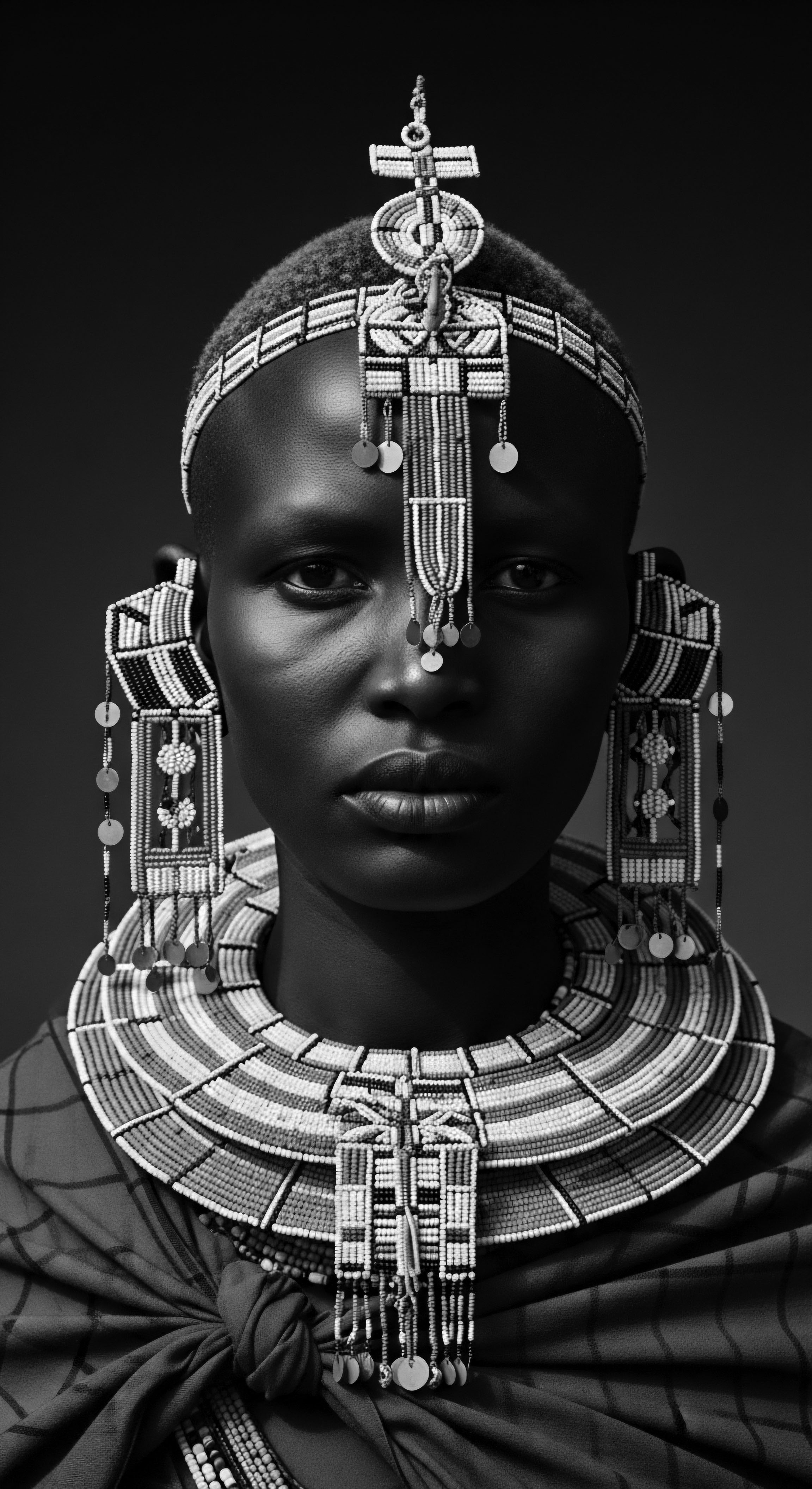

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Laws compelled Black women to cover their hair, yet they transformed this mandate into a powerful declaration of textured hair heritage and defiance.

How Did Ancestral Practices Inspire Modern Bonnets?
Ancestral head coverings for protection and identity directly shaped modern bonnets for textured hair care.

How Did Historical Oppression Shape Protective Hair Styling?
Protective hair styling was reshaped by historical oppression, becoming a defiant act of preserving textured hair heritage and identity.

How Does African Hair Heritage Shape Identity?
African hair heritage shapes identity by chronicling resilience, spiritual connection, and vibrant communal life within its unique biological architecture.

How Did Ancient Cultures Preserve Hair Moisture in Arid Lands?
Ancient cultures preserved textured hair moisture using rich botanical oils and butters, along with protective styles, reflecting deep ancestral wisdom.

How Did Ancient Combs Ease Textured Hair?
Ancient combs eased textured hair through wide-toothed designs and natural materials, reflecting deep ancestral care knowledge.
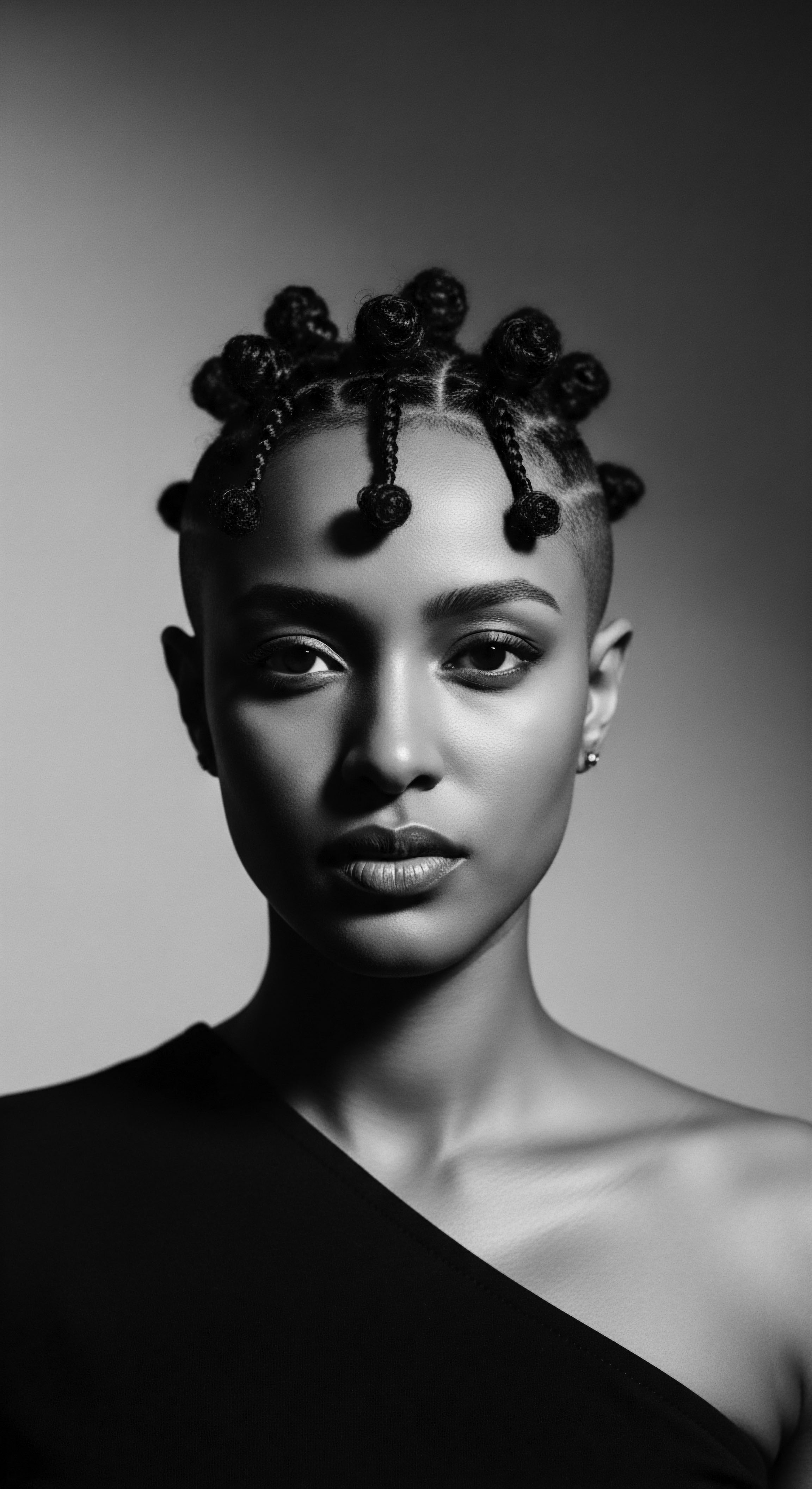

What Is the Historical Significance of Hair Wraps in Black Culture?
Hair wraps hold profound historical significance in Black culture, symbolizing protection, resilience, identity, and a deep connection to textured hair heritage.
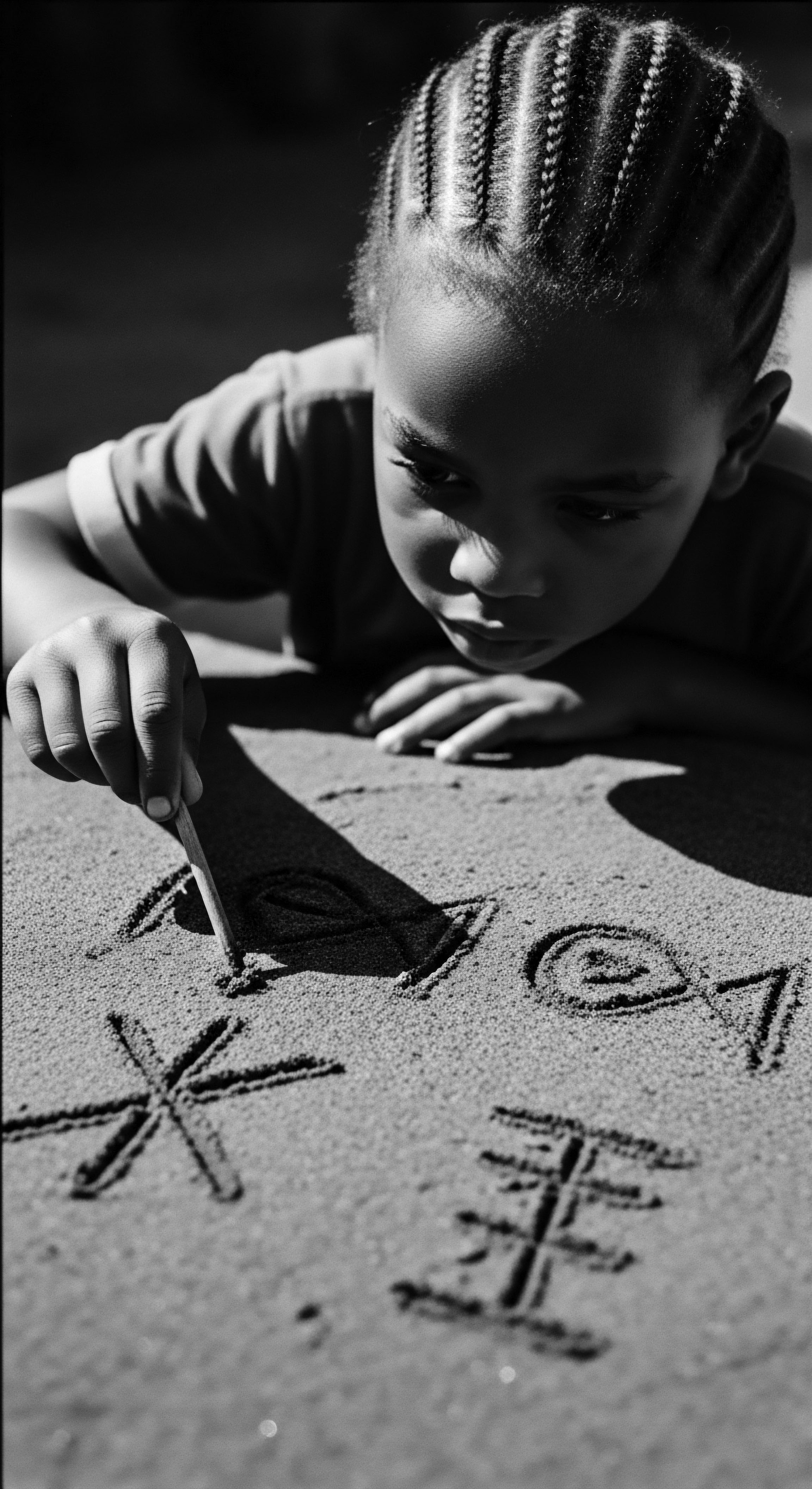

Why Did Textured Hair Become a Canvas for Secret Messages?
Textured hair transformed into a canvas for secret messages through its inherent structural qualities and profound cultural heritage as a medium for identity, status, and clandestine communication.

