
How Did Ancient Egyptian Wig Styles Influence African Hair Adornment?
Ancient Egyptian wig styles, symbols of status and hygiene, directly influenced the rich hair adornment heritage across Africa.

What Ancestral Hair Oils Did Ancient Egyptians Use?
Ancient Egyptians used oils like castor and moringa, alongside animal fats, for nourishing and styling diverse textured hair.

Can Traditional Ingredients Benefit Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Traditional ingredients profoundly benefit modern textured hair regimens by grounding care in ancestral wisdom and natural potency.

In What Ways Did Shea Butter Shape Cultural Identity through Hair Care?
Shea butter profoundly shaped cultural identity through hair care by anchoring practices in ancestral wisdom, supporting communal rituals, and symbolizing Black and mixed-race heritage.

Which Natural Ingredients Preserved Moisture in Ancient Textured Hair?
Ancient textured hair was moisturized using natural plant-derived oils and butters, rooted in ancestral practices.

How Did Cultural Significance Shape Shea Butter’s Role in Textured Hair Heritage?
Shea butter's cultural significance deeply rooted its role in textured hair heritage through generations of ancestral care, economic empowerment, and ritual.

What Is Shea Butter’s Role in Ancestral Hair Practices?
Shea butter provides ancestral moisture, scalp soothing, and structural support for textured hair, connecting deeply to heritage beauty practices.
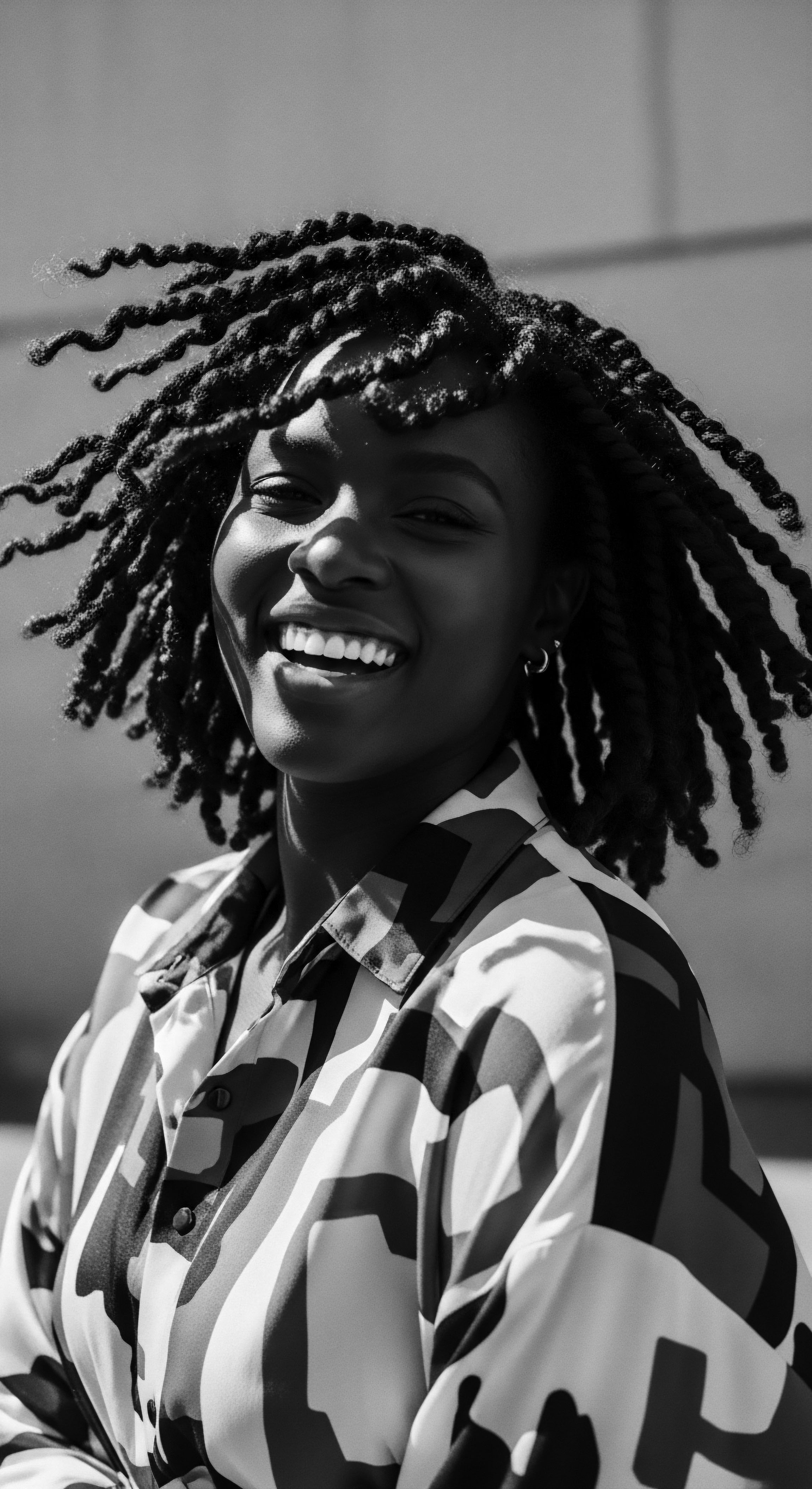

Can Textured Hair Be a Conduit for Spiritual Connection and Identity?
Textured hair serves as a profound conduit for spiritual connection and identity, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage and cultural memory.

What Ancestral Knowledge Informs Shea Butter’s Benefits for Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancestral knowledge affirms shea butter as a time-honored source of moisture, protection, and cultural identity for textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Did Historical Practices Shape the Resilience of Black Hair Traditions?
Historical practices deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom shaped the resilience of Black hair traditions as acts of survival, identity, and cultural continuity.
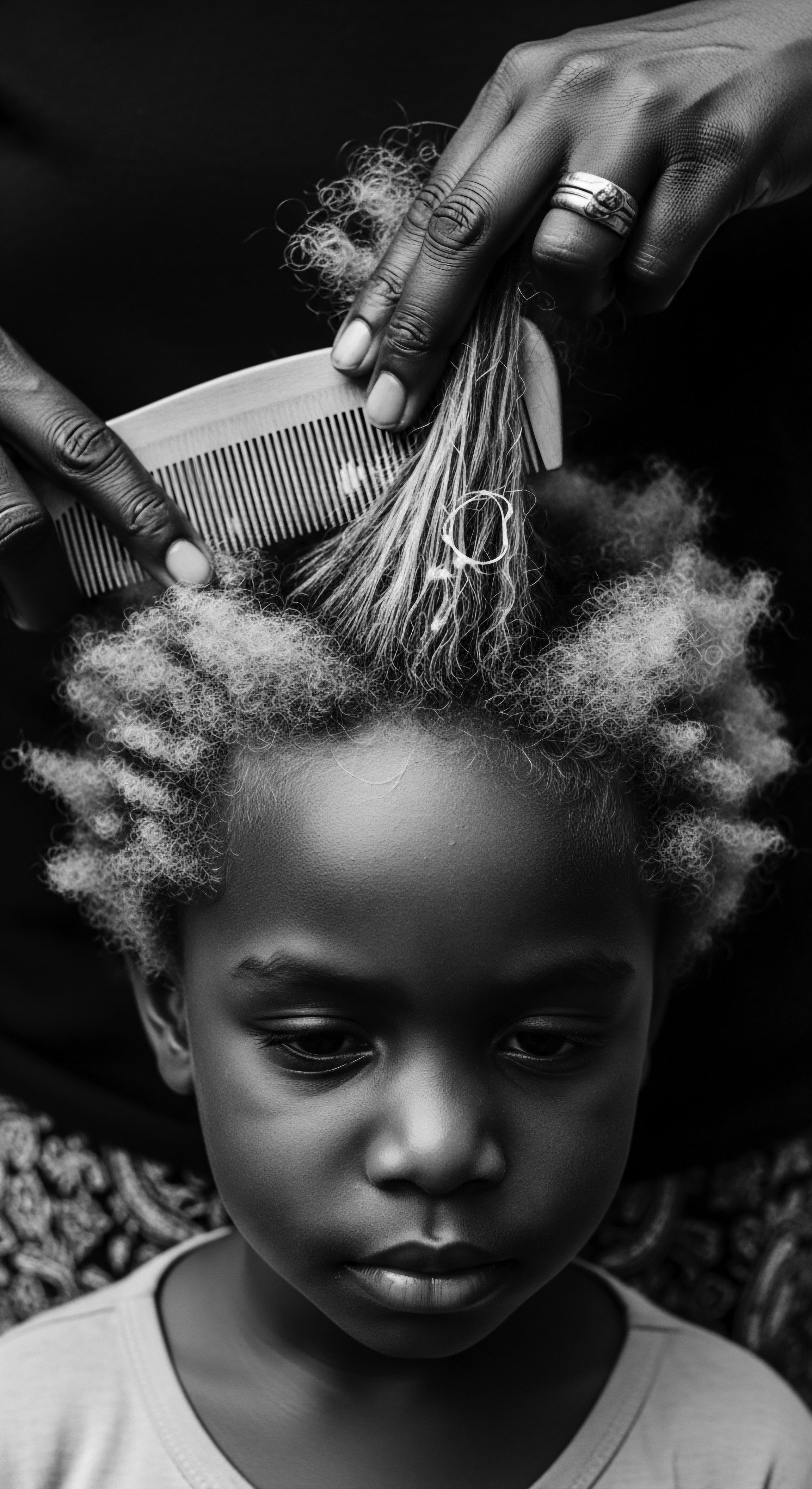

In What Ways Did Early Scientific Observations Shape Textured Hair Care Rituals?
Early observations of hair's properties and environmental responses shaped ancestral textured hair care rituals, preserving heritage.
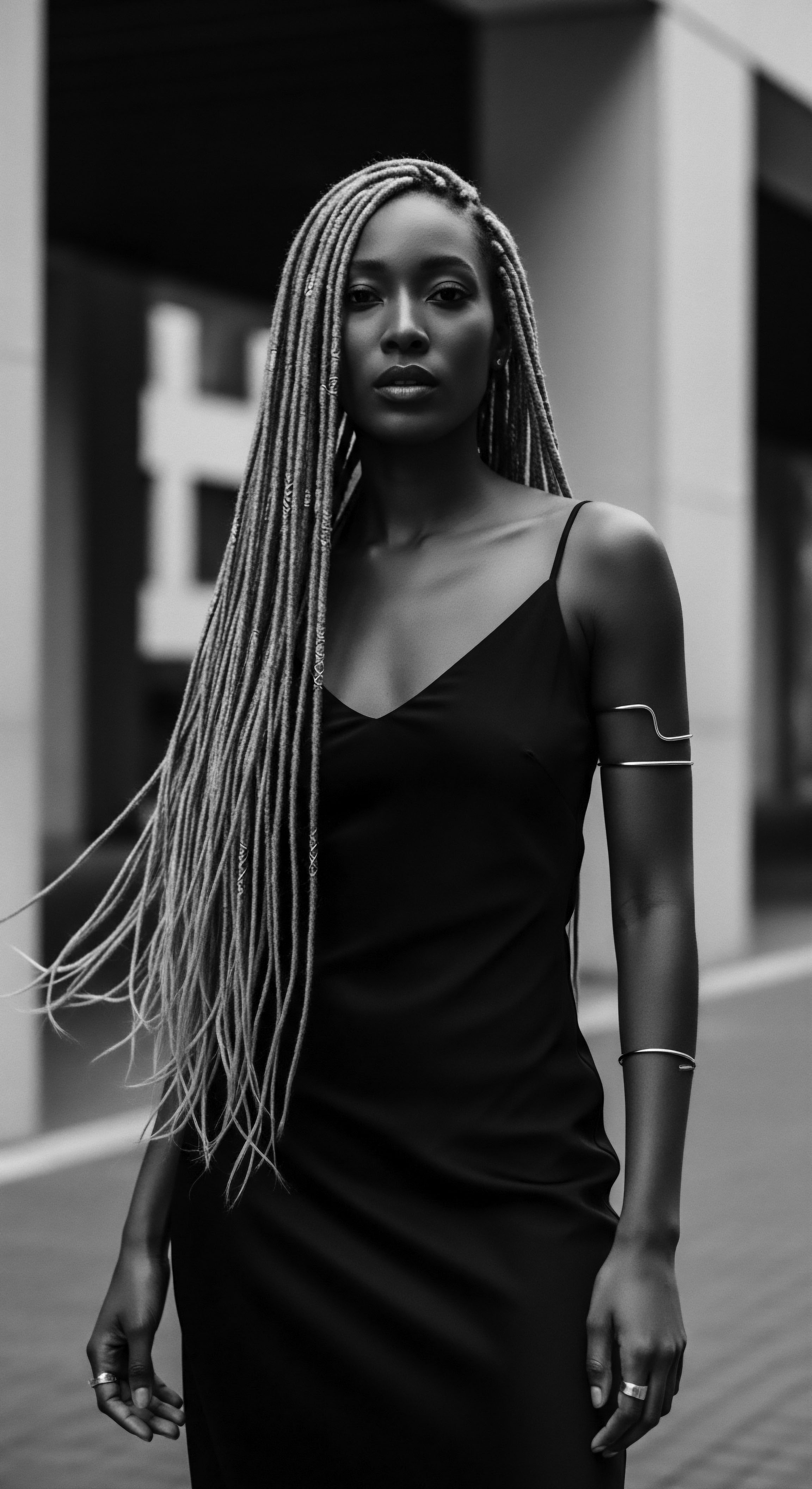

What Cultural Meanings Did Hair Carry in Pre-Colonial Africa?
Hair in pre-colonial Africa embodied deep social, spiritual, and communal meanings, serving as a powerful expression of textured hair heritage.
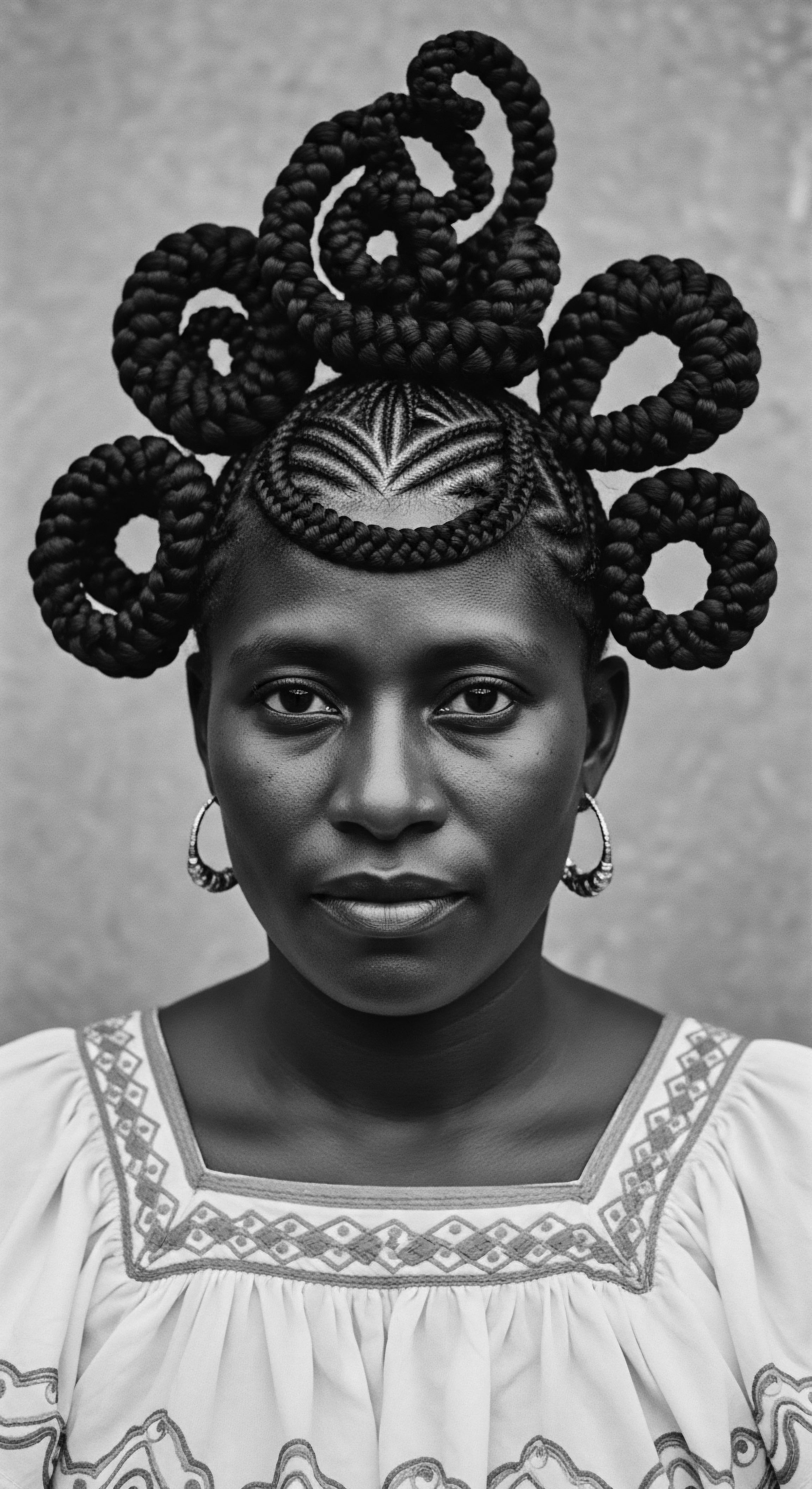

What Specific Hair Rituals Marked Life Stages in Historical African Communities?
Historical African hair rituals marked life stages through intricate styling, adornment, and ceremonial shaving, signifying birth, initiation, marriage, and elderhood, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

How Did Ancient African Hairstyles Convey Status?
Ancient African hairstyles conveyed status through intricate patterns, adornments, and grooming rituals, signifying identity and social standing.

How Do Historical African Hair Rituals Connect to Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical African hair rituals connect to modern textured hair care through a living heritage of deep cultural reverence, protective practices, and natural ingredient use.

In What Ways Do Traditional Nighttime Hair Rituals Connect to Contemporary Practices?
Traditional nighttime hair rituals for textured hair connect to contemporary practices through enduring ancestral wisdom of protection and nourishment.

How Did Ancestral Traditions Shape Textured Hair Resilience?
Ancestral traditions fortified textured hair's resilience through practices, natural remedies, and communal rituals rooted in cultural heritage.

What Historical Adaptations Shaped Textured Hair Structure?
Textured hair structure adapted for climate protection and thermoregulation, a biological heritage profoundly shaped by ancestral ingenuity.
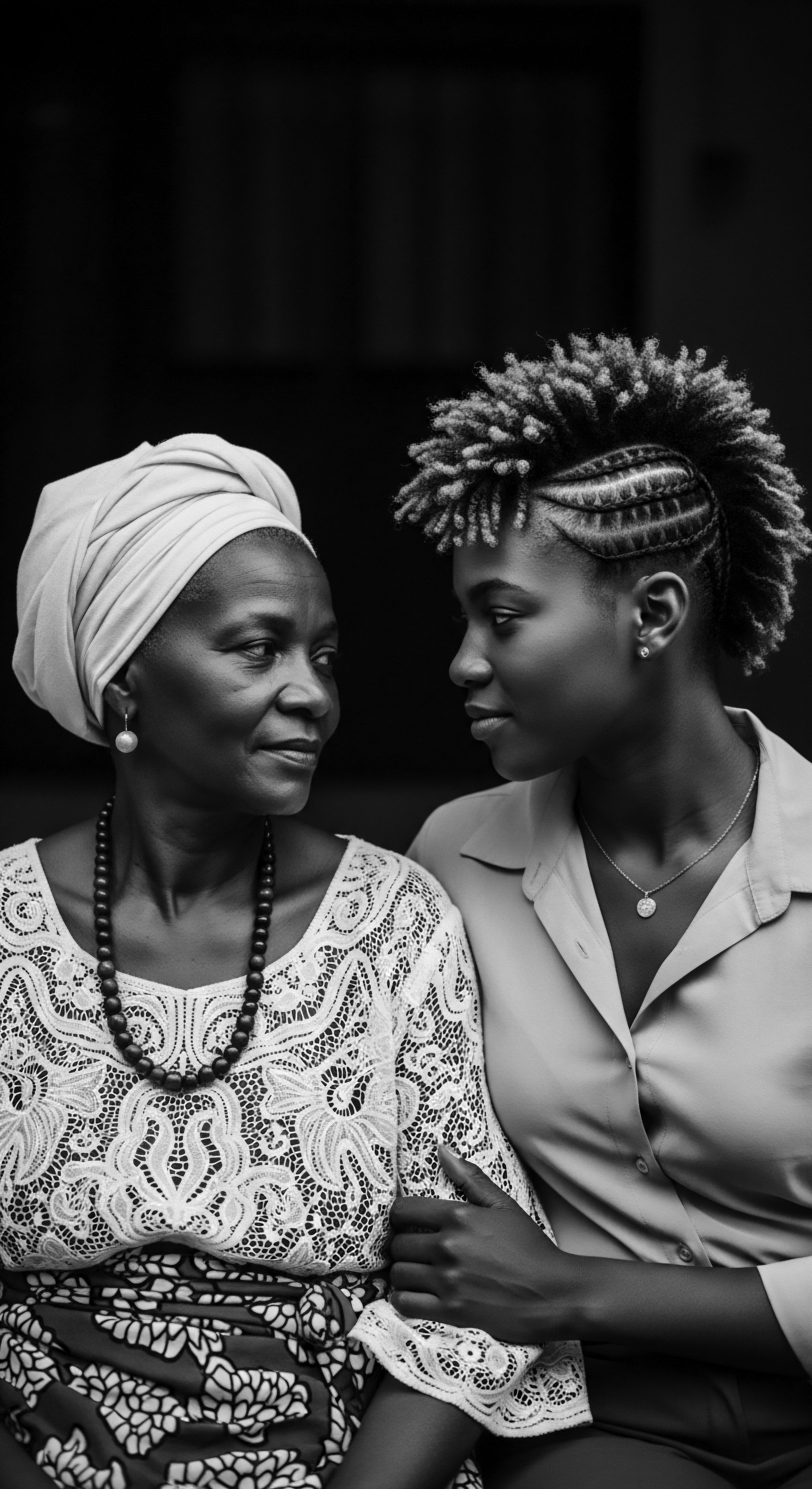
What Ancestral Ingredients Are Used in Today’s Coily Hair Products?
Today's coily hair products frequently contain ancestral ingredients like shea butter and coconut oil, honoring a rich heritage of natural hair care wisdom.

What Ancestral Practices Link Textured Hair Care to Identity?
Ancestral practices link textured hair care to identity through deep cultural symbolism, communal rituals, and acts of resistance that honor heritage.

What Scientific Benefits Do Headwraps Offer for Textured Hair Hydration?
Headwraps, through ancestral wisdom and material science, preserve textured hair's hydration by reducing friction and preventing moisture evaporation.
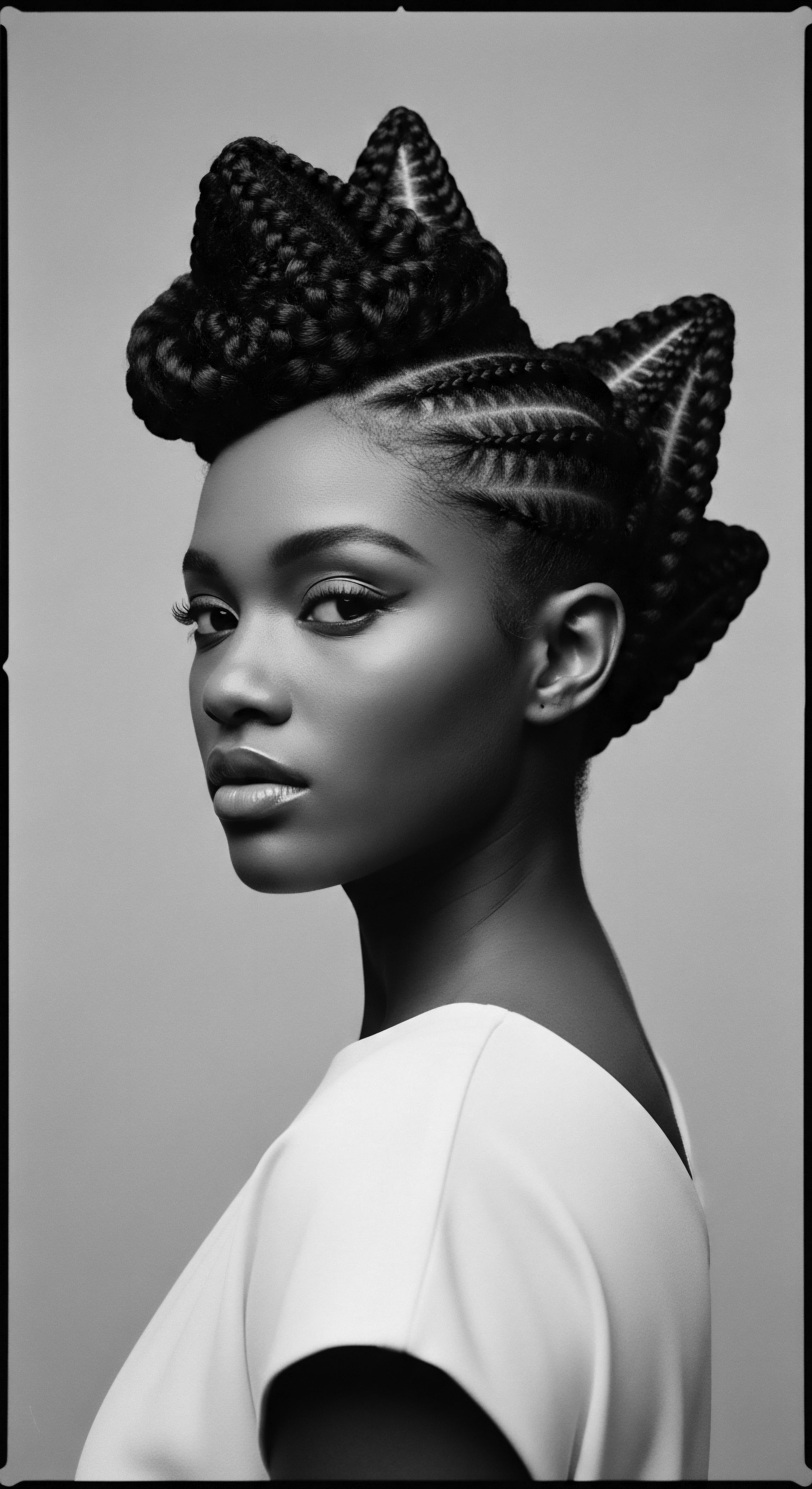

What Structural Properties of Textured Hair Informed Ancient Care Practices?
Textured hair's fragility and need for moisture inspired ancient care rituals deeply rooted in heritage.

How Did Early Societies Maintain Textured Hair?
Early societies maintained textured hair through protective styles, natural ingredients, and communal rituals rooted in cultural identity.

How Did Ancient African Hair Practices Contribute to Length Retention in Textured Hair?
Ancient African hair practices fostered length retention through protective styling, nourishing ingredients, and cultural rituals.

What Is the Long-Term Impact of Heritage-Based Hair Routines?
Heritage-based hair routines provide a profound, long-term connection to cultural identity, communal resilience, and ancestral wisdom for textured hair.
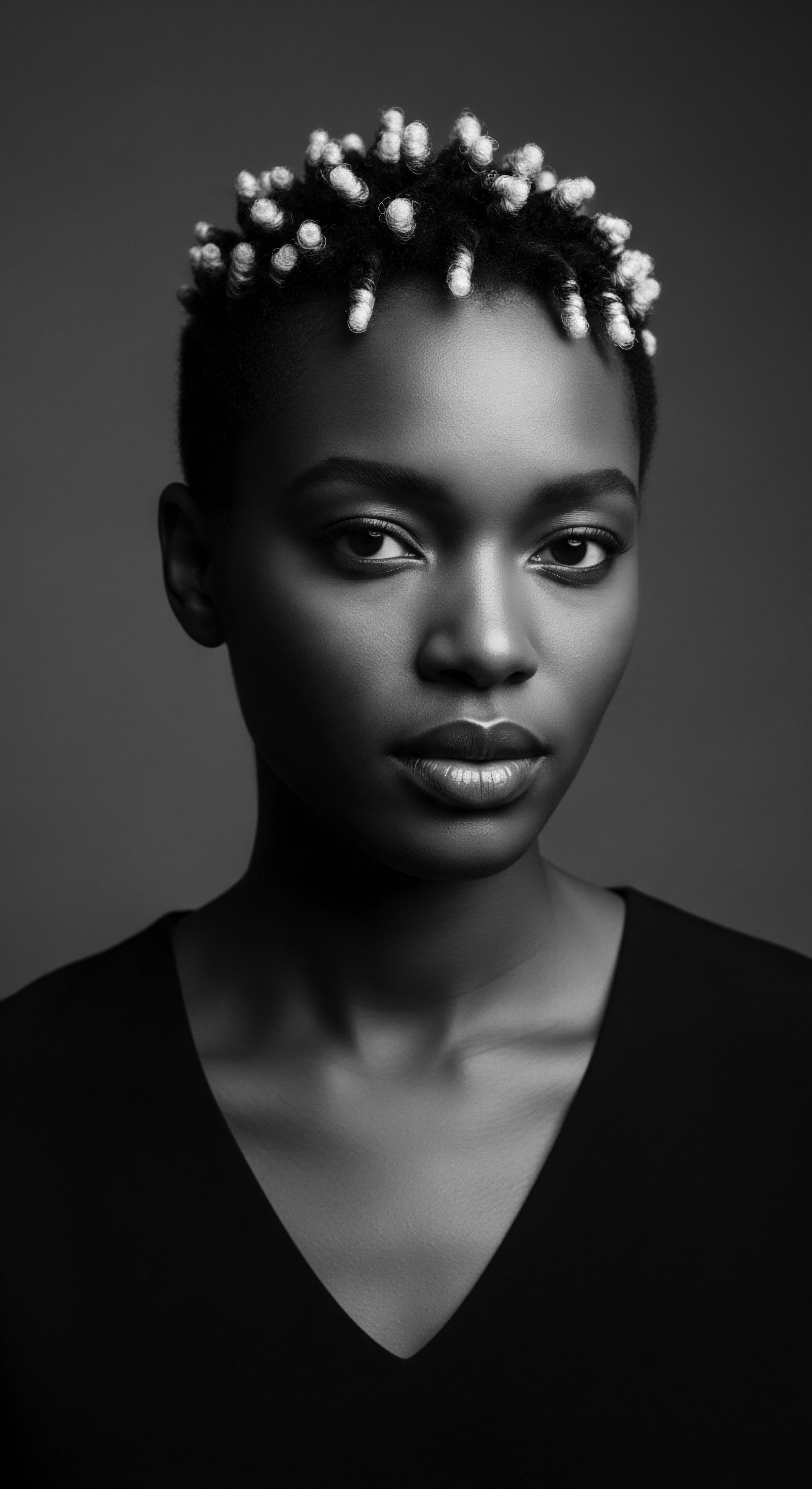

Which Ancestral Ingredients Preserved Textured Hair’s Inherent Oils?
Ancestral ingredients, like shea butter and Chebe powder, preserved textured hair's inherent oils by forming protective barriers.

How Do Black Hair Care Businesses Preserve Cultural Heritage?
Black hair care businesses preserve heritage by serving as cultural hubs, passing down ancestral styling practices, and reintroducing traditional ingredients.

What Historical Laws Relate to Textured Hair Discrimination?
Historical laws aimed to control identity by dictating hair, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and ancestral practices.
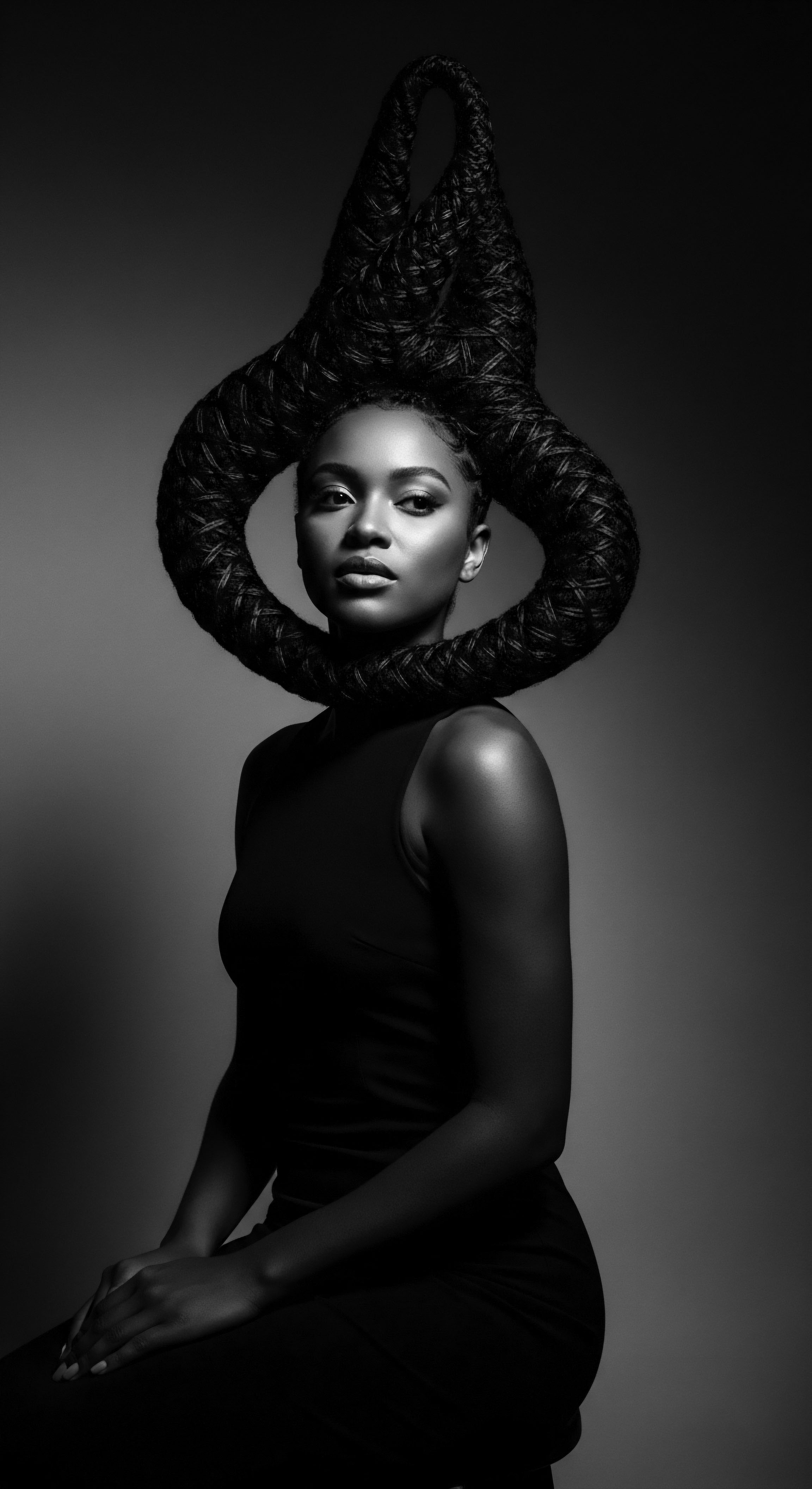

How Did Colonialism Impact Black Hair Identity?
Colonialism profoundly distorted Black hair identity by devaluing ancestral textures and practices, forcing assimilation while inspiring acts of cultural preservation and resistance.

