Roots
To truly understand the enduring spirit of textured hair, one must journey back to its origins, not as a trend, but as a living legacy. Consider the ancestral hands that first sculpted coils and kinks into patterns reflecting cosmos and community. Our exploration of what enduring cultural significance ancient hair care practices hold for textured hair heritage begins with the very structure of the strand itself, echoing millennia of care and cultural meaning. This is more than merely about historical footnotes; it speaks to the very soul of a strand, vibrating with echoes of a shared past and a resilient present.

The Sacred Strand Its Ancestral Blueprint
The unique architecture of textured hair, from tight coils to gentle waves, carries a biological signature that has shaped human care practices for millennia. Ancient peoples, observing the ways their hair responded to climate, activity, and adornment, developed sophisticated methods to tend to it. Archaeological findings, particularly from ancient Egypt, Kush, and various West African cultures, reveal that hairstyles transcended simple aesthetics; they were expressions of power, spirituality, and social cohesion. Imagine the rhythmic sound of fingers deftly braiding, a tradition stretching back to Namibia around 3500 BC, where the twisting of locks first gained cultural momentum.

Hair Anatomy and Physiology from an Ancestral Lens
For our ancestors, hair was not just a covering; it was an external extension of the self, a conduit for spiritual energy and ancestral connection. The very shape of the hair follicle, determining its curl pattern, dictated how light interacted with it, how moisture was held, and how it could be styled. This intimate understanding, though not articulated in modern scientific terms, guided practices. They instinctively knew, for instance, that coiled hair retained less natural oil distributed from the scalp, leading to the development of deep conditioning rituals long before science named lipids and proteins.
- Melanin Distribution ❉ The rich melanin that gives textured hair its deep hues also provided natural protection against the sun’s intense rays, a biological shield honed over generations.
- Follicle Shape ❉ The elliptical or flattened cross-section of the textured hair follicle results in its characteristic curls and coils, influencing how ancient hands approached detangling and styling.
- Moisture Needs ❉ The helical structure of textured hair often makes it prone to dryness. Ancient practices, as we will explore, often centered on sealing in moisture and protection from environmental elements.

Classification Systems and Their Cultural Origins
While modern science offers classification systems based on curl patterns, ancient societies had their own intricate ways of ‘reading’ hair. A hairstyle could signal one’s marital status, age, social status, ethnic identity, religion, wealth, or even surname. This intricate system acted as a visual language, allowing individuals to communicate complex social information without uttering a word. The Maasai, for instance, used hair shaving and regrowth as integral parts of rites of passage, marking new life stages and spiritual reconnection.
Ancient hairstyles were a visual language, communicating social standing, tribal identity, and spiritual connection.
In West African societies of the 1400s, an individual’s hairstyle could immediately reveal their tribal affiliation, their standing within the community, or their journey through life. This level of detail speaks volumes about the value placed on collective identity and the deep understanding of hair as a marker of belonging.

The Enduring Lexicon of Textured Hair
The words we use to describe textured hair today often have roots in traditional practices and observations. Terms like ‘cornrows’ (often called ‘canerows’ in the Caribbean) are a testament to the enduring nature of these styles, their resilience, and their historical context. These are not just hairstyles; they are living archives of cultural memory, passed down through generations.
The longevity of certain hairstyles and care techniques underscores their deep cultural significance. From the precise parting of cornrows to the meticulous layering of wigs in ancient Egypt, each practice carried a story, a purpose beyond mere appearance. Hair in ancient Egypt, for example, was a marker of status, gender, age, and even held religious and magical connotations.

Ritual
The care of textured hair, for ancestral communities and for those who carry that heritage today, was rarely a solitary act. It was, and remains, a deeply communal affair, a ritual passed down through whispers and skilled hands, a tender thread connecting generations. This communal aspect, often overlooked in the hurried pace of modern life, holds a profound cultural significance, rooted in shared experiences and mutual support.

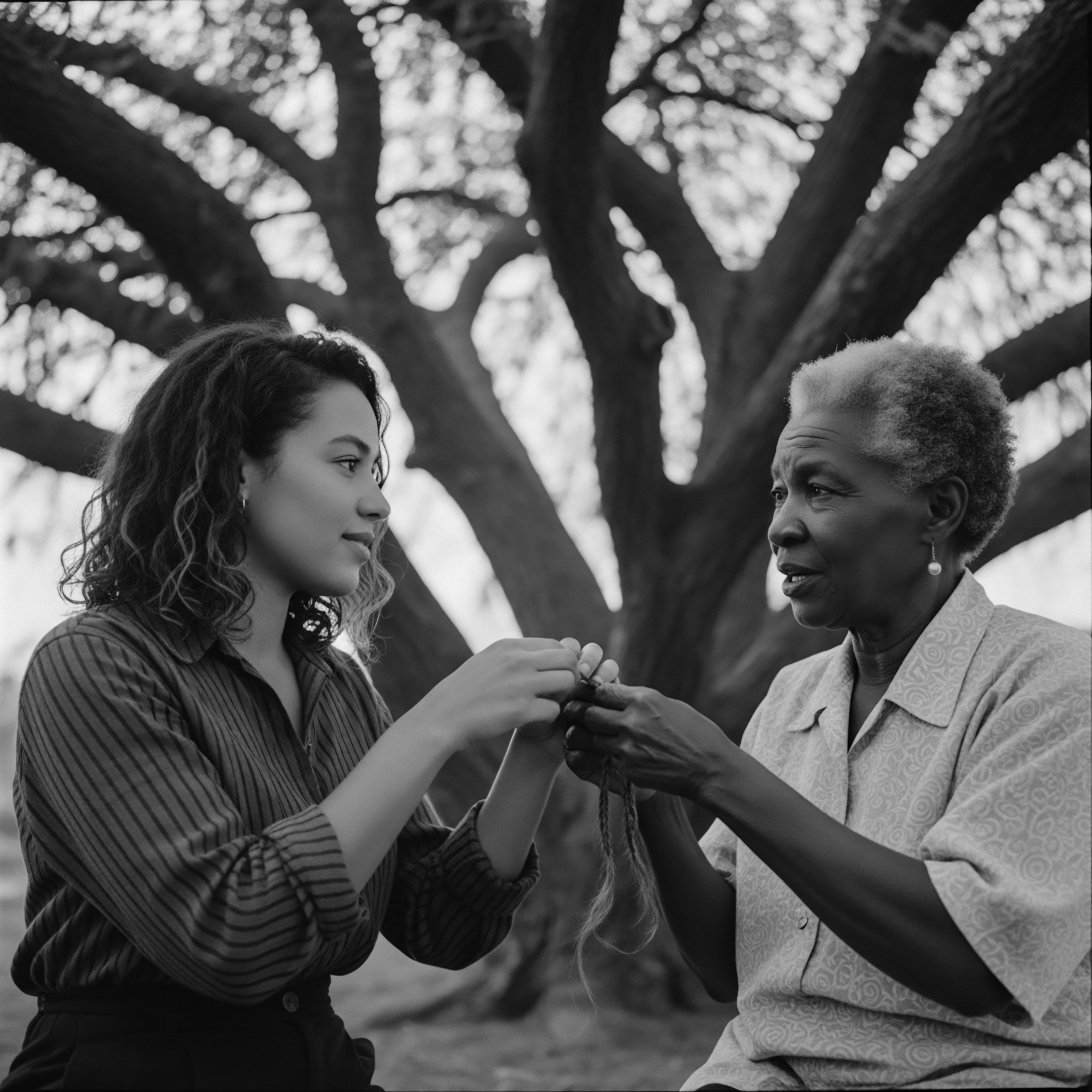
Communal Care and Sacred Bonds
The act of braiding or styling hair in many African societies was an intimate social experience. Mothers, sisters, aunts, and friends would gather, their conversations intermingling with the rhythmic sounds of styling. These sessions served as spaces for sharing stories, wisdom, and advice, strengthening communal bonds and transmitting cultural knowledge. This tradition of collective care persists today, a silent affirmation of lineage and belonging.

Braiding as Communication and Resistance
Beyond aesthetic appeal or communal bonding, ancient hair practices, particularly braiding, held critical roles in communication and acts of resistance, especially during periods of oppression. The intricate patterns of cornrows, for instance, were used by enslaved people as a code to communicate secretly, sometimes even to create maps for escape. Research suggests that enslaved individuals braided rice and seeds into their hair, smuggling grains from Africa and later planting them to create a source of food after escape. This powerful historical example demonstrates how hair, a seemingly personal feature, became a tool for survival and an emblem of unyielding spirit.
Hair braiding transformed into a language of freedom during enslavement, carrying coded messages and seeds of survival.
The Tignon Law of 1786 in Louisiana, which forced women of African descent to cover their hair, highlights the attempts to control Black women’s appearances and perceived status. However, this act of oppression inadvertently fueled resistance, with head wraps becoming symbols of defiance and continued cultural expression. The very act of maintaining one’s hair heritage in the face of such adversity became a silent, yet powerful, form of resistance.

Ancestral Ingredients and Their Efficacy
The bounty of the earth provided ancient communities with a wealth of ingredients for hair care. These were not random choices, but informed by generations of observation and experimentation. The use of natural oils, butters, and plant extracts formed the backbone of traditional regimens, tailored to the specific needs of textured hair in varying climates.
For instance, the use of Chébé powder, sourced from the Northern Chad mountains, was rumored to be the secret to the long, lustrous hair of Bassara/Baggara Arab women in Chad. This finely ground powder, mixed with water, was applied to the hair, demonstrating an ancient understanding of its conditioning properties. Similarly, henna was widely used in ancient Egypt, not only for coloring but also for strengthening hair, improving its texture, and adding shine, particularly effective in the arid desert climate.
Traditional hair oils, still widely used today, were crafted from locally available resources. These oils, such as palm oil, beeswax, and various plant extracts, served multiple purposes:
- Moisture Retention ❉ Oils create a hydrophobic film, reducing water loss from the scalp and preventing dryness.
- Scalp Health ❉ Many traditional ingredients possess antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, maintaining a healthy environment for hair growth.
- Hair Strengthening ❉ Certain oils, like coconut oil, can penetrate the hair shaft, reducing protein loss and fortifying the strands.
The knowledge of these ingredients and their applications was meticulously passed down, forming an ancestral pharmacopeia of hair wellness.

The Significance of Indigenous Hair Practices
Beyond the African continent, Indigenous cultures globally also hold profound significance for hair care, often connecting it to spirituality, land, and identity. For many Indigenous peoples, long hair represents a strong cultural identity, promoting self-esteem and a sense of belonging. Knowledge Keeper Ernie Michel of the Nlaka’pamux people shares that for Indigenous men and boys, long hair is a connection to the land, a source of strength, and an embodiment of one’s spirit.
Cutting hair is often reserved for times of mourning, symbolizing a new stage of growth and healing. This reverence for hair as a sacred extension of the self speaks to a universal wisdom, deeply embedded in diverse heritage narratives.

Relay
The journey of ancient hair care practices for textured hair is not a relic of the past; it is a vibrant, living relay, passed from elder to youth, from ancestor to descendant, adapting, enduring, and continuously shaping contemporary expressions of identity. This continuation speaks to a deep, inherent resilience, a refusal to let go of what connects us to our origins.

The Unbound Helix Hair as Identity
The history of textured hair is inextricably linked to narratives of identity, resistance, and self-expression within Black and mixed-race experiences. In pre-colonial Africa, hairstyles served as markers of social status, age, occupation, rank, religion, and ethnic group. When enslaved Africans were forced to cut or shave their hair, it was a deliberate act of stripping away their identity and cultural ties. Yet, this assault on their personhood birthed new forms of resistance, allowing hair to become a potent symbol of defiance and a silent assertion of humanity.
The natural hair movement of the 1960s, for example, saw the Afro hairstyle rise as a symbol of the fight for equal rights and a rejection of Eurocentric beauty standards. This historical moment powerfully illustrates how hair becomes a political statement, a visual declaration of self-acceptance and cultural pride. Today, the acceptance and celebration of natural hair continues to grow globally, with initiatives like World Afro Day and National Crown Day.

How Does Ancient Wisdom Inform Modern Hair Science?
The enduring efficacy of ancient hair care practices is now being substantiated by modern scientific inquiry. The centuries-old tradition of hair oiling, for instance, finds scientific validation in its ability to reduce protein loss and help hair retain moisture. Oils, rich in fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants, provide essential nutrients to the scalp and hair follicles, promoting healthy growth.
Consider the simple act of wrapping hair at night. This practice, passed down through generations, finds its scientific grounding in the need to protect delicate strands from friction and moisture loss during sleep. Traditional head wraps, often made from natural fibers, minimized tangling and preserved moisture, mirroring the modern function of a silk bonnet. These historical solutions, born of necessity and observation, align remarkably with current dermatological understanding of hair preservation.
A study conducted by Ingrid Banks (2000) through interviews and focus groups, explored how Black women and girls of diverse ages and socioeconomic backgrounds felt about their hair choices and, in turn, their identities. Banks asserts that “hair shapes black women’s ideas about race, gender, class, sexuality, images of beauty, and power,” and provides a specific lens through which one investigates how “social and cultural ideas are transmitted through bodies” (Banks, 2000, p. 3-4). This ethnographic research highlights the enduring social and cultural role hair plays among Black people.

The Resilient Thread of Hair Rituals
Even in the face of systemic attempts to erase ancestral practices, the rituals of textured hair care persisted. Enslaved women, despite brutal conditions, found ingenious ways to maintain their hair heritage, using fabrics, scarves, and protective hairstyles to protect their hair and preserve a connection with their culture. This resilience is a testament to the profound significance of these practices, not merely as cosmetic routines, but as acts of cultural survival.
- Cornrows as Maps ❉ During the transatlantic slave trade, the intricate patterns of cornrows were reportedly used to conceal rice grains and seeds for cultivation after escape, or to create actual maps for freedom routes. This act transformed hair into a silent, yet powerful, instrument of liberation.
- Protective Styling Lineage ❉ Styles like braids and twists, practiced for millennia across Africa, offered both aesthetic beauty and practical protection from environmental elements. These styles continue to protect textured hair from breakage and moisture loss, showcasing a timeless wisdom.
- Communal Grooming Spaces ❉ The hair salon or home braiding circle, where stories are shared and bonds are strengthened, carries the legacy of ancient communal hair care sessions, providing a space for identity formation and emotional support.

Reflection
The enduring cultural significance of ancient hair care practices for textured hair heritage resonates far beyond mere historical footnotes. It echoes as a vibrant, living narrative, woven into the very fabric of identity for Black and mixed-race communities worldwide. The ancestral wisdom, steeped in centuries of observation and communal care, offers a profound meditation on the resilience of the human spirit. From the intricate braiding patterns that served as maps to freedom, to the intentional use of natural ingredients that nourished both scalp and soul, these practices speak to a legacy of ingenuity, adaptation, and self-preservation.
To truly understand textured hair, then, is to understand a lineage of self-care, a chronicle of resistance, and a testament to the power of cultural memory. It is a recognition that every coil, every kink, every strand carries a whisper from the past, a story of belonging, and a blueprint for a future where heritage is celebrated and revered. The ‘Soul of a Strand’ ethos, in its deepest sense, acknowledges that our hair is more than just biology; it is a repository of history, a living archive of a people’s journey, continually informing how we nurture, style, and affirm ourselves in the present moment. This connection ensures that ancient practices remain not just relevant, but essential, guiding us toward a more holistic, respectful, and joyful relationship with our textured hair.

References
- Banks, I. (2000). Hair Matters: Beauty, Power, and Black Women’s Consciousness. New York University Press.
- Byrd, A. D. & Tharps, L. R. (2001). Hair Story: Untangling the Roots of Black Hair in America. St. Martin’s Press.
- Jacobs-Huey, L. (2006). From the Kitchen to the Parlor: Language and Becoming in African American Women’s Hair Care. Oxford University Press.
- Mercer, K. (1994). Welcome to the Jungle: New Positions in Cultural Studies. Routledge.
- Patton, M. M. (2006). Black Hair: Art, Culture, and History. Apprentice House.
- Rooks, N. M. (1996). Hair Raising: Beauty, Culture, and African American Women. Rutgers University Press.
- Rosado, S. (2003). The Grammar of Hair: How African American Women’s Hair Decisions Convey Cultural Meaning. Howard University.
- Sieber, R. & Herreman, D. (2000). Hair in African Art and Culture. The Museum for African Art.
- Thompson, C. (2009). Black Women, Beauty, and Power. University of Illinois Press.
- Zeleza, P. T. (2005). The Transformation of Africa, Vol. 2: The Global Impact of Africans in the Making of the Modern World. Africa World Press.