Roots
For generations, within the vast expanse of textured hair, there lie statements not merely spoken, but lived. These are not ephemeral trends or fleeting fads. They are deeply etched pronouncements, whispered across centuries from ancestor to descendant, about identity, about strength, about spirit.
Your textured hair, in its glorious spirals, waves, and coils, carries a wisdom that echoes from the very source of humanity, a heritage undeniably vibrant and resilient. We speak not of simple aesthetics, but of a profound, enduring language spoken through the crowning glory of our heads.

The Architecture of Ancestral Strands
To truly comprehend the enduring statements embodied by textured hair practices, one must first look at its very foundation. Consider the biological marvel of a textured strand. Unlike straight hair, which tends to be round or oval in cross-section, textured hair often presents as elliptical, sometimes even flattened. This distinct shape, coupled with a varied distribution of keratin, dictates the characteristic curl patterns we observe.
These patterns range from expansive waves to tight, coiling spirals and zig-zagging kinks, each a unique expression of genetic inheritance. The hair shaft, a protective outer cuticle, varies in how tightly its scales lie, influencing light reflection and vulnerability. A more open cuticle, typical of some textured patterns, requires a particular vigilance in care, a truth understood by our forebears through observation and practice, long before microscopes revealed cellular structures. The very structure of textured hair means it is more prone to dryness and breakage if not handled with consideration. This biological reality has profoundly shaped ancestral care practices, prompting the development of rituals centered on moisture, protection, and gentle handling.

Hair Morphology and Its Echo in Ancient Practices
The unique curvature of textured hair means that natural oils, sebum, do not easily travel down the length of the strand. This biological reality necessitated intentional methods of lubrication and sealing. Ancient societies, across the African continent, instinctively addressed this.
They employed rich butters, like shea, and various plant-based oils, passed down through family lines, not just for shine but for the vital purpose of hydration and preservation. These early cosmetic applications were not merely about adornment; they were about maintaining the health and integrity of the hair, ensuring its capacity to serve as a canvas for cultural expression and a vessel for spiritual connection.

Classifying the Crown’s Diversity
The myriad expressions of textured hair have, over time, led to various classification systems. While modern systems often categorize hair types by curl pattern (e.g. 3A, 4C), reflecting a scientific desire for order, it is important to remember that such categorizations are relatively recent. Historically, the distinctions were drawn from social, tribal, and spiritual affiliations, often reflected in the styling itself.
In many African societies, hair denoted age, religion, social rank, or marital status. For example, a young Wolof girl might partially shave her head to signal she was not of marrying age, while a Himba bride’s intricate braids and red ochre indicated readiness for marriage. These social markers, rather than curl definition, provided the primary framework for understanding hair identity in ancestral communities.
The intrinsic form of textured hair has always dictated a distinct lineage of care, rooted in ancestral wisdom and an intuitive understanding of its biological needs.
The historical context of hair classification also reveals periods of imposed narratives. During the transatlantic slave trade, the deliberate shaving of heads upon arrival in the Americas was a brutal act of dehumanization, a systematic stripping away of cultural identity and familial connections. This act underscored the profound role hair played in African societies as a marker of self and heritage. Despite this violent erasure, the memory of these diverse expressions persisted, shaping new forms of hair practices in the diaspora, often imbued with layers of hidden meaning and resistance.

The Living Language of Textured Hair
Every coil, every braid, every twist in textured hair carries a word, a sentence, a full pronouncement. This vocabulary, passed down across centuries, connects us to a heritage rich with meaning. The language of textured hair is not confined to spoken words, but expresses itself through style, adornment, and the communal acts of care.
A lexicon has formed around textured hair, blending ancestral terms with those born of diasporic experience. Some key terms include:
- Coil ❉ A tight, helical curl pattern, often found in hair types 4A, 4B, and 4C. It speaks to strength and resilience, holding memory within its spiraled form.
- Twist Out ❉ A style achieved by twisting damp hair and allowing it to dry, then unraveling for definition. This practice echoes ancestral methods of shaping hair without harsh tools, prioritizing its natural spring.
- Protective Style ❉ Styles that minimize manipulation and exposure to environmental stressors, such as braids, twists, or locs. These styles carry the heritage of preservation, safeguarding the hair’s health.

Cycles of Growth, Echoes of Seasons
Hair grows in cycles: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting/shedding). Textured hair, particularly its coiling nature, can lead to shed hairs tangling with growing strands, contributing to what is often perceived as slower growth or more breakage. Ancestral communities, without modern scientific explanations, understood these realities through keen observation. Their care practices often aligned with the rhythms of nature, much like agricultural cycles.
They would adjust their hair routines, perhaps incorporating more protective styles during periods of intense labor or environmental stress, and more elaborate communal styling during times of celebration and rest. This innate understanding of environmental impact on hair health mirrors a holistic approach to wellness, where the body, including its crowning glory, is viewed in continuum with its surroundings and heritage.

Ritual
The enduring statements of textured hair practices extend beyond its inherent structure, breathing life into the techniques and artistry that have shaped it across generations. These are not mere styling choices; they are rituals, deeply embedded in a heritage of self-expression, community, and resistance. From the meticulously crafted braids of ancient Africa to the contemporary artistry of protective styles, each practice carries a narrative of ingenuity and cultural continuity.

Preserving Lineage through Protective Styles
Protective styling forms a central pillar of textured hair heritage. These styles, designed to minimize manipulation and exposure to external elements, were born of necessity and elevated to art. The ancestral roots of these practices are visible in archaeological finds and historical accounts, demonstrating a long-standing understanding of hair preservation.
Styles like cornrows, box braids, and various forms of twists served practical purposes, keeping hair tidy and secure during demanding daily activities or spiritual rites. Yet, their purpose transcended utility; they also functioned as elaborate forms of communication, identity markers, and even covert maps during periods of profound hardship.

Did Cornrow Patterns Guide Escapes?
One powerful historical example highlighting the communicative power of textured hair is the use of cornrows by enslaved Africans in the Americas. During the transatlantic slave trade, enslaved people were often forcibly shaven upon arrival, a deliberate act to strip them of their identity. Despite this, traditional practices persisted. In a profound act of defiance and survival, women would braid intricate patterns into their hair, which reportedly served as maps to freedom or repositories for seeds and gold.
Accounts, particularly from Colombia, cite how the self-proclaimed King Benkos Biohó, an escaped royal from the Bissagos Islands, established a network where women used cornrow patterns to communicate escape routes and meeting points, sometimes even hiding rice grains or seeds within the braids for sustenance during flight. This extraordinary practice speaks volumes about the intelligence, resilience, and ingenuity embedded in textured hair heritage. This was not simply styling; it was a complex system of encoded knowledge, a silent testament to the unwavering pursuit of liberty.
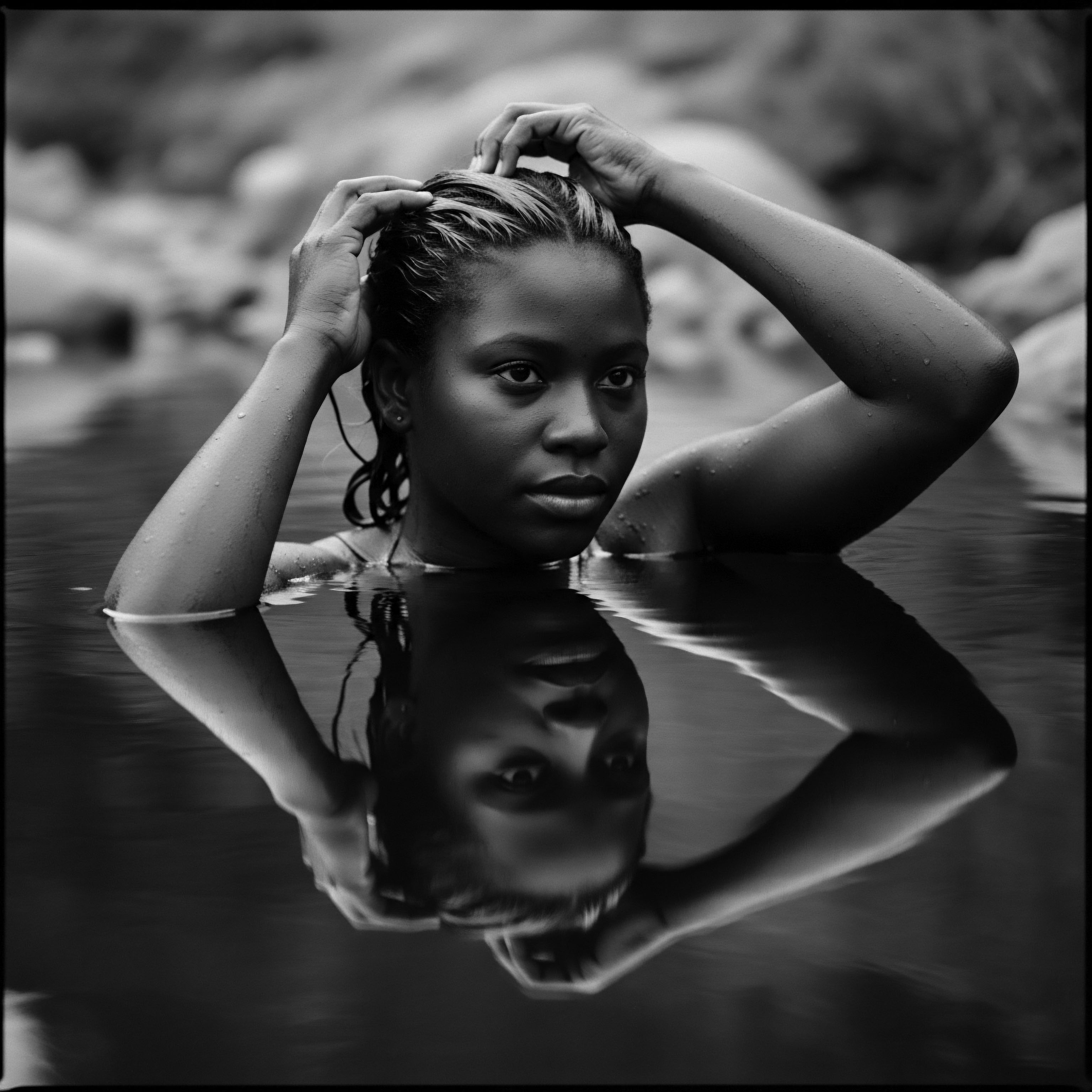

The Art of Natural Styling and Definition
Beyond protective measures, natural styling techniques have always celebrated the innate beauty of textured hair. Methods for defining curls, whether through finger coiling, braiding, or twisting, have been passed down through generations. These techniques, often requiring patience and a tender touch, represent a communion with the hair’s inherent structure.
The emphasis was not on altering the hair’s original form, but on enhancing its natural presentation, drawing out its definition and vibrancy. These traditional methods are reflected in modern routines, where products designed to clump curls and reduce frizz echo the ancestral desire for polished, defined hair.
The enduring cultural statements of textured hair are often whispered through the silent communication of its styles and the shared experience of its care.
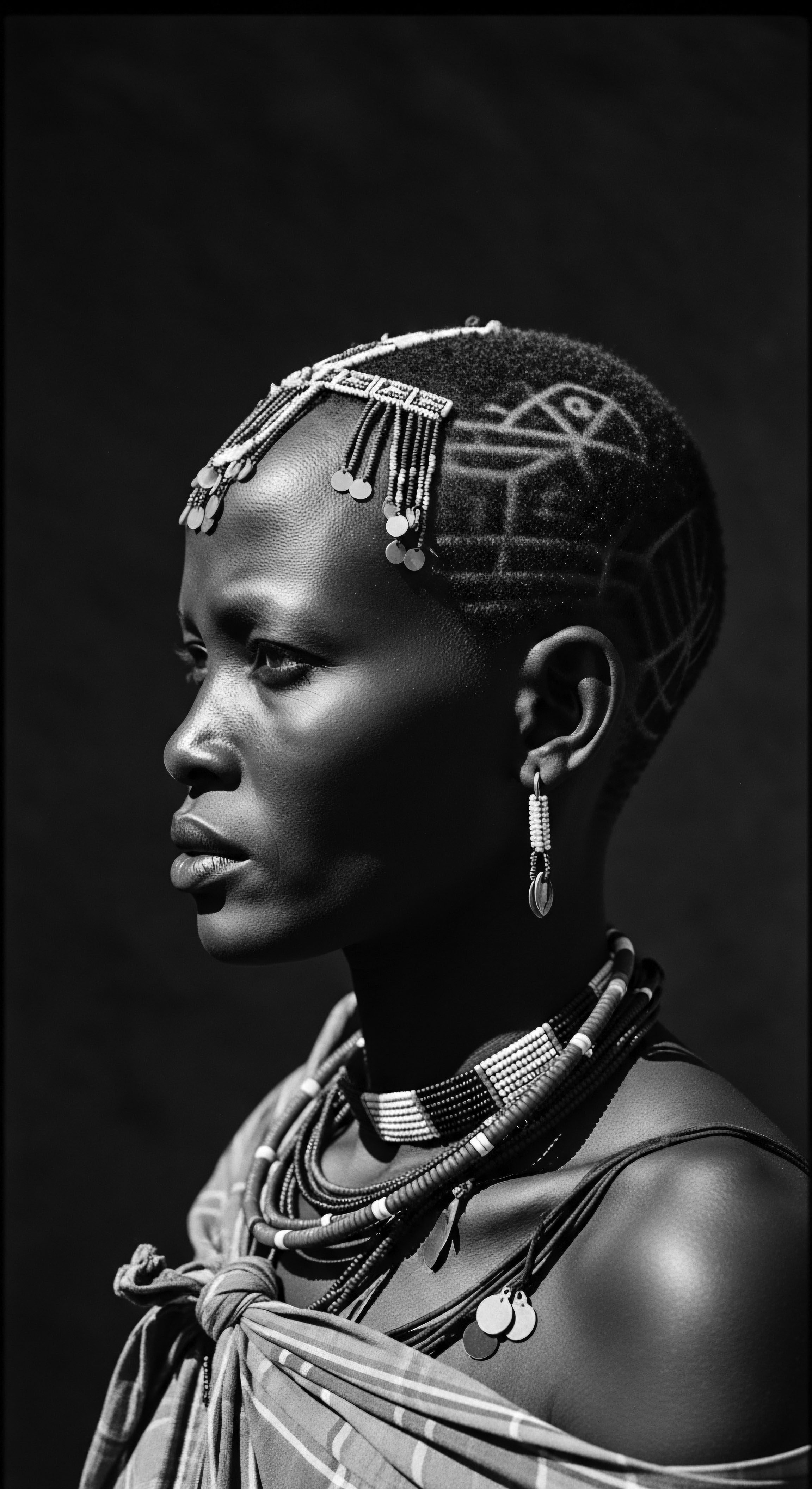

The Legacy of Adornment: Wigs and Extensions
The use of wigs and hair extensions also possesses a deep historical and cultural context within textured hair heritage. Contrary to popular Western notions that often link extensions solely to modern trends, their use in African societies dates back millennia. Ancient Egyptians, for example, wore elaborate wigs for status, protection, and ceremonial purposes. These were often crafted from human hair, plant fibers, or wool, sometimes adorned with gold and jewels.
The practice was not about concealing natural hair but about amplifying expression, denoting power, or fulfilling spiritual requirements. This heritage of augmentation highlights a desire for versatility and grand presentation, a statement of artistry and social standing. The connection to ancestral wisdom here is profound; it reveals a long-standing understanding of hair as a malleable medium for identity.

Considering Heat and Alteration through Time
The relationship with heat styling and thermal reconditioning is complex. While modern tools offer swift, dramatic alterations, ancestral methods of straightening or stretching hair existed, though often without the same degree of intense heat. Techniques like hair threading, particularly among the Yoruba people of Southwestern Nigeria, stretched hair without chemical or excessive thermal application, offering length retention and a particular texture. This historical practice, rooted in the preservation of hair integrity, stands as a quiet counterpoint to contemporary high-heat methods.
It prompts reflection on the balance between desired aesthetics and the long-term health of the hair, inviting a perspective grounded in the wisdom of gentle manipulation. The heritage speaks of respecting the hair’s natural capabilities.

The Tools of Tradition and Transformation
From the simplest wooden combs to more elaborate bone instruments, the tools used in textured hair care have always been extensions of the hand, designed to respect the unique properties of coils and curls. Ancient combs, often adorned with symbolic carvings, were not merely functional objects; they were cultural artifacts, carrying stories within their teeth. The communal practice of hair dressing, often involving multiple generations, passed down the tactile knowledge of how to manipulate hair with sensitivity, avoiding breakage and preserving length. This collective memory, held in skilled hands, forms the bedrock of the ‘complete textured hair toolkit’, reminding us that the most sophisticated tools are often those wielded with understanding and care, a direct inheritance from those who first mastered the art of tending to these glorious strands.

Relay
The continuing statements embodied by textured hair practices represent a living relay, transmitting wisdom across generations. This is a discourse on holistic well-being, on problem-solving rooted in ancestral ingenuity, and on the profound significance of daily rituals, particularly those performed as the day gives way to night. Roothea’s vision understands hair not merely as a biological structure, but as a sentinel of ancestral wisdom, a vibrant repository of cultural memory that shapes identity and future paths.

Crafting Care from Ancestral Wisdom
Building a personalized textured hair regimen is a contemporary endeavor, yet its deepest springs flow from ancestral wisdom. Across various African communities, hair care was rarely a solitary act. It was often a communal ceremony, a time for sharing stories, transferring knowledge, and reinforcing social bonds. The ingredients used were local, harvested from the earth, and chosen for their specific properties, often reflecting an intuitive ethnobotanical understanding.
Shea butter, for instance, a staple across West Africa, was prized for its moisturizing and protective qualities, applied generously to hair and scalp. Its enduring presence in modern products speaks to its historical efficacy. Our modern regimens, while incorporating scientific advancements, echo this heritage in their layered approach to cleansing, conditioning, and sealing moisture. They honor the notion that consistent, mindful care fosters health and allows the hair to flourish as a statement of vibrancy.
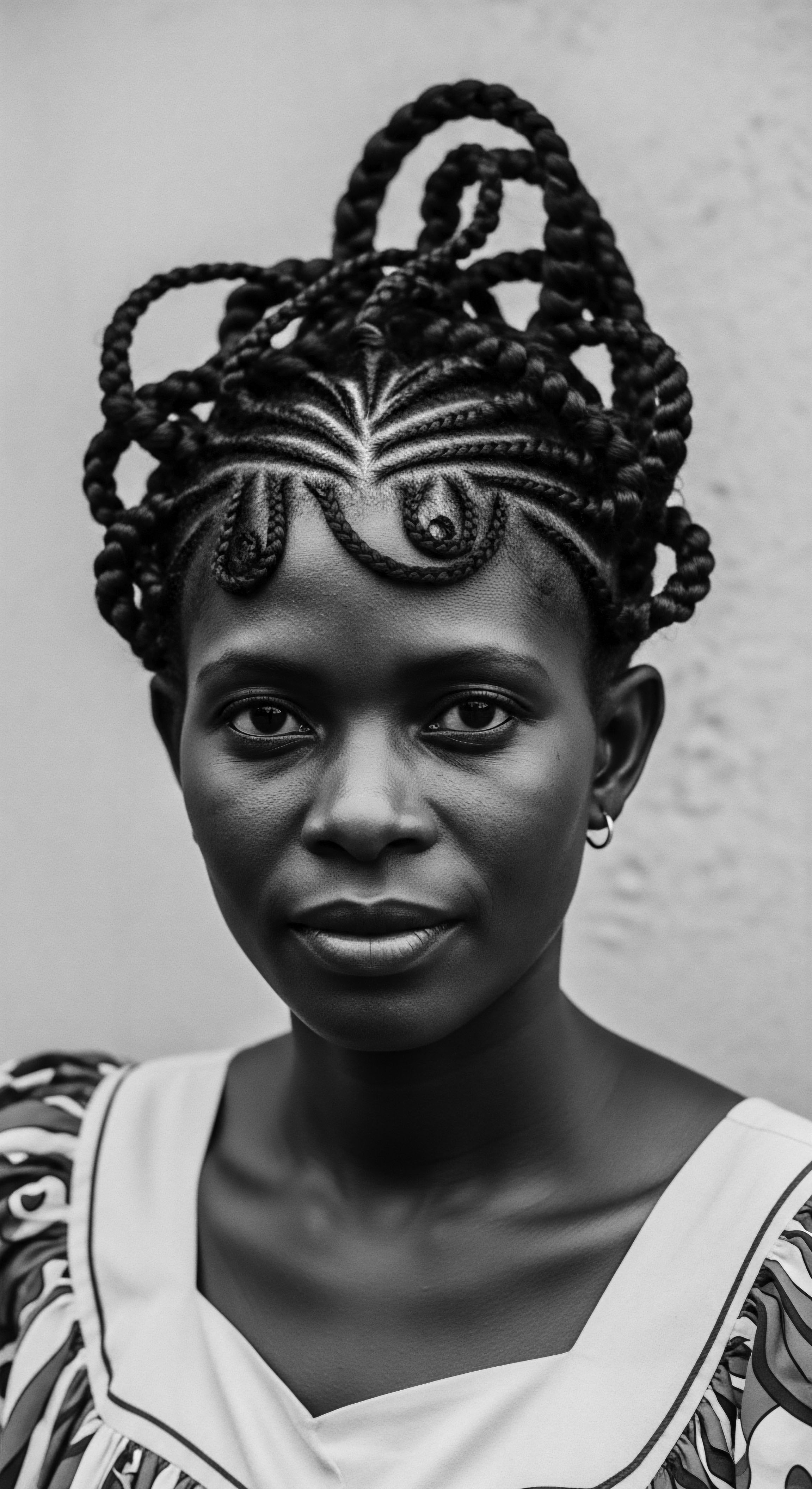

How Do Ancient Ingredients Inform Modern Hair Formulations?
The wisdom of ancestral ingredient usage provides a compelling blueprint for contemporary formulations. Before laboratories synthesized complex compounds, communities relied on what the land provided. For instance, the use of various plant mucilages, derived from plants like okra or aloe, for detangling and conditioning, represents an early form of natural polymer application. These substances, when applied to hair, would reduce friction and aid in managing curls, a property that modern science now attributes to their polysaccharide content.
Consider the following traditional ingredients and their modern counterparts:
- Shea Butter ❉ A rich emollient, historically used across West Africa for deep conditioning and sealing moisture. Today, it forms a base in countless conditioners and styling creams, its benefits validated by scientific analysis of its fatty acid profile.
- Coconut Oil ❉ Employed in various tropical regions for its penetrative moisturizing capabilities. Research now supports its ability to reduce protein loss in hair due to its molecular structure.
- Various Clays (e.g. Rhassoul) ❉ Used traditionally for gentle cleansing and scalp detoxification, absorbing impurities without stripping natural oils. Modern detox masks often feature these mineral-rich clays.
- Herbal Rinses (e.g. hibiscus, rosemary) ❉ Infusions used for scalp health, stimulating growth, and enhancing shine. Current science validates their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, often found in scalp treatments.
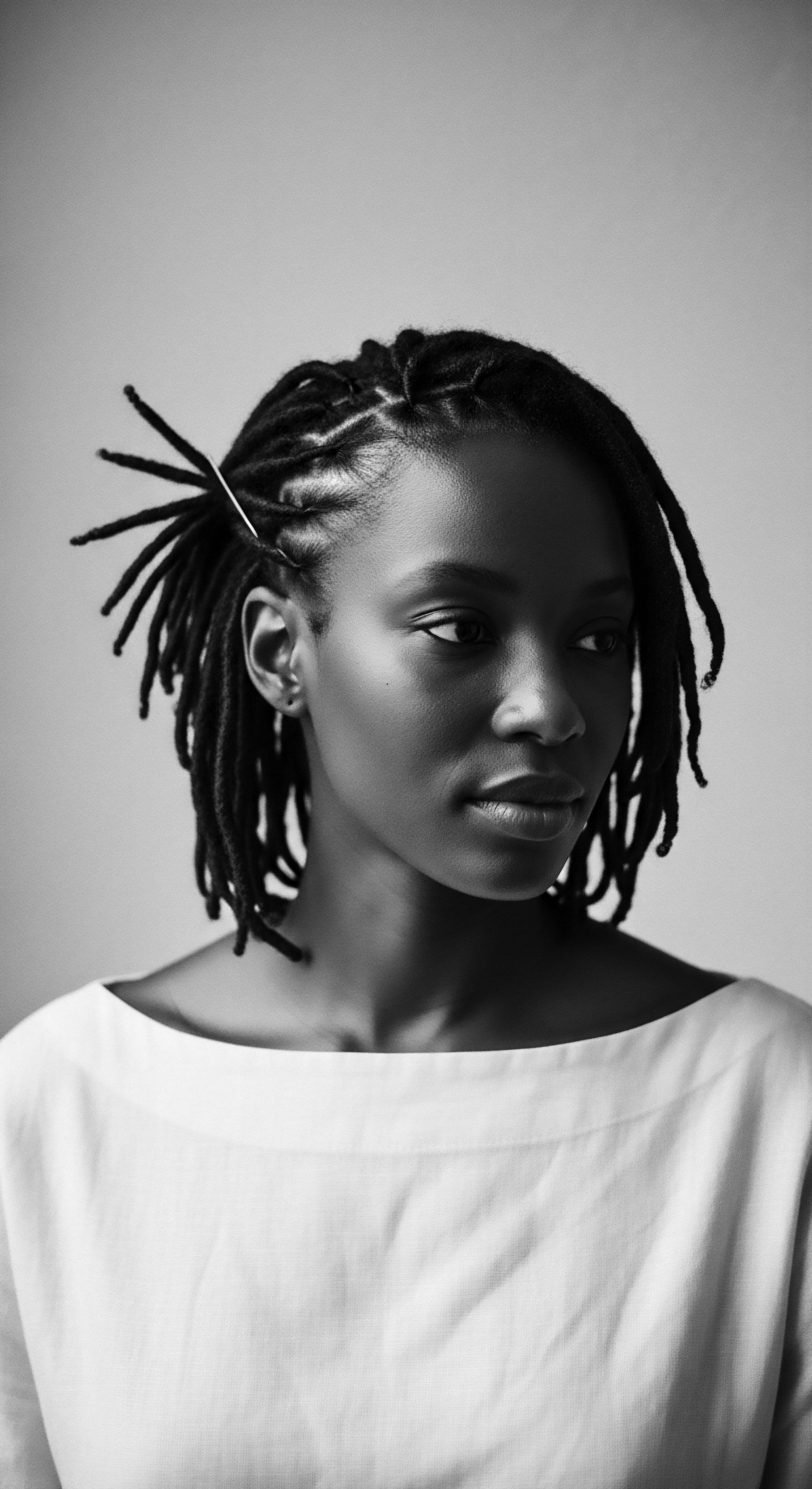

The Nighttime Sanctuary: Protecting the Crown
The ritual of nighttime hair protection is a profound statement of self-care and preservation, with roots stretching back through generations. The practice of wrapping the hair or sleeping on protective surfaces was not simply for aesthetic preservation; it was a way to maintain the integrity of delicate strands, reduce tangling, and extend the life of styles. The bonnet, in its various forms, serves as a contemporary manifestation of this ancestral wisdom. It speaks to a deep, ingrained understanding of how friction, moisture loss, and environmental exposure during sleep can harm textured hair.
This nightly ritual acknowledges the hair as a vital part of self, deserving of mindful protection. The widespread adoption of bonnets and silk scarves within diasporic communities underscores a shared legacy of practical hair care, a silent agreement across time that the crown must be guarded even in slumber.
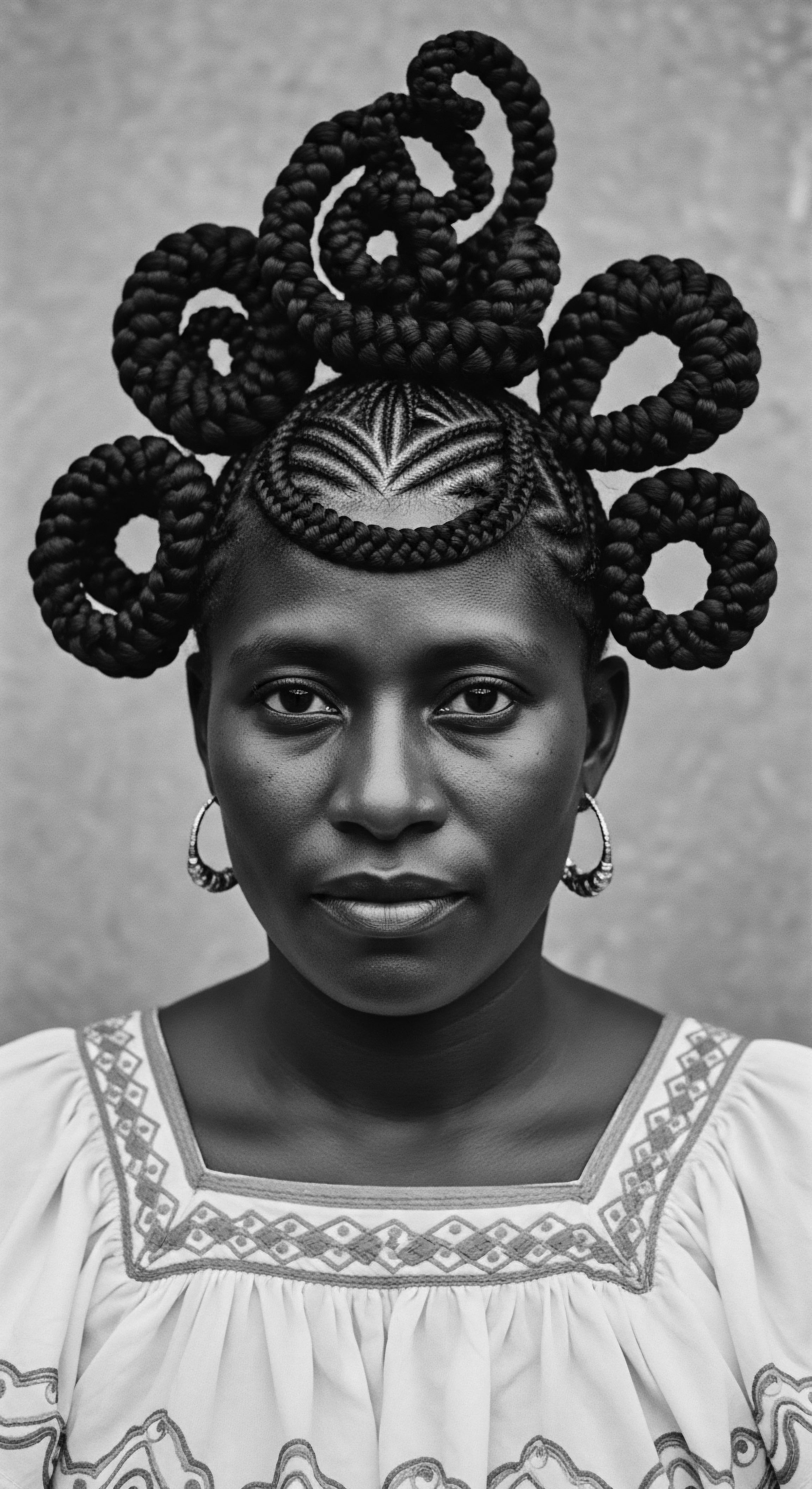

Addressing Hair Challenges through Ancestral Lenses
Textured hair, with its unique structure, sometimes presents specific challenges: dryness, breakage, and scalp conditions. The compendium of textured hair problem-solving draws heavily from both inherited wisdom and modern scientific understanding. Ancestral practices often involved a holistic approach, recognizing the interconnectedness of diet, environment, and physical well-being with hair health. For instance, dietary choices rich in nutrient-dense foods were understood to promote strong hair, even if the biochemical pathways were not explicitly known.
A significant aspect of hair health, particularly in the context of textured hair, involves the challenges arising from societal pressures and discrimination. Studies indicate that Black women’s hair is often perceived as unprofessional. Research from the CROWN 2023 Study found that 41% of Black women altered their hair from curly to straight for job interviews, and 54% felt they needed straight hair for such occasions. This data points to an enduring cultural statement of adaptation and resistance, where the personal choice of hair expression meets external biases.
Addressing these issues extends beyond product application to advocating for systemic change, acknowledging the profound socio-cultural weight hair carries. This situation highlights how practices of care and styling are not solely about personal preference but also about navigating broader societal perceptions, a struggle deeply embedded in the heritage of textured hair.

Reflection
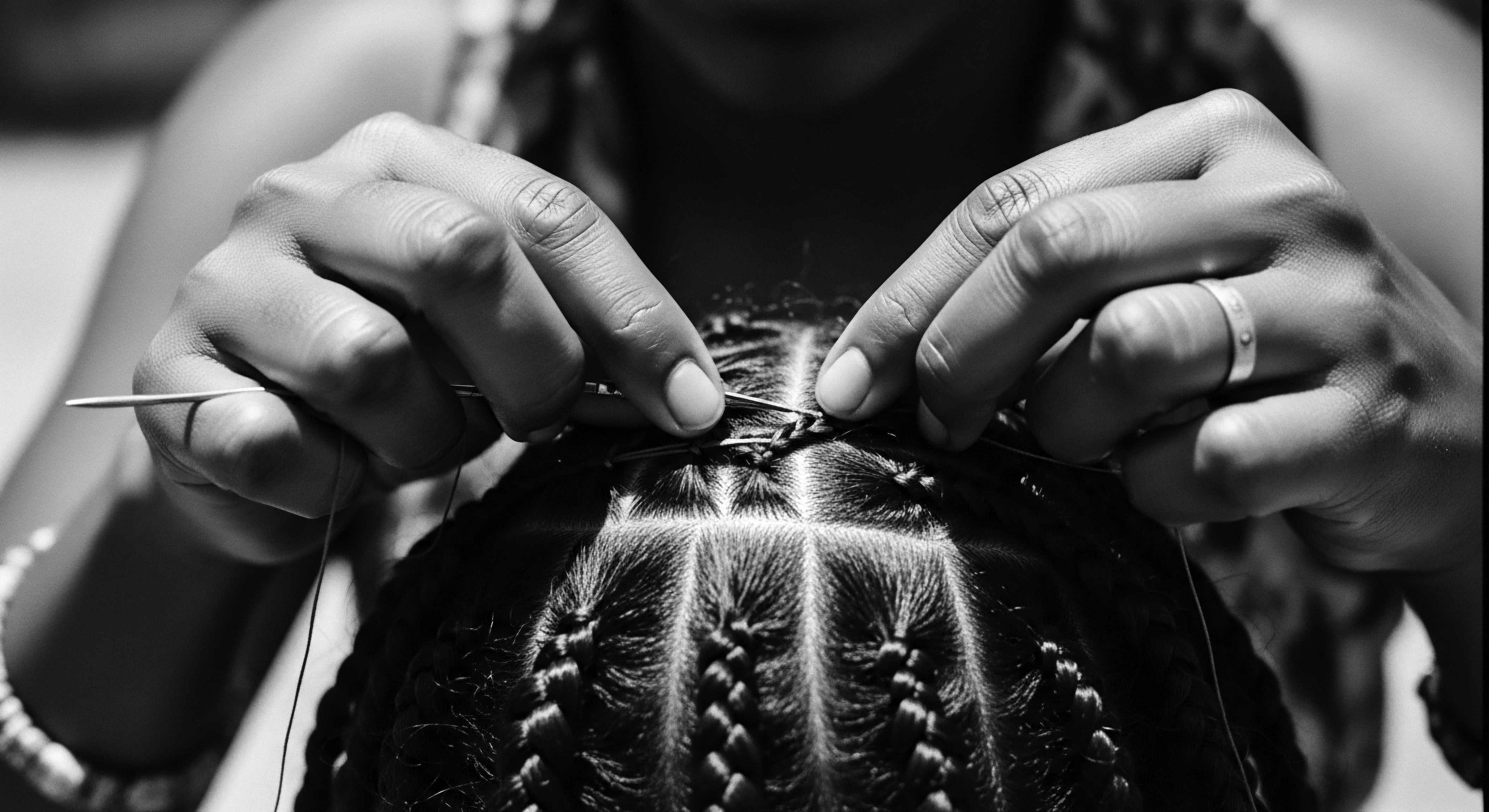
The enduring cultural statements embodied by textured hair practices reach far beyond the visible. They reside in the quiet strength of a coil, in the historical echoes of a meticulously crafted braid, and in the communal embrace of shared care. This is a living archive, a repository of resilience, identity, and profound ancestral wisdom. From the fundamental biology that shaped its unique structure to the intricate rituals of daily care and the broad societal narratives it navigates, textured hair remains a powerful testament to continuity.
Each strand carries a whisper of those who came before, speaking of survival, beauty, and unwavering spirit. The journey of textured hair, from ancient source to contemporary expression, continues to affirm a heritage that refuses to be silenced or forgotten. It is a constant reminder that true beauty and strength reside in authenticity, a legacy passed down through every curl, every wave, every glorious pattern.

References
- Black History Month 2022: The History Behind Cornrows. Beds SU, 2022.
- Hair It Is: Examining the Experiences of Black Women with Natural Hair. 1996.
- The Power of Hair in African Folklore: Rituals and Traditions. Bebrų Kosmetika, 2024.
- 10 Books On the Evolution of Black Culture Through Hair. She Reads, 2022.
- nappy hair in the diaspora: exploring the cultural politics of. UFDC Image Array 2.
- African hair tells a story and inspires the future. Kodd Magazine.
- ROAD TO FREEDOM: How Enslaved Africans in America Used Hair Styles to Map Escape Routes. childish mane llc, 2023.
- African Slaves Used Braids to Communicate Escape Routes in Colombia. Ancient Origins, 2022.
- A History Lesson On Hair Braiding. Odele Beauty, 2024.
- Descriptions of some traditional West African hairstyles still worn today. Creative Alia, 2024.
- Adinkra Symbols and Meanings.
- Cornrows and The TransAtlantic Slave Trade. the afro curly hair coach, 2022.
- New Growth: The Art and Texture of Black Hair. Duke University Press.
- Hair in Black Art and Culture. Duke University Libraries, 2023.
- Black History Month: The Rich History of Our African Hair. Livara Natural Organics, 2023.
- The History and Cultural Significance of African Hair Braiding. 2023.
- Braided Archives: Black hair as a site of diasporic transindividuation Océane Nyela A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Gradua. YorkSpace, 2021.
- Hair as Freedom. BUALA, 2024.
- Twisted: The Tangled History of Black Hair Culture by Emma Dabiri.
- Textures: The History and Art of Black Hair. Amazon.com.
- Ujima Natural Hair and the Black Community Black Paper_kmc.docx.
- Akan Symbols. Adventures in Ghana, 2010.
- Hair in African Art and Culture. ResearchGate.
- Mpuannum. Adinkra Symbols & Meanings.
- Adinkra Symbols. African Beads & Fabrics.