Roots
There are whispers that stretch across generations, a silent wisdom carried on the wind from the Sahel to every corner of the diaspora. These are not merely stories; they are the genetic memory of strands, the very code of textured hair speaking through ancestral practices. We are invited to listen, to feel the profound connection between ancient rituals and the modern dance of hair care, a connection where the echo of Chebe rituals rings clear.
This historical substance, born from the unique flora of Chad, extends an invitation to rediscover not just hair health, but a deeper part of collective heritage. It reminds us that our hair is a living archive, each coil and kink holding tales of resilience, ingenuity, and enduring beauty.

The Hair’s Intricate Structure
To truly comprehend Chebe’s influence, one must first recognize the inherent characteristics of textured hair. Unlike its straighter counterparts, textured hair ❉ ranging from loose waves to tight coils ❉ possesses a unique elliptical cross-section and often a more flattened hair shaft. This structural difference means that natural sebum, the scalp’s protective oil, struggles to travel down the hair shaft, leaving the ends particularly vulnerable to dryness and breakage. This anatomical reality has long been understood, not through modern microscopy, but through generations of lived experience and observation within African communities.
Early practices developed precisely to counteract this inherent dryness. The hair of individuals of African and mixed-race descent often exhibits a higher density of disulfide bonds, contributing to its strength, yet paradoxically, also its susceptibility to breakage if not properly cared for. The Basara Arab women of Chad, for whom Chebe powder is a way of life, possess exceptionally long, thick hair, a testament to their deep understanding of these characteristics and their unique care practices.

Ancient Understanding of Hair
Ancestral cultures viewed hair as far more than biological fibers; it was a potent symbol, often linking the individual to their family, community, and spiritual realm. In many African societies, hair symbolized one’s identity, social status, spirituality, tribe, and marital status. This sacred view meant that hair care was never a casual act. It was a communal ritual, a time for sharing wisdom, stories, and strengthening bonds.
The knowledge of hair’s needs, its tendency to dry, its capacity for growth, was passed down orally, through observation, and direct participation in care routines. This inherited wisdom laid the groundwork for solutions like Chebe, developed in response to specific environmental challenges and hair characteristics.
The journey to healthy hair begins with a recognition of its inherent structure and the ancestral wisdom that has long guided its care.

What Is Chebe Powder’s Origin and Ingredients?
Chebe powder hails from Chad, a country in Central Africa, and is deeply associated with the Basara Arab women there, known for their waist-length hair. This isn’t a single ingredient but a blend of natural elements sourced from the Sahel region. The primary component is the seeds of the Croton zambesicus plant, often called Lavender Croton.
These seeds are harvested, dried, and ground into a fine powder. Other elements contribute to its efficacy and unique properties:
- Mahllaba Soubiane (cherry kernels),
- Cloves,
- Missic Stone (an incense resin for fragrance),
- Samour Resin (gum from Acacia tree),
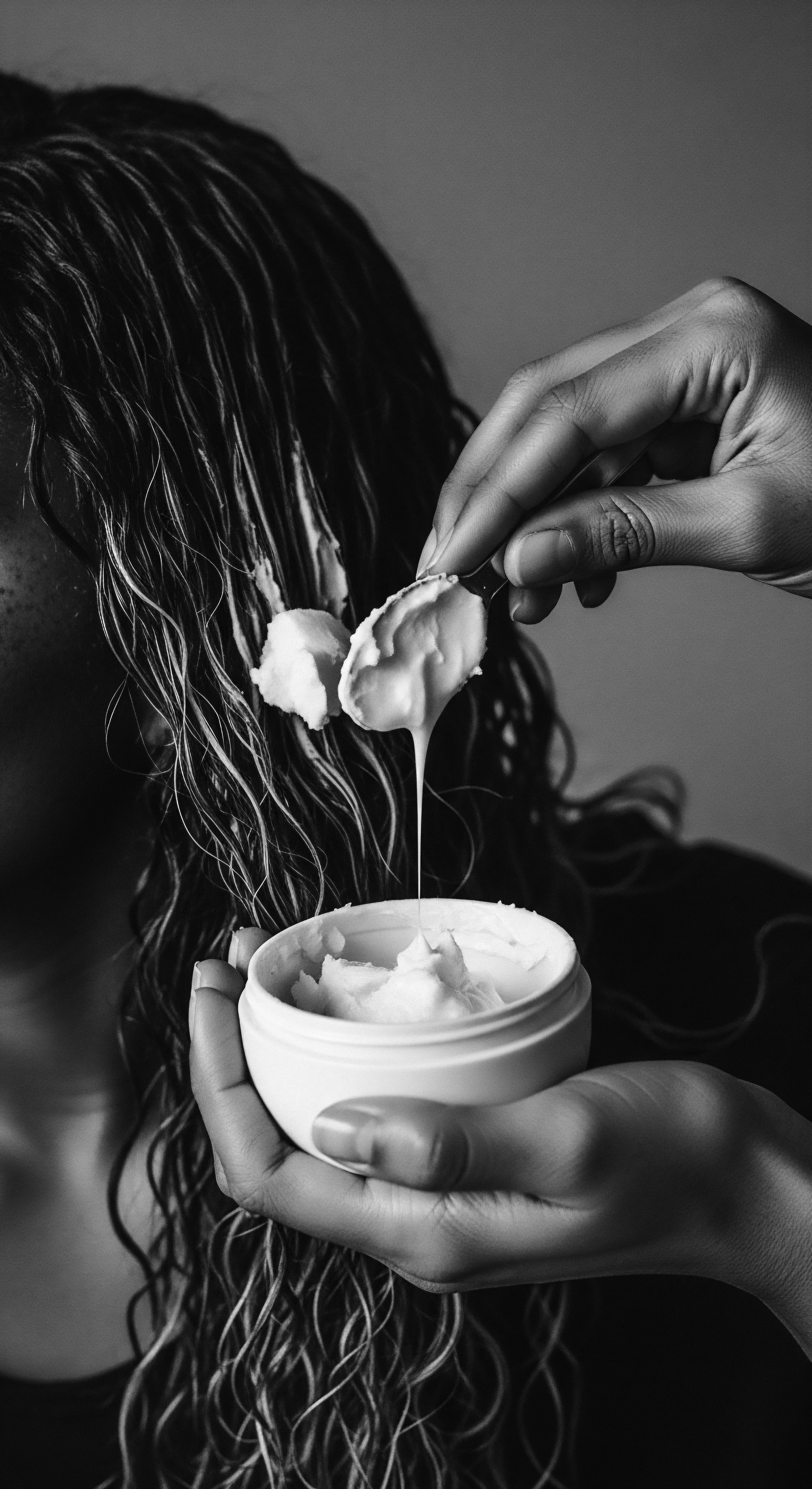
Traditionally, these components are roasted, pulverized, and then combined with oils or butters, often beef fat, to create a paste. This mixture, applied to damp, sectioned hair and then braided, remains on the hair for days, acting as a protective coating. The power of Chebe comes not from stimulating hair growth from the scalp, but from preventing breakage, strengthening the hair shaft, and retaining moisture, allowing natural length retention to become visible.

Ritual
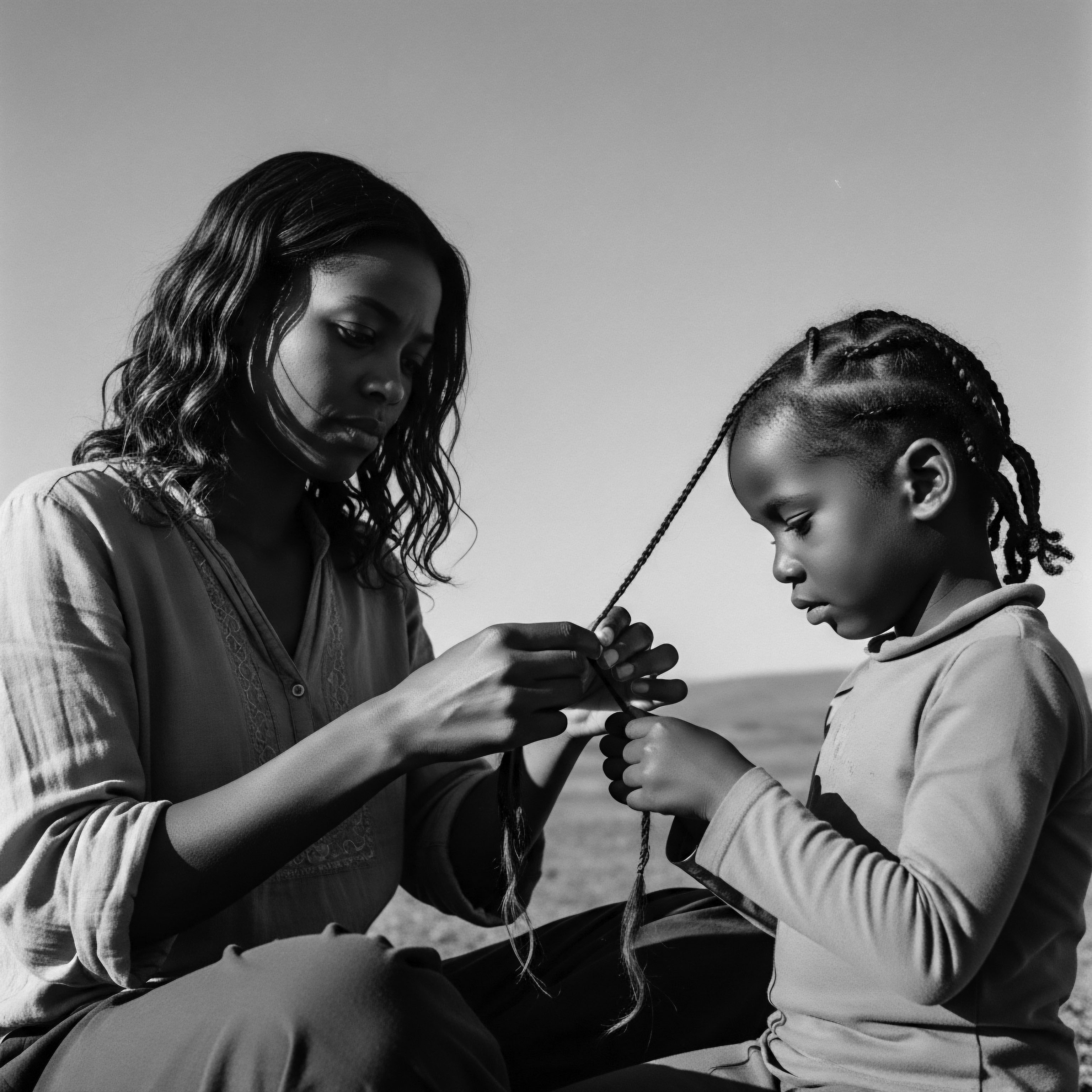
The essence of Chebe rituals reaches beyond simple application; it is a profound testament to communal care, ancestral ingenuity, and the enduring human connection to beauty rooted in practice. These rituals, preserved by the Basara Arab women of Chad, serve as a living manuscript, guiding modern textured hair care routines toward a more holistic, heritage-informed approach. The rhythmic gestures, the shared laughter, the whispered stories during application all speak to a deeper purpose than just aesthetics. This is about sustaining a collective memory through action.

The Practice of Application
The traditional method of applying Chebe is a deliberate, multi-day affair. It involves preparing the powder into a paste by mixing it with oils or butters. This paste is then meticulously applied to damp, sectioned hair, typically from mid-shaft to ends, avoiding the scalp. The hair is then braided, and the Chebe mixture remains on the strands for several days.
This process is repeated regularly. This creates a protective coating around the hair shaft, shielding it from environmental stressors like the harsh Chadian climate and locking in moisture. Modern practices have adapted this, with many opting for Chebe-infused oils, conditioners, and butters that rinse out, making the ritual more adaptable to contemporary lifestyles.
Chebe application, a ritual of mindful layering, serves to protect and strengthen textured hair, much like ancestral wisdom guards cultural legacy.

Chebe’s Influence on Styling Methods
The very nature of Chebe’s traditional use has protective styling at its core. By coating the hair and then braiding it, breakage is minimized, allowing the hair to retain length. This aligns perfectly with the ancient practice of protective styling in African cultures, which dates back millennia. Braids, twists, and locs were not merely decorative; they communicated social status, age, marital status, and even spiritual beliefs.
The use of Chebe historically reinforced the longevity and health of these styles. Today, its influence is visible in the renewed focus on low-manipulation styles and length retention within the natural hair movement. People are seeking to replicate the results of traditional Chebe use by incorporating Chebe products into their protective styling routines, whether it’s through braided styles, twists, or even under wigs and extensions.

A Toolkit Rooted in Tradition
The tools associated with Chebe rituals, though seemingly simple, are deeply meaningful. Beyond the ingredients themselves, the hands that mix and apply, the combs used for sectioning, and the act of braiding are all instruments of heritage. Traditionally, simple wooden combs, often handcrafted, were used for detangling and parting. The very fingers of the women applying the mixture became the primary tools, distributing the paste with care and precision.
Modern textured hair toolkits, with their wide-tooth combs, sectioning clips, and application brushes, echo these basic functions. The continued popularity of these simple yet effective tools is a quiet acknowledgment of the ancestral methods that proved their worth through centuries of practice.

Relay
The resonance of Chebe rituals extends far beyond the physical application of powder and oils; it is a profound cultural relay, transmitting ancient wisdom across generations and continents. This journey from elemental practice to global acknowledgment underscores how deeply ancestral knowledge informs present-day beauty standards and self-perception, especially within Black and mixed-race communities. The very existence of Chebe in modern hair care signifies a powerful reclamation of heritage, a conscious decision to look backward for paths forward in affirming identity.

Hair as a Beacon of Identity
For individuals of African descent, hair has historically served as a potent symbol of identity, community, and resistance. In pre-colonial African societies, hairstyles conveyed messages about social status, religion, age, and family heritage. During periods of enslavement, the forced shaving of heads aimed to strip individuals of their cultural markers and humanity. Despite this, hair became a defiant act, a means to reclaim control over appearance and assert pride in African heritage.
The Natural Hair Movement, which gained traction in the late 20th century, drew heavily from this history, asserting natural textures as symbols of self-acceptance and political defiance. Chebe’s emergence onto the global stage reinforces this movement, offering a tangible link to an uninterrupted line of ancestral hair care. It represents a living connection to communities like the Basara Arab women, whose traditional practices maintained hair health through extreme conditions, preserving a legacy of beauty that defies imposed standards.

Bridging Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science
The scientific understanding of Chebe’s benefits often aligns with centuries of observed practice. While traditional use of Chebe was passed down through generations, modern science provides insights into why it works. Chebe powder functions primarily as a powerful moisture sealant, coating the hair shaft and trapping hydration inside the strand, reducing water loss. This is particularly significant for coily and kinky hair types, which are more prone to dryness and breakage due to their unique structure.
By strengthening the hair shaft, reducing split ends, and improving elasticity, Chebe allows natural hair to grow longer without breaking off. Research into botanicals used in hair care across Africa supports the efficacy of traditional plant-based remedies. A study by Yetein et al. (2013) on ethnobotanical practices in Benin identified numerous medicinal plants used for hair treatment, validating the widespread knowledge of natural ingredients for scalp and hair health. This intersection of empirical wisdom and scientific explanation provides a robust foundation for Chebe’s continued relevance.
The quiet power of Chebe echoes the collective strength of ancestral practices, grounding modern hair care in a profound heritage.

Communal Care and Self-Reliance
One of the most compelling aspects of Chebe rituals is their communal nature. Women gather to apply the paste, braiding each other’s hair, sharing stories and advice. This act of hairstyling serves as a form of social solidarity, fostering a sense of belonging and maintaining unity. This collective spirit stands in gentle contrast to the often individualistic approach of modern beauty routines.
The historical commitment to self-reliance in hair care, particularly among Black and mixed-race women, has been a constant thread. Faced with beauty standards that often denigrated their natural hair, communities developed their own solutions, preserving methods and ingredients that honored their textures. This spirit lives on in the current embrace of Chebe, as individuals actively seek out traditional practices, often supporting local artisans and ethical sourcing, rather than solely relying on mainstream commercial products. The conscious choice to use Chebe is a vote for ancestral knowledge, a nod to enduring communal support, and a recognition that true beauty can be found in the inherited wisdom of one’s past.
The practice of preparing and applying Chebe is a deliberate act of choosing heritage, reaffirming ancestral links with each strand. It is a quiet rebellion, a continuation of a legacy, and a testament to the fact that tradition is not static; it is a living, breathing current flowing into the future.

The Enduring Legacy of Adornment
Adornment of hair in African cultures also holds deep significance, stretching back to ancient Egyptian depictions of elaborate hairstyles and intricate beadwork found at sites like Kerma in Sudan. These practices weren’t just about beauty; they were about communicating social class, life stages, and personal narratives. The Himba people of Namibia, for example, use a mixture of ground ochre, goat hair, and butter to create their dreadlocks, which signify age, life stage, and marital status. The longevity and health that Chebe rituals promote allow for such intricate, long-lasting styles to be maintained, ensuring that hair continues to be a canvas for cultural expression.
The modern natural hair movement, by re-adopting traditional styles like Bantu knots, cornrows, and box braids, directly honors these ancestral adornments, making Chebe’s protective qualities even more relevant. This continuity in styling and care represents a profound connection to a vibrant past, a visible marker of heritage worn with pride. As we consider the journey of Chebe from its Chadian origins to its global presence, we recognize a testament to the resilience of cultural practices and the timeless wisdom held within textured hair heritage.

Reflection
As we conclude this exploration, the story of Chebe rituals reveals itself not as a static historical artifact, but as a vibrant, living current within the vast river of textured hair heritage. It is a testament to the intuitive wisdom of our ancestors, a clear whisper from generations past that guides our hands in the present. The ‘Soul of a Strand’ ethos, which reminds us that every hair holds a history, finds a powerful voice in the traditions surrounding Chebe. This ancient practice, born from the intimate knowledge of specific environments and unique hair characteristics, offers more than a regimen for length retention; it offers a path to reconnect with the enduring spirit of self-care, communal bonding, and cultural preservation that has always defined Black and mixed-race hair experiences.
The journey of Chebe from the sun-drenched plains of Chad into the hands of those seeking mindful, effective hair care is a powerful symbol. It speaks to the ongoing dialogue between ancestral knowledge and contemporary understanding, demonstrating that some truths simply transcend time. Our hair, in its myriad coils, kinks, and waves, remains a profound canvas for identity, a connection to our roots, and a declaration of our past. Embracing Chebe is not merely about choosing a product; it is about choosing to honor a legacy, to listen to the whispers of our grandmothers, and to walk forward with strands that carry the luminous light of heritage.

References
- Yetein, M. H. Houessou, L. G. Lougbégnon, T. O. Teka, O. & Tente, B. (2013). Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used for the treatment of malaria in plateau of Allada, Benin (West Africa). Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 146(1), 154 ❉ 163.
- Johnson, D. A. (2018). The African Diaspora: A History Through the Lens of Hair and Beauty. University Press of Florida.
- Brown, T. (2020). Hair Story: Untangling the Roots of Black Hair in America. St. Martin’s Press.
- Byrd, A. D. & Tharps, L. D. (2001). Hair Story: Untangling the Roots of Black Hair in America. St. Martin’s Press.
- Cole, S. (2009). Hair: A Cultural History. Berg Publishers.
- Okoro, N. (2022). African Hair: A Journey Through History and Culture. Black Classic Press.
- Hunter, C. (2011). Beauty and the Burden: The History of Black Hair. New York University Press.