
What Historical Plants Moisturized African Textured Hair?
Historical African plants like shea butter, palm oil, and Chebe powder deeply moisturized textured hair, rooted in ancestral practices.

Bristle Types
Meaning ❉ An editorial definition of 'Bristle Types' exploring hair's intrinsic properties, tool design, and their deep connection to textured hair heritage.

Which Natural Oils Were Significant in Black Hair Heritage?
Ancestral natural oils, like shea butter and castor oil, deeply nourished and protected textured hair across Black heritage.

What Historical Adaptations Shaped Textured Hair Care during Enslavement?
Historical adaptations in textured hair care during enslavement transformed survival needs into enduring ancestral practices, profoundly shaping Black hair heritage.

Which Traditional Oils Fortified African Textured Hair?
African textured hair found fortification through traditional oils like shea, castor, and palm, rooted in ancestral wisdom and deep cultural heritage.

How Did Traditional Dyes Signify African Hair Heritage?
Traditional dyes for African hair served as potent cultural markers, communicating identity and ancestral wisdom through color and ritual.
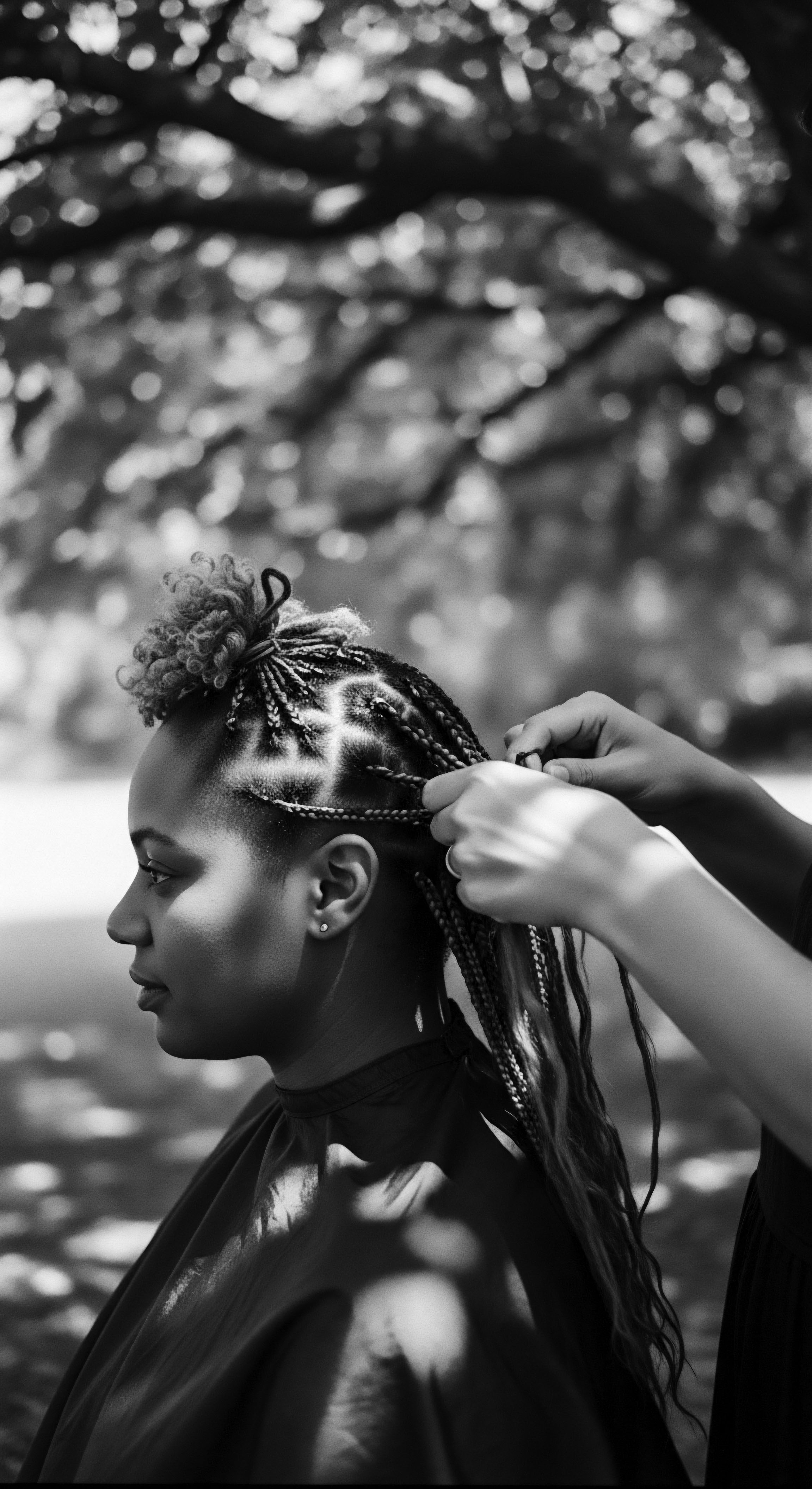
Did Historical Migrations Affect Textured Hair’s Resilience?
Historical migrations profoundly shaped textured hair's resilience, through both genetic adaptation and the enduring ingenuity of ancestral care practices.

How Do Clay Minerals Nourish Textured Scalp?
Clay minerals cleanse and nourish textured scalps by drawing impurities and providing essential elements, continuing a legacy of ancestral care.
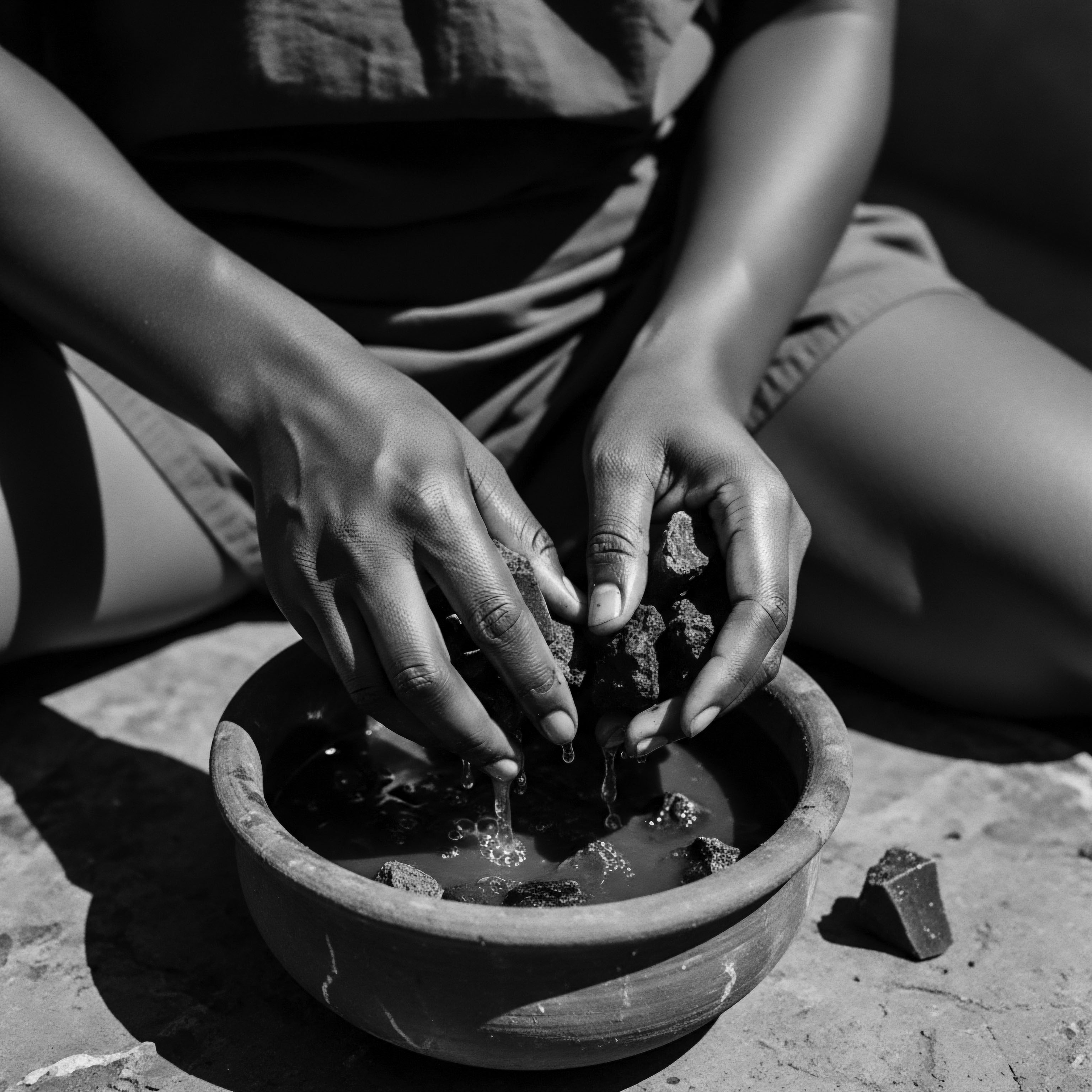

Arid Land Oils
Meaning ❉ Arid Land Oils are botanical lipid extracts from resilient plants, central to ancestral hair care and cultural identity in arid regions.

Why Did Textured Hair Care Traditions Prioritize Moisture?
Textured hair traditions prioritized moisture due to unique biological structure and its profound cultural ties to heritage and wellness.

What Compounds in Historical Plant Oils Support Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical plant oils for textured hair heritage contained fatty acids, phytosterols, and antioxidants, nourishing strands for resilience.

What Traditional Grains Were Used for Textured Hair Care?
Traditional grains like rice, millet, and sorghum were used in ancient hair care for their cleansing and strengthening properties.

Why Did Textured Hair Become a Marker of Oppression after Colonial Contact?
Textured hair became an oppression marker when colonial powers weaponized its unique biology to justify racial hierarchies, diminishing its rich heritage.

What Is the Ancestral and Scientific Connection of Clays to Textured Hair Heritage?
Clays connect to textured hair heritage by offering ancestral cleansing, defining, and protective benefits rooted in their mineral composition and unique physical properties.

Why Are Traditional Ingredients Suitable for Textured Hair?
Traditional ingredients suit textured hair through ancestral wisdom, providing ideal moisture and protection aligned with hair's structure.

What Historical Roles Did Textured Hair Play in Expressing Identity?
Textured hair has historically expressed identity through social status, spiritual connection, and acts of resistance, profoundly linking to Black and mixed-race heritage.

What Impact Does Heritage Have on Understanding Textured Hair’s Biological Needs?
Heritage informs textured hair's biological needs by revealing centuries of ancestral care practices uniquely suited to its natural attributes.

Can Traditional North African Grooming Rituals Enhance Modern Textured Hair Health?
Traditional North African rituals offer potent, heritage-rooted enhancement for textured hair health, prioritizing moisture and resilience.

What Nutritional Shifts Affected Textured Hair during Slavery?
Nutritional shifts during slavery severely compromised textured hair's health, yet cultural care rituals adapted, affirming heritage and resilience.

What Specific Compounds in Fenugreek Benefit Textured Hair Vitality?
Fenugreek’s compounds, like proteins and mucilage, fortify textured hair, continuing a legacy of ancestral care.

What Historical Role Did Oils Play in Textured Hair Resilience?
Oils historically provided vital moisture, sealed strands, and enabled protective styling for textured hair across ancestral communities, fostering resilience.

How Does Historical Red Palm Oil Use Impact Textured Hair Today?
Historical red palm oil use provides a deep heritage of nourishment and cultural identity for textured hair, echoed in modern care.

What Traditional Applications of Natural Oils Honored Textured Hair?
Traditional natural oil applications deeply honored textured hair by providing ancestral nourishment, protection, and cultural significance across generations.

What Historical Natural Dyes Were Used on Dark Textured Hair?
Ancestral communities tinted dark textured hair using plants like henna and indigo, and mineral pigments such as red ochre, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

Cross-Cultural Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Cross-Cultural Hair Traditions define the historical transmission, adaptation, and profound symbolic meaning of hair care practices across diverse societies.

What Ancestral Dyes Colored Textured Hair?
Ancestral dyes for textured hair, rooted in plant and mineral sources, were deeply connected to cultural identity and protective heritage practices.

What Natural Ingredients Were Employed for Hair Coloring by Ancestral Communities with Textured Hair?
Ancestral communities with textured hair used plant and mineral pigments from the earth to color their strands, intertwining beauty with deep cultural identity and heritage.

Racialized Hair Bias
Meaning ❉ Racialized Hair Bias is the systemic prejudice against textured hair, particularly affecting Black and mixed-race individuals, rooted in Eurocentric beauty standards.

How Does Traditional Hawaiian Botany Benefit Textured Hair?
Traditional Hawaiian botany deeply nourishes textured hair by offering natural moisture, strength, and scalp care, reflecting a profound ancestral heritage of botanical wisdom.

