In What Ways Do Traditional Oils Validate Modern Scientific Understanding of Textured Hair Needs?
Traditional oils preserve textured hair's health, their ancient practices affirmed by modern science and cultural heritage.

Gossypium Barbadense
Meaning ❉ Gossypium Barbadense, a cotton species, signifies deep ancestral hair care, embodying resourcefulness and cultural continuity for textured hair.

Ayurvedic Hair Science
Meaning ❉ Ayurvedic Hair Science is a traditional system of holistic care that links hair vitality to internal balance and ancestral practices, particularly for textured hair.

Gabon Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ Gabon Hair Heritage defines the ancestral wisdom, cultural practices, and profound meanings tied to textured hair traditions of Gabonese peoples.

How Did Ancient Butter Applications Enhance Textured Hair Health?
Ancient butter use provided essential moisture and protection for textured hair, a practice rooted deeply in Black and mixed-race heritage.

Textured Hair Light
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Light signifies the profound visual and symbolic radiance of coiled strands, rooted in heritage and vital well-being.

Can Traditional Plant-Based Remedies Soothe Scalp Irritation on Textured Hair?
Traditional plant remedies, rooted in textured hair heritage, often soothe scalp irritation through natural anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties.

Bodily Autonomy Hair
Meaning ❉ Bodily Autonomy Hair is the inherent right to self-determine hair choices, a concept deeply rooted in heritage, identity, and freedom for textured hair.

Hair Loss Disparities
Meaning ❉ Hair Loss Disparities denote observable differences in hair loss prevalence and outcomes among diverse populations, particularly textured hair communities.

How Did Ancient Communities Utilize Natural Oils for Textured Hair Protection?
Ancient communities guarded textured hair with natural oils, a core practice of ancestral heritage for protection and reverence.

Can Ancient Hair Care Methods Prevent Modern Textured Hair Damage?
Ancestral hair care methods, grounded in heritage, offer profound strategies to prevent modern textured hair damage.

Tsogho Mitsogho Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Tsogho Mitsogho Heritage defines ancestral practices and spiritual beliefs concerning hair from Gabonese communities.

Plant Choices
Meaning ❉ Plant Choices signify the intentional selection and application of botanical elements for textured hair, rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural significance.

What Ancestral Practices Using African Botanicals Supported Textured Hair Vitality?
Ancestral African practices used botanicals like shea butter, Chebe powder, and baobab oil to deeply nourish and protect textured hair, honoring a rich heritage.

Punu Cultural Heritage
Meaning ❉ A unique exploration of Punu Cultural Heritage, its profound significance, and its deep connection to textured hair, ancestral wisdom, and identity.

What Ancestral Practices Supported Textured Hair Health with Natural Oils?
Ancestral practices supported textured hair health with natural oils through deep reverence for hair and earth's bounty, leveraging botanicals for protection and nourishment.

What Traditional Oils Offer Deeper Hair Penetration for Textured Hair?
Traditional oils like coconut, olive, and avocado deeply penetrate textured hair, continuing an ancestral legacy of nourishment.
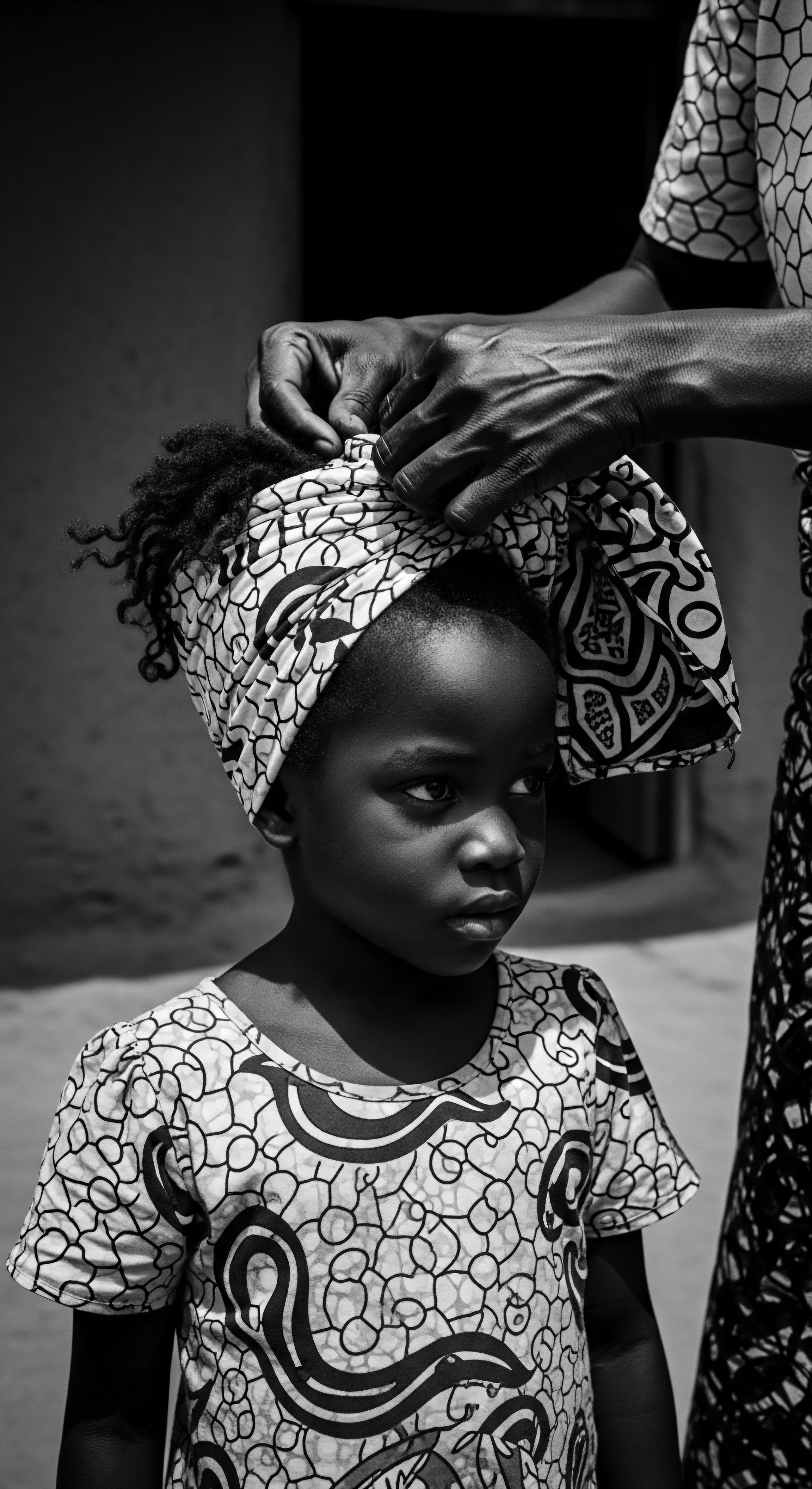

UV Blocking Textiles
Meaning ❉ UV Blocking Textiles are fabrics designed to reduce ultraviolet radiation transmission, safeguarding hair and skin, building upon ancestral protective wisdom.

Fulani Hair Adornment
Meaning ❉ The Fulani Hair Adornment embodies ancient West African braiding traditions, signifying identity, wealth, and status through intricate styles and embellishments.
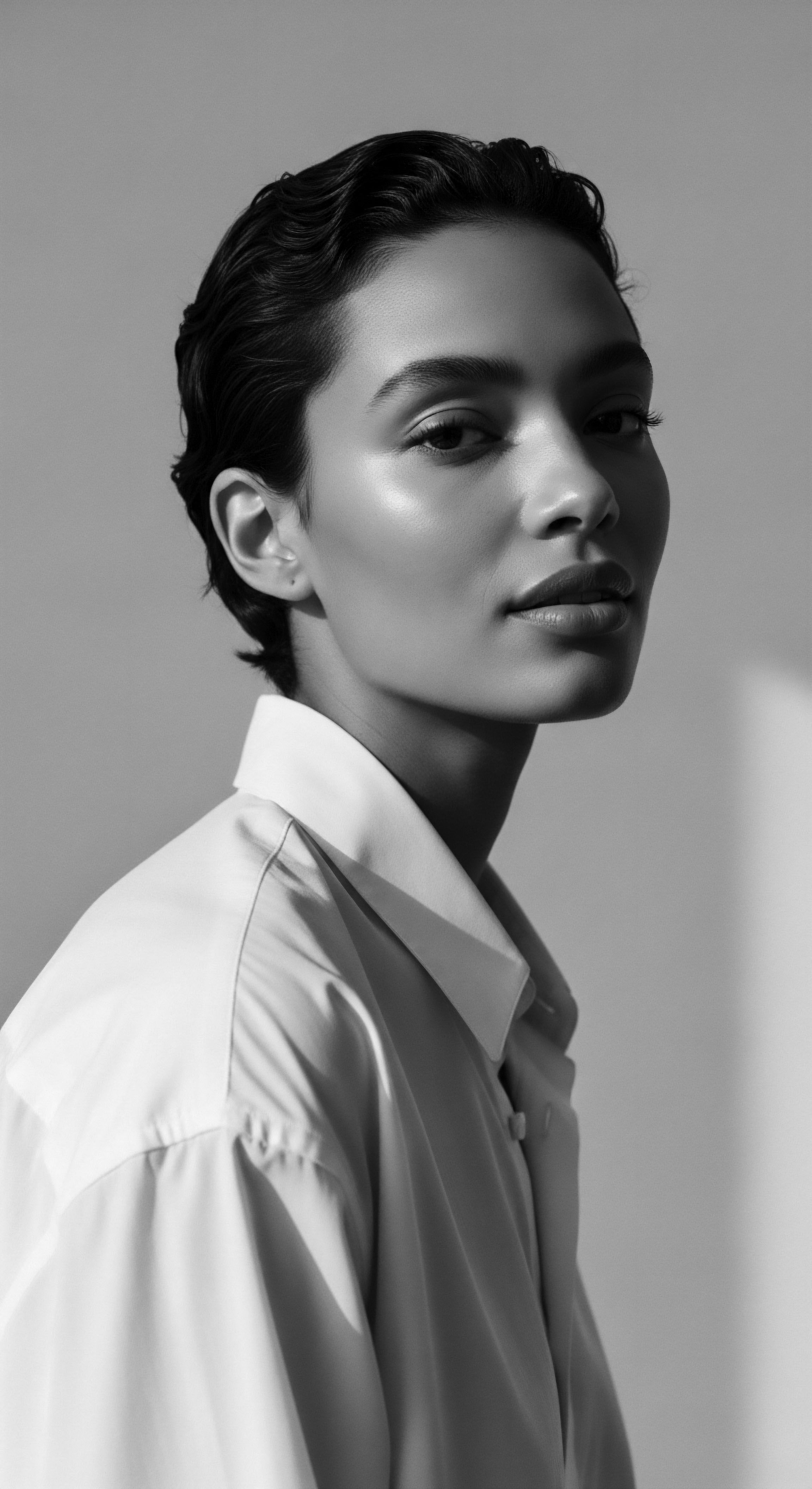

What Ancestral Hair Tools Were Adapted for Textured Hair?
Ancestral hair tools, particularly the afro comb, were adapted for textured hair through wide-tooth designs, evolving from practical grooming implements into profound symbols of heritage, status, and resistance.
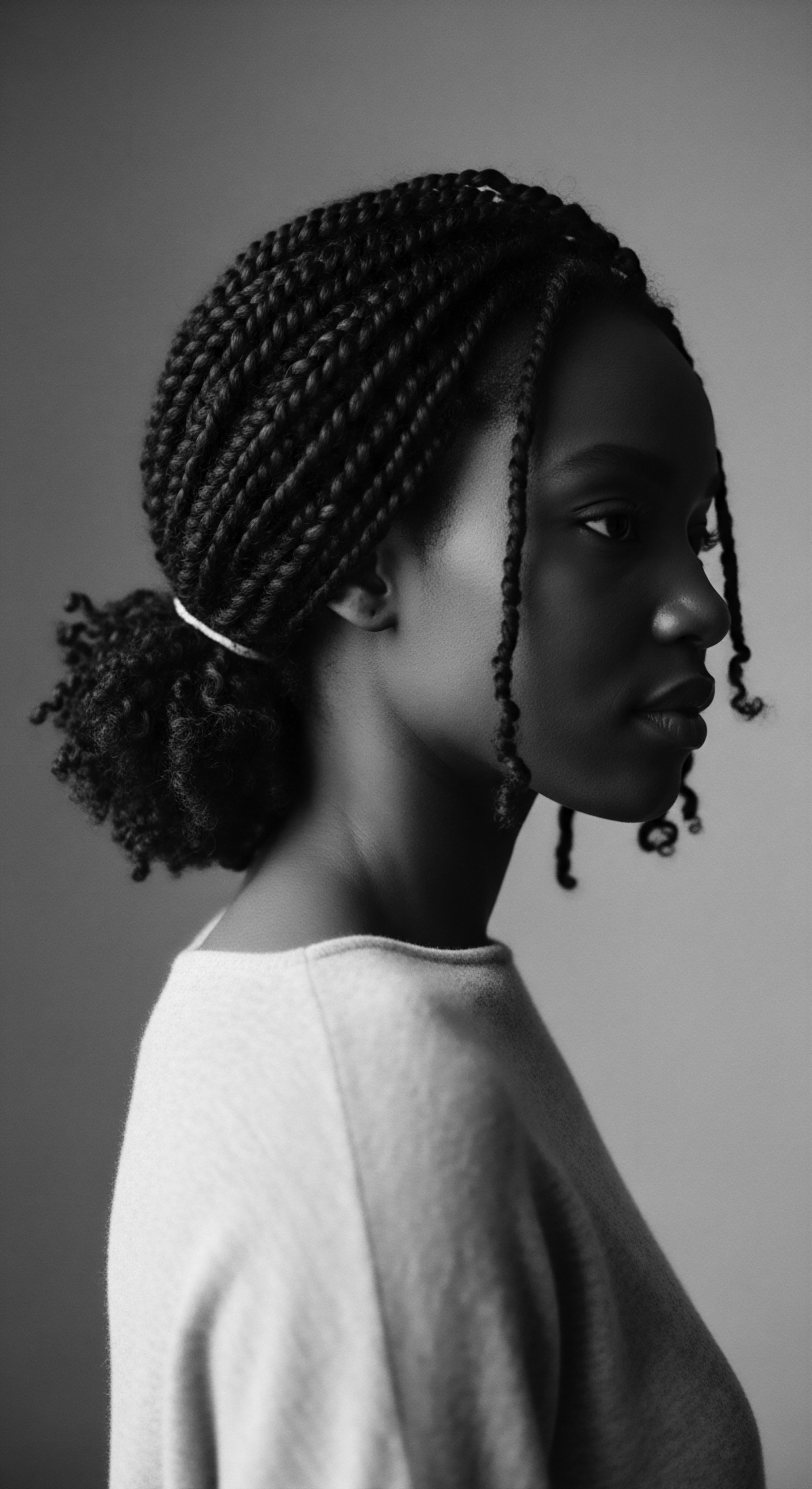

What Is the Lasting Heritage of Textured Hair as Resistance?
Textured hair’s heritage as resistance is seen in its historical use for covert communication and ongoing self-affirmation against discrimination.
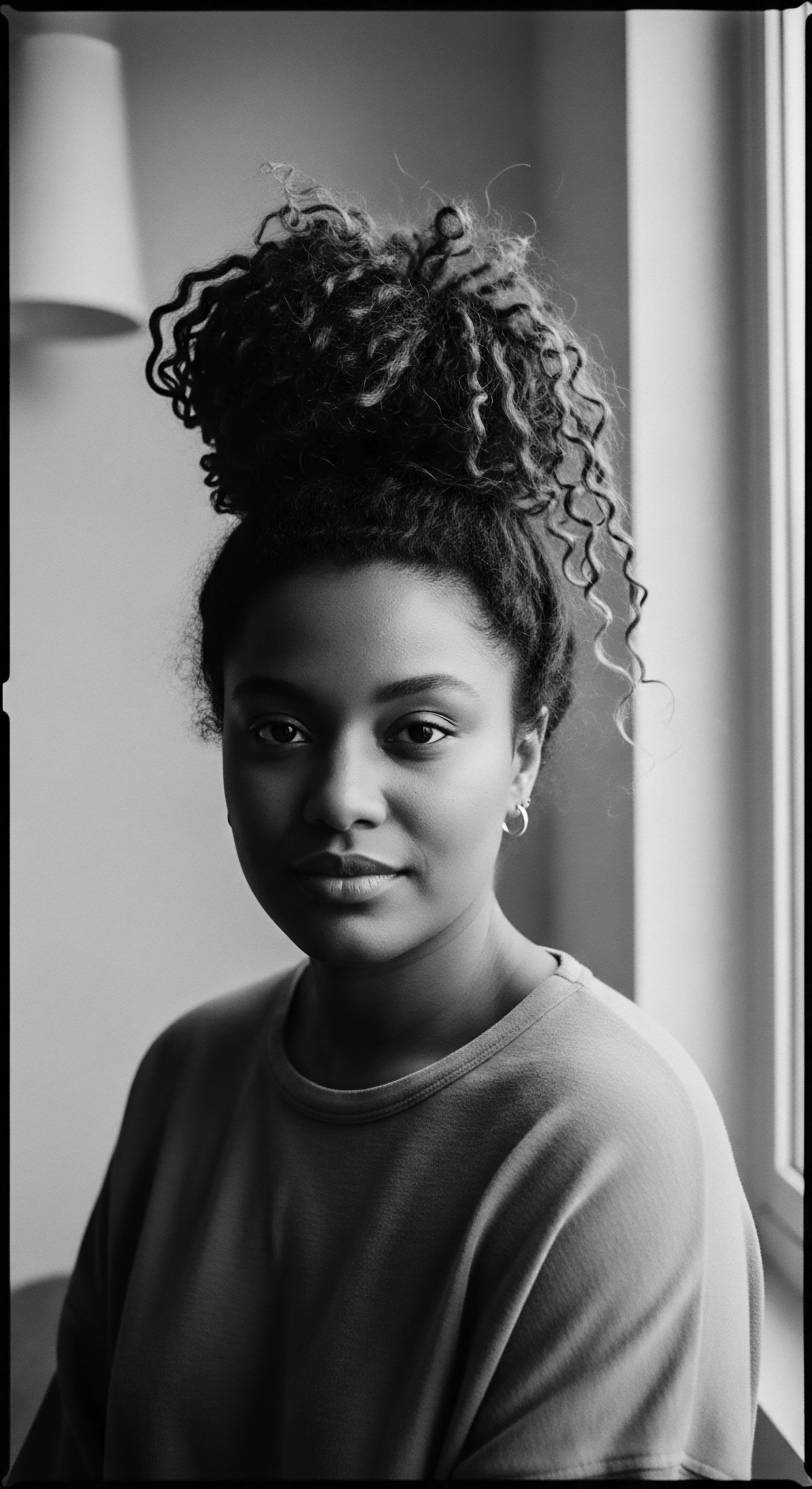

Why Do Communal Grooming Rituals Still Hold Cultural Significance for Textured Hair?
Communal grooming rituals persist for textured hair as a profound celebration of heritage, shared identity, and enduring cultural resilience.

Food Identity
Meaning ❉ Food Identity is the profound meaning derived from the origin and cultural practices surrounding food, intrinsically linked to the heritage and care of textured hair.

How Does Textured Hair Legislation Relate to Ancestral Beauty Traditions?
Textured hair legislation legally protects the cultural and historical expression of ancestral beauty traditions.

Can Historical Hair Care Practices Inform Modern Moisture Strategies for Textured Strands?
Historical hair care practices, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer timeless, holistic moisture strategies for textured strands today.

What Traditional Ingredients Protected Textured Hair from Environmental Exposure?
Ancestral practices and natural emollients like shea butter, coconut, and argan oil fortified textured hair against environmental exposure.

What Makes Silk Uniquely Protective for Textured Hair during Sleep?
Silk safeguards textured hair during sleep by reducing friction and retaining essential moisture, continuing a heritage of protective hair rituals.

Coily Hair Artistry
Meaning ❉ Coily Hair Artistry is the culturally informed, scientifically rooted practice of caring for and celebrating tightly coiled hair, honoring its profound heritage and unique biological needs.