What Were the Tignon Laws?
The Tignon Laws, a 1786 mandate in Louisiana, forced free women of color to cover their textured hair, sparking an artful heritage of resistance through headwraps.

What Is the Ancestral Meaning of Hair?
The ancestral meaning of hair, especially textured hair, is a living record of heritage, identity, communication, and resilience.

What Historical Roles Did Textured Hair Play in Survival?
Textured hair’s historical roles in survival span biological protection, cultural communication, and covert resource storage, underscoring its deep heritage.

What Traditional African Plants Moisturize Coils?
Traditional African plants such as shea butter, baobab oil, and Chebe powder naturally hydrate coils, honoring a deep heritage of ancestral care.

Crown Significance
Meaning ❉ Crown Significance denotes the profound cultural, spiritual, and historical meaning of hair atop the head, particularly within textured hair traditions.

Akan Personhood
Meaning ❉ Akan Personhood is a holistic understanding of being, rooted in spiritual and ancestral lineage, profoundly expressed through textured hair heritage and care.

How Do Traditional Oils Protect Scalp Resilience through Heritage?
Traditional oils preserve scalp resilience by drawing on ancestral knowledge, offering protective, nourishing care for textured hair rooted in heritage.

How Do Historical Styling Practices Relate to Modern Hair Science?
Historical styling practices for textured hair form the ancestral foundation, validated by modern science, revealing a rich heritage of ingenious care.

How Did Historical Oppression Influence Early Hair Care?
Historical oppression profoundly altered early hair care by devaluing textured hair, forcing assimilation, and disrupting ancestral practices and identity.

What Ancestral Practices Preserved Textured Hair from Environmental Wear?
Ancestral practices shielded textured hair from environmental wear through physical barriers and natural emollients, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

What Ancestral Plants Aided Hair Growth?
Ancestral plants like aloe vera, amla, and rosemary nourished textured hair, fostering growth through time-honored heritage practices.

How Do West African Grains Support Textured Hair’s Strength?
West African grains strengthen textured hair by providing essential proteins and amino acids, a legacy deeply rooted in ancestral care practices.

How Do Ancestral African Hair Practices Relate to Humectants?
Ancestral African hair practices utilized natural ingredients with humectant properties and protective styles to maintain textured hair's vital moisture, rooted in deep heritage.

What Traditional Oils Were Favored for African Hair?
Ancestrally, oils like shea butter, palm oil, and castor oil were favored for African hair, revered for their deep connection to textured hair heritage and protective qualities.

African Diaspora Spirituality
Meaning ❉ A unique definition of African Diaspora Spirituality, exploring its profound connection to textured hair heritage and ancestral practices.

Afro-Spanish Hair History
Meaning ❉ Afro-Spanish Hair History explores the evolution and cultural significance of hair practices among people of African descent in Spain.

In What Ways Did Hair Oiling Shape Cultural Identity across Diasporic Communities?
Hair oiling solidified cultural identity in diasporic communities by preserving ancestral textured hair care.

How Did Headwraps Protect Textured Hair in Traditional Societies?
Traditional headwraps shielded textured hair from environmental damage, friction, and moisture loss, preserving its health and cultural heritage.

What Is the Historical Connection between Hair Tools and Social Status in Ancient Cultures?
Hair tools in ancient cultures served as potent symbols of social status, directly connected to textured hair heritage.

Why Did Head Coverings Become Culturally Significant for Textured Hair?
Head coverings became culturally significant for textured hair as vital protectors and profound symbols of heritage, identity, and resilience.
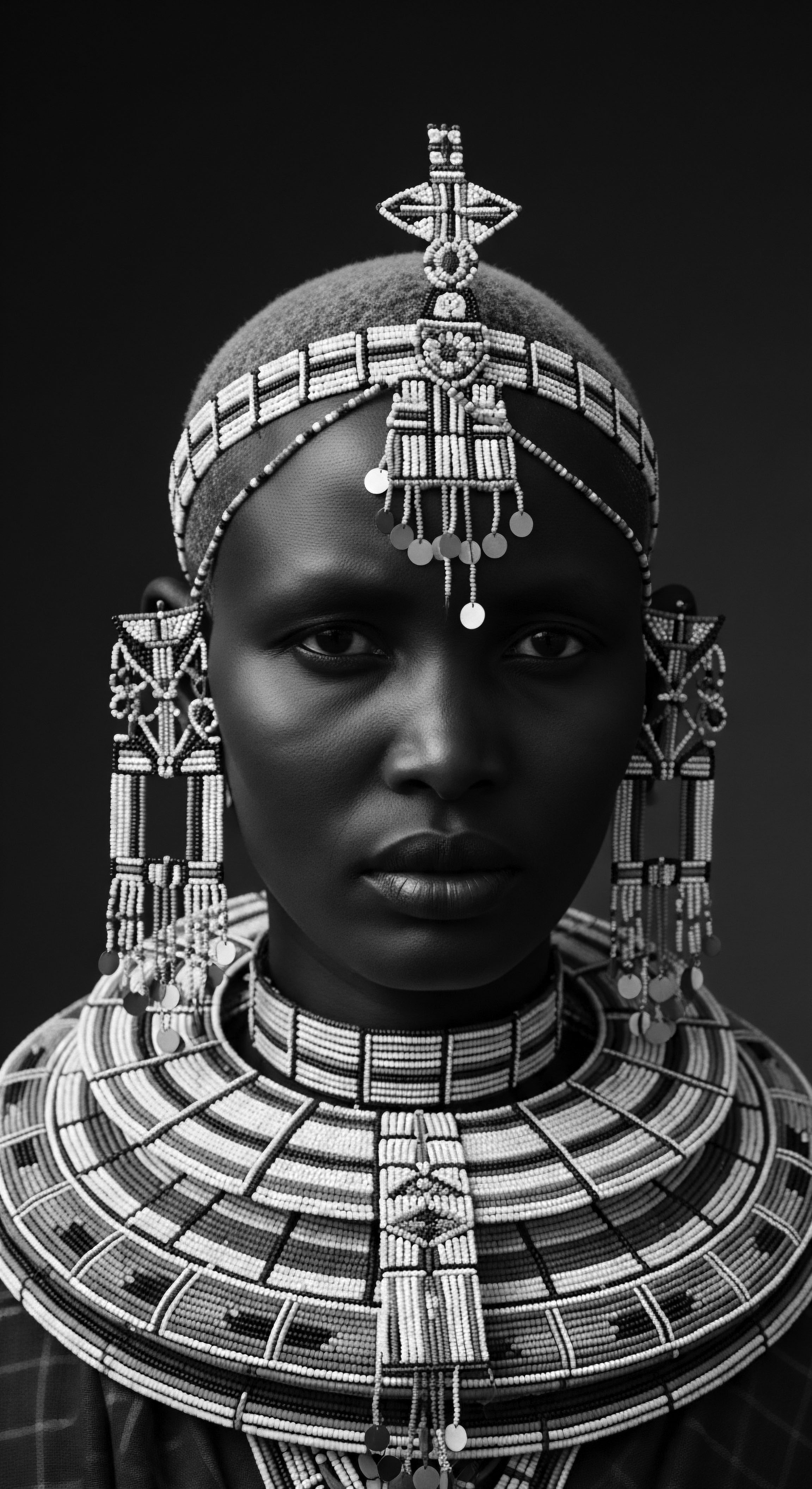

How Does Ancestral Hair Care Connect to Scalp Health?
Ancestral hair care for textured hair protects scalp vitality through natural remedies and deeply embedded cultural practices.

Ori-Ode Meaning
Meaning ❉ The Ori-ode Meaning defines textured hair as a profound, living extension of ancestral lineage and collective identity across Black and mixed-race communities.
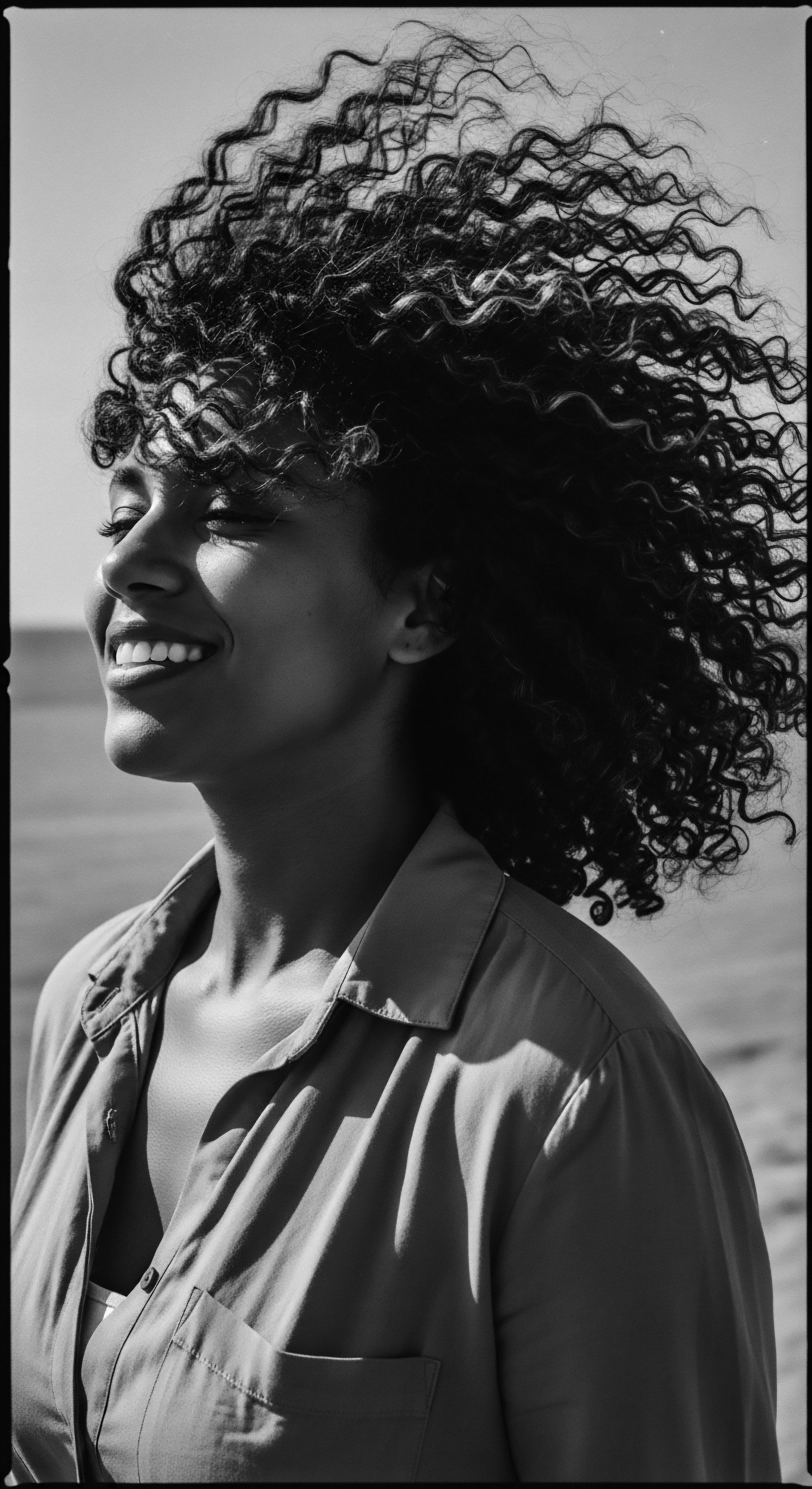

What Is the Role of Hair in Black Cultural Resistance?
Hair has served as a powerful emblem of Black cultural resistance, preserving identity and heritage across generations.
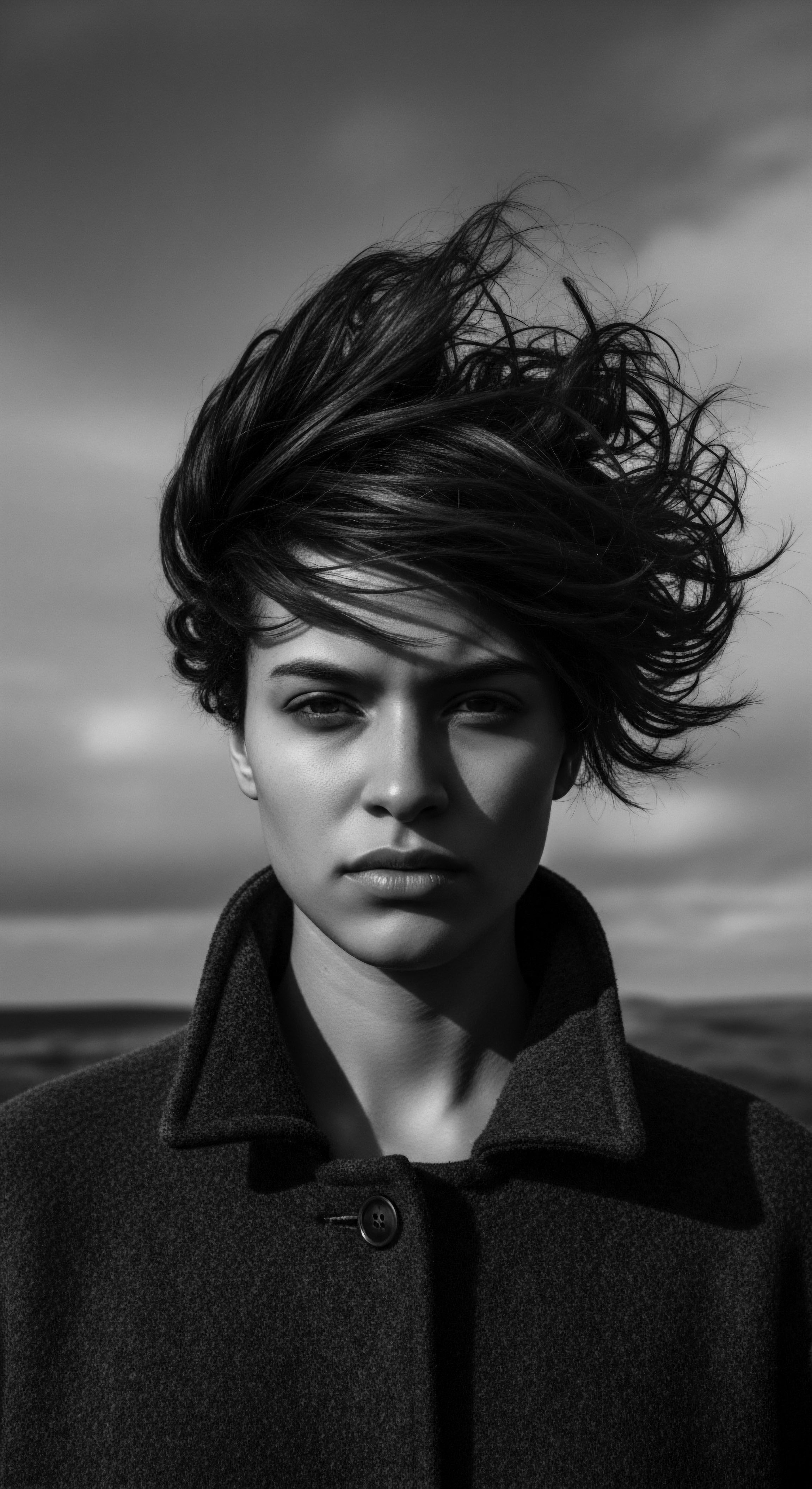

Why Do Textured Hair Types Require Unique Moisture Practices?
Textured hair's distinct structure and heritage require diligent moisture practices to sustain its innate health and resilience.
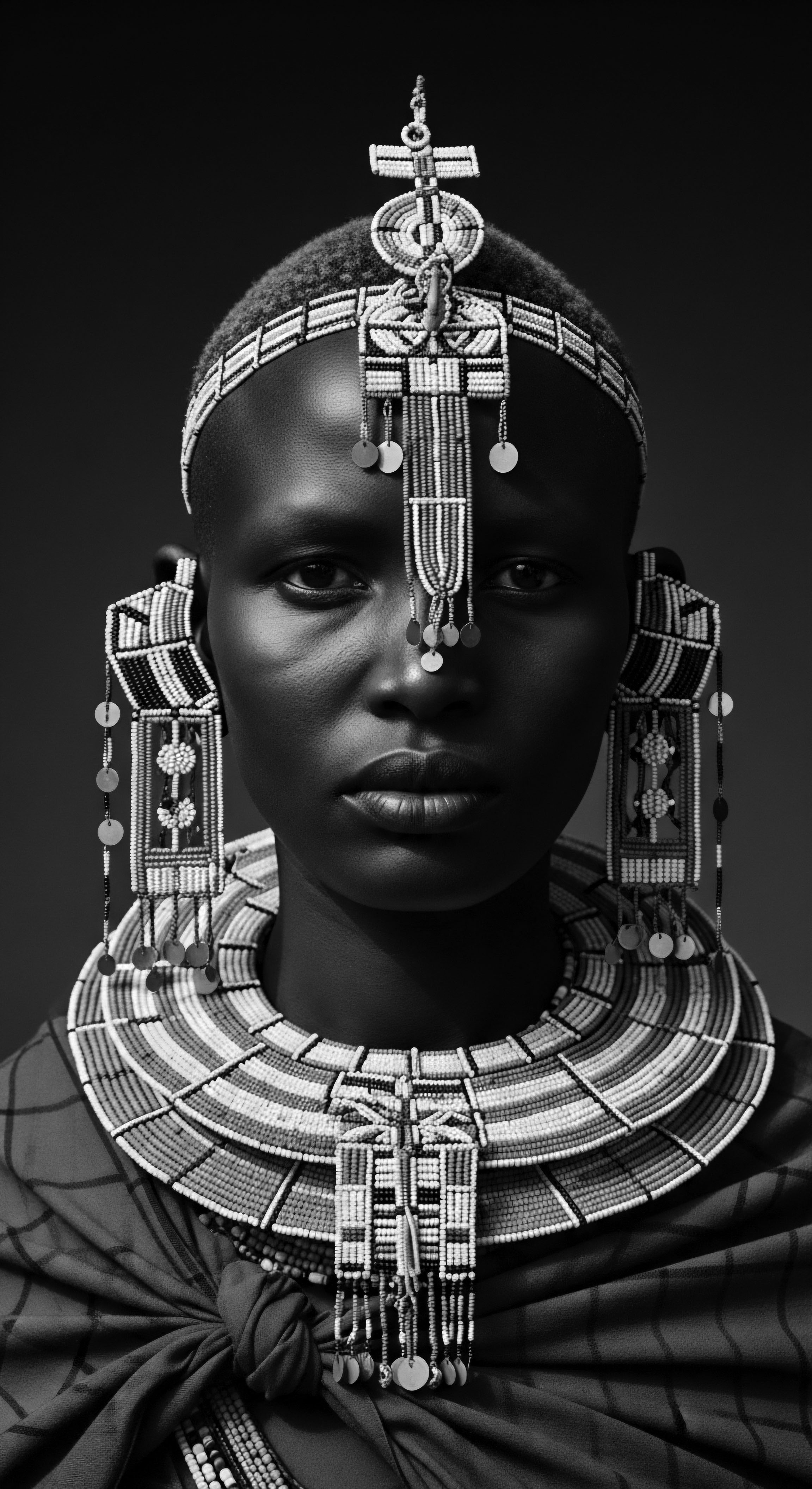

Persian Hair Adornment
Meaning ❉ Persian Hair Adornment encompasses the historical and cultural practices of styling, beautifying, and ornamenting hair within ancient Iranian societies.
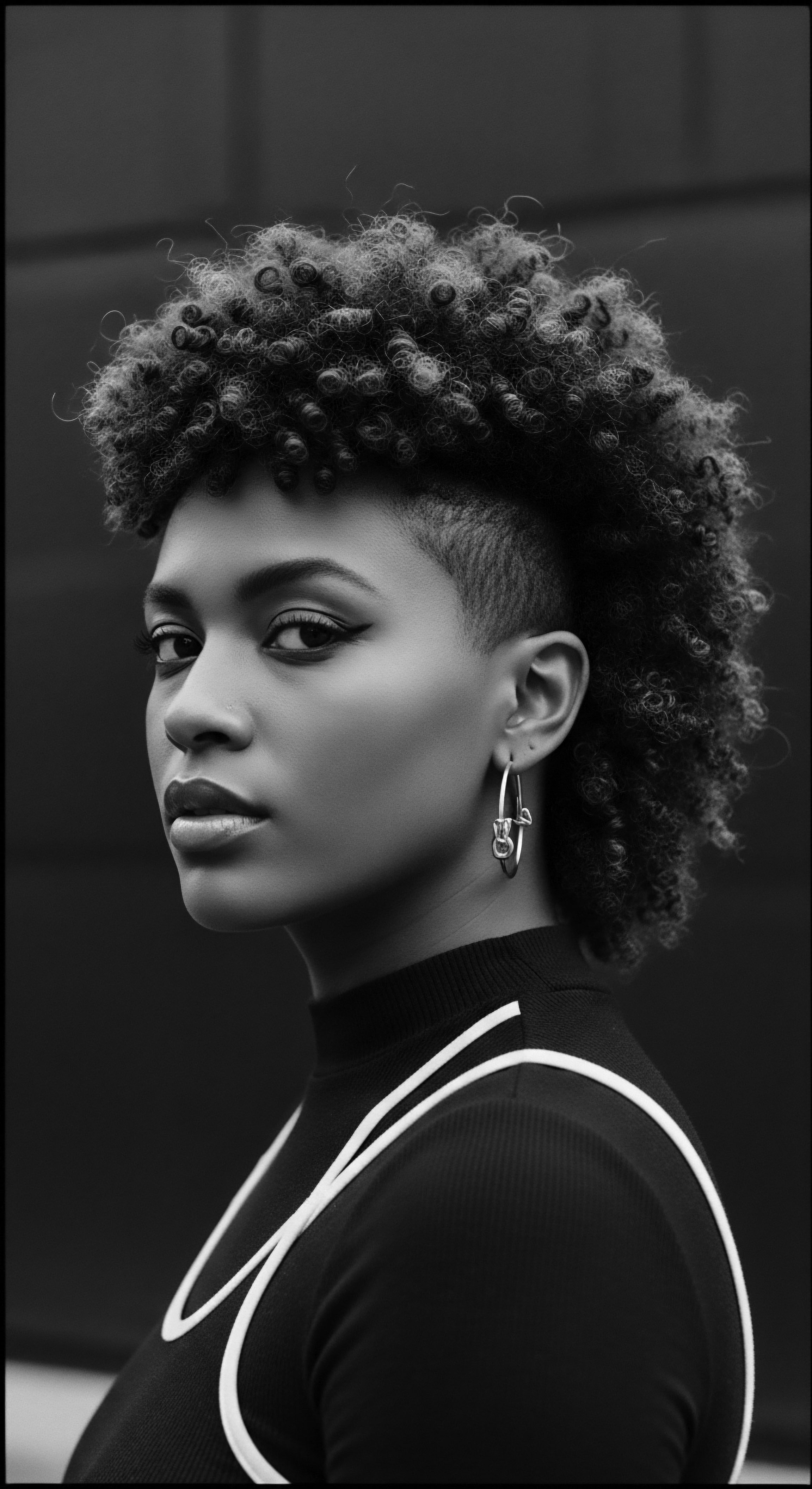

Can Ancient Hair Styling Methods Truly Strengthen Modern Textured Hair?
Ancient styling methods, rooted in ancestral heritage, strengthen textured hair by promoting protection, moisture retention, and scalp health.

Cultural Ecological Resilience
Meaning ❉ Cultural Ecological Resilience is the ability of a cultural system to adapt, thrive, and retain identity through intertwined relationships with its environment.
Acts of Resistance
Meaning ❉ Acts of Resistance, in textured hair, signifies a profound declaration of identity, cultural preservation, and defiance against imposed norms.
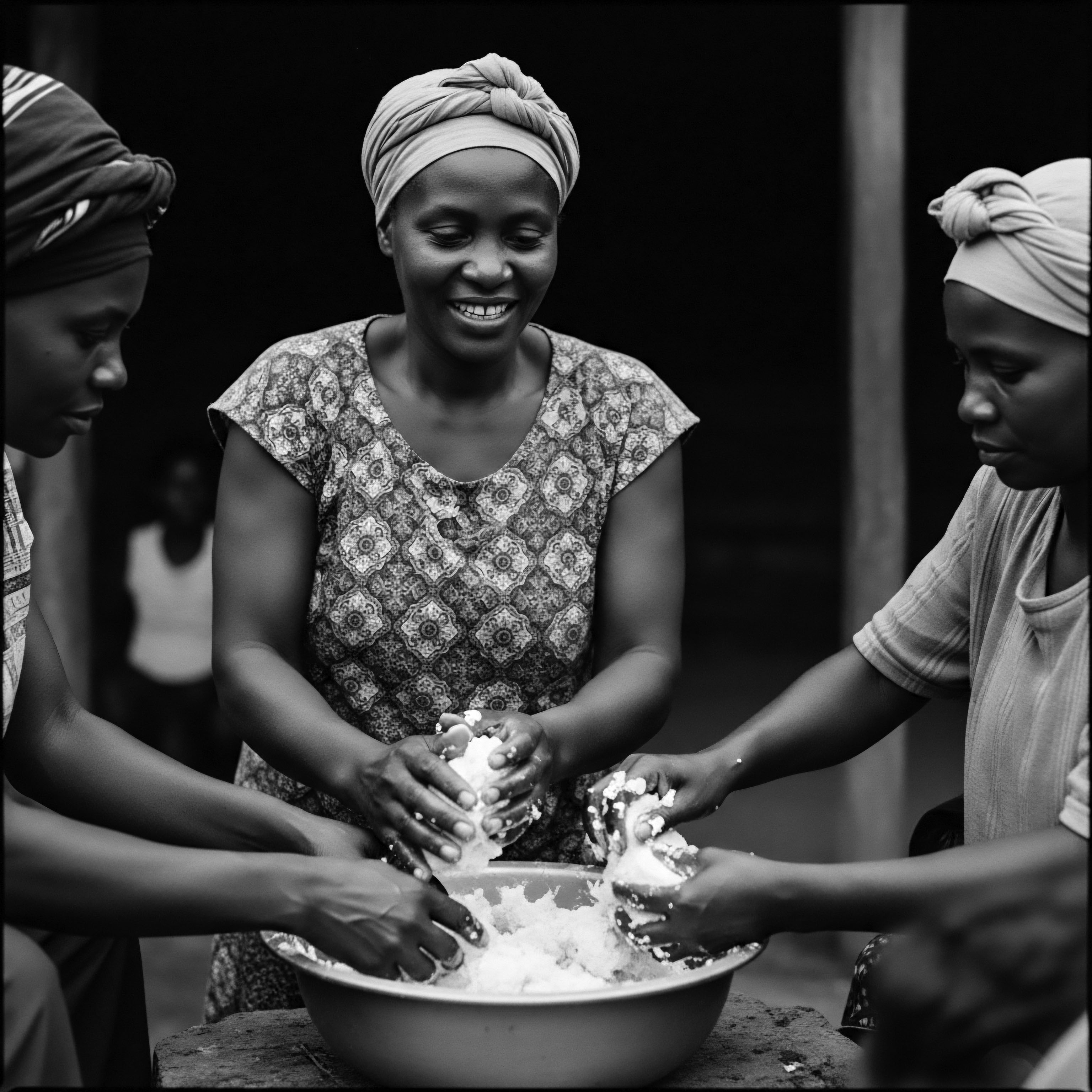

How Did Ancient Societies Understand Textured Hair Strength?
Ancient societies understood textured hair strength through its cultural, spiritual, and communal significance, deeply woven into ancestral practices.

