
How Did West African Communities Apply Black Soap for Textured Hair?
West African communities applied black soap for textured hair as a natural, heritage-rich cleanser, nourishing scalp and strands through ancestral practices.

What Is Shea Butter’s Role in West African Heritage?
Shea butter serves as an ancestral foundation for textured hair care, deeply rooted in West African heritage and communal practices.

How Does Oiling Aid Textured Hair?
Oiling textured hair deeply aids moisture retention and resilience, honoring ancestral practices of nourishing strands.

What Traditional Ingredients Are Used for Black Hair Cleansing?
Ancestral practices employed natural ingredients such as saponin-rich plants and plant-based ashes for gentle, heritage-centered hair cleansing.

What Ancestral Oils Nurtured West African Hair?
West African hair heritage was nurtured by shea, palm kernel, and baobab oils, deeply entwined with cultural identity.

How Did Historical Practices Use Traditional Oils for Hair Protection?
Historical practices utilized natural oils from plants and animals to shield textured hair from environmental damage and preserve its vitality, a core element of ancestral heritage.

What Are Ancient Hair Oiling Practices?
Ancient hair oiling practices are ancestral rituals for textured hair nourishment and cultural expression.

West African Butters
Meaning ❉ West African butters are traditional lipid extracts from indigenous trees, profoundly shaping textured hair care through ancestral wisdom and cultural continuity.

Botanical Softeners
Meaning ❉ Botanical Softeners are plant-derived agents enhancing textured hair's flexibility and manageability, rooted in rich ancestral traditions.

Coiled Hair Vitality
Meaning ❉ Coiled Hair Vitality is the inherent strength and cultural resonance of helical hair, rooted in ancestral knowledge and biomechanical design.

What Historical Significance Do Hair Care Practices Hold for Identity?
Hair care practices for textured hair are profound historical statements of identity, resilience, and cultural legacy.
Mary Johnson Boston
Meaning ❉ The Mary Johnson Boston represents the profound historical, cultural, and scientific connection of textured hair to identity and ancestral wisdom.

How Did West African Communities Retain Moisture in Textured Hair?
West African communities maintained textured hair moisture using natural oils, protective styles, and communal knowledge passed through generations, honoring a deep hair **heritage**.

West African Soaps
Meaning ❉ West African Soaps, a traditional plant-based cleanser, embodies ancestral wisdom for textured hair care rooted in African heritage.

How Did Ancient Hair Practices Survive?
Ancient hair practices survived by deep integration into identity, community, and practical efficacy, transmitting through generations and cultural adaptation.

What Natural Ingredients Shielded Textured Hair Historically?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and plant oils shielded textured hair, preserving its integrity and cultural identity.

How Does Heritage Influence Textured Hair Care Today?
Textured hair care today is a direct extension of ancestral wisdom, adapting ancient practices for modern needs.

How Does Ancient Oil Use Connect to Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancient oil applications for textured hair provided ancestral protection, moisture, and cultural connection, directly influencing modern care regimens.

How Did West African Butters Defend Hair from Sun?
West African butters provided ancestral textured hair with a protective, moisturizing shield against solar damage.

West African
Meaning ❉ The West African designation encompasses the ancestral heritage, diverse textures, and profound cultural practices linked to textured hair globally.

In What Ways Do Traditional Hair Rituals Connect to Cultural Identity and Resilience?
Traditional hair rituals intertwine with identity and resilience by serving as living archives of cultural memory for textured hair heritage.

3c Hair Definition
Meaning ❉ 3c hair defines a tightly coiled curl pattern, holding profound historical and cultural significance within textured hair heritage.

Nontombi Plaits
Meaning ❉ Nontombi Plaits define an ancestral method of hair intertwining that preserves hair health while conveying deep cultural and historical significance.

How Does Historical Hair Care Reflect Broader Cultural Identity and Ancestral Wisdom?
Historical hair care practices, particularly for textured hair, are deeply woven into cultural identity and ancestral wisdom, acting as vital expressions of heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Mirror the Modern Use of Hair Bonnets?
Modern hair bonnets mirror ancestral practices of protective head coverings for textured hair, rooted in heritage and hair health.
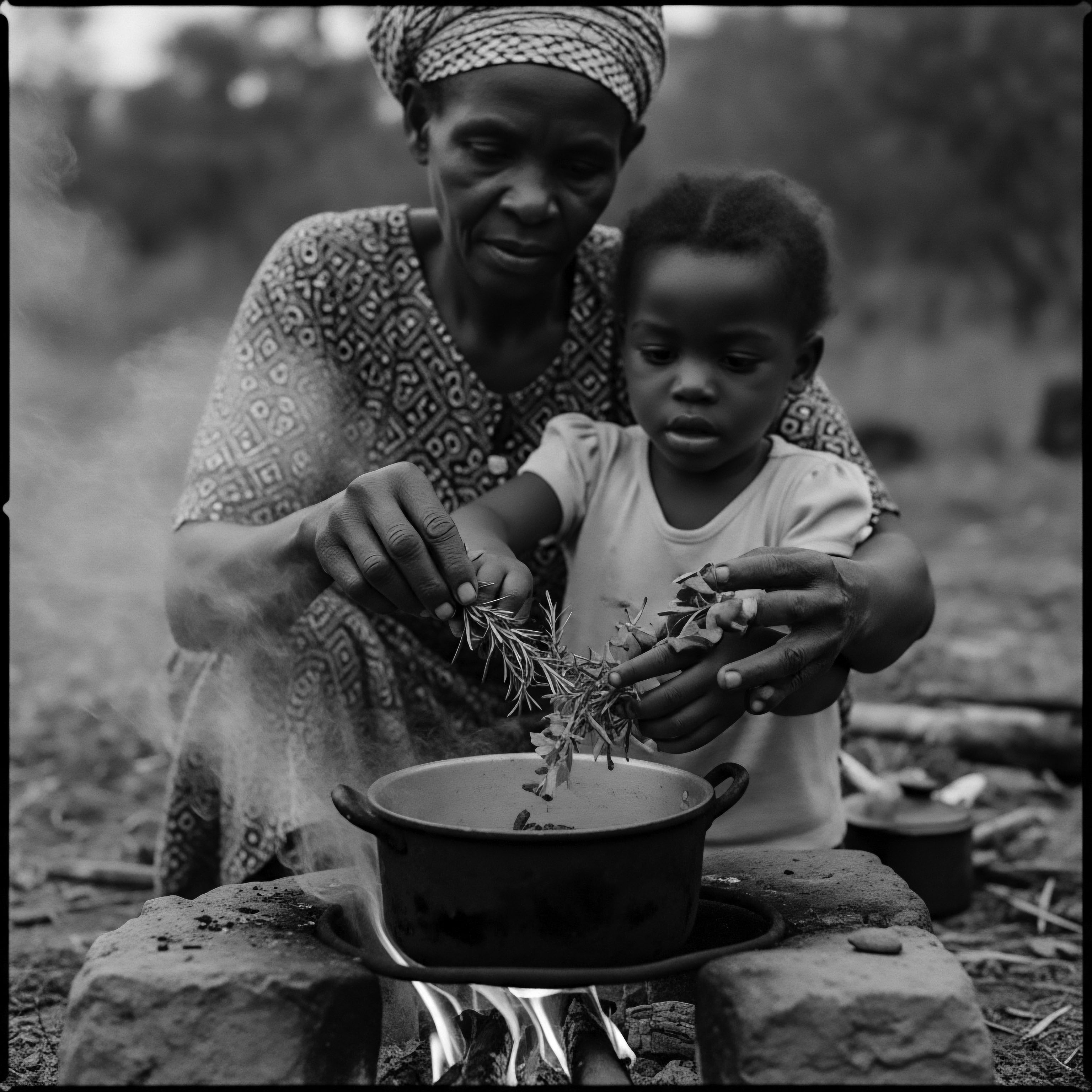

How Did Indigenous Cultures Use Botanicals for Hair Protection?
Indigenous cultures protected textured hair with plant-based remedies, drawing on ancestral wisdom to shield against environmental harm.

How Do Plants Support Hair Health?
Plants support textured hair health by providing natural nutrients and protective compounds, deeply rooted in ancestral care practices and heritage.

How Does Ancestral Hair Wisdom Influence Contemporary Science?
Ancestral hair wisdom offers foundational insights and practices for textured hair care, validating contemporary scientific understanding.

Which Traditional Oils Were Preferred for Unique Textured Hair Needs?
Ancestral communities preferred oils like shea butter and batana oil for unique textured hair, recognizing their deep moisturizing and protective qualities.

