What Role Did Hair Oiling Play in West African Heritage Styling?
Hair oiling in West African heritage styling protected, nourished, and symbolized communal identity for textured hair.

Why Did Shea Butter Become a Central Element in West African Beauty Heritage?
Shea butter became central to West African beauty heritage for textured hair through its exceptional moisturizing properties, deep cultural integration, and economic significance for women.

West African Women’s Economy
Meaning ❉ The West African Women's Economy signifies the enduring economic contributions of women, deeply linked to cultural heritage and textured hair practices.

How Did West African Plants Support Heritage Hair Care?
West African plants provided ancestral communities with natural emollients and nutrients vital for protecting and nurturing textured hair heritage.

How Did West African Heritage Shape Shea Butter Use?
West African heritage deeply shaped shea butter use by integrating it into traditional hair care for textured strands, emphasizing moisture, protection, and cultural identity.

How Did West African Heritage Shape Hair Oil Choices?
West African heritage shaped hair oil choices by valuing indigenous plant-based emollients for moisture, protection, and cultural significance.

In What Ways Does Shea Butter Reflect the Economic Heritage of West African Women?
Shea butter embodies West African women's economic heritage through its ancestral harvesting, communal processing, and income generation, deeply connected to textured hair traditions.

What Is the Historical Significance of Black Soap in West African Heritage?
Black soap is a West African heritage cleanser for textured hair, made from plant ash and natural oils.

Grain-Based Hair Solutions
Meaning ❉ Grain-Based Hair Solutions signify traditional and contemporary hair care practices utilizing cereal derivatives, deeply rooted in the heritage of textured hair communities.

Which West African Ingredients Enhance Textured Hair?
West African ingredients enhance textured hair through ancestral wisdom, offering deep moisture, protective properties, and a profound link to cultural identity.

West African Grain
Meaning ❉ The West African Grain is the intrinsic, ancestral essence of textured hair, embodying its unique biology, traditional care, and deep cultural heritage.
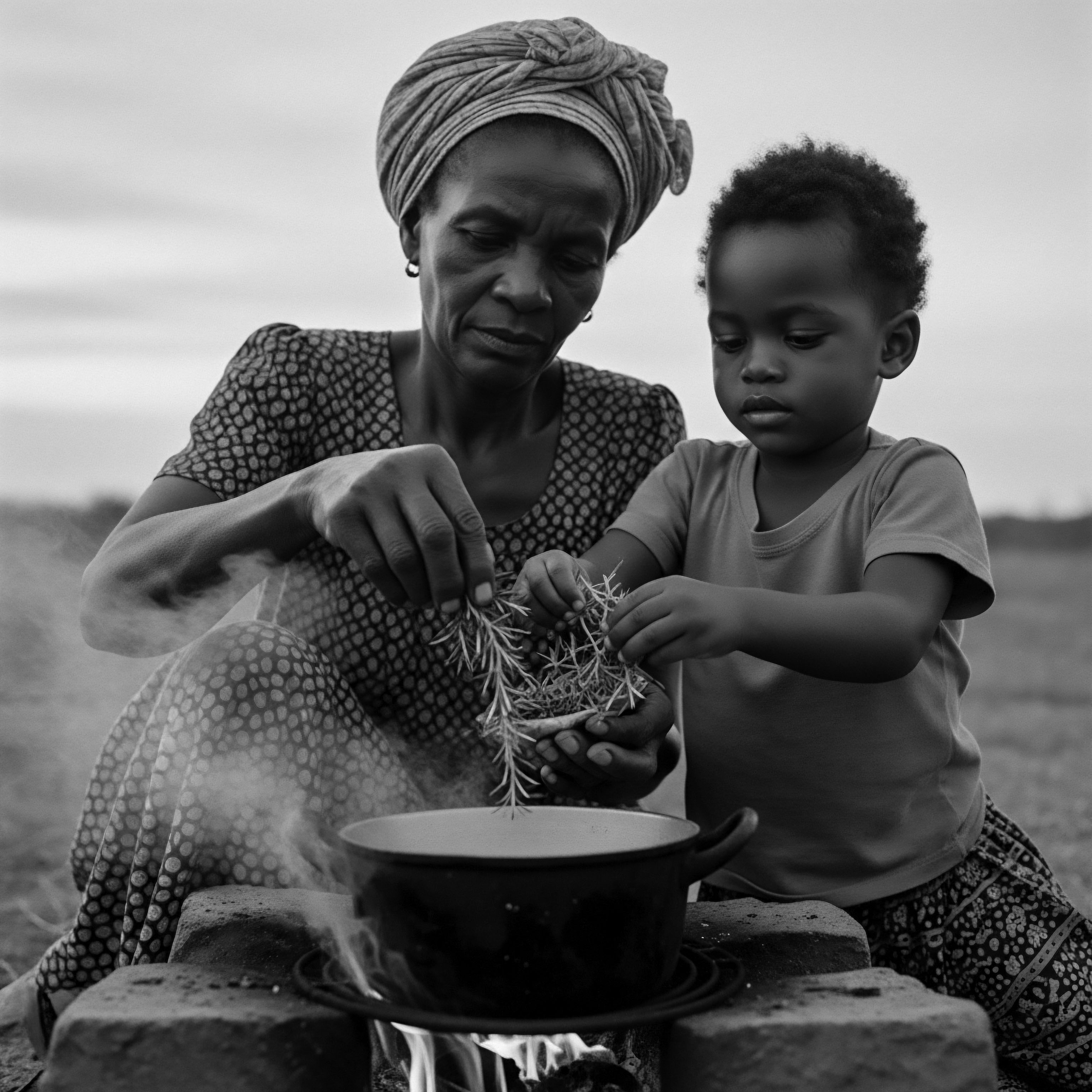

Grain Remedies
Meaning ❉ Grain Remedies encompass ancestral and scientific applications of cereal grains for nurturing textured hair, reflecting deep cultural heritage.

In What Ways Do Traditional Grain-Based Remedies Inform Modern Textured Hair Care Regimens?
Traditional grain remedies deeply inform modern textured hair care by offering ancestral wisdom, validated by science, preserving a rich cultural **heritage**.

In What Ways Do Traditional West African Hair Rituals Connect to Modern Textured Hair Heritage?
Traditional West African hair rituals provide foundational knowledge and continuous inspiration for modern textured hair heritage.
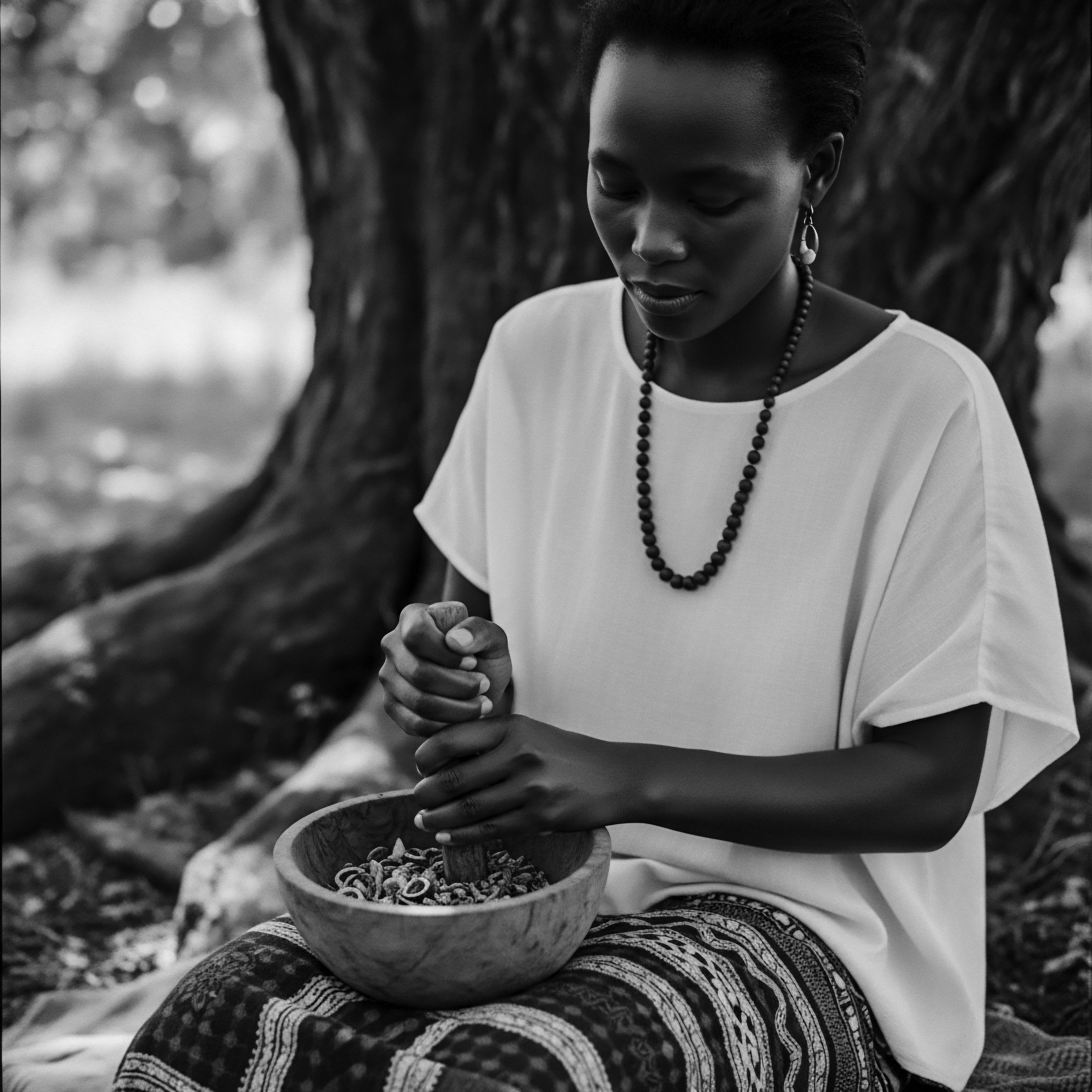

Can Ancient West African Remedies Benefit Modern Textured Hair?
Ancient West African remedies offer profound benefits for modern textured hair by linking its care to a rich heritage of natural ingredients and mindful traditions.

What Is Fonio’s Unique Contribution to Textured Hair?
Fonio's methionine and cysteine content supports textured hair strength, a legacy rooted in West African ancestral diets.

How Does Shea Butter Connect with West African Heritage?
Shea butter connects to West African heritage through ancient hair care rituals, communal practices, and its natural benefits for textured hair.
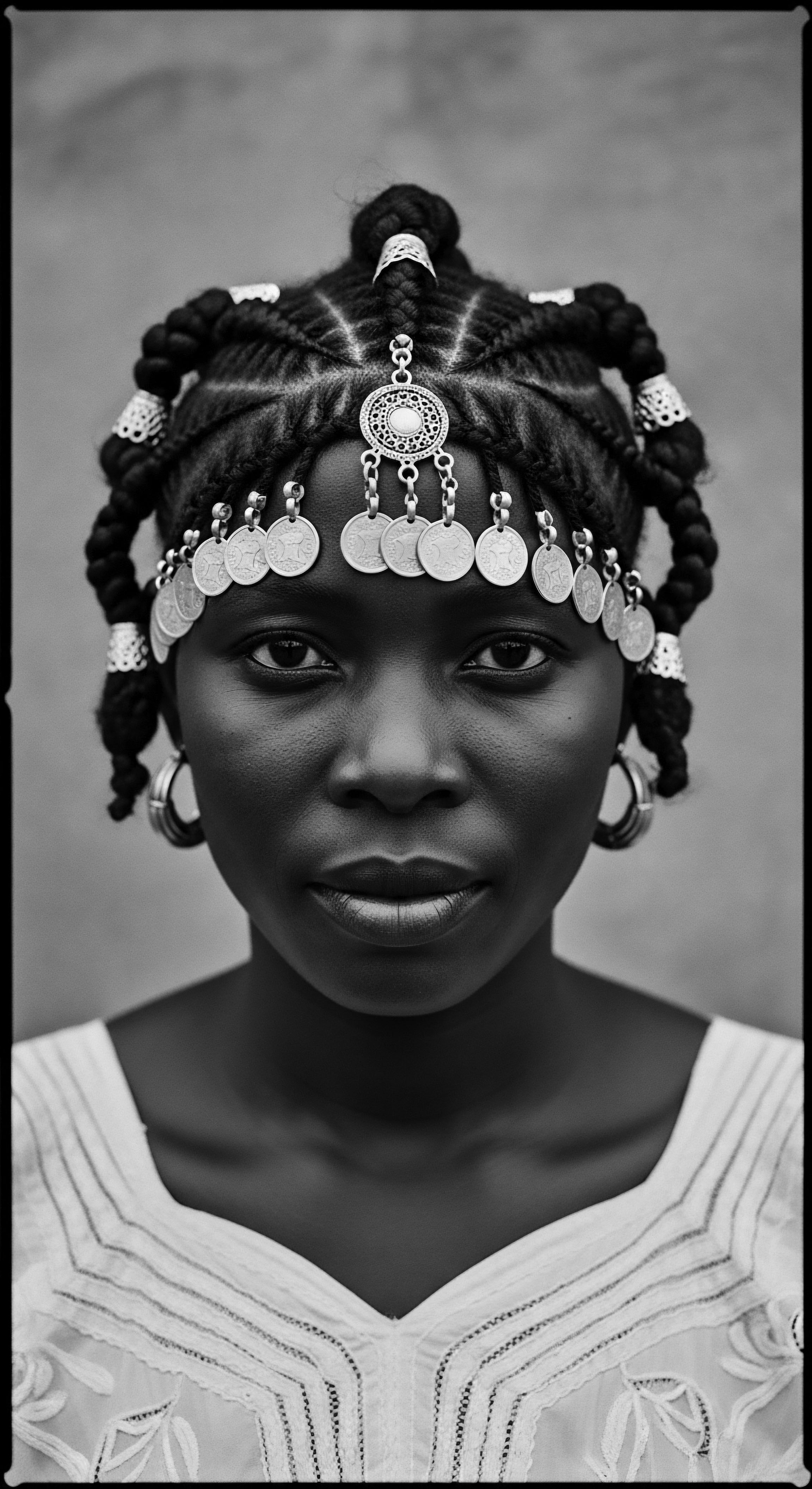

How Do Communal Cleansing Rituals Reflect West African Cultural Heritage?
West African communal cleansing rituals mirror a rich textured hair heritage, symbolizing spiritual purification, communal identity, and ancestral connection.

Grain Practices
Meaning ❉ Grain Practices defines the inherent nature of textured hair and the ancestral care methods that honor its unique characteristics and cultural significance.
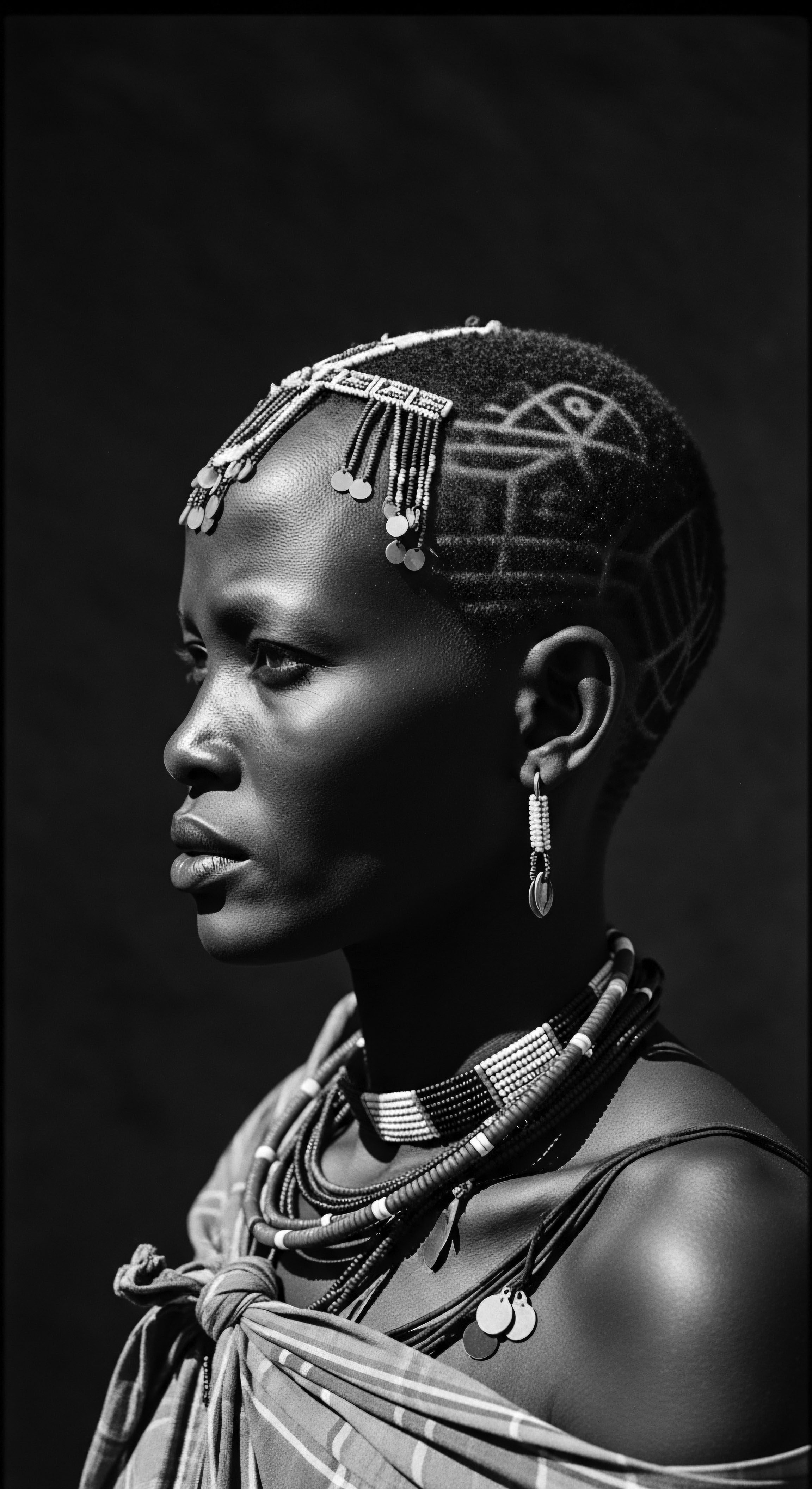

What Cultural Heritage Is Embodied in West African Hair Cleansing Rituals?
West African hair cleansing rituals embody a rich heritage of honoring textured hair through natural ingredients, communal care, and ancestral wisdom.

Can Ancestral Grain Practices Inspire Modern Textured Hair Routines?
Ancestral grain practices offer profound inspiration for textured hair routines, providing natural ingredients and a heritage of holistic care.

How Did West African Communities Traditionally Cleanse Textured Hair?
West African communities traditionally cleansed textured hair using natural, plant-based preparations like African Black Soap and Ambunu leaves, honoring hair heritage.

How Did West African Ancestors Cleanse Textured Hair?
West African ancestors cleansed textured hair using plant-based ingredients like African Black Soap and natural clays, honoring their hair heritage.

How Did Ancient West African Communities Cleanse Textured Hair?
Ancient West African communities cleansed textured hair using natural, plant-based soaps and clays, deeply connecting practices to heritage and community.

West African Foods
Meaning ❉ West African Foods, in the context of textured hair, represents a profound connection between ancestral botanical wisdom and holistic self-care practices.

Can Ancient West African Foods Promote Modern Textured Hair Resilience?
Ancient West African foods, rich in specific nutrients and traditionally used for care, promote modern textured hair resilience by grounding it in deep heritage.
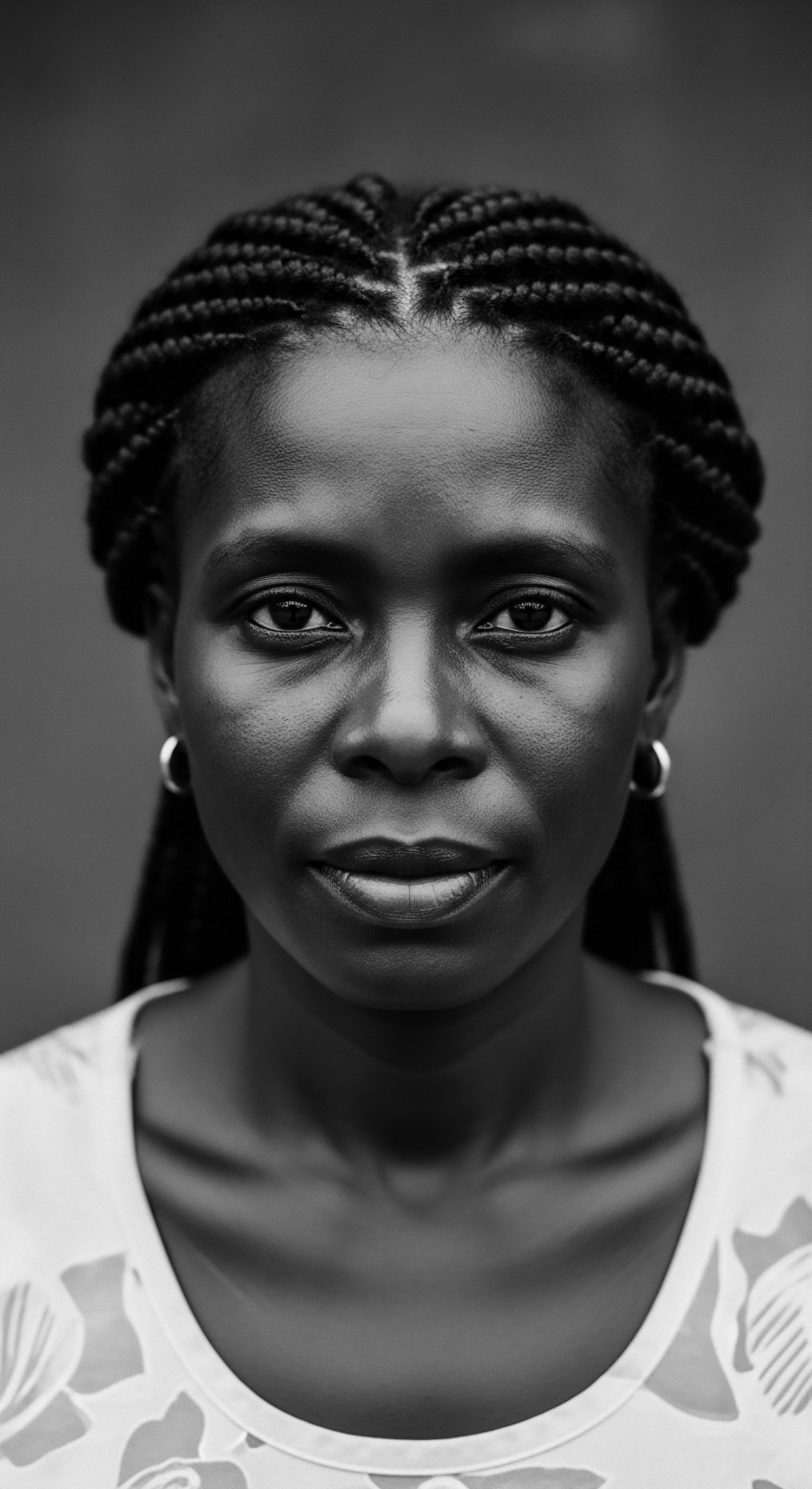

How Does West African Hair Care Embody Heritage?
West African hair care embodies heritage through ancestral practices, communal rituals, and the deep symbolic meaning woven into each strand and style.
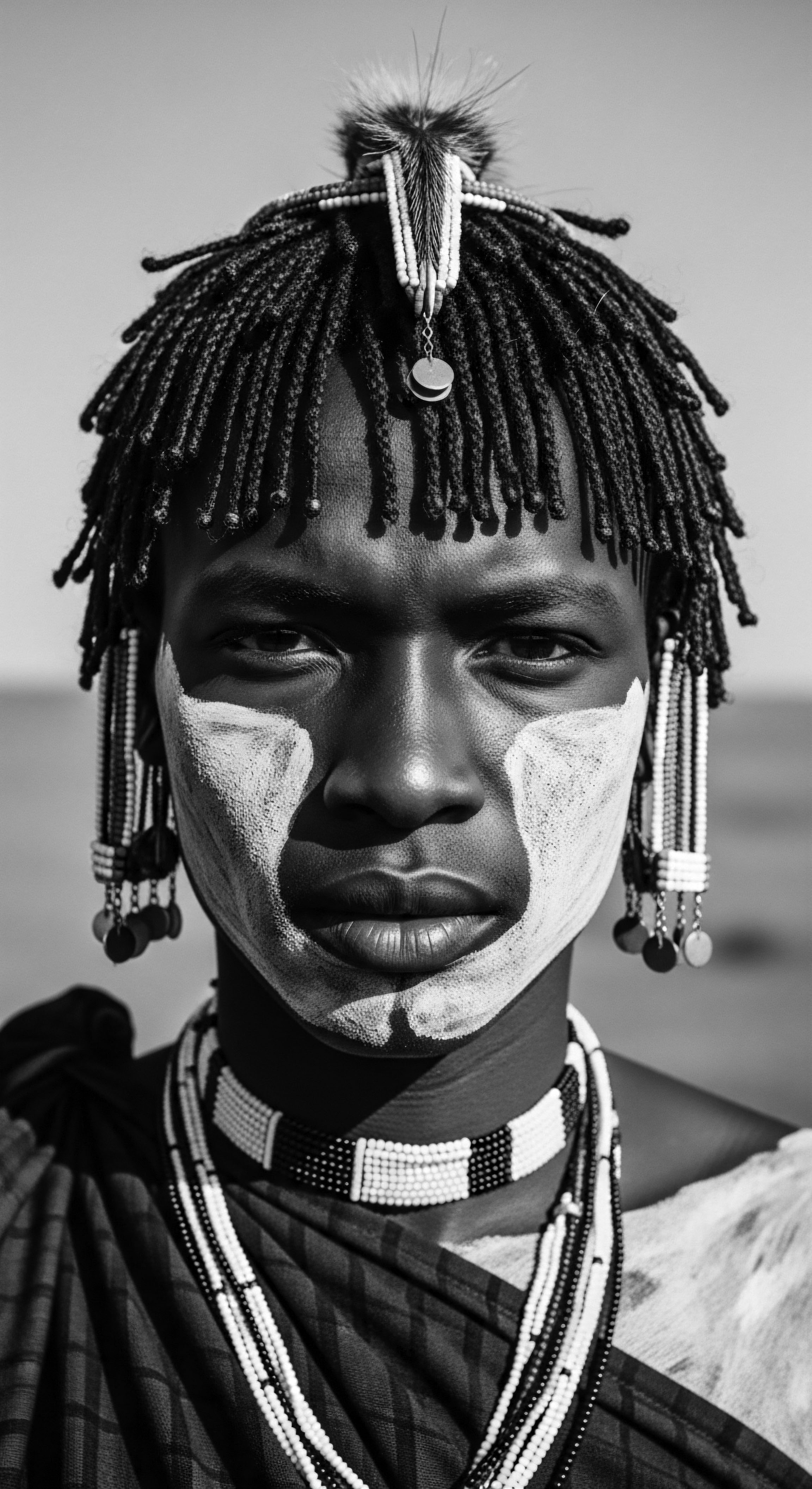

What Is the Cultural Purpose of Braiding in West African Heritage?
Braiding in West African heritage is a profound expression of identity, communication, and resilience, deeply intertwined with textured hair history.

How Did West African Plant Traditions Aid Textured Hair?
West African plant traditions deeply aided textured hair by offering natural emollients and cleansers, securing its heritage through profound cultural care.

