
What Ancestral Wisdom Shapes Head Covering Practices?
Ancestral wisdom shapes head covering practices for textured hair through protection, status, spiritual connection, and cultural resistance, echoing heritage.

What Enduring Legacy Do Hair Appearance Laws Leave on Black Identity?
Hair appearance laws left an enduring legacy of resilience, propelling Black identity and textured hair heritage forward.
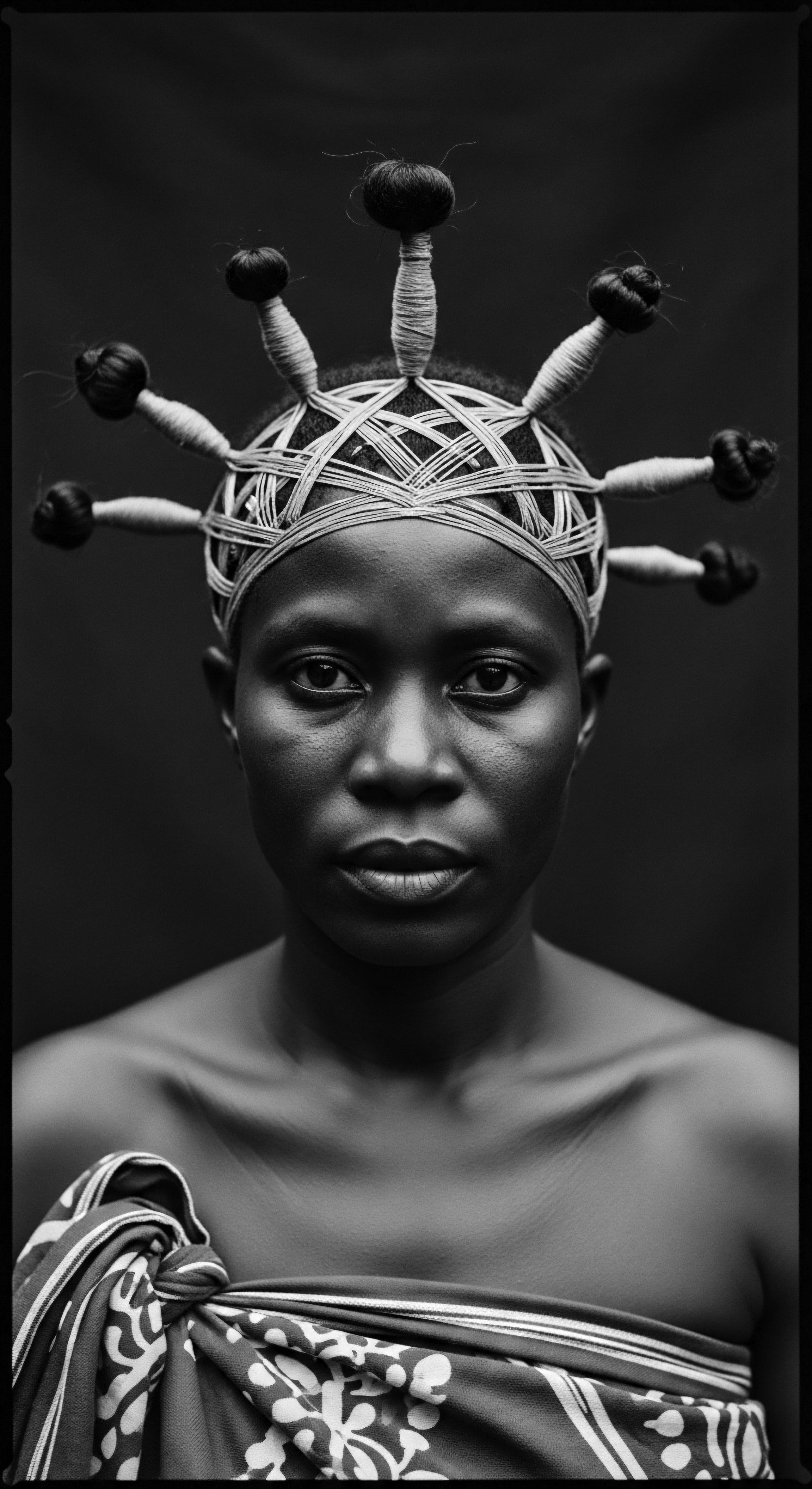

What Modern Laws Protect Textured Hair Heritage from Discrimination?
Modern laws, like the CROWN Act, protect textured hair heritage by prohibiting discrimination based on hair texture and styles.

What Were the Earliest Laws Impacting Black Hair?
Earliest laws affecting Black hair, often born from colonial control, sought to suppress identity, yet fostered resilient cultural adaptations.

Textured Hair Valuing
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Valuing is the profound recognition of the inherent beauty, cultural significance, and historical meaning of coiled hair.
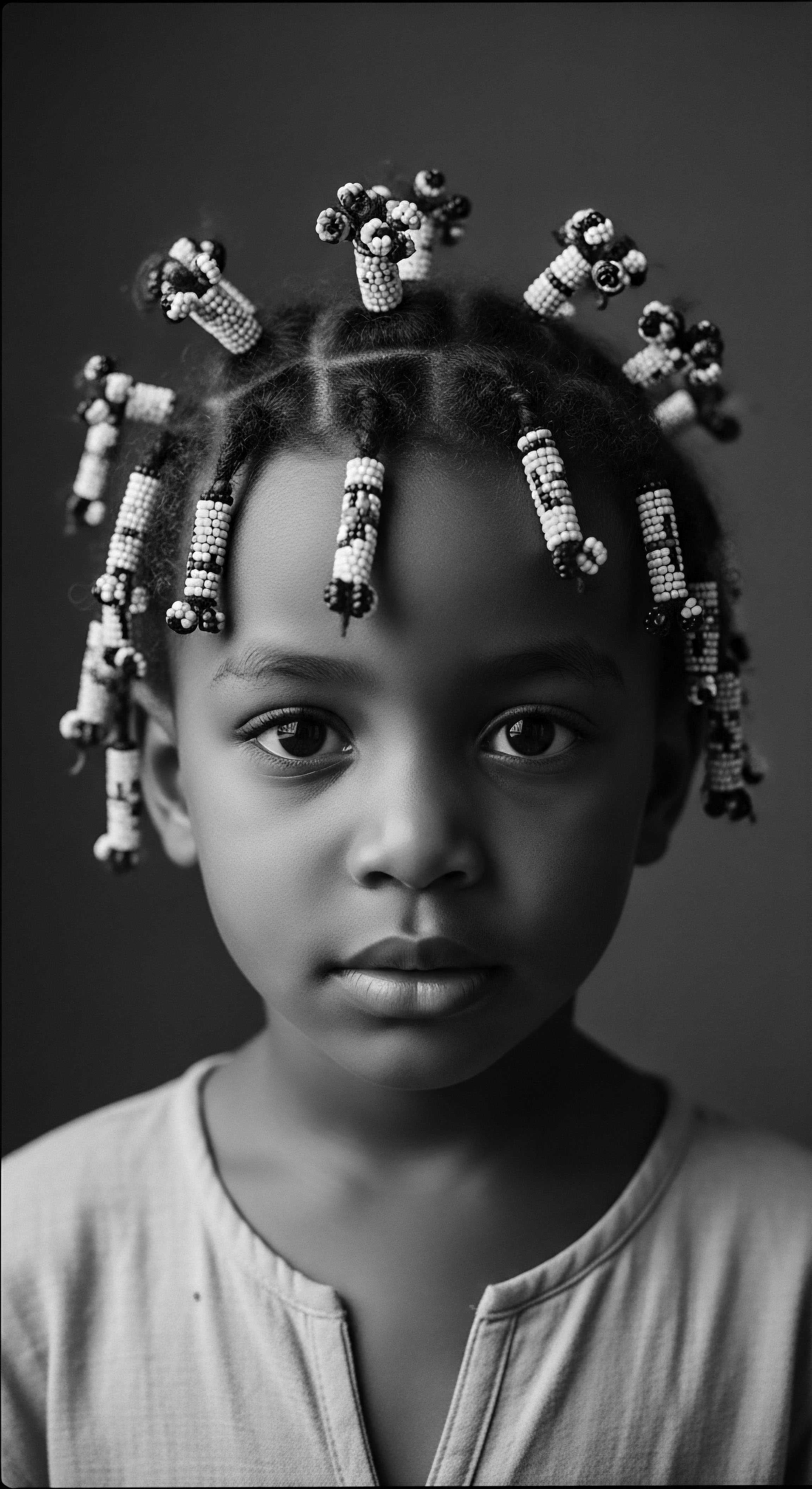

Can Historical Hair Discrimination Inform Current International Law?
Historical hair discrimination, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage, provides crucial insights for strengthening international law to protect cultural identity.

What Historical Laws Suppressed Traditional Black Hair Practices?
Historical laws often suppressed traditional Black hair practices by imposing Eurocentric standards, aiming to strip identity and control cultural expression.
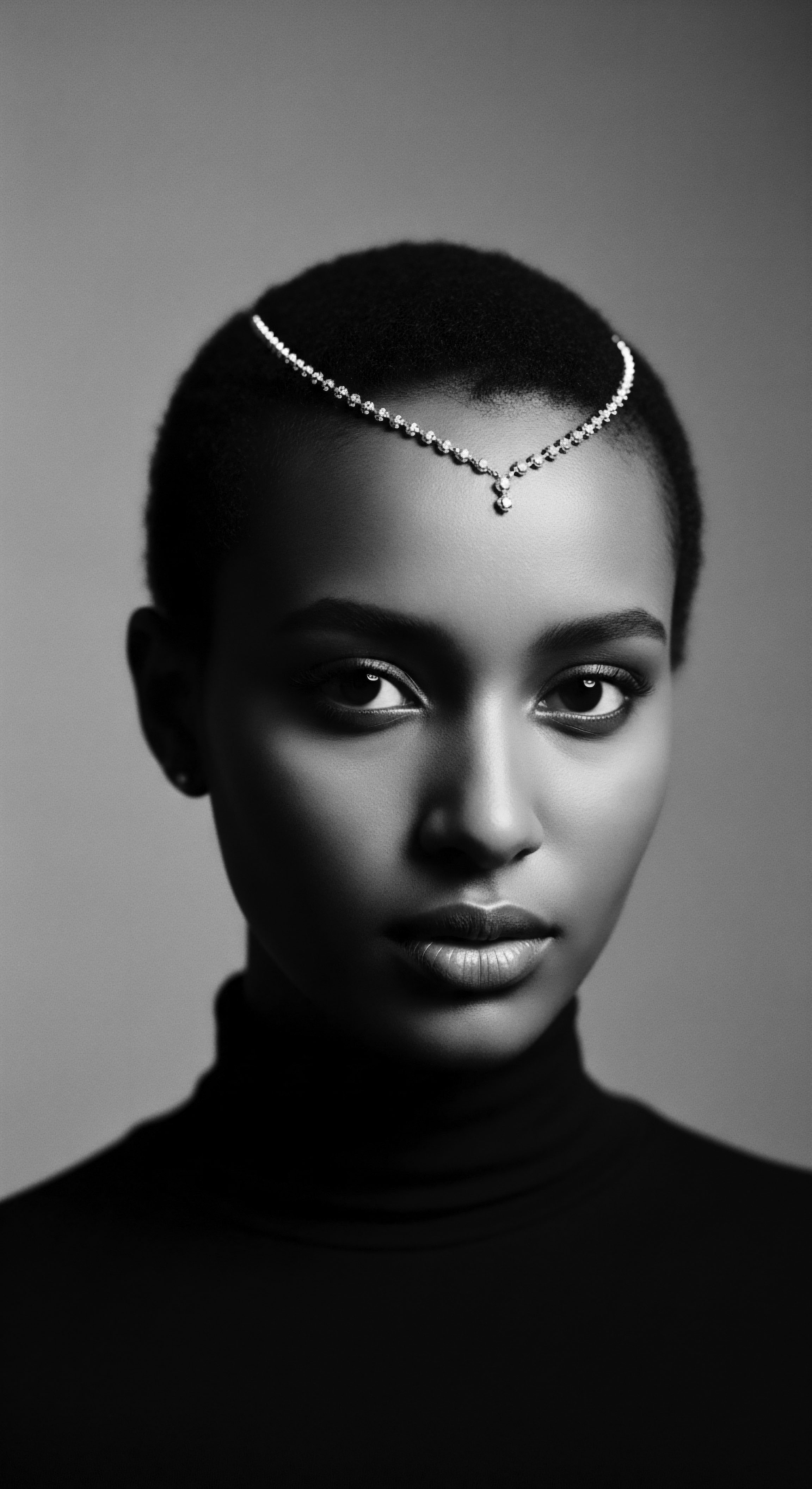

Coerced Identity Definition
Meaning ❉ Coerced Identity Definition is the systemic imposition of external standards upon an individual’s or community’s self-conception, particularly concerning hair.
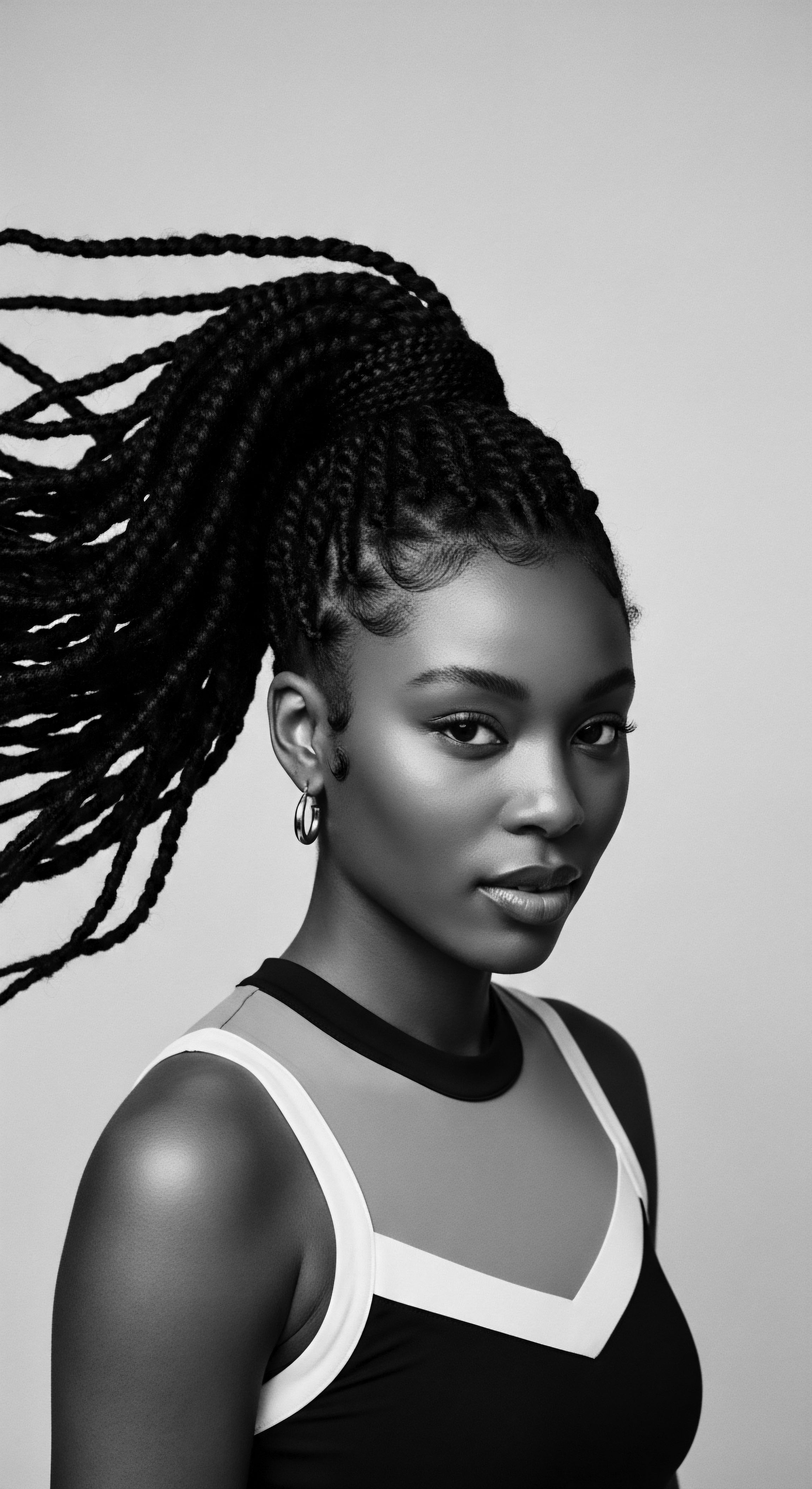

What Was the Specific Aim of the Tignon Laws in Louisiana?
The Tignon Laws aimed to diminish Black women's social standing by forcing them to cover hair, but sparked a powerful heritage of expressive defiance.

How Did Colonial Laws Impact Textured Hair Traditions?
Colonial laws systematically suppressed textured hair traditions, yet communities transformed these impositions into powerful acts of heritage preservation and resistance.

Sumptuary Legislation
Meaning ❉ Sumptuary Legislation refers to laws governing personal expenditure and appearance, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage by controlling identity expression.
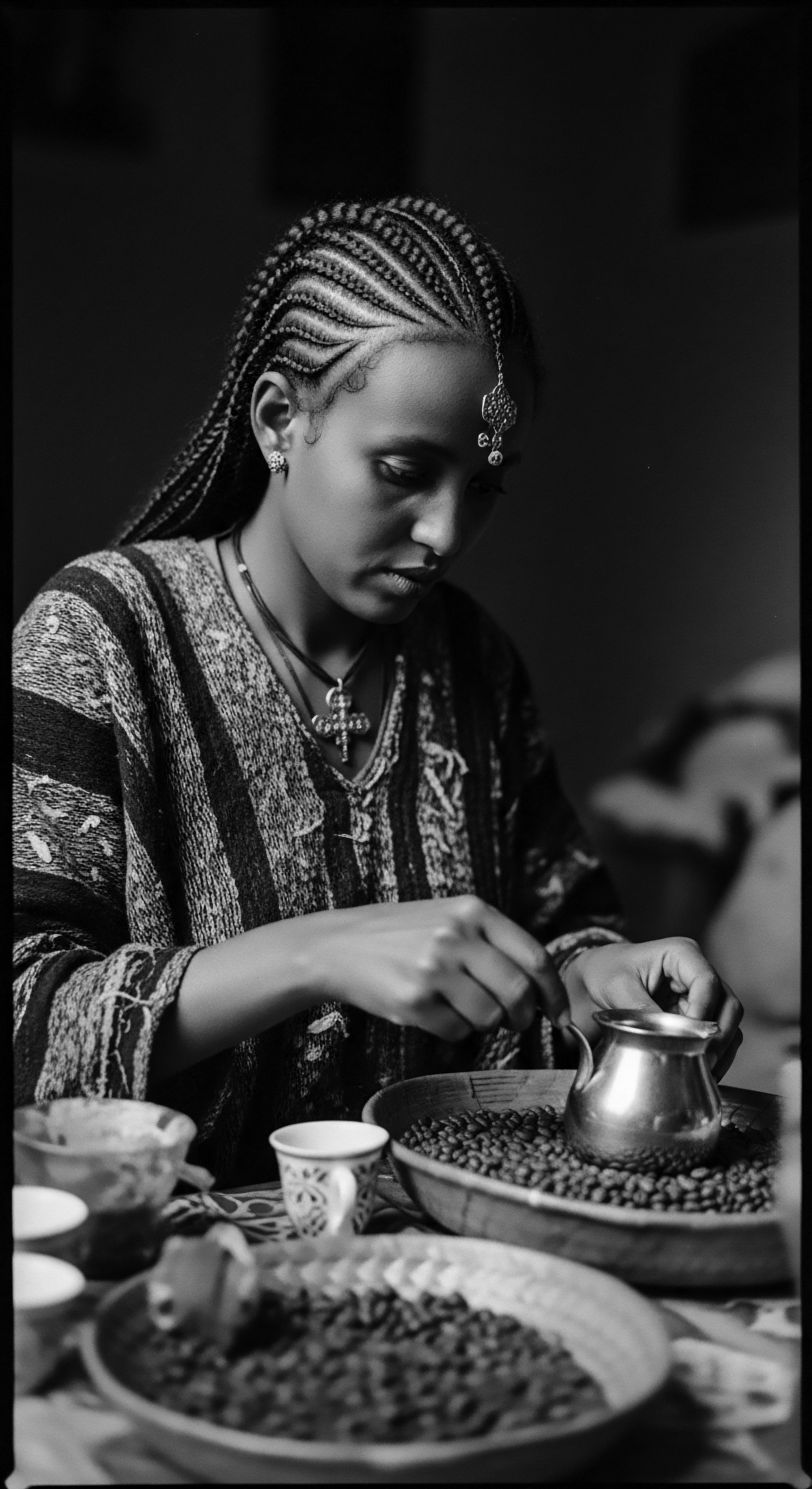

In What Ways Does Historical Legislation Continue to Echo in Contemporary Hair Acceptance?
Historical legislation, by imposing appearance norms rooted in racial bias, continues to shape contemporary hair acceptance for textured hair heritage.

What Specific Historical Laws Targeted Black Hair in the Americas?
Historical laws in the Americas sought to control Black hair, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and identity.

What Ancestral Hair Traditions Did Tignon Laws Target?
The Tignon laws targeted Black women's elaborate hair expressions of identity, status, and heritage, seeking to enforce colonial racial hierarchies.

Psychological Stress
Meaning ❉ Psychological stress is the emotional and physical burden stemming from perceived threats, deeply informed by historical and cultural experiences concerning textured hair.

What Historical Laws Specifically Targeted Black Women’s Hair Expression?
The Tignon Laws were historical mandates compelling Black women to cover their hair, yet they were transformed into symbols of cultural heritage and defiance.

What Historical Laws Targeted Black Hair Heritage?
Historical laws aimed to control Black hair, revealing its deep connection to personal and collective textured hair heritage.

How Did Colonial Perceptions Alter Hair’s Ancestral Meaning?
Colonial perceptions weaponized hair, stripping its ancestral meaning and forcing conformity, yet heritage persists in textured hair.

What Ancestral Hair Practices Endured despite Legal Suppression?
Ancestral textured hair practices endured legal suppression by transforming oppression into profound acts of cultural defiance and identity preservation.

Cultural Concealment
Meaning ❉ Cultural Concealment describes the historical suppression and ingenious reinterpretation of textured hair heritage amidst dominant societal norms.

What Historical Acts of Resistance Are Tied to Black Hair?
Black hair has consistently embodied resistance through its heritage, serving as a powerful symbol of identity, communication, and defiance against oppression.
What Historical Roles Did Hair Play in Black Communities?
Black hair, in its diverse forms, has historically served as a profound symbol of heritage, identity, and resistance for Black communities.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Women Transform Imposed Head Coverings into Symbols of Resistance?
Enslaved women transformed imposed head coverings into defiant statements of identity, cultural heritage, and silent resistance.

What Historical Moments Shaped Black Hair as a Symbol of Defiance?
Black hair's defiance stems from ancestral veneration, cultural preservation under oppression, and its role as a visible symbol of identity and resistance.

How Did Bonnets Aid Hair Protection Historically?
Bonnets historically shielded textured hair from environmental damage, retaining moisture and preserving styles, evolving into a symbol of Black heritage and resilience.

What Historical Laws Attempted to Control Black Hair Expression?
Historical laws attempted to control Black hair expression by forcing conformity, but textured hair heritage consistently found avenues for powerful resistance.

Hair History Resistance
Meaning ❉ Hair History Resistance is the enduring assertion of Black and mixed-race hair heritage and identity against systemic pressures to conform.

What Are the Origins of Hair Discrimination against Textured Hair?
Hair discrimination against textured hair originates in colonial efforts to erase African heritage, reinforced by pseudoscientific racism.

What Historical Head Coverings Influenced Modern Bonnet Use?
Historical head coverings influenced modern bonnets through their protective function and profound cultural heritage in caring for textured hair.

