In What Ways Do Tignon Laws Connect to Modern Textured Hair Movements?
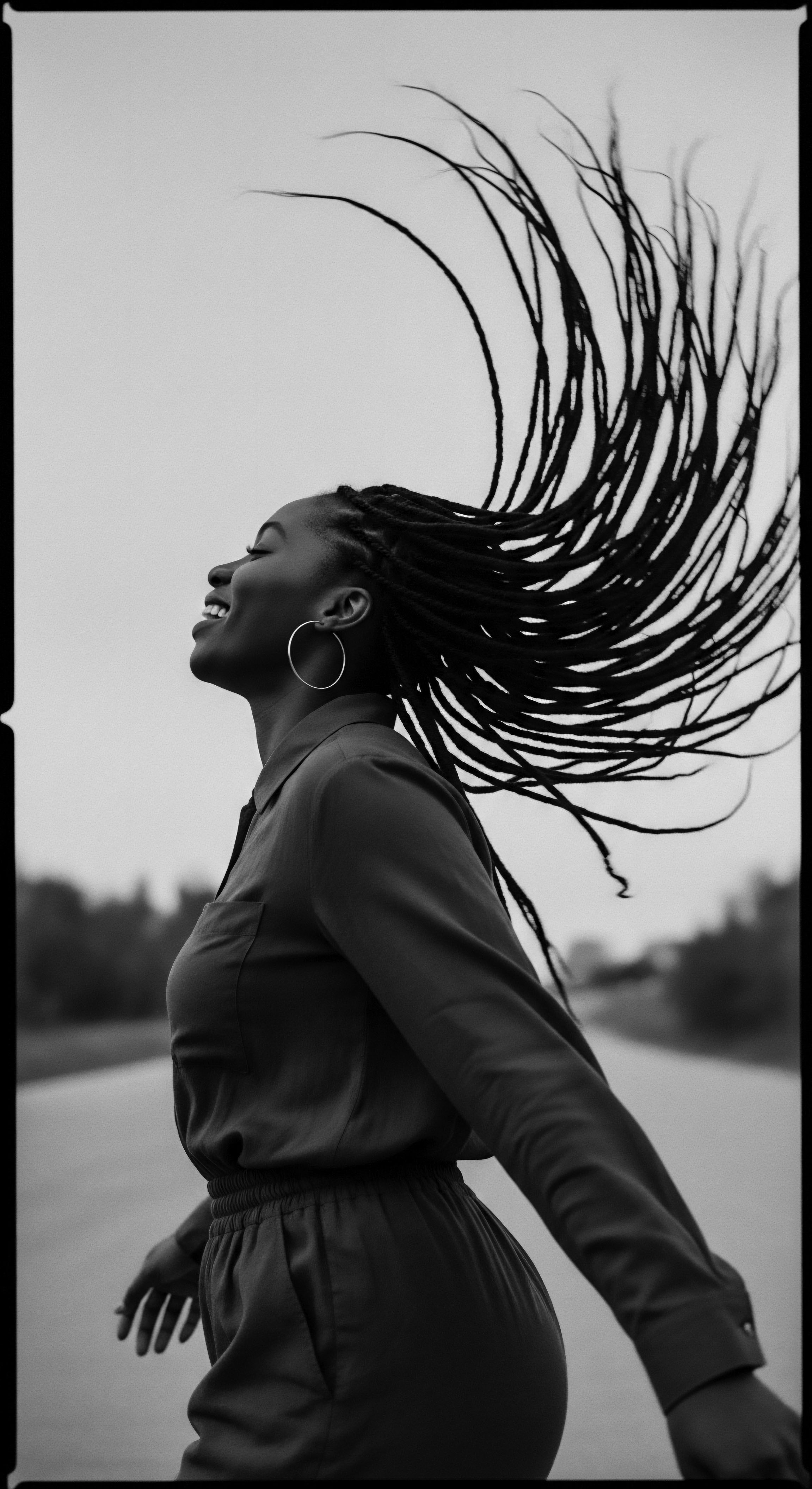
Tignon Laws connect to modern textured hair movements through a shared heritage of resistance against hair policing and the reclamation of identity.

What Enduring Heritage Practices Defied Hair Regulation Laws?
Textured hair heritage practices defied laws through creative adaptation and preservation of ancestral identity.
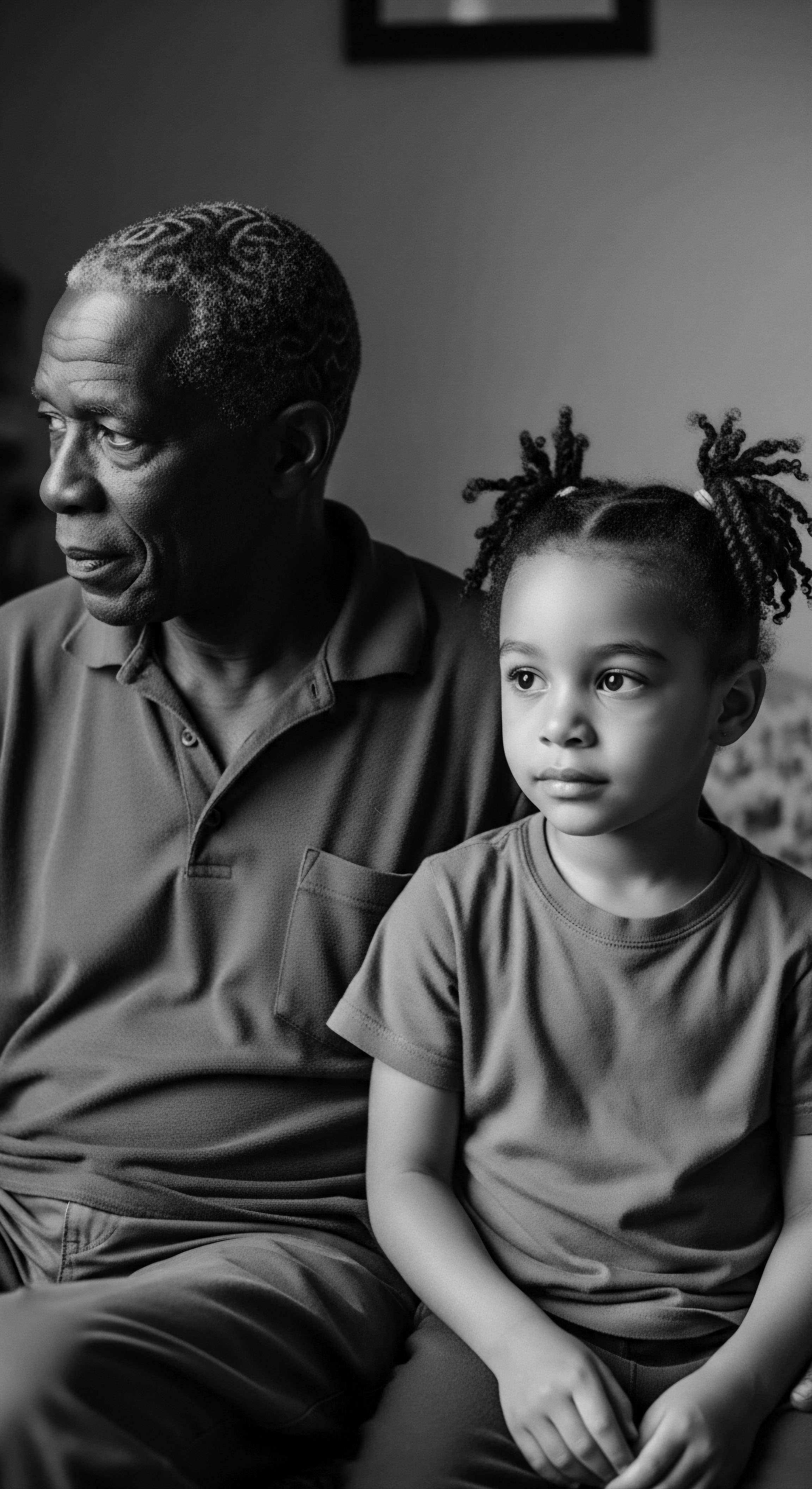

What Is the Biological Reason for Textured Hair’s Moisture Needs?
Textured hair’s unique coiled structure and follicle shape limit natural oil distribution and increase moisture evaporation, a challenge traditionally met with heritage care.

Why Do Head Coverings Hold Cultural Significance for Textured Hair?
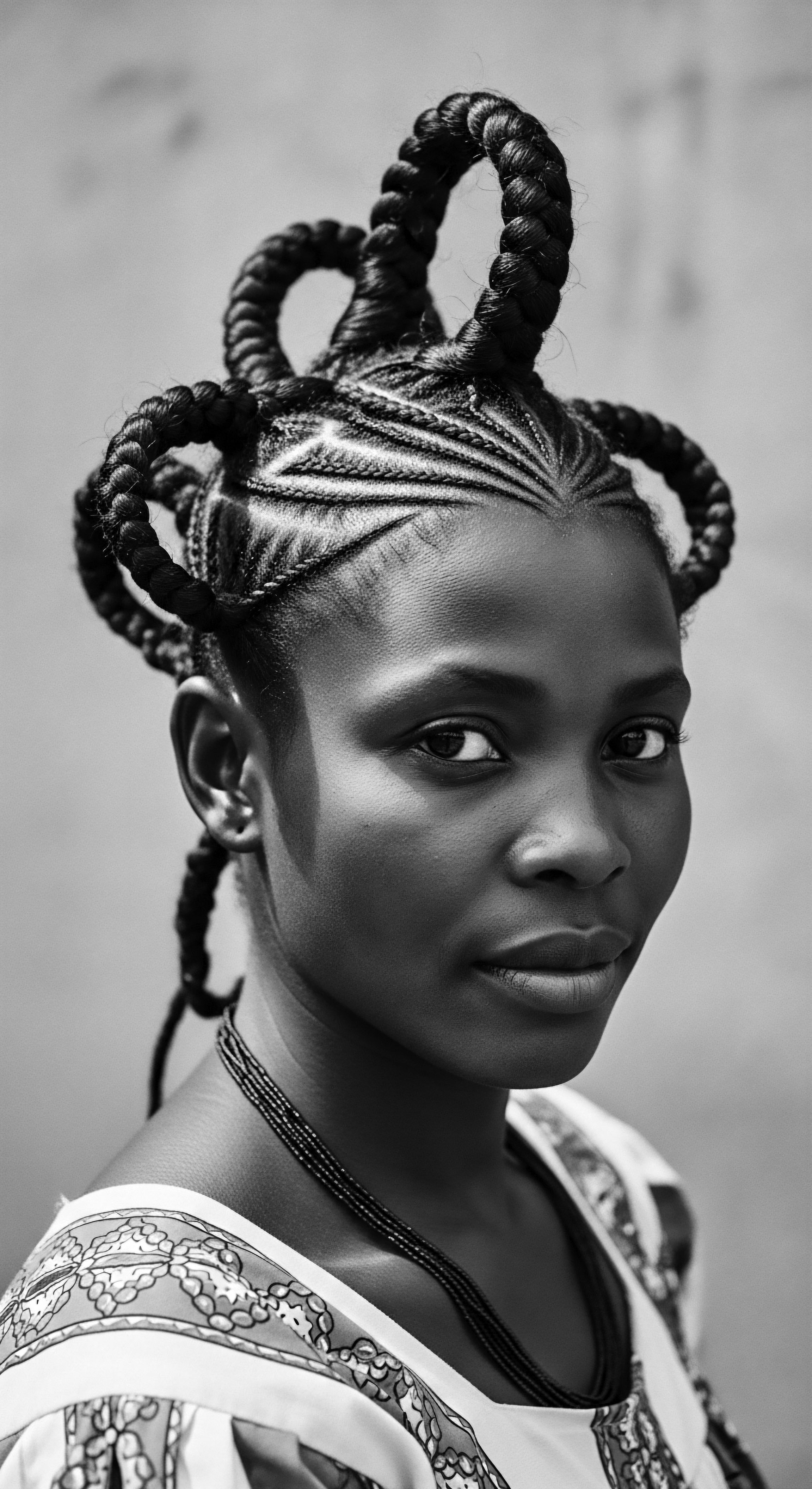
Head coverings protect textured hair and serve as powerful symbols of Black and mixed-race heritage and identity.

What Historical Laws Regulated Textured Hair?
Historical laws often enforced Eurocentric hair norms, attempting to suppress natural textured hair as an act of cultural control and heritage erasure.

Aesthetic Self-Determination
Meaning ❉ Aesthetic Self-Determination is the autonomous declaration of one's visual identity, especially through hair, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and personal agency.

Hair Texture Definition
Meaning ❉ Hair Texture Definition delineates the biological and cultural characteristics of hair, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and identity.

How Did Textured Hair Care Adapt through Historical Challenges?
Textured hair care adapted through history by preserving ancestral wisdom while innovating to survive systemic challenges and assert cultural heritage.

Head Coverings Heritage
Meaning ❉ Head Coverings Heritage signifies the cultural, protective, and expressive traditions of head adornment, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race hair experiences.

Why Do Bonnets Hold Cultural Importance for Textured Hair?
Bonnets hold cultural importance for textured hair by serving as a historical symbol of protection, resistance, and enduring cultural heritage.
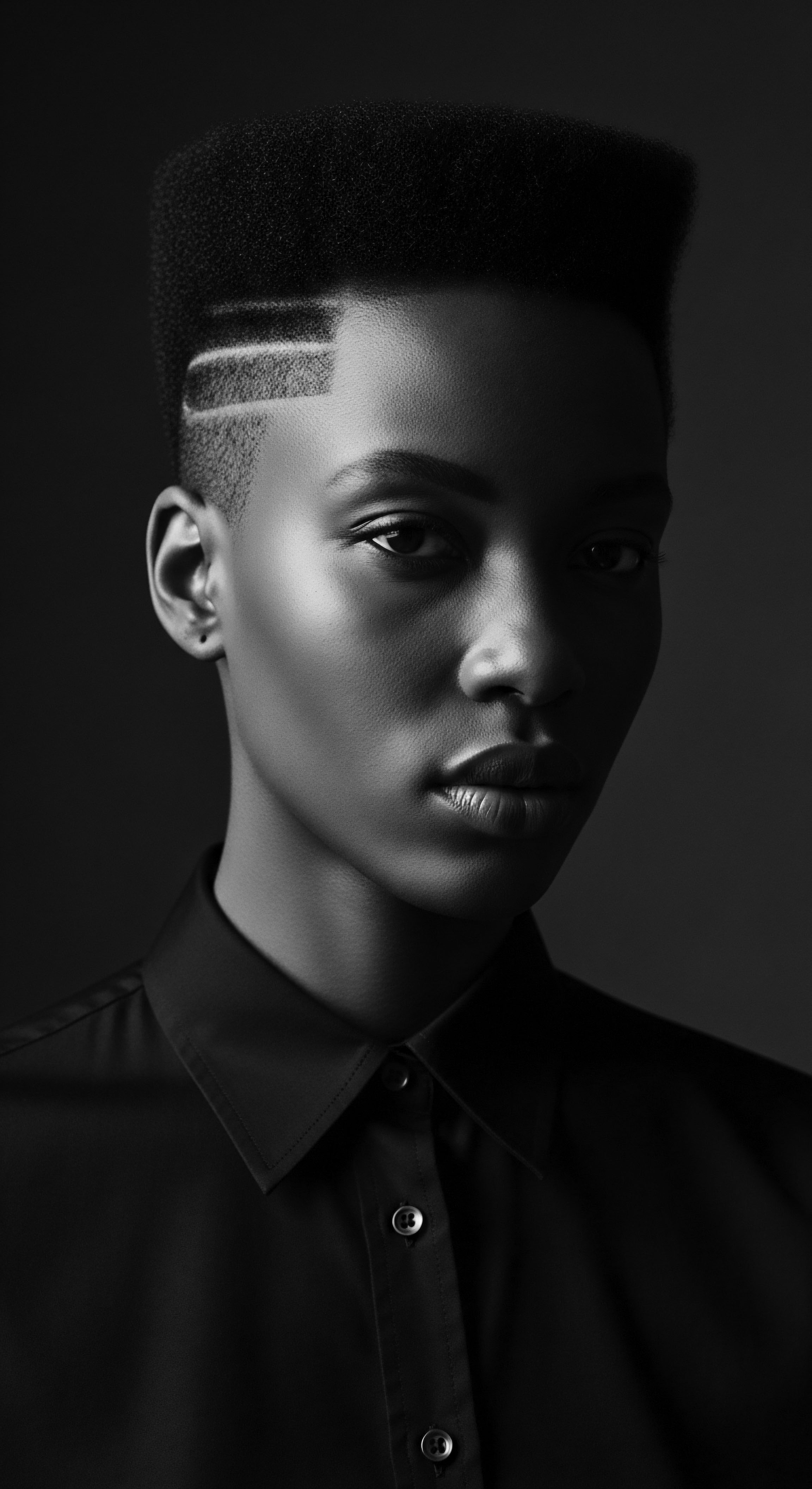

Resistance through Styling
Meaning ❉ Resistance Through Styling defines how hair, through intentional styling, expresses identity and defiance against oppressive norms, rooted deeply in ancestral heritage.

What Are Modern Uses of Headwraps for Textured Hair Care?
Modern headwraps for textured hair care merge ancestral protection with contemporary style, safeguarding strands while celebrating cultural heritage.
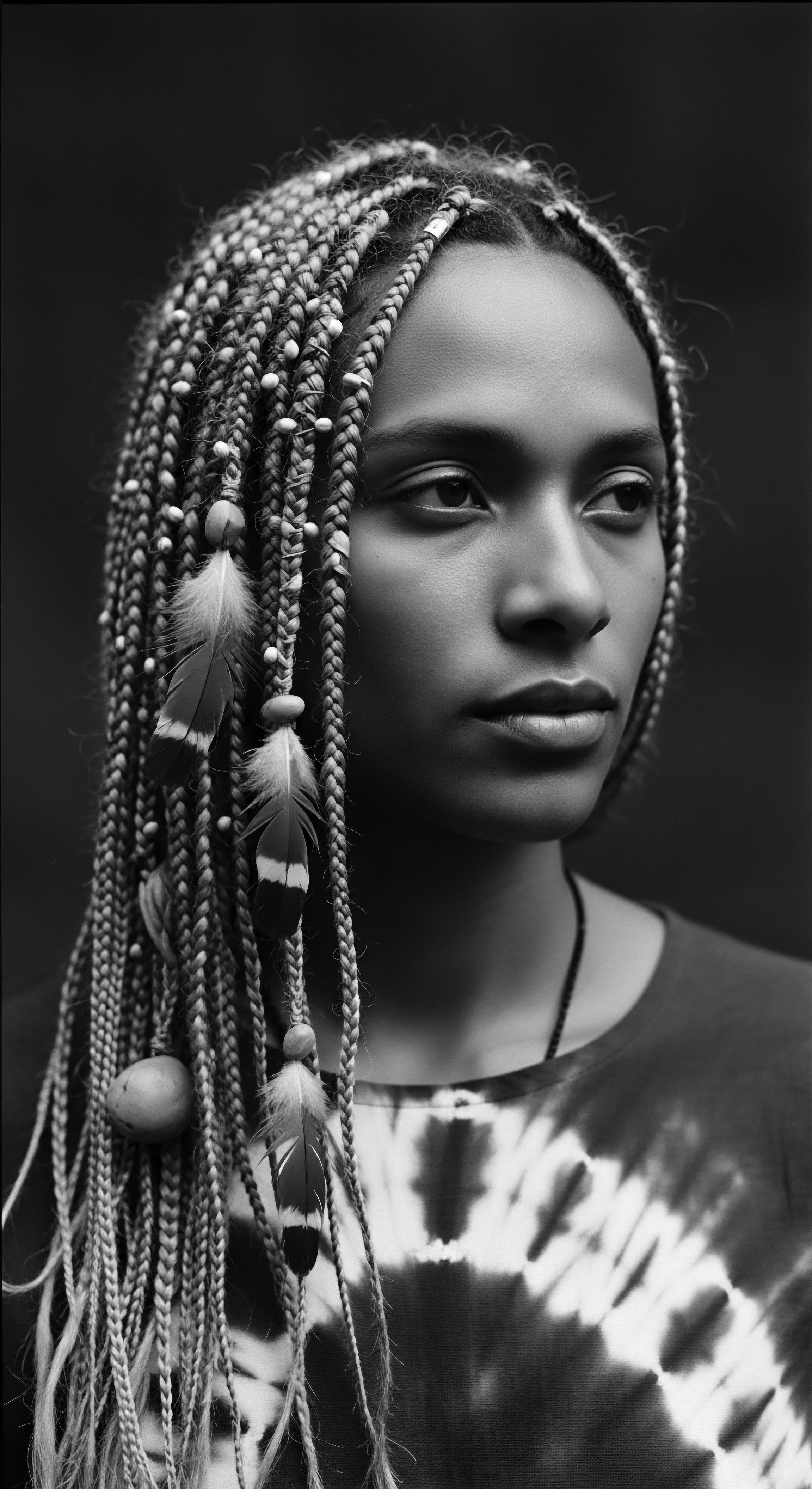

Hair Adornment Culture
Meaning ❉ Hair Adornment Culture encompasses the profound practices of styling and embellishing hair as a conduit for identity, heritage, and communal expression.

Beauty Injustice
Meaning ❉ Beauty Injustice refers to systemic biases that devalue natural hair textures and culturally significant styles, particularly impacting Black and mixed-race communities.

What Cultural Meanings Are Linked to Textured Hair Styles in the Diaspora?
Textured hair styles in the diaspora represent a powerful continuum of heritage, identity, and resistance against cultural erasure.
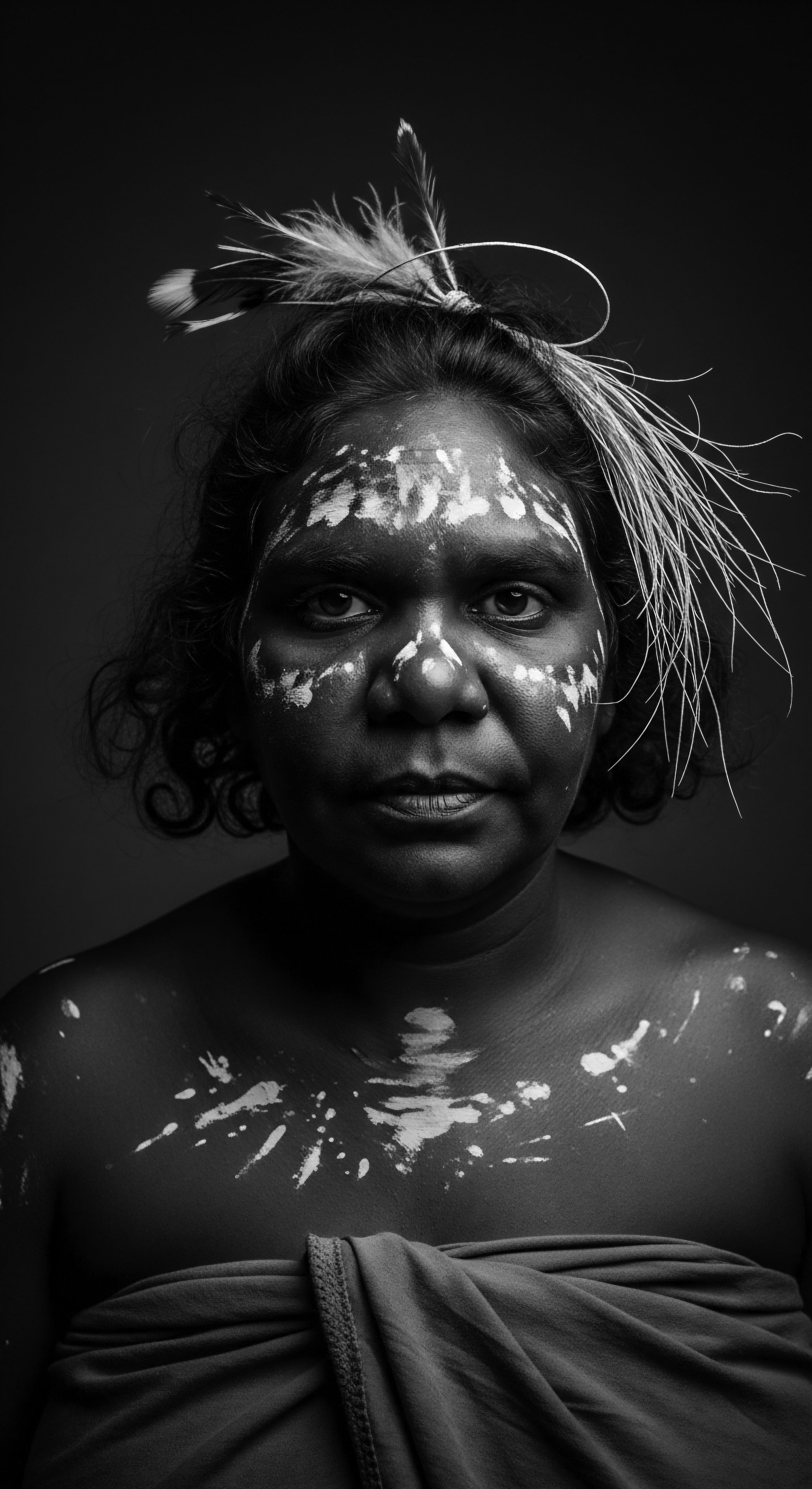

How Did Historical Events Shape Textured Hair Perception?
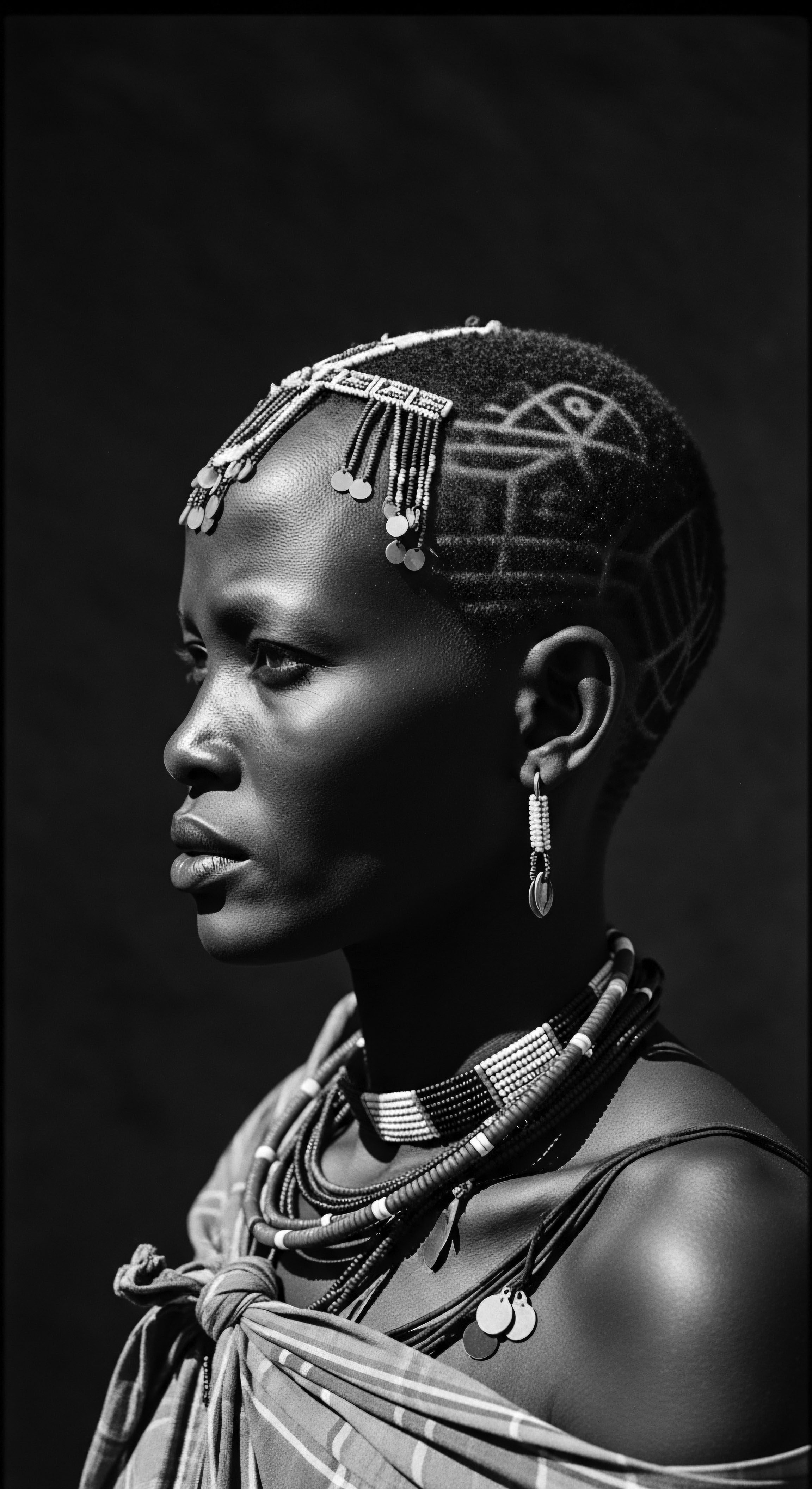
Historical events reshaped textured hair perception from sacred heritage to a marker of subjugation, later reclaimed as powerful identity.

What Are the Historical Roots of Bonnets for Textured Hair?
Bonnets for textured hair carry a heritage of ancestral protection, oppression, resistance, and self-love.

What Historical Role Did Hair Bonnets Play in Preserving Black Hair Heritage?
Hair bonnets preserve Black hair heritage by safeguarding textured strands and symbolizing cultural identity and resilience.
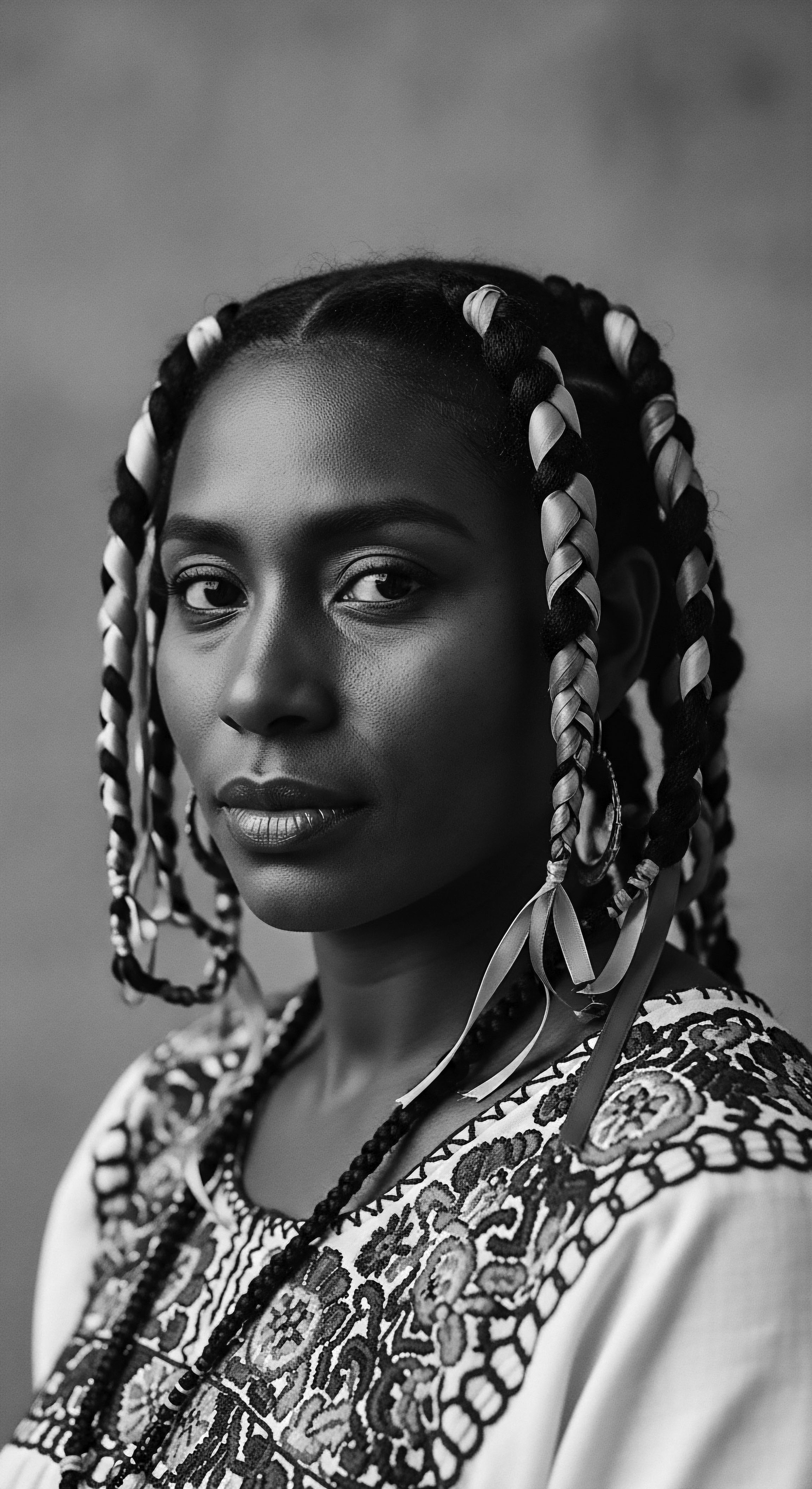

Mixed-Race Hair History
Meaning ❉ Mixed-Race Hair History explores the interwoven legacies of genetic inheritance, cultural practices, and societal perceptions of hair from diverse ancestries.

Indigenous Resistance
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Resistance, through textured hair, embodies the unwavering assertion of identity and cultural preservation against historical and ongoing oppression.
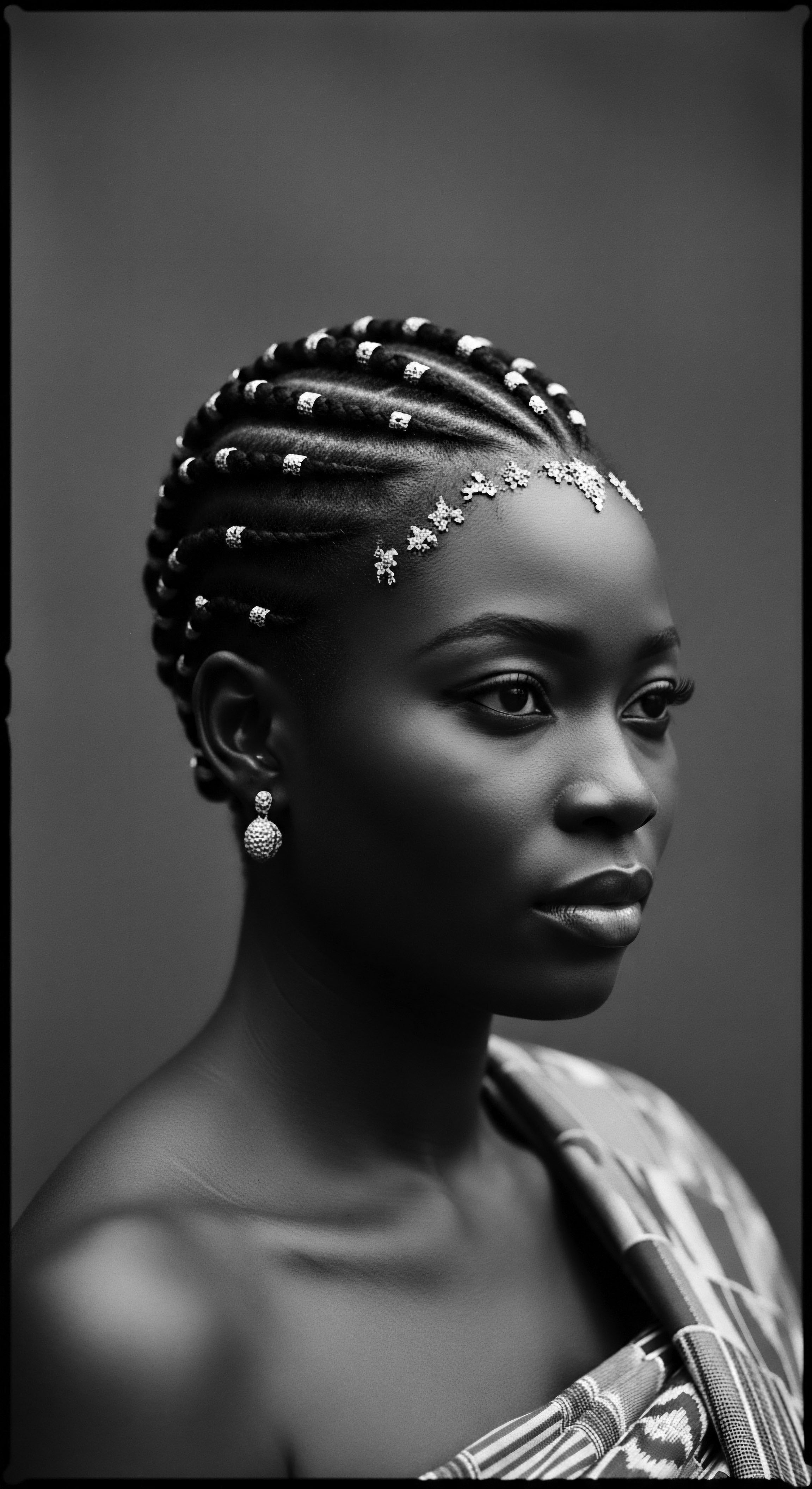

How Did the Tignon Laws Transform Hair as a Symbol of Heritage?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress, instead transformed hair wraps into enduring symbols of cultural defiance and heritage.

What Traditional Hair Care Practices Support Textured Hair Strength?
Traditional hair care practices support strength by deeply moisturizing, protecting, and gently handling textured hair, echoing ancestral heritage.

Anti-Assimilation
Meaning ❉ Anti-Assimilation is a conscious refusal to conform to dominant beauty norms, celebrating inherent textured hair identity and ancestral practices.

What Scientific Principles Explain Bonnets’ Moisture Preservation for Textured Hair?
Bonnets preserve textured hair moisture through reduced friction and creating a stable microclimate, honoring a deep heritage of hair protection.
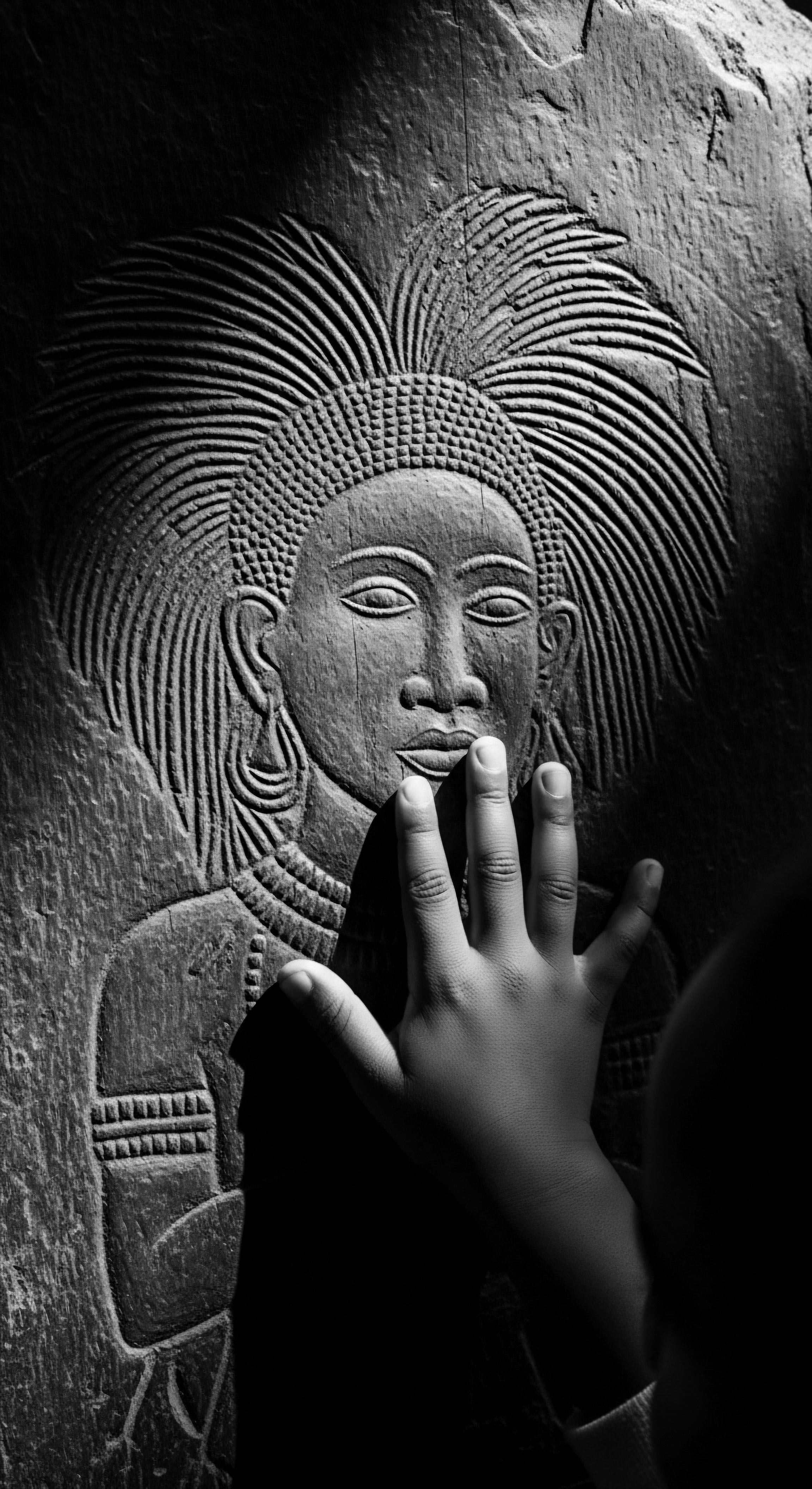

Pelo Malo History
Meaning ❉ Pelo Malo History delves into the colonial roots and enduring impact of devaluing textured hair, revealing a journey of discrimination and cultural reclamation.
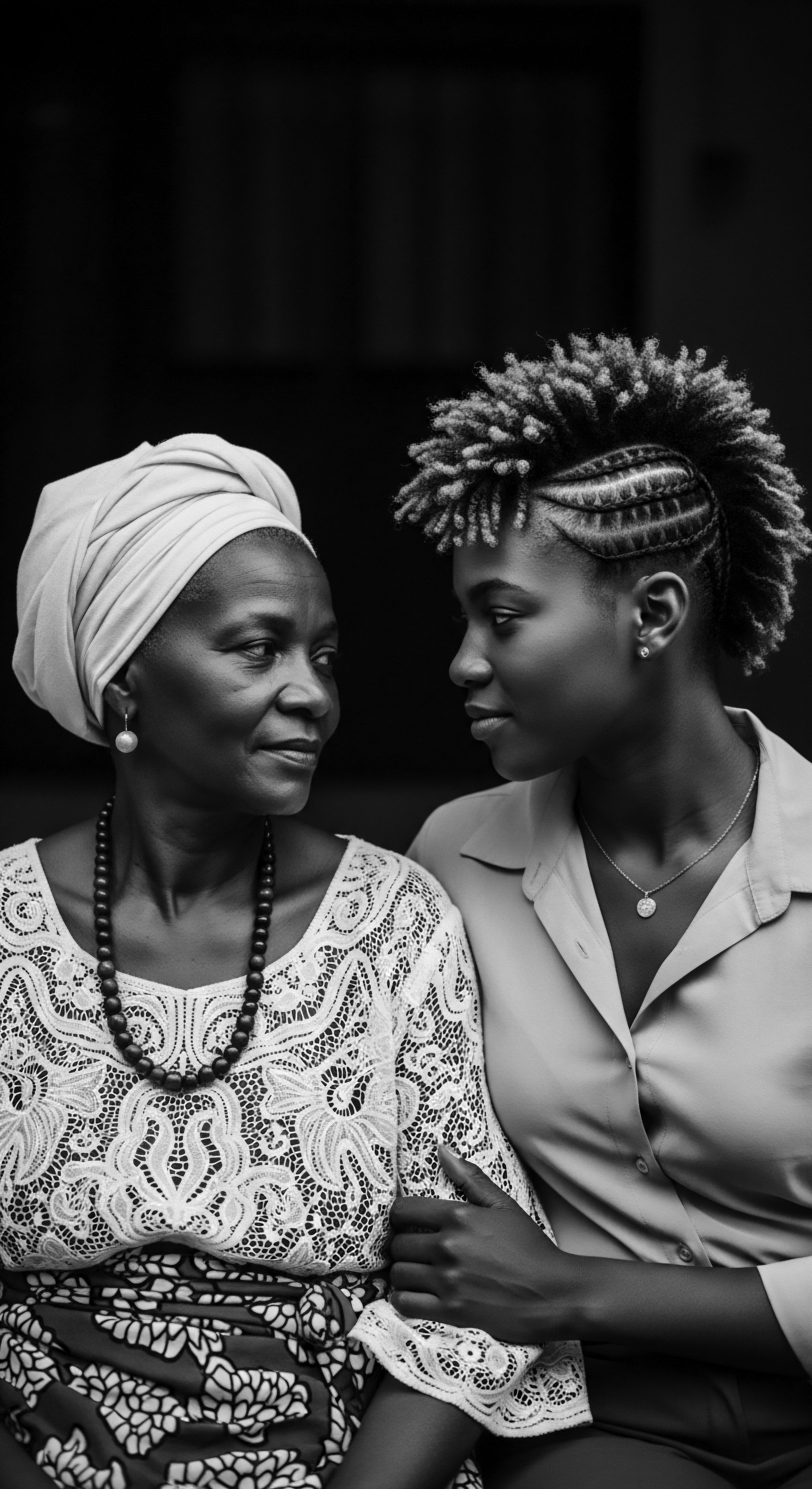
What Ancestral Methods Supported Textured Hair Length through Generations?
Ancestral methods for textured hair length involved protective styles, natural emollients, and intergenerational knowledge transfer.




