Tignon Laws Economic Impact
Meaning ❉ The Tignon Laws Economic Impact describes the coercive redirection of economic activity and suppression of visible Black prosperity through hair regulations.

How Did Tignon Laws Impact Black Women’s Hair Heritage?
Tignon Laws forced free women of color to cover their hair, paradoxically igniting a heritage of defiant self-expression through elaborate headwraps and preserving hidden hair traditions.

What Was the Tignon Law’S Influence on Black Women’s Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Law aimed to suppress Black women's visible identity, yet spurred creative defiance within textured hair heritage.

What Ancestral Rituals Shaped Contemporary Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral rituals shaped textured hair care by establishing holistic practices, spiritual connections, and protective styling rooted in profound cultural heritage.

How Did Tignon Laws Shape Textured Hair Identity?
The Tignon Laws aimed to subjugate Black women by forcing head coverings, yet they sparked creative resistance, affirming textured hair identity and heritage.

How Did Black Women’s Responses to Tignon Laws Influence Future Hair Expression Heritage?
Black women transformed oppressive tignon mandates into statements of beauty, shaping a powerful heritage of hair as identity and resistance.
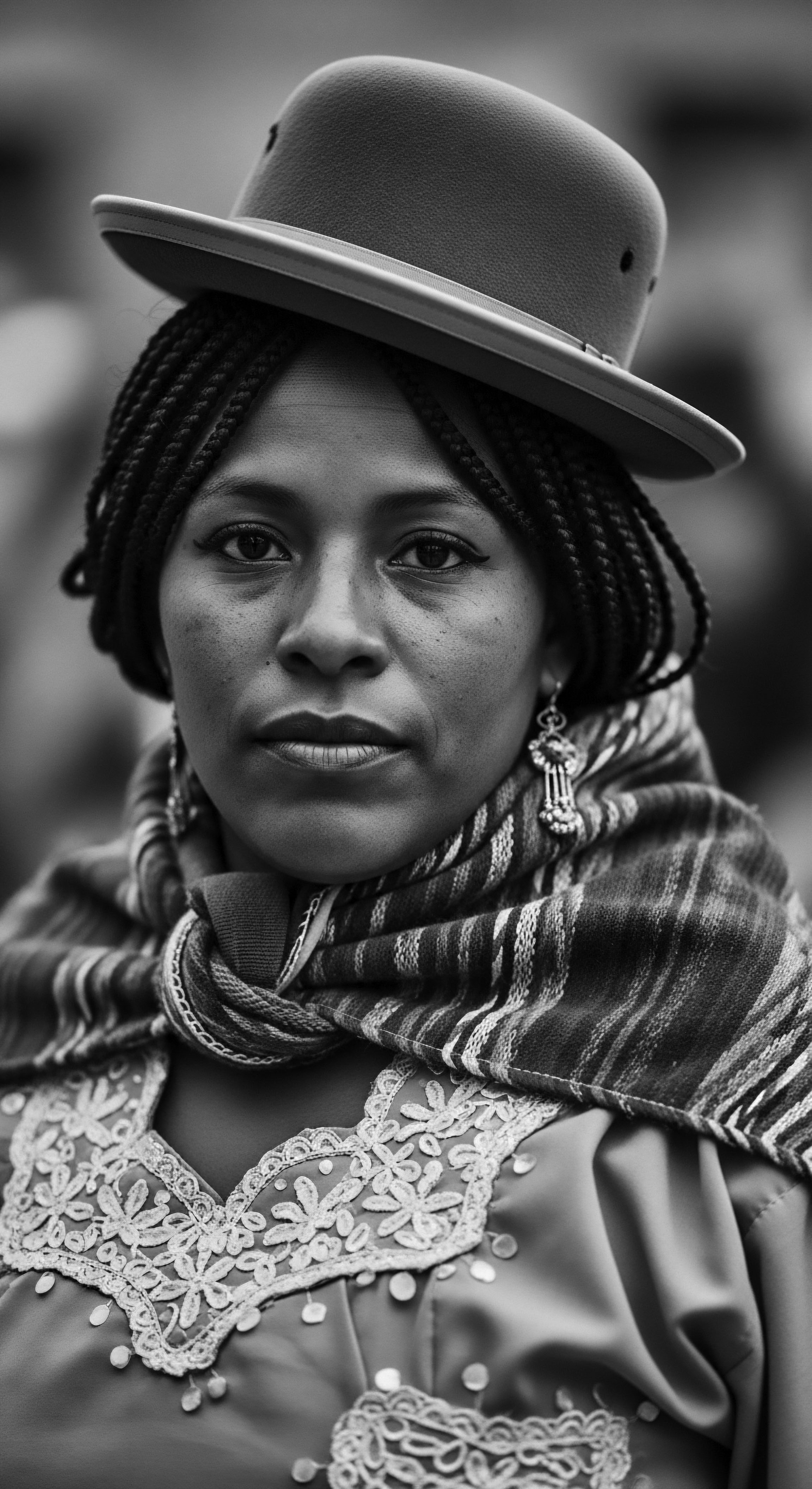

How Did Black Women Defy the Tignon Law and Preserve Hair Heritage?
Black women transformed headwraps into defiant statements of style, secretly maintaining intricate ancestral hairstyles beneath, preserving their textured hair heritage.
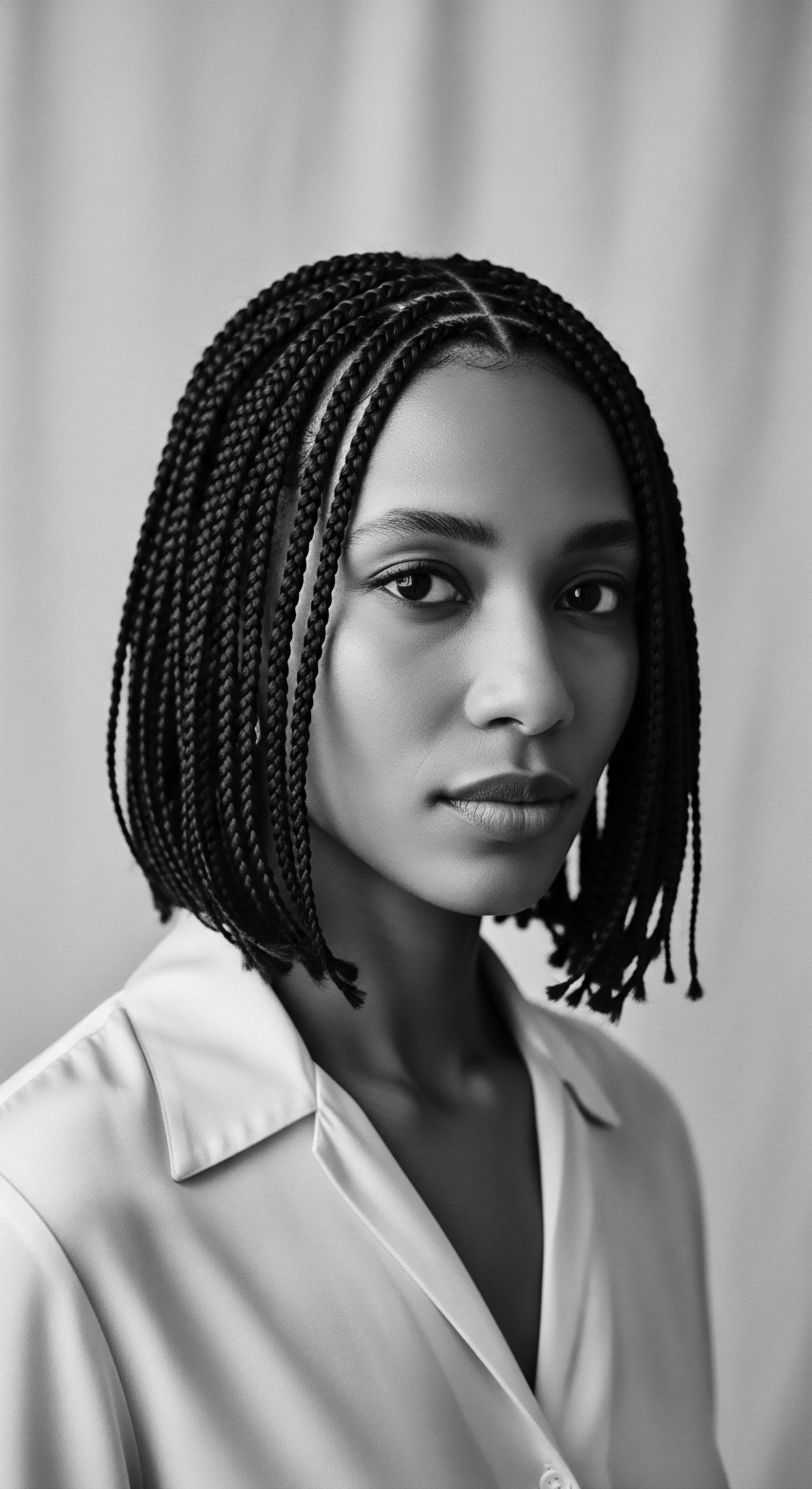

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Hair Expression?
The Tignon Laws compelled free women of color to cover their hair, paradoxically sparking innovative expressions of textured hair heritage through defiant headwraps.

What Enduring Impact Did the Tignon Law Have on Black Hair Heritage Today?
The Tignon Law, aimed at suppressing Black women's beauty, ignited a legacy of creative defiance in textured hair heritage.

What Was the Tignon Law’s Impact on Black Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Law forced free women of color to cover their hair, but they transformed this mandate into a powerful statement of cultural pride and defiance.

How Did Tignon Laws Shape Textured Hair?
Tignon Laws forced free women of color to cover their hair, inadvertently strengthening textured hair heritage through defiant artistry.

How Did Tignon Laws Reshape Heritage?
Tignon Laws sought to diminish free Black women's public presence, but they transformed mandated head coverings into symbols of cultural heritage.

How Did Tignon Laws Shape Heritage Expression?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress Black women's hair as heritage, unexpectedly spurred vibrant self-expression through headwraps, redefining cultural pride.

What Were Tignon Laws?
Tignon Laws mandated free women of color in 1786 Louisiana cover their hair, an act of colonial control met with resilient textured hair heritage.

How Did the Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Hair Practices and Cultural Expression?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress Black women's visible identity, became a powerful catalyst for textured hair heritage.

What Historical Impact Did Tignon Laws Have on Textured Hair?
The Tignon laws, meant to oppress, ignited a powerful heritage of creative defiance through adorned headwraps, asserting cultural identity.

Tignon Act
Meaning ❉ The Tignon Act was a 1786 colonial Louisiana decree mandating head coverings for free women of color, an attempt to suppress their visible identity and cultural hair expressions.

What Are the Enduring Legacies of Tignon Laws on Modern Perception of Textured Hair?
The Tignon Laws, intended to control appearance, inadvertently solidified the heritage of self-expression in textured hair culture.

What Enduring Impact Did the Tignon Laws Have on Textured Hair Identity and Care?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress Black women's hair identity, instead sparked a powerful heritage of creative defiance through headwraps.

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Black Hair Care Heritage?
The Tignon Laws, meant to suppress, instead galvanized Black women’s ingenuity, deeply shaping textured hair heritage through defiant style and enduring care practices.

How Did the Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Hair Practices and Heritage?
Tignon Laws spurred Black women to transform forced head coverings into expressions of vibrant cultural heritage and defiance.

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Textured Hair Heritage?
Tignon Laws mandated head coverings for Black women, but they transformed them into ornate displays of enduring cultural heritage and resistance.

What Enduring Heritage Did Tignon Laws Create for Black Hair Care?
Tignon Laws inadvertently strengthened Black hair heritage by sparking creative resistance and elevating cultural identity through headwraps.

What Ancestral Practices Influenced Textured Hair Resilience against Tignon Laws?
Ancestral practices like intricate styling and head wrapping became acts of defiance, transforming mandated coverings into powerful symbols of cultural identity and resilience.

What Ancestral Rituals Sustained Textured Hair Growth?
Ancestral rituals sustained textured hair growth through holistic care, communal practices, and reverence for natural elements, deeply linking hair to identity and heritage.
What Is the Cultural Meaning of Bonnets for Textured Hair?
The bonnet culturally signifies textured hair heritage, rooted in protection and resilience against historical oppression.

How Does the Legacy of Tignon Laws Impact Textured Hair Care Today?
Tignon Laws, an 18th-century decree, compelled Black women to cover hair, inadvertently fueling a heritage of hair artistry and resistance still seen today.

What Enduring Heritage Did Tignon Laws Create for Black Hair?
Tignon Laws inadvertently catalyzed defiant creative expression, cementing headwraps as a powerful symbol within textured hair heritage.

How Did Tignon Laws Target Black Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Laws targeted Black hair heritage by forcing concealment, aiming to dismantle social standing and identity, but women defiantly transformed headwraps into symbols of cultural pride.

