What Is the Cultural Significance of Textured Hair Rituals Historically?
Textured hair rituals historically signify a deep cultural legacy, embodying identity, resilience, and ancestral wisdom through styling and care.

What Historical Significance Do Traditional Oils Hold for Textured Hair Sun Defense?
Traditional oils historically protected textured hair from sun, rooted in ancestral knowledge and resilience across diverse cultures.
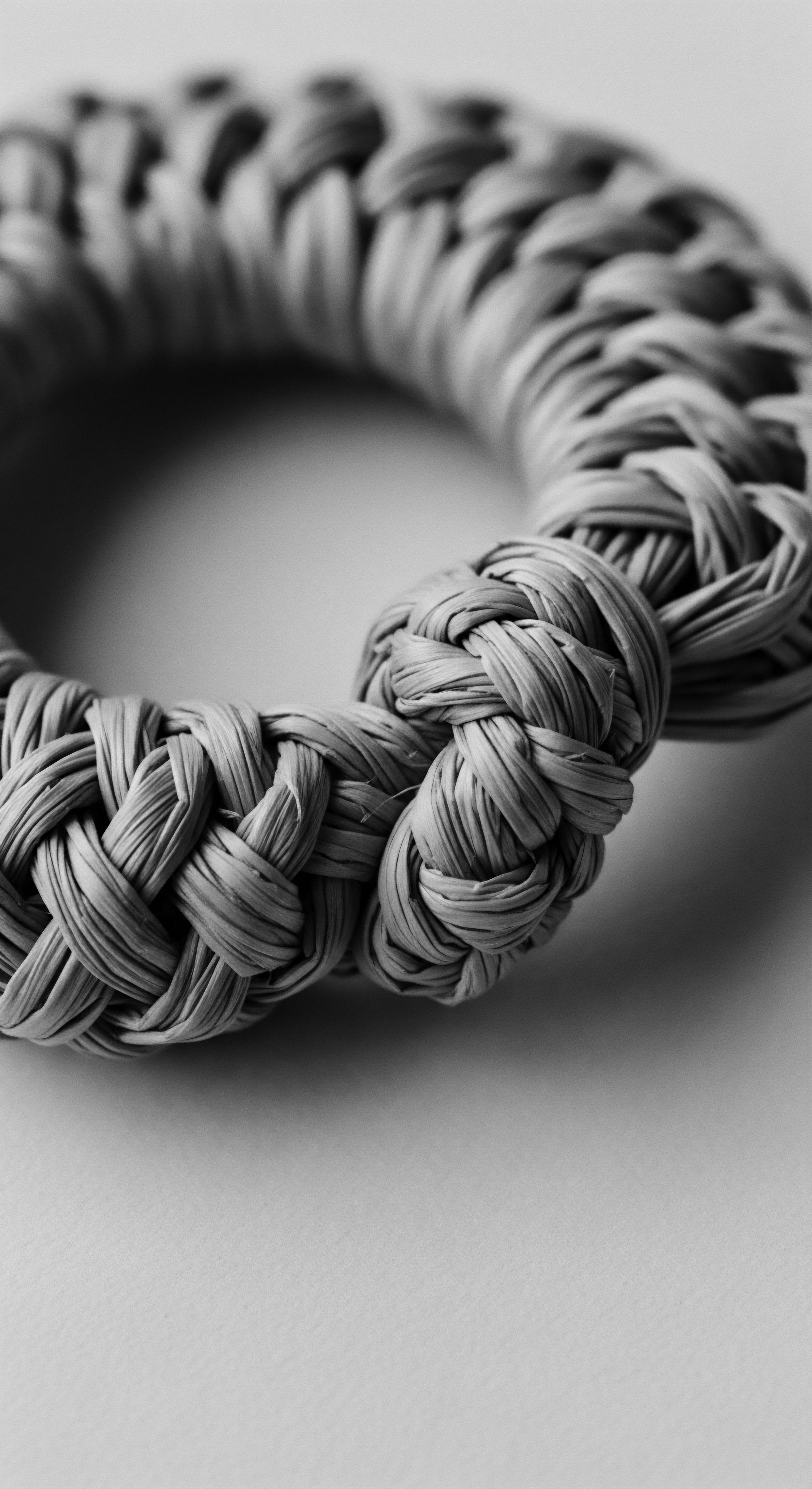

Do Ancient Combs Truly Protect Textured Hair?
Ancient combs, made from natural materials and designed with wider teeth, genuinely protected textured hair by reducing friction and honoring its heritage.

How Does Historical Hair Care Connect to Modern Textured Hair Science?
Historical hair care practices, rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer insights into modern textured hair science, preserving heritage.

What Scientific Insights Support Traditional Hair Oiling for Textured Strands?
Traditional hair oiling supports textured strands by providing ancestral protection and moisture, validated by modern science.

How Did Ancient Oils Shape Heritage Hair?
Ancient oils deeply influenced heritage hair by providing nourishment, protection, and cultural significance, shaping ancestral care practices.

In What Ways Do Kemetian Hair Practices Connect to Modern Textured Hair Heritage?
Kemetian hair practices connect to modern textured hair heritage through shared principles of protective styling, natural ingredient use, and hair's profound role in identity.

In What Ways Did Clay Symbolize Heritage for Textured Hair in Ancient Societies?
Clay symbolized heritage for textured hair in ancient societies through practical care, spiritual connection, and cultural identity markers, echoing ancestral wisdom.

Can Ancient Hair Care Methods Still Help Textured Hair Today?
Ancient methods offer a direct path to textured hair health, deeply rooted in ancestral knowledge and cultural heritage.

Why Do Historical Oiling Practices Reduce Breakage in Textured Hair?
Historical oiling provided ancestral textured hair with essential moisture, lubrication, and protein protection, stemming breakage and preserving heritage.

How Does Cultural Heritage Influence Hair Practices Globally?
Cultural heritage profoundly influences hair practices globally, particularly textured hair, revealing ancestral wisdom and identity.

What Cultural Meanings Did Heritage Hair Hold?
Heritage hair conveys identity, status, and spirituality, serving as a powerful cultural archive for textured hair.

How Does the Heritage of Shea Butter Inform Its Benefits for Textured Hair?
Shea butter’s heritage for textured hair stems from centuries of traditional West African use, informing its deep moisturizing and protective qualities.

Why Is Textured Hair Often More Porous than Straight Hair?
Textured hair’s helical structure creates natural cuticle lift, leading to greater porosity, a characteristic long understood and managed by ancestral care practices.

How Did Ancestral Practices of Moisture Retention Shape Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral practices of moisture retention, deeply rooted in heritage, shaped modern textured hair care by emphasizing natural ingredients and protective techniques.

Do Natural Oils Truly Absorb Damaging UV Radiation for Textured Hair?
Natural oils offer minimal direct UV absorption, but ancestral practices used them to coat, moisturize, and strengthen textured hair for resilience against environmental damage.

How Does African Oil Heritage Impact Hair Health?
African oil heritage nourishes textured hair, drawing from centuries of ancestral wisdom for health and cultural vitality.

Why Do Textured Hair Types Require Specific Care Routines?
Textured hair requires specific care due to its unique structure, prone to dryness and breakage, and its rich heritage shaped by ancestral wisdom.

Why Is Natural Hair Important for Black Identity and Heritage?
Natural hair is a powerful expression of Black identity, inextricably linked to ancestral traditions and enduring cultural heritage.

How Has Shea Butter Shaped Textured Hair Care?
Shea butter has shaped textured hair care by serving as an ancient, culturally significant moisturizer, protector, and styling aid, deeply rooted in African heritage.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Serve as a Tool of Resistance Historically?
Textured hair historically served as a profound tool of resistance by preserving Black and mixed-race heritage and identity against oppression.

What Role Did the Natural Hair Movement Play in Heritage Reclamation?
The natural hair movement significantly reclaimed textured hair heritage by celebrating ancestral beauty, validating traditional care, and affirming cultural identity.

What Is the Historical Link between Textured Hair and Human Rights?
Textured hair’s historical link to human rights lies in its enduring role as a central marker of identity, cultural resilience, and freedom from racial discrimination.

How Do Ancestral Amazonian Practices Guide Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancestral Amazonian practices offer a heritage-rich guide to textured hair, emphasizing plant-based care and holistic well-being.

What Resistance Movements Connect to Textured Hair Heritage?
Textured hair heritage connects to resistance through acts of cultural preservation, identity affirmation, and legal challenges against discrimination.

How Does Traditional Amazonian Hair Care Relate to Textured Hair Heritage?
Traditional Amazonian hair care mirrors textured hair needs, offering natural solutions deeply connected to ancestral heritage.

How Did Ancient Egyptian Hairstyles Influence Modern Textured Hair?
Ancient Egyptian hairstyles provided a foundation for modern textured hair heritage through techniques, tools, and the deep cultural meaning given to hair.

How Does Shea Butter Nurture Textured Hair?
Shea butter deeply nurtures textured hair by echoing ancestral practices of moisture preservation and scalp health, aligning heritage with biochemistry.

How Does Chebe Support Length Retention for Textured Hair?
Chebe supports length retention by coating and fortifying hair strands, thereby reducing breakage, a practice rooted in Chadian ancestral heritage.

