
How Did Ancient Communities Care for Textured Hair Length?
Ancient communities cared for textured hair length through natural ingredients, protective styles, and communal rituals deeply rooted in heritage.

What Are the Historical Benefits of Clay for Textured Hair?
Ancestral communities utilized mineral-rich clays to gently cleanse, detoxify, and strengthen textured hair, preserving its natural vitality.

What Ancestral Oils Were Significant for Textured Hair Traditions?
Ancestral oils, like shea, castor, coconut, and olive, formed the historical backbone of textured hair care traditions.

Why Are Bonnets Historically Significant for Textured Hair Heritage?
Bonnets are historically significant for textured hair heritage as protective tools, symbols of resistance, and carriers of ancestral care wisdom.

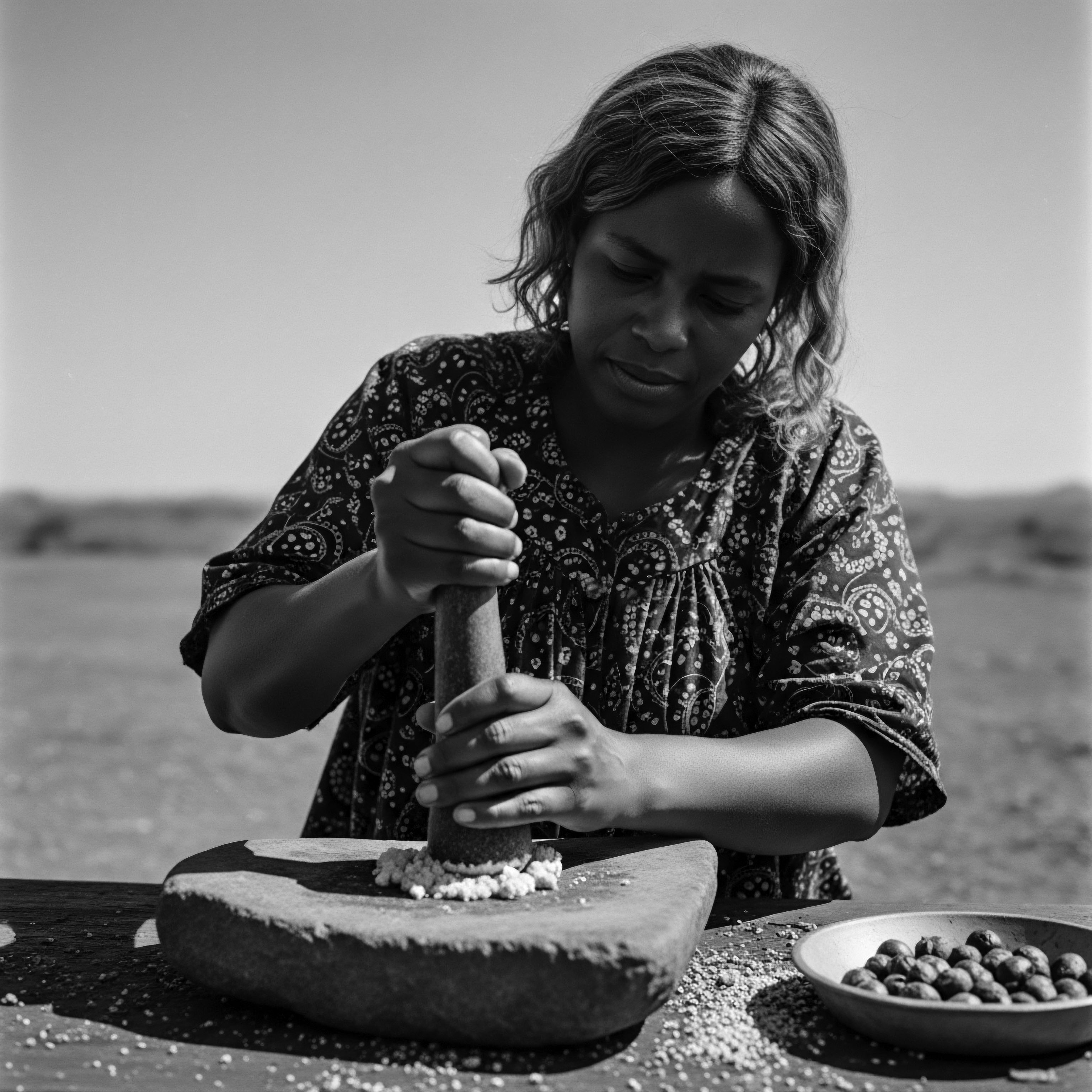
Which Natural Ingredients Historically Moisturized Textured Hair?
Historically, textured hair was moisturized using natural plant-derived butters and oils, reflecting deep ancestral knowledge of its unique needs and inherent heritage.

Llullaillaco Maiden
Meaning ❉ The Llullaillaco Maiden is a preserved Inca girl whose hair reveals ancient ritual practices and connections to deep cultural heritage.

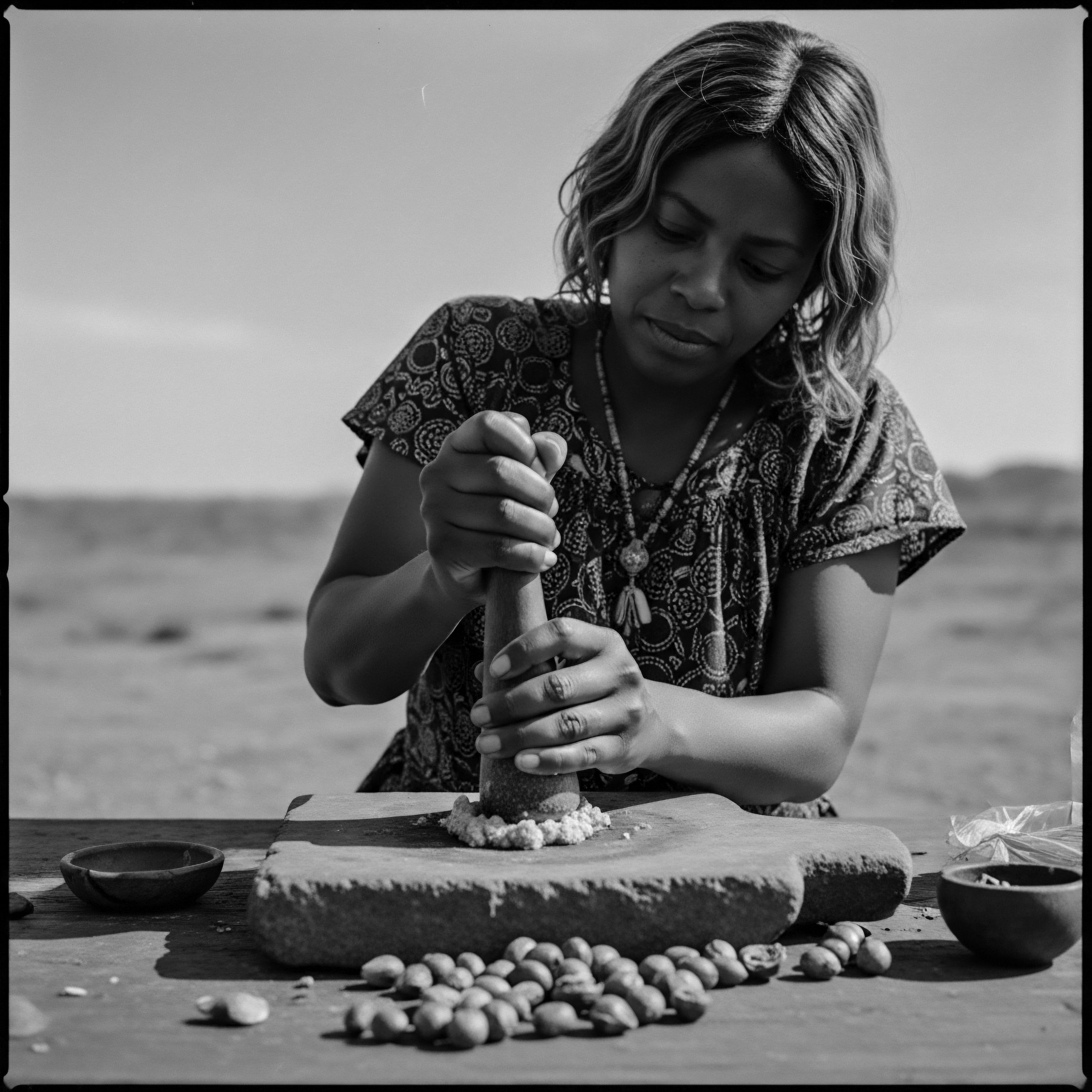
Which Clays Fortify Textured Hair?
Clays fortify textured hair by cleansing, delivering vital minerals, balancing the scalp, and enhancing natural curl patterns, a legacy from ancestral practices.

How Did Early Colonial Laws Impact Textured Hair Heritage?
Early colonial laws sought to suppress textured hair heritage, yet sparked powerful acts of cultural resistance and identity reclamation.

Coral Gardens Atrocities
Meaning ❉ The Coral Gardens Atrocities denote the brutal 1963 state-sanctioned violence against Rastafarians in Jamaica, highlighting systemic hair discrimination.

Indigenous Hair Technology
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Hair Technology is the ancestral knowledge, practices, and tools for caring for and expressing identity through textured hair.

What Ancestral Plant Ingredients Benefited Textured Hair?
Ancestral plant ingredients like shea butter, aloe vera, and hibiscus provided nourishment and protection for textured hair, reflecting a deep cultural heritage.

Curl Fiber Dynamics
Meaning ❉ Curl Fiber Dynamics describes the inherent biological and structural properties of textured hair strands, influencing their behavior and cultural significance.

What Ancestral Hair Care Practices Used Coconut Oil for Textured Hair?
Ancestral textured hair care leveraged coconut oil for its profound ability to nourish, protect, and connect to heritage.

Cultural Hair Liberation
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Liberation signifies the profound reclamation of autonomy and pride in textured hair, rooted in ancestral knowledge and defying historical oppression.

How Did Ancestors Protect Textured Hair?
Ancestors protected textured hair through protective styles, natural ingredients, and culturally significant rituals, preserving hair health and heritage.

In What Ways Do Tignon Laws Connect to Modern Textured Hair Movements?
Tignon Laws connect to modern textured hair movements through a shared heritage of resistance against hair policing and the reclamation of identity.

Coiled Hair Thermoregulation
Meaning ❉ Coiled Hair Thermoregulation is the unique biological function of spiraled hair textures in regulating scalp temperature for human adaptation.

Traditional Hair Aromas
Meaning ❉ Traditional Hair Aromas are the culturally significant scents from natural ingredients historically used in textured hair care, embodying ancestral knowledge and identity.

Societal Hair Pressure
Meaning ❉ Societal Hair Pressure is the external expectations and norms that dictate hair appearance, profoundly impacting self-perception and cultural identity, especially for textured hair.

What Scientific Reasons Explain Plant Oils’ Historical Use for Textured Hair?
Plant oils have historically provided essential moisture and protection for textured hair, rooted in ancestral knowledge of its unique needs.
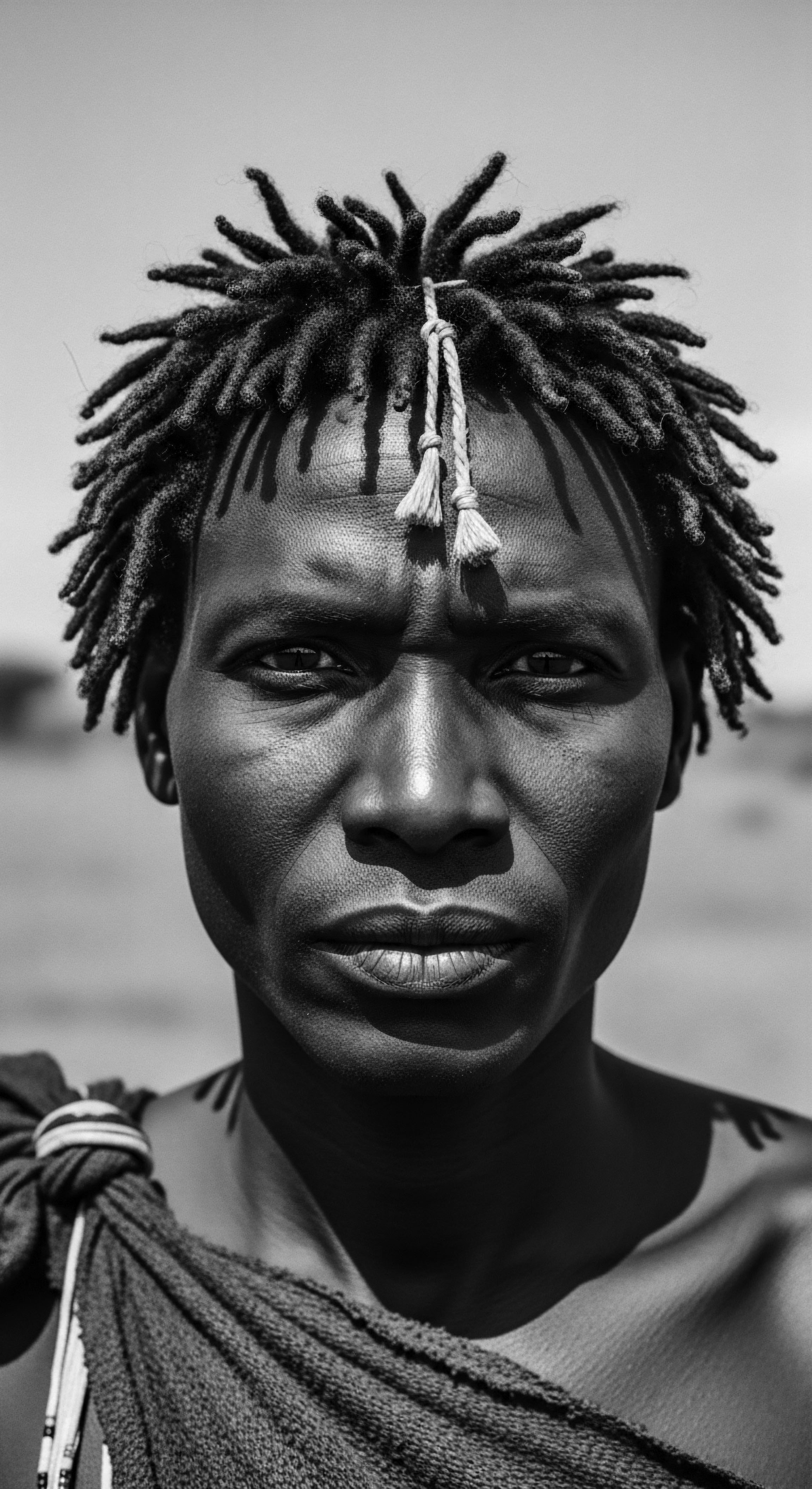

Divine Beauty Hair
Meaning ❉ Divine Beauty Hair is the inherent, sacred value and resilience of textured hair, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race ancestral traditions.
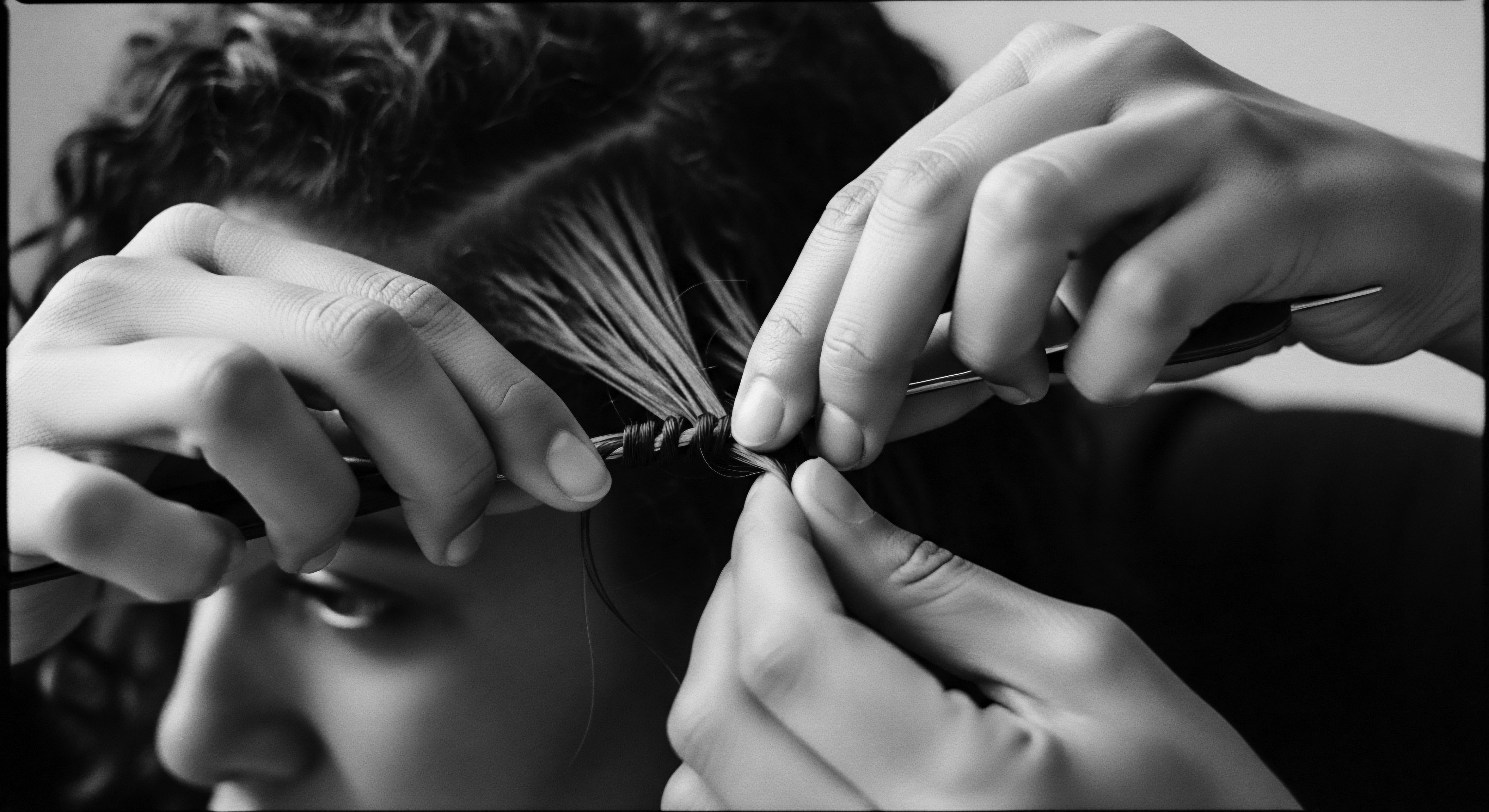

Mixed Heritage Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Mixed Heritage Hair Care is a specialized approach to nurturing hair types resulting from diverse genetic backgrounds, honoring complex biology and rich cultural narratives.

Olfactory Cultural Memory
Meaning ❉ Olfactory Cultural Memory is the collective aromatic knowledge and associations within a community, shaping identity through shared scent experiences across generations.

What Historical Significance Do Hair Oiling Rituals Hold for Textured Hair?
Hair oiling rituals for textured hair signify a deep heritage of ancestral knowledge, communal bonding, and enduring resilience.

Nok Terracotta Hair
Meaning ❉ Nok Terracotta Hair encompasses the sculpted hairstyles on ancient Nigerian figures, a key to understanding ancestral African hair heritage and its deep cultural meanings.

What Ancestral Oils Aid Moisture for Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, castor, and coconut oil hydrate textured hair by sealing in moisture, a practice deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race heritage.
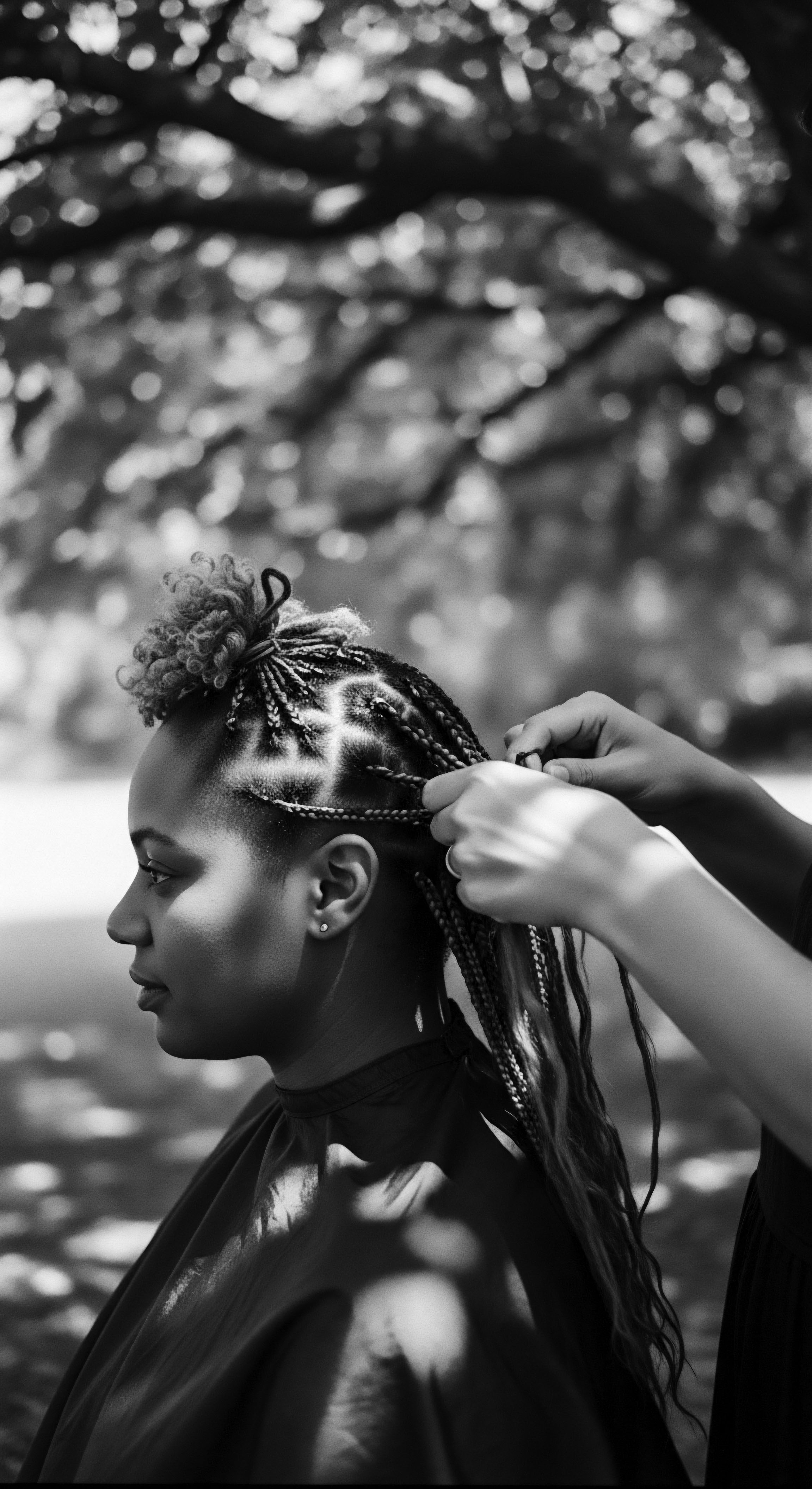
How Does Ayurvedic Wisdom Connect to Textured Hair Wellness?
Ayurvedic wisdom honors textured hair wellness by affirming holistic nourishment and mindful practices rooted deeply in ancestral heritage.
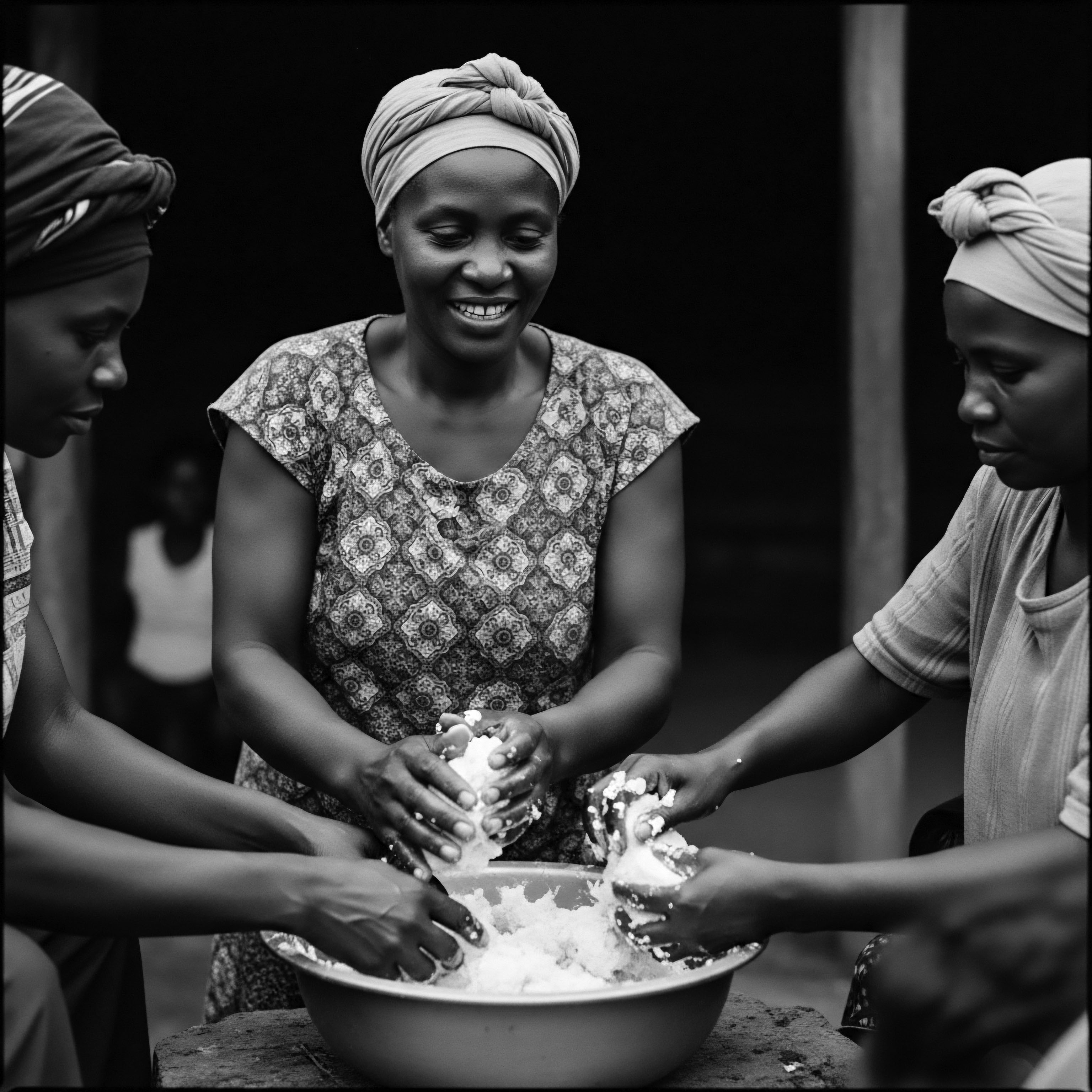

What Traditional Methods Shaped Shea Butter’s Use for Hair Heritage?
Traditional methods for shea butter production, perfected by African women, provided ancestral textured hair with vital moisture and protection.
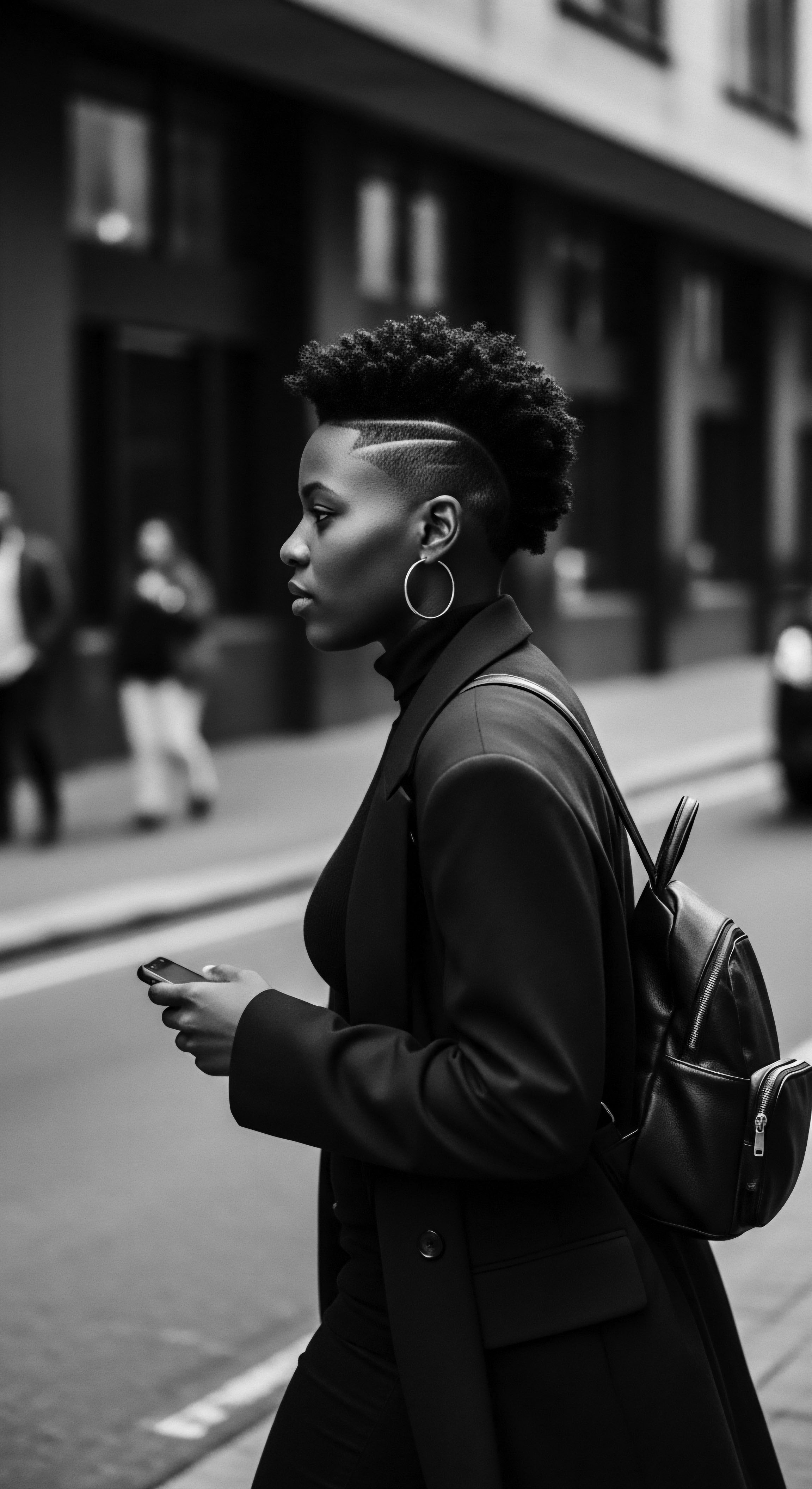

What Hidden Histories Do Textured Hair Styles Convey about Cultural Survival?
Textured hair styles embody cultural survival by echoing ancestral wisdom and resilience through centuries of heritage.

