Kalenjin Cultural Practices
Meaning ❉ Kalenjin Cultural Practices embody a rich heritage of beliefs and rituals, where hair often serves as a powerful symbol of identity and transition.

Social Institutions
Meaning ❉ Social institutions are established patterns of beliefs and behaviors that deeply shape identity, cultural norms, and experiences related to textured hair heritage.

Cultural Imperialism
Meaning ❉ Cultural Imperialism is the imposition of dominant cultural values, often displacing ancestral hair practices and shaping beauty standards through power dynamics.

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Hair and Why?
Historical laws aimed to control Black hair as a means of social subordination, inadvertently strengthening textured hair heritage through resilience.

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Hair Identity?
Historical laws aimed to control Black hair, most notably the Tignon Laws, served to suppress identity and enforce social hierarchy.

What Specific Historical Laws Targeted Black Hair in the Americas?
Historical laws in the Americas sought to control Black hair, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and identity.

What Historical Laws Attempted to Control Black Hair Expression?
Historical laws attempted to control Black hair expression by forcing conformity, but textured hair heritage consistently found avenues for powerful resistance.

Colonial Hair Discrimination
Meaning ❉ Colonial Hair Discrimination is the historical imposition of Eurocentric beauty standards to subjugate and erase the cultural identity expressed through textured hair.

Sistema De Castas
Meaning ❉ The Sistema de Castas was a colonial socio-racial hierarchy that significantly influenced perceptions and discrimination related to textured hair in the Americas.

Barbershop History
Meaning ❉ Barbershop history is a cultural chronicle of communal resilience and identity for textured hair, rooted in ancestral practices and evolving into vital community centers.
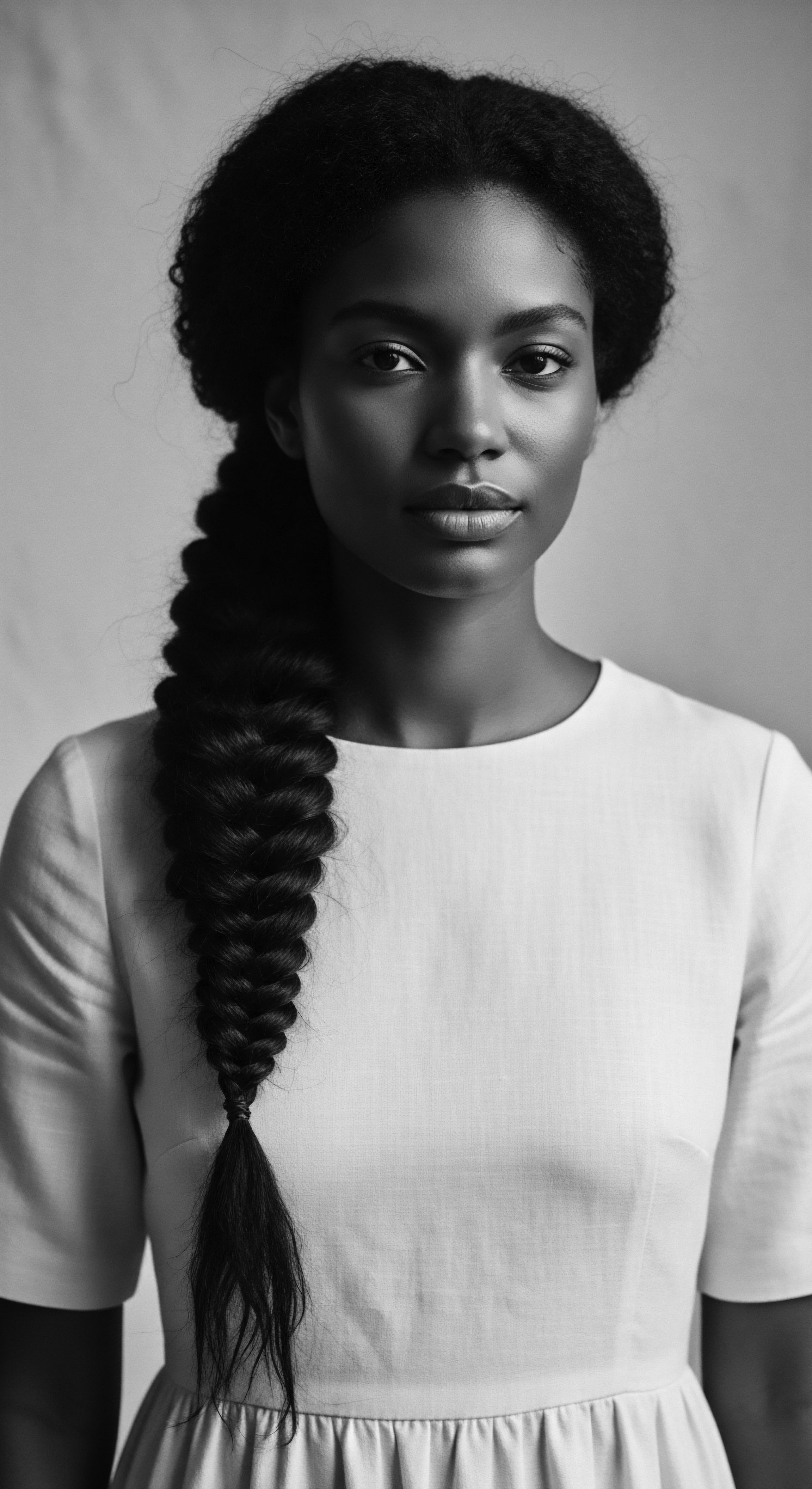
How Did Hair Defy Colonial Control?
Textured hair defied colonial control by serving as a profound vessel for ancestral knowledge, cultural identity, and enduring self-expression.

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Women’s Hair?
Historical laws sought to control Black women's hair by devaluing natural styles, forcing conformity, and suppressing cultural heritage.

How Did Ancient Hair Practices Resist Colonial Control?
Ancient hair practices preserved textured hair heritage by embodying cultural identity, self-sufficiency, and continuous defiance against colonial control.

How Did Historical Laws Attempt to Control Black Women’s Hair?
Historical laws sought to diminish Black women's beauty and social standing by regulating their textured hair, a profound attack on heritage.

Tzniut and Hair
Meaning ❉ Tzniut and Hair signifies the inherent reverence, cultural sanctity, and enduring dignity of textured hair within Black and mixed-race heritage.

Racial Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Racial Hair Control designates societal systems, legal actions, and biases that historically and presently impose Eurocentric beauty standards on textured hair.

Identity Control Theory
Meaning ❉ Identity Control Theory explains how individuals strive to align internal self-conceptions with external social perceptions to maintain a coherent sense of self.

Systemic Racial Control
Meaning ❉ Systemic Racial Control defines the pervasive societal mechanisms historically devaluing and policing textured hair, influencing identity and opportunity.

Sumptuary Law
Meaning ❉ Sumptuary Law defines historical societal mandates regulating personal display, often impacting hair as a marker of identity and status.

Identity Control
Meaning ❉ Identity Control refers to the ongoing process of aligning one's internal sense of self with external perceptions, often expressed powerfully through hair and heritage.

What Historical Mandates Sought to Control Afro-Descendant Hair Styles?
Historical mandates sought to control Afro-descendant hair, aiming to suppress identity and uphold racial hierarchies, yet sparking powerful acts of cultural resilience.
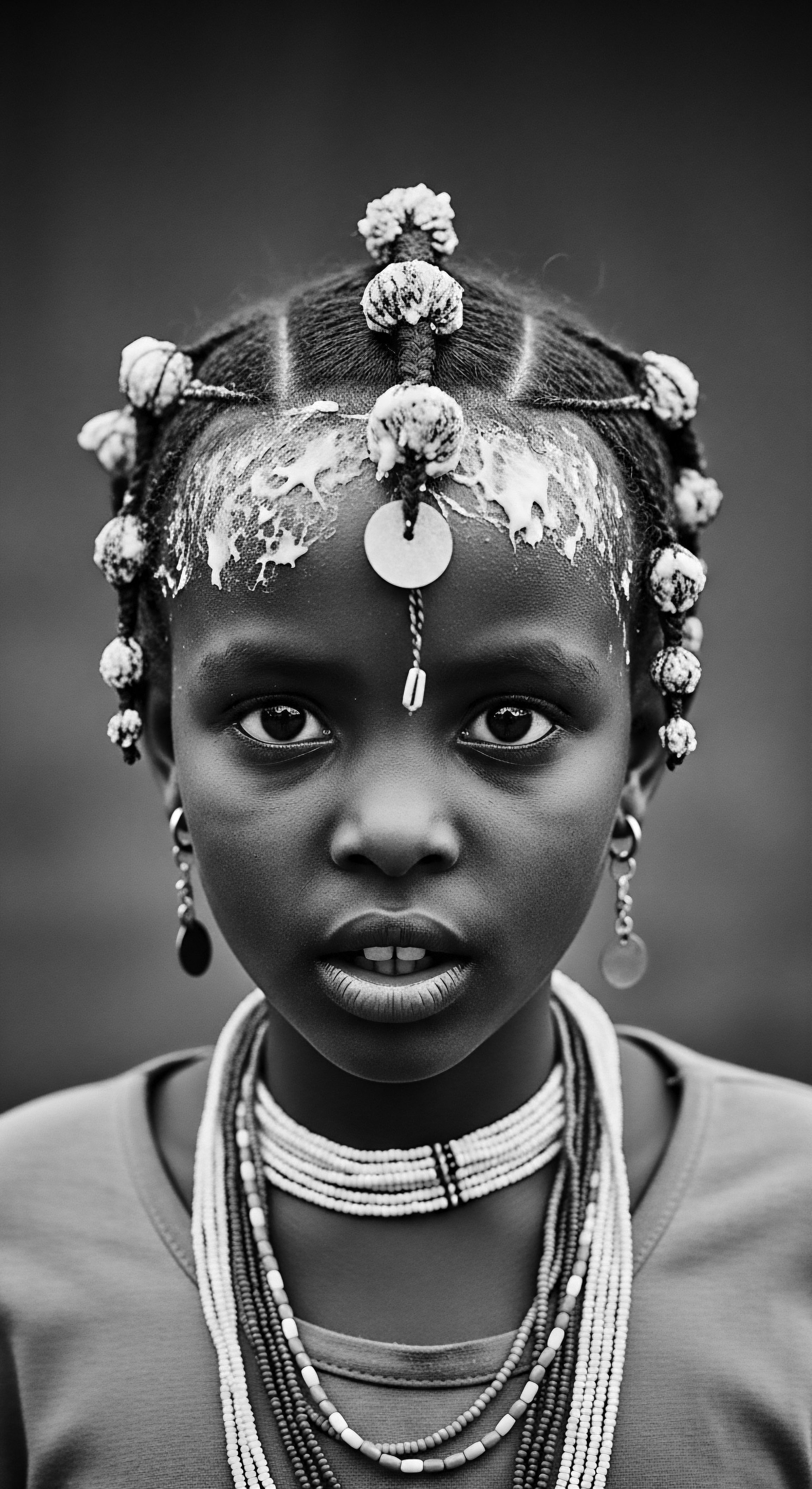

How Did Tignon Laws Control Black Women’s Appearance?
The Tignon Laws aimed to control Black women's appearance by forcing head coverings, yet they sparked powerful expressions of textured hair heritage.

Institutional Hair Policing
Meaning ❉ Institutional Hair Policing is the systemic control of hair appearance, often marginalizing textured hair of Black and mixed-race individuals, rooted in historical racial bias.

Jim Crow Hair Discrimination
Meaning ❉ Jim Crow Hair Discrimination systematically devalued natural Black hair, enforcing Eurocentric standards through societal pressure and economic coercion.

Prison Discrimination
Meaning ❉ Prison Discrimination, in the context of hair, is the systemic denial of self-expression and cultural identity through hair within carceral settings, primarily impacting Black and mixed-race individuals.

Black Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Control signifies the multifaceted assertion of agency, understanding, and stewardship over textured hair, deeply rooted in ancestral knowledge and identity.

Aesthetic Control
Meaning ❉ Aesthetic Control for textured hair is the deliberate shaping and maintenance of hair, reflecting cultural values, historical resistance, and personal identity.

Societal Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Societal Hair Control defines the formal and informal mechanisms that regulate hair appearance, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and Black identities.

Humidity Control
Meaning ❉ Humidity control involves managing how atmospheric moisture interacts with hair, vital for maintaining the health and style of textured hair.

