
What Is the Historical Significance of Black Hair in Legislation?
Black hair legislation historically targeted identity but now works to protect textured hair heritage, affirming cultural dignity.

In What Ways Did Traditional Hair Tools Adapt during Slavery?
Traditional hair tools adapted during slavery through ingenious repurposing of everyday objects and persistent ancestral wisdom, affirming textured hair heritage.

Slavery Laws
Meaning ❉ Slavery laws were legal constructs that codified human bondage, impacting ancestral hair practices and defining racial hierarchies.

How Did Ancestral African Hair Traditions Influence Covert Communication during Slavery?
Ancestral African hair traditions transformed textured styles into covert maps and communication systems, safeguarding heritage and aiding escape during slavery.

How Did Styling African Textured Hair Communicate in Slavery?
Styling African textured hair in slavery covertly conveyed messages, acting as maps and cultural symbols, a true testament to textured hair heritage.
Did Styling African Textured Hair Aid Cultural Survival during Slavery?
Styling African textured hair during slavery profoundly aided cultural survival by serving as a hidden language, preserving ancestral practices, and fostering community.

How Did Ancestral Hair Oiling Practices Adapt during Periods of Slavery?
Ancestral hair oiling adapted through ingenious substitution of available materials and transformed into a powerful cultural preservation tool.

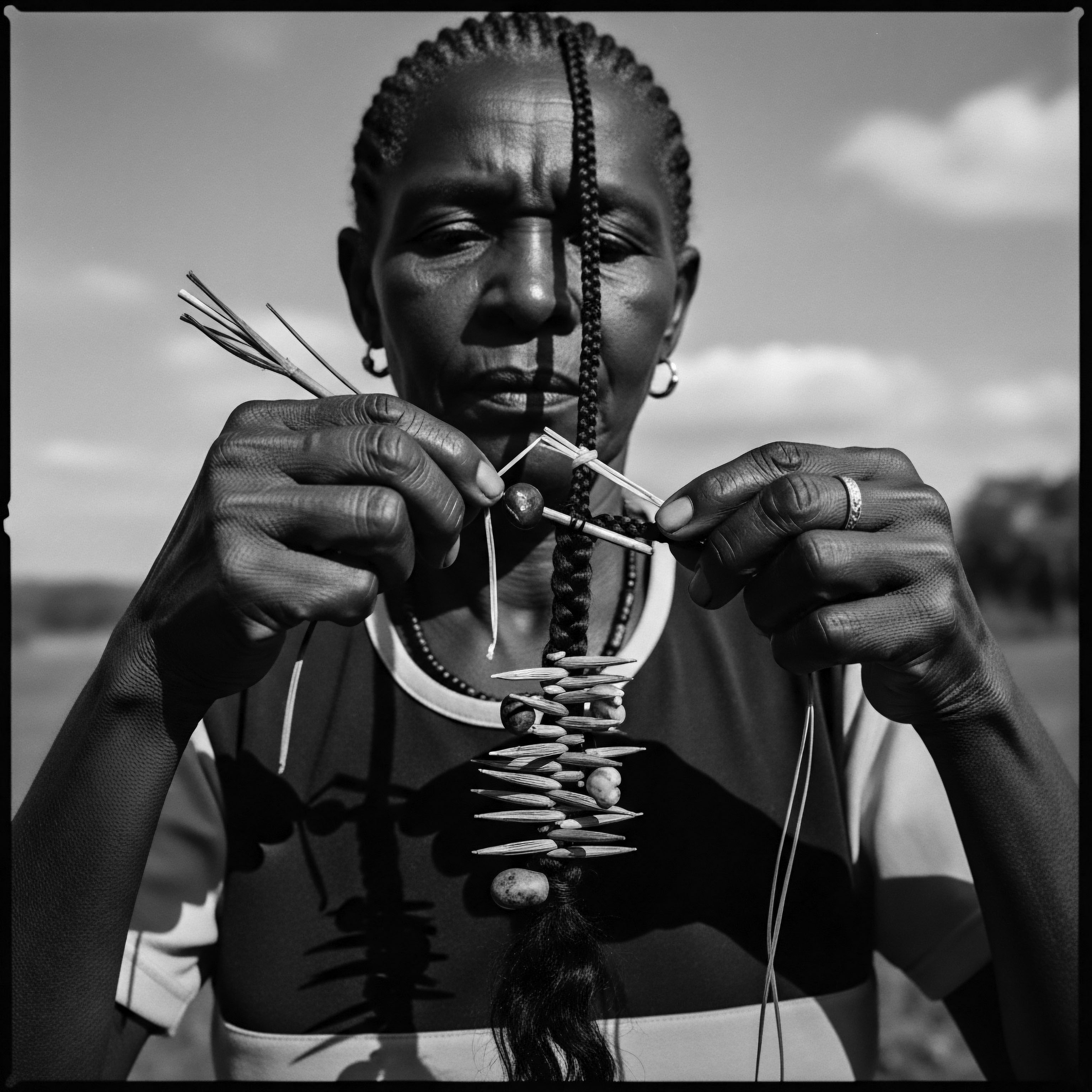
How Did Cornrows Serve as Survival Tools during Slavery?
Cornrows served as survival tools during slavery by concealing provisions and mapping escape routes, preserving cultural identity and providing essential hygiene.

Post-Slavery Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Hair Practices represent the evolving traditions, economic ventures, and cultural affirmations surrounding textured hair after emancipation.

Slavery Resilience
Meaning ❉ Slavery Resilience is the enduring spirit and adaptive strength of textured hair heritage that resisted oppression and became a profound symbol of identity and liberation.

How Did Textured Hair Traditions Persist during Transatlantic Slavery?
Textured hair traditions persisted through resilience and adaptation, maintaining cultural ties despite slavery's brutality.

How Did Slavery Impact Traditional Textured Hair Practices and Their Continuity?
Slavery severely disrupted traditional textured hair practices, yet communal ingenuity and resilience ensured continuity as acts of heritage reclamation.

What Natural Ingredients Sustained Hair during Slavery?
Natural ingredients like animal fats, castor oil, and okra sustained textured hair during slavery, linking directly to inherited ancestral care.

How Did Cultural Heritage Influence Pre-Slavery Hair Care?
Cultural heritage shaped pre-slavery hair care through complex social codes, spiritual beliefs, and the skilled use of natural resources.

How Did Textured Hair Practices Serve as Communication during Slavery?
Textured hair practices served as a coded language during slavery, encoding escape routes and cultural identity for liberation.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Practices Serve as Resistance during Slavery?
Textured hair practices during slavery served as covert communication, a means of cultural preservation, and a powerful assertion of identity.
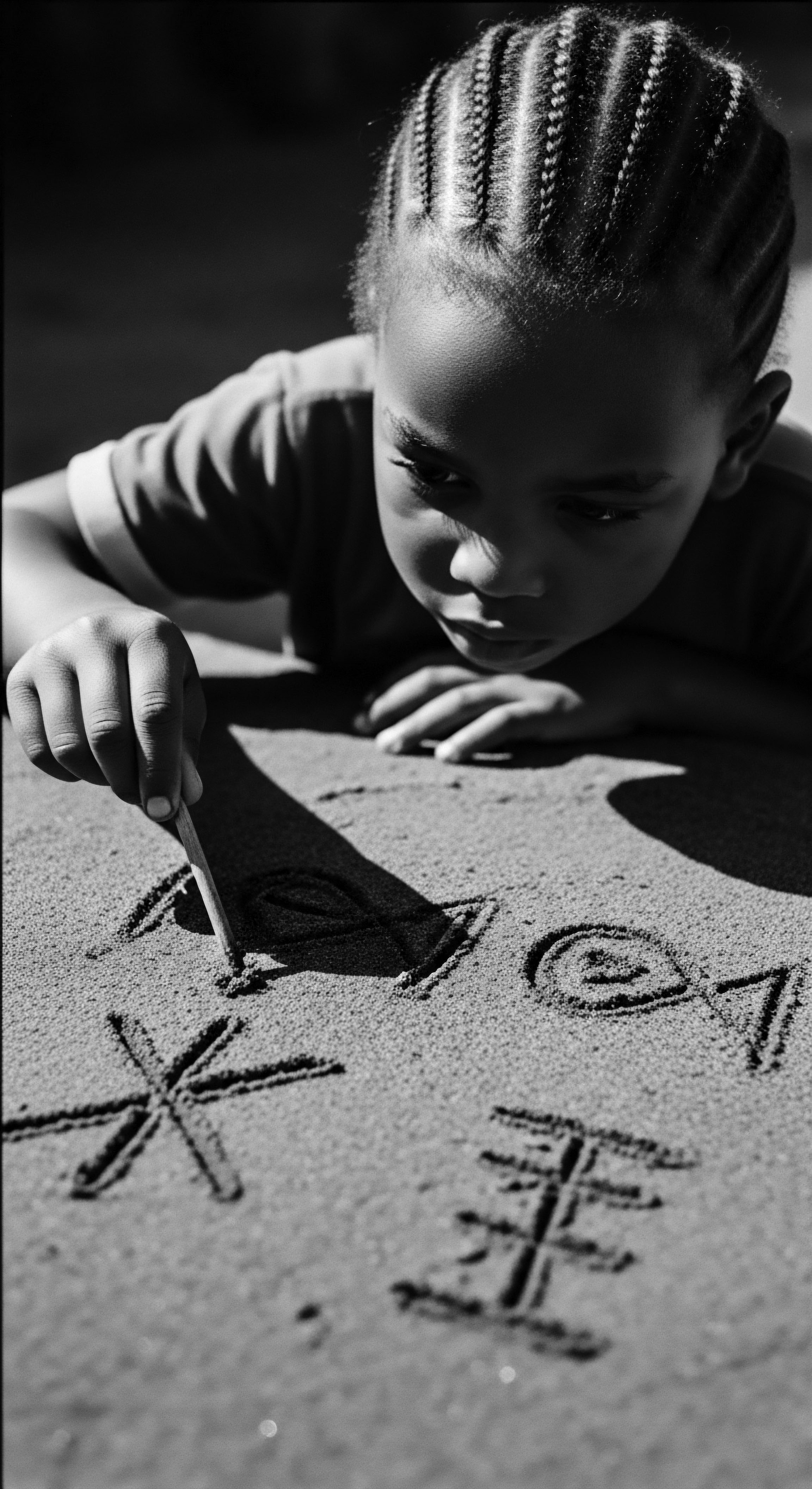

How Did Textured Hair Symbolize Covert Communication during Slavery?
Textured hair patterns, especially cornrows, served as covert maps and carriers of hidden items, symbolizing a profound act of resistance and heritage preservation.
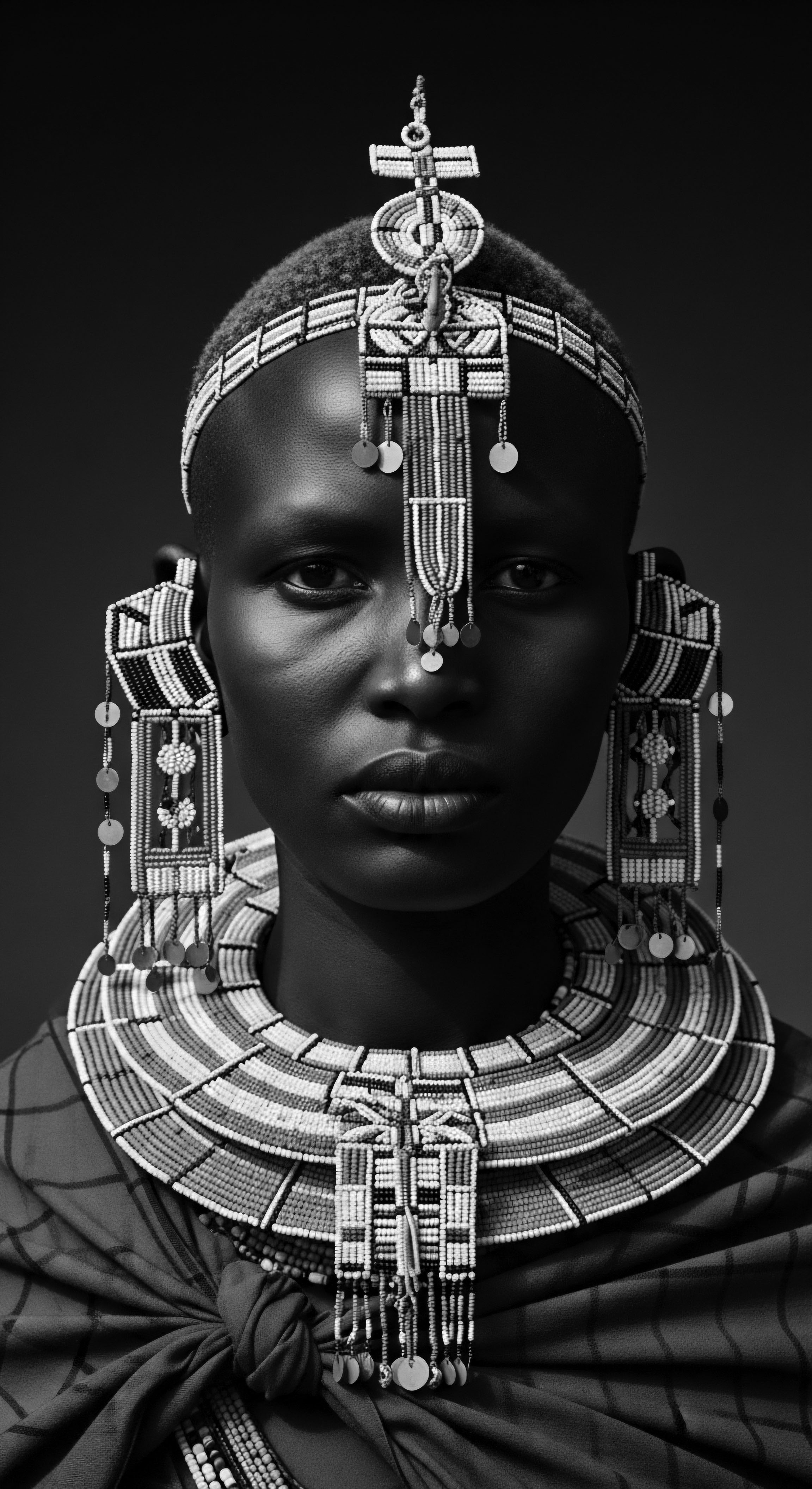

How Did Textured Hair Styling Methods Become Cultural Symbols during Slavery?
Textured hair styling transformed into covert communication and powerful identity statements, asserting cultural heritage amidst oppression.

What Historical Prejudices Influenced Textured Hair Legislation?
Historical prejudices led to laws controlling textured hair, aiming to suppress Black identity and its rich heritage.

How Did Slavery Impact the Cultural Identity of Textured Hair?
Slavery deeply altered textured hair's cultural identity, transforming it from a symbol of heritage and community to a marker of subjugation, yet also resistance.

Can Textured Hair Truly Reclaim Its Pre-Slavery Heritage Today?
Reclaiming textured hair heritage means consciously integrating ancestral wisdom with contemporary insights to honor its profound cultural lineage.

How Did Slavery Influence Black Hair Care Heritage?
Slavery forcibly stripped Black individuals of their hair’s heritage, altering practices and imposing Eurocentric beauty standards that textured hair continues to reclaim.

What Historical Biases against Textured Hair Does Legislation Address in Education?
Legislation addresses historical biases against textured hair in education by protecting cultural expressions and dismantling Eurocentric beauty standards.
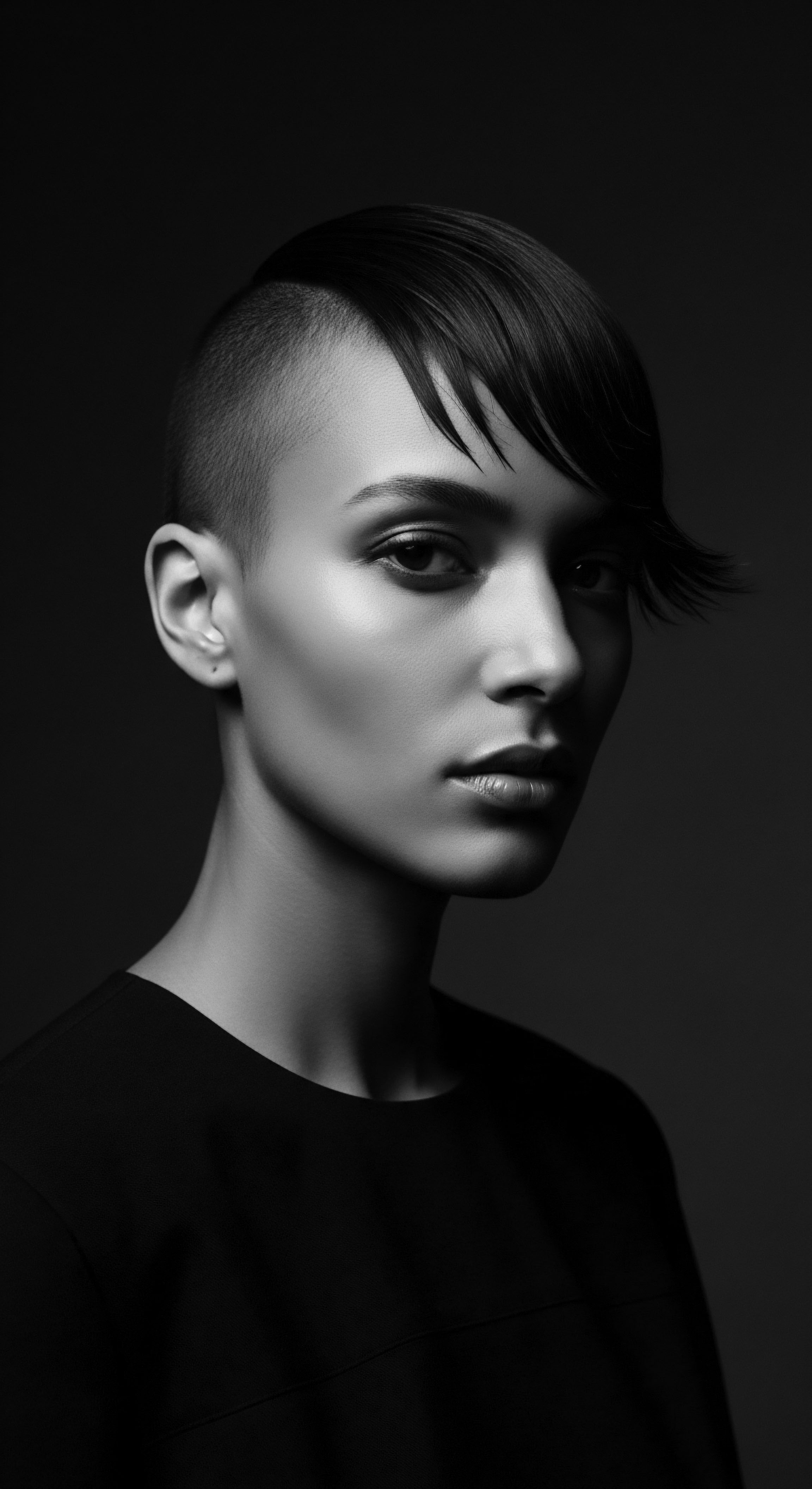

What Impact Did Slavery Have on Textured Hair Practices?
Slavery deeply fractured textured hair heritage, yet fueled remarkable resilience and innovative adaptations in care and identity.

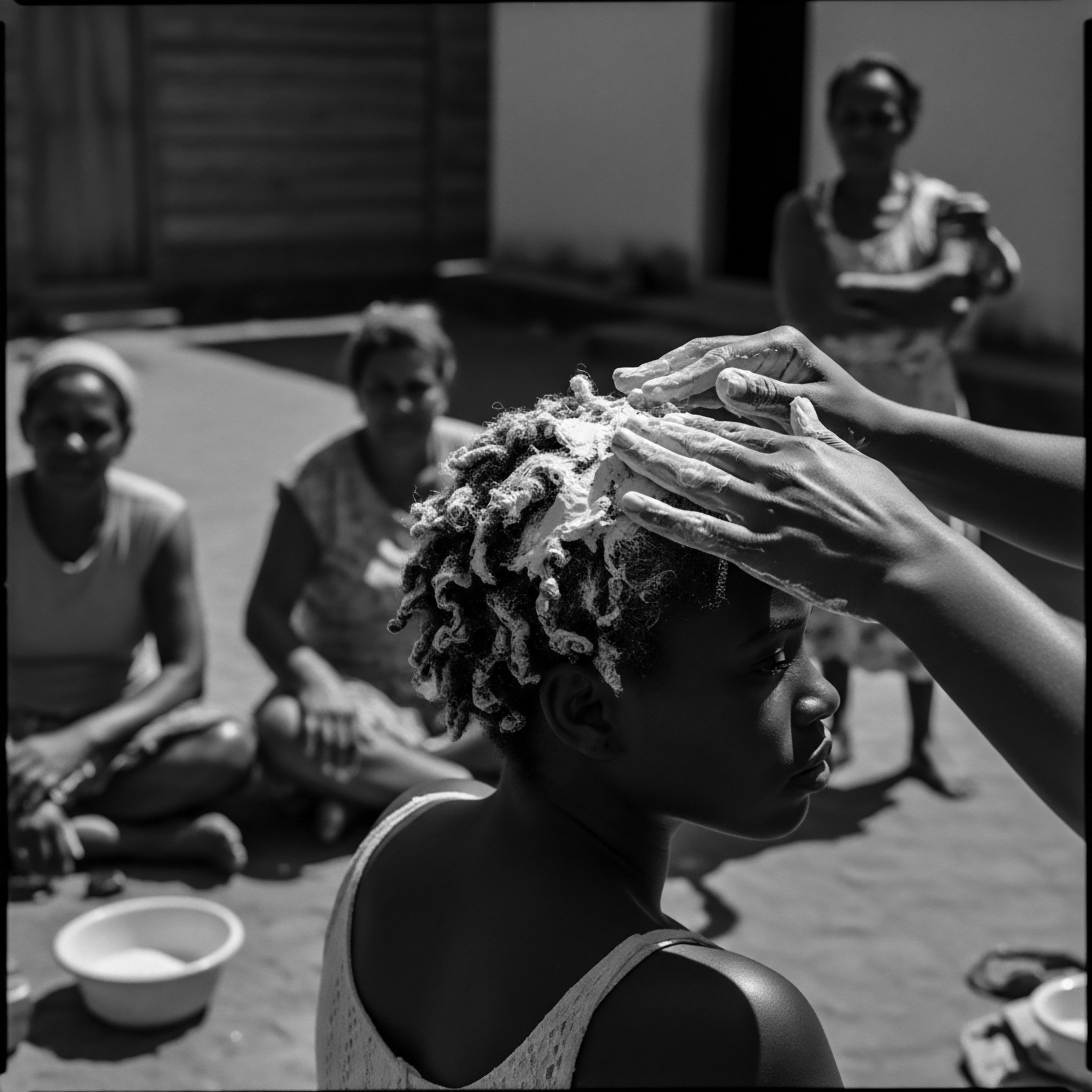
How Does the Legacy of Slavery Impact Textured Hair Care Practices Today?
The legacy of slavery profoundly shapes textured hair care by influencing perceptions, fostering adaptation, and inspiring a reclamation of ancestral practices and self-acceptance.

What Historical Biases Does Hair Protection Legislation Dismantle for Heritage?
Hair protection legislation actively dismantles historical biases by affirming textured hair as a protected aspect of racial identity and cultural heritage.

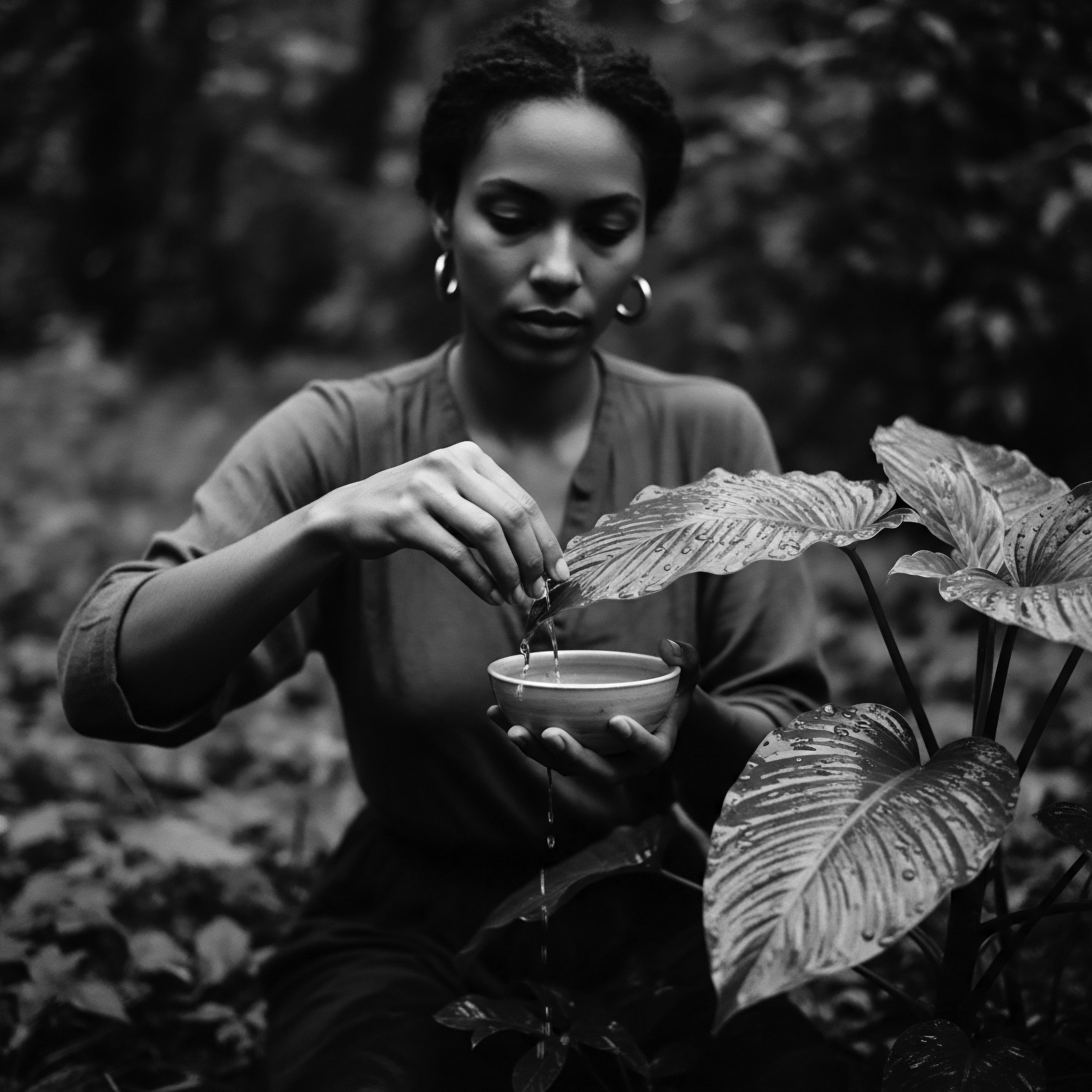
How Did Oiling Rituals Maintain Heritage during Slavery?
Oiling rituals during slavery preserved textured hair heritage by fostering communal bonds, adapting ancestral knowledge, and serving as acts of quiet cultural defiance.
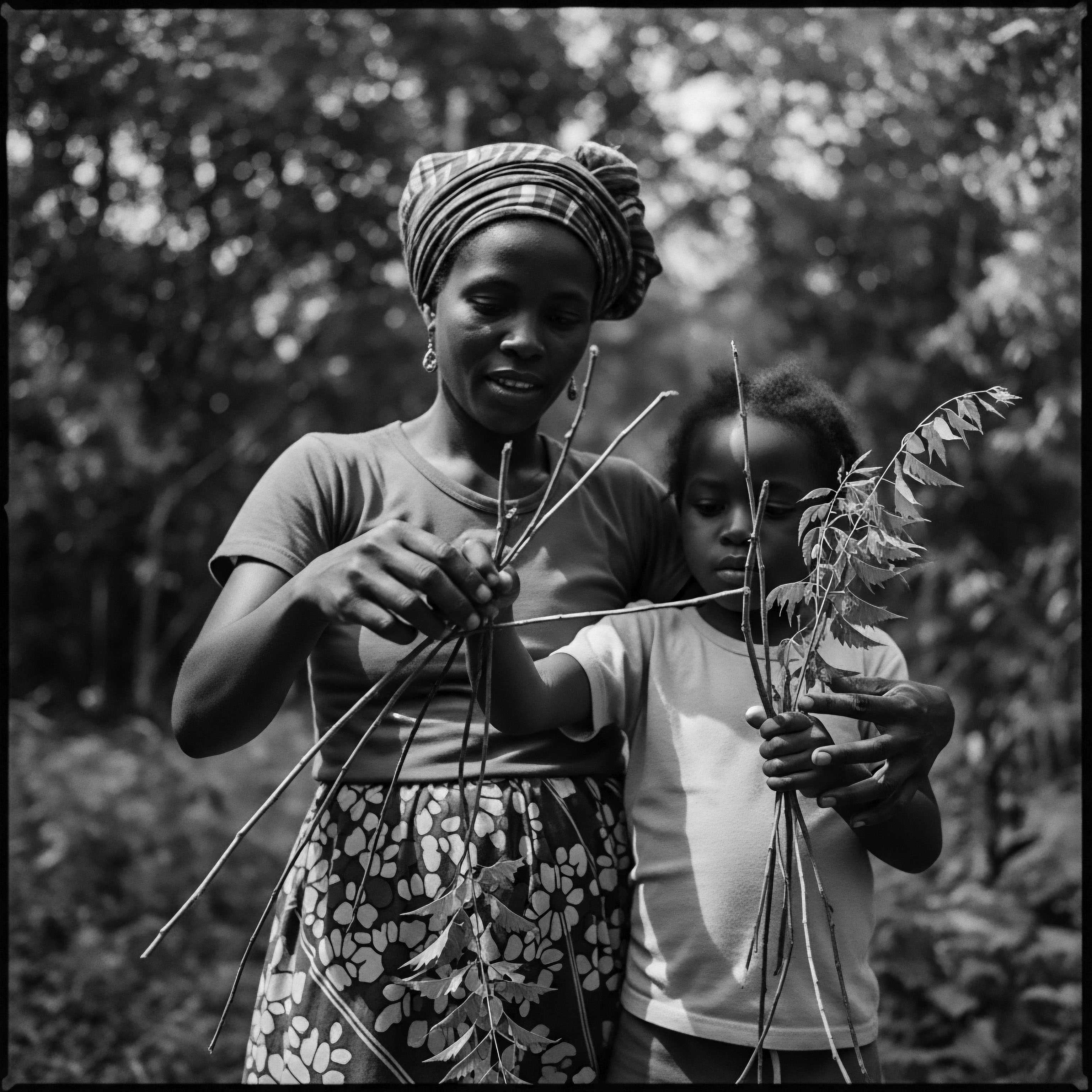

In What Ways Does Hair Protection Legislation Honor Heritage?
Hair protection legislation honors heritage by affirming textured hair as an integral, protected expression of racial and cultural identity.

How Did Textured Hair Biology Help Resistance Efforts during Slavery?
Textured hair's coiled structure and styling versatility helped enslaved people conceal tools and messages, preserving their **heritage** and aiding resistance.

