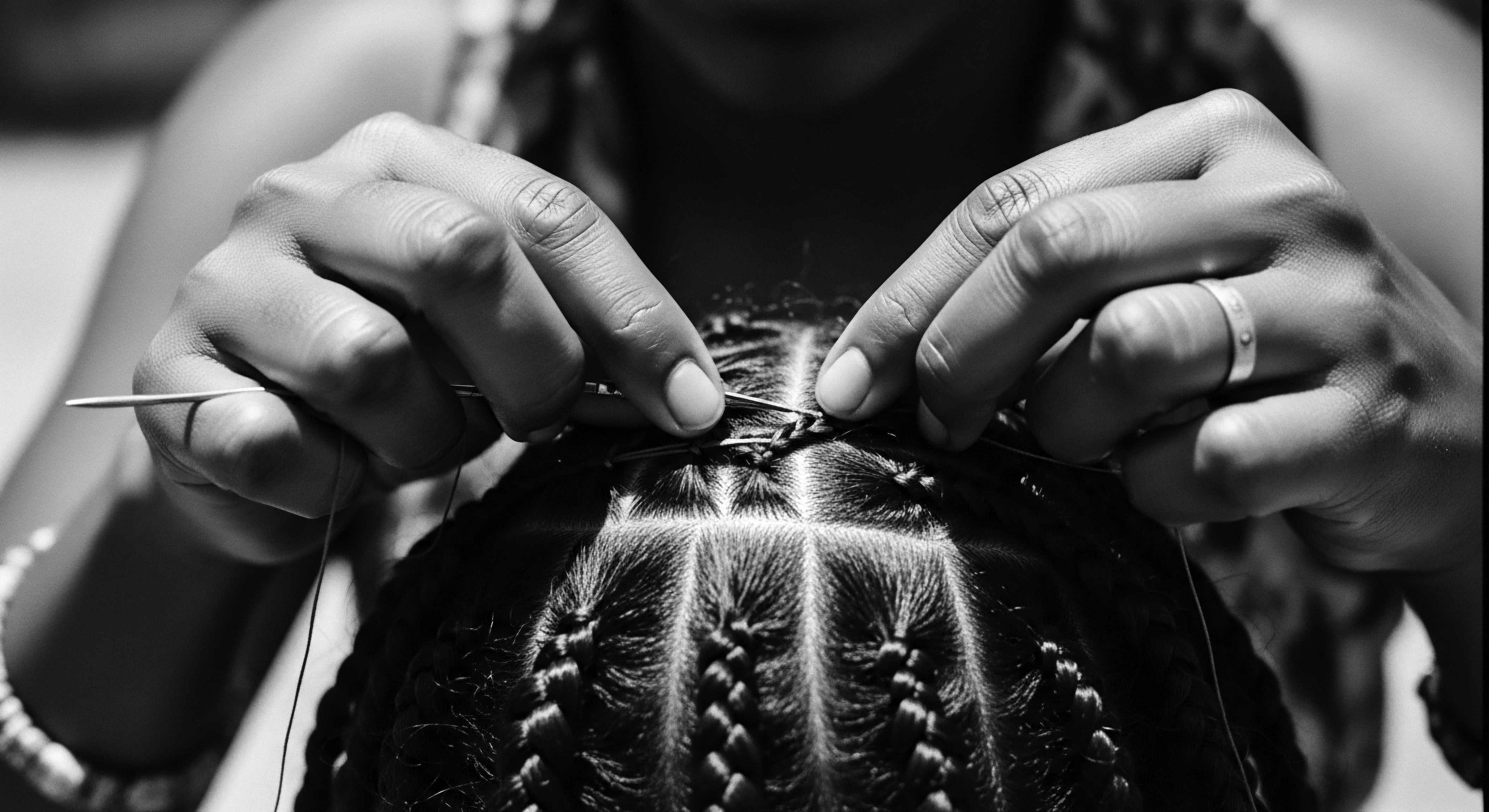

In What Ways Do Ancestral Plant Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral plant practices inform modern textured hair care by providing foundational knowledge for conditioning, styling, and scalp health, deeply rooted in heritage.

What Biological Distinctions Cause Textured Hair’s Moisture Needs?
Textured hair's unique follicular shape and cuticle structure cause its inherent moisture needs, deeply rooted in ancestral care traditions.

How Do Headwraps Protect Textured Hair?
Headwraps shelter textured hair by reducing friction, retaining moisture, and guarding against environmental damage, upholding a rich cultural heritage.

Hair Coverings
Meaning ❉ Hair Coverings are a profound cultural and practical expression for textured hair, embodying ancestral protection, identity, and resilience across generations.

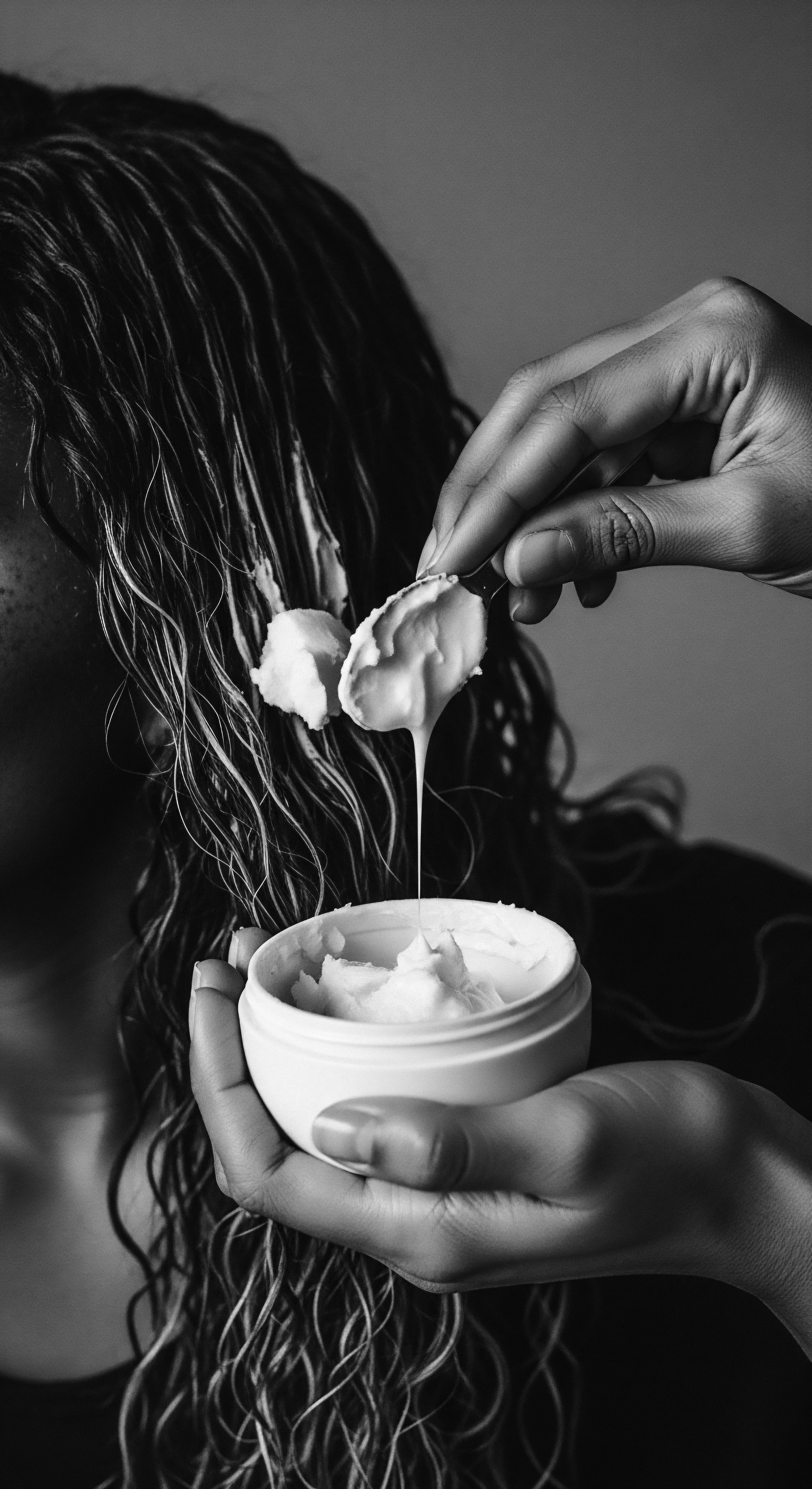
Can Traditional Hair Oil Practices Validate Modern Hair Science for Textured Hair?
Traditional hair oil practices affirm modern hair science by showcasing ancient wisdom's efficacy in nourishing and protecting textured hair heritage.

How Did Ancient Coverings Shield Textured Hair?
Ancient coverings shielded textured hair by providing physical barriers against elements, preserving moisture, and maintaining styles, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

How Do Head Coverings Protect Textured Hair at Night?
Head coverings protect textured hair at night by reducing friction, retaining moisture, and preserving ancestral styles, honoring a deep heritage of care.

Silk Bonnets
Meaning ❉ The Silk Bonnet is a protective head covering, often silk, that preserves textured hair's moisture and reduces friction, rooted in ancestral care traditions.

What Materials Are Best for Textured Hair Protection at Night?
Protecting textured hair at night with silk or satin honors a heritage of care, preserving moisture and preventing damage rooted in ancestral wisdom and modern science.

What Historical Significance Do Protective Hair Coverings Hold for Heritage?
Protective hair coverings signify a deep connection to textured hair heritage, safeguarding health and embodying ancestral wisdom across generations.

Do Traditional Hair Oiling Methods Hold Modern Scientific Merit for Textured Strands?
Traditional hair oiling methods for textured strands hold significant scientific merit, rooted in centuries of ancestral knowledge and cultural heritage.

What Historical Hair Practices Align with Modern Science?
Historical hair practices for textured hair often align with modern science through their focus on moisture retention, gentle manipulation, and natural ingredient benefits, deeply rooted in heritage.

What Materials Make the Best Hair Bonnets?
The best hair bonnet materials, such as silk, satin, and bamboo lyocell, minimize friction and retain moisture, continuing a long heritage of textured hair protection.
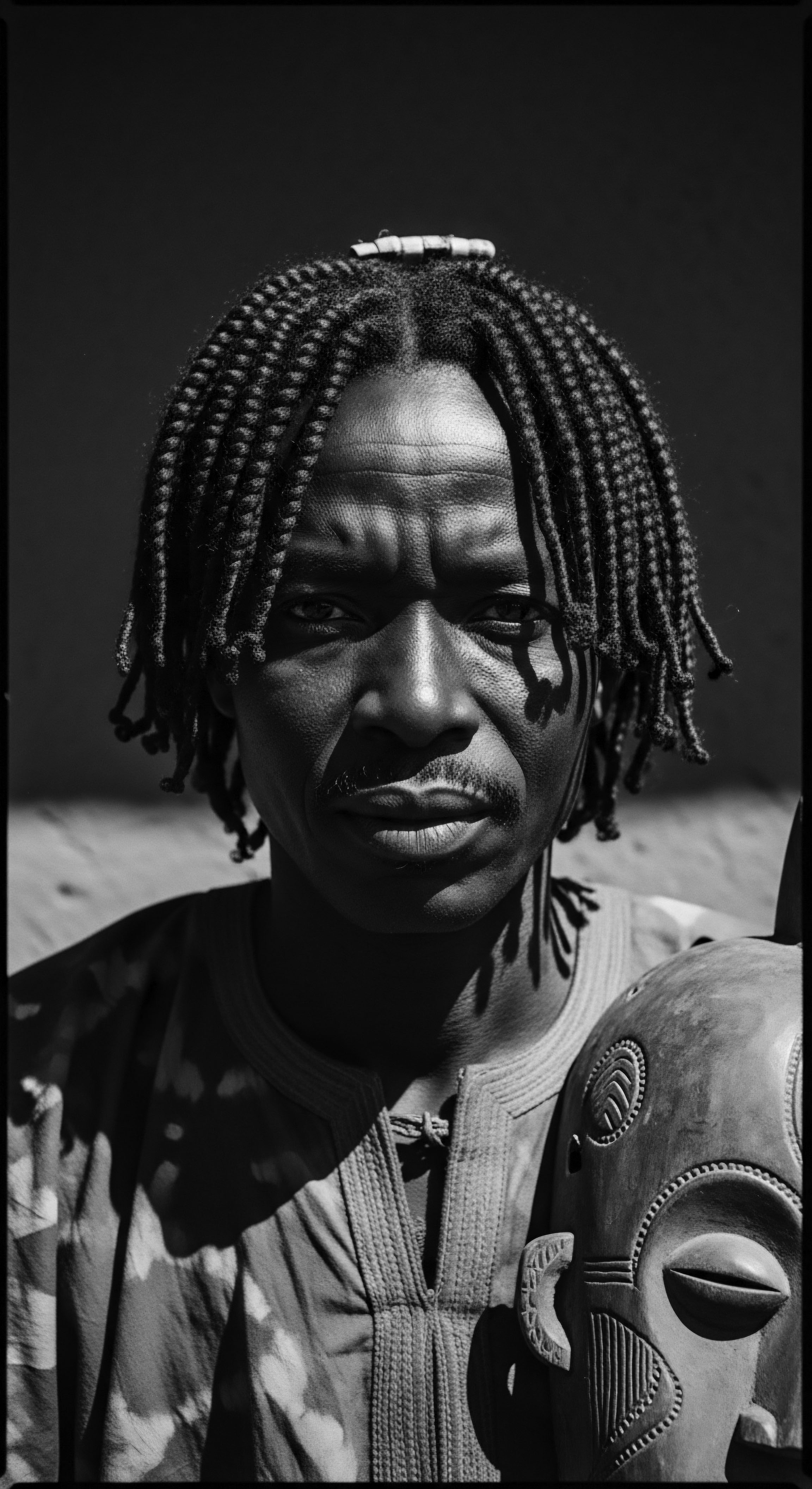

What Traditional Plant Oils Aided African Hair Vitality?
Traditional African plant oils, deeply rooted in heritage, nourished textured hair by providing moisture, protection, and cultural identity.

How Does Historical Hair Wisdom Influence Contemporary Care for Textured Hair?
Historical hair wisdom shapes contemporary textured hair care by offering ancestral blueprints for protective styling, natural ingredient use, and holistic wellness.

Why Is Textured Hair Hydration Crucial?
Textured hair hydration is crucial because its unique structure readily loses moisture, making consistent replenishment a heritage practice for vitality.

Why Does Textured Hair Need Specific Historical Ingredients?
Textured hair needs specific historical ingredients because ancestral wisdom provided unique, potent solutions for its distinct structure and moisture needs.
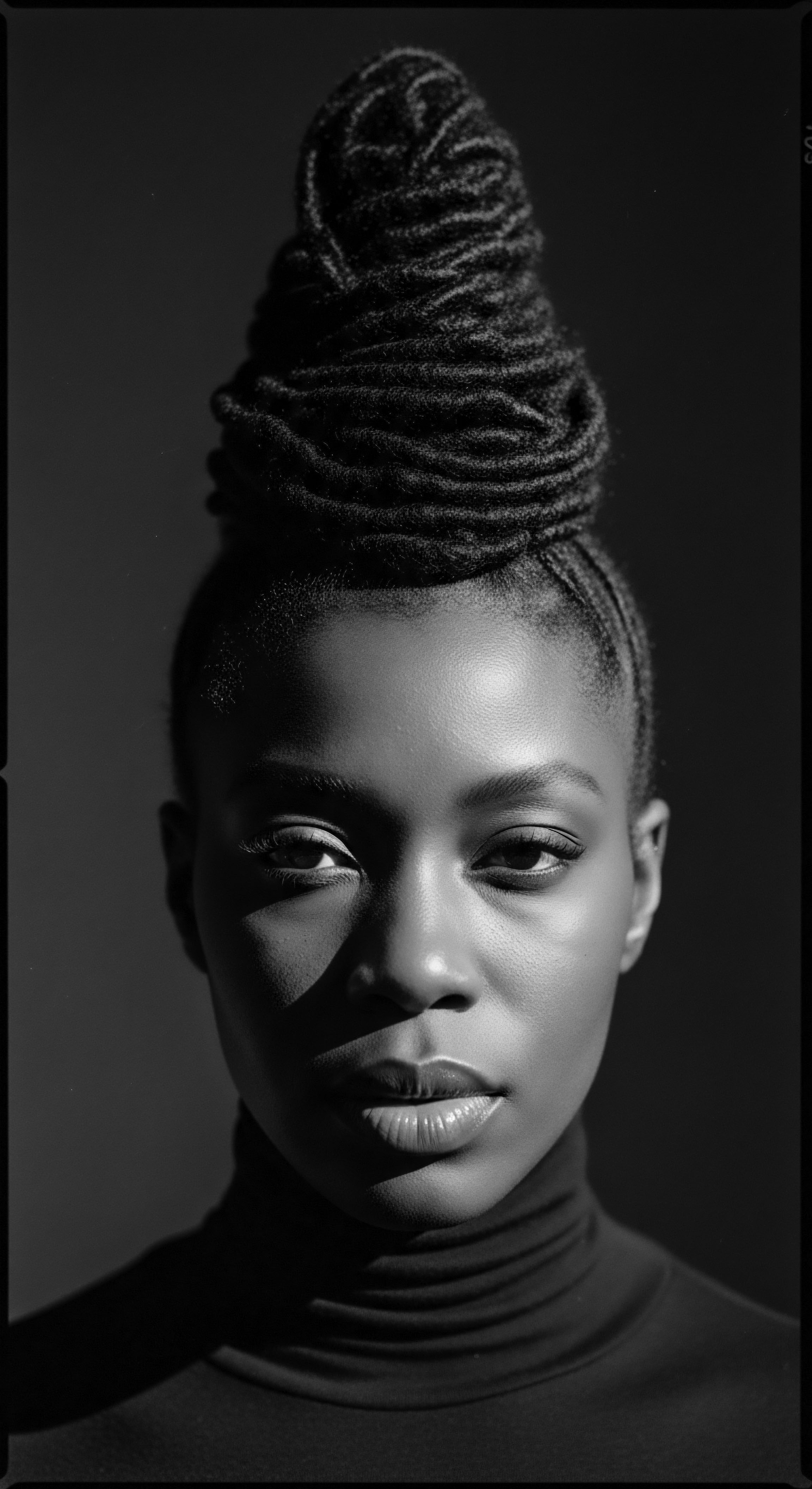

Can Modern Science Validate the Heritage of Silk and Satin for Hair Preservation?
Modern science confirms silk and satin reduce friction and retain moisture, validating ancestral textured hair preservation customs.

What Ancient Coverings Protected Textured Hair?
Ancient coverings protected textured hair by minimizing environmental damage, preserving intricate styles, and acting as powerful cultural and spiritual declarations.

What Ancestral Ingredients Protect Textured Hair?
Ancestral ingredients protect textured hair by providing deep moisture, fortifying strands, and creating environmental shields rooted in heritage wisdom.

What Biophysical Principles Validate the Heritage of Textured Hair Protection?
Biophysical principles validate textured hair protection heritage by showing how ancestral practices counter hair's unique structural vulnerabilities.

Silk Hair Coverings
Meaning ❉ Silk hair coverings are protective headwear, historically and culturally significant for preserving textured hair health and identity.
Silk Headwraps
Meaning ❉ The Silk Headwrap is a protective textile for textured hair, embodying ancestral care traditions and serving as a symbol of cultural identity and resilience.

In What Ways Does Modern Science Affirm Traditional Textured Hair Care Rituals?
Modern science confirms traditional textured hair care rituals preserve hair health by reducing manipulation and providing moisture, affirming a deep heritage of wisdom.

Can Modern Science Explain Why Textured Hair Benefits from Silk and Satin?
Modern science affirms that silk and satin benefit textured hair by reducing friction and preserving moisture, validating ancestral care practices.

Silk Benefits
Meaning ❉ Silk Benefits refer to the advantageous properties of silk for hair, rooted in its smooth texture and protein composition, enhancing moisture and reducing friction, echoing ancestral care traditions.

Silk Hair Wraps
Meaning ❉ Silk Hair Wraps are protective textile enclosures, often made from silk, safeguarding textured hair and embodying a rich cultural heritage of care and identity.

Silk Hair Benefits
Meaning ❉ Silk Hair Benefits refers to the protective advantages of silk fiber for textured hair, rooted in ancestral practices and scientifically validated for reducing friction and preserving moisture.

Why Do Head Coverings Matter for Textured Hair Heritage?
Head coverings protect textured hair from environmental elements and friction, deeply connecting to ancestral practices of care and cultural identity.

