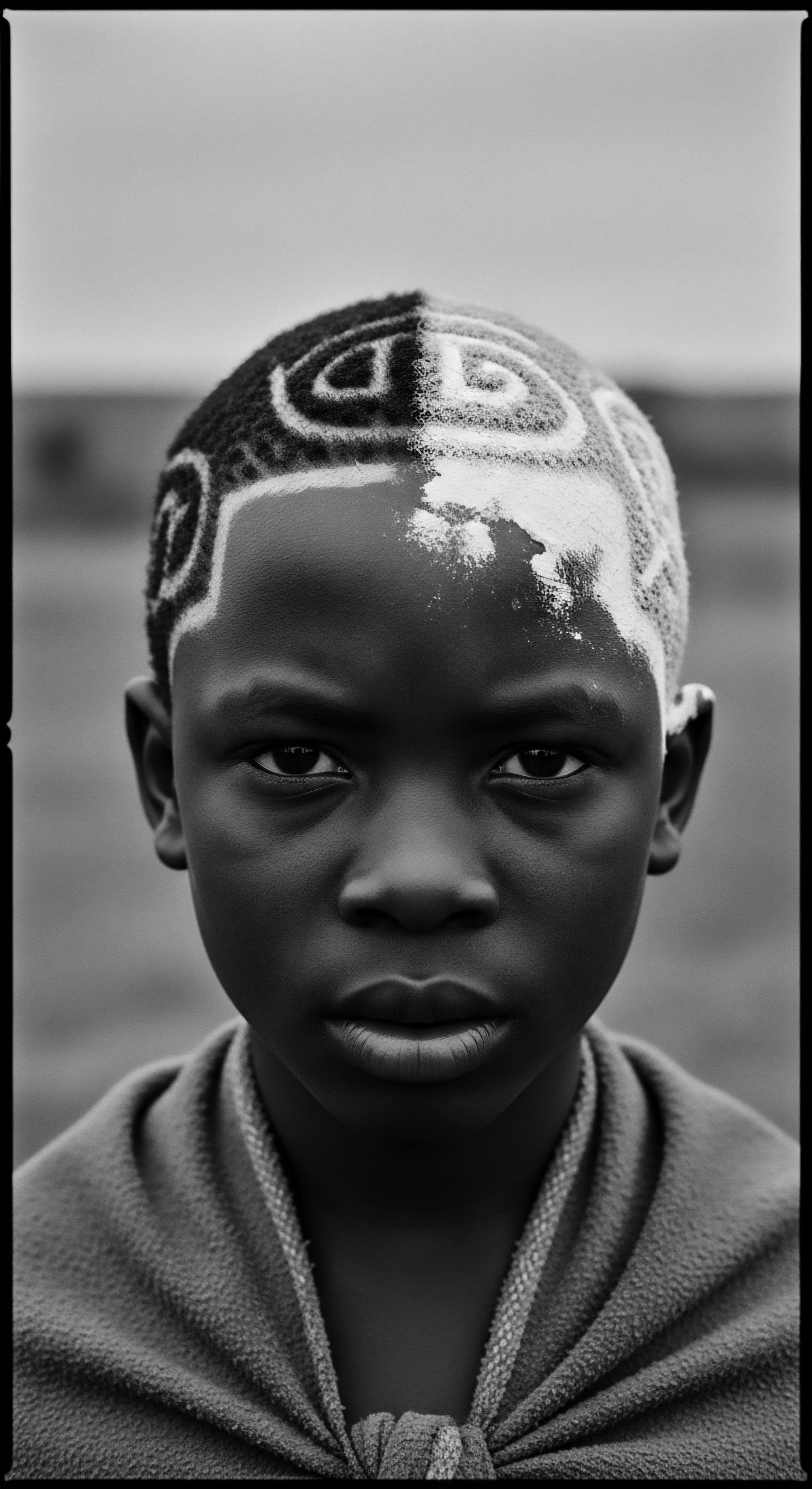
In What Ways Does Hair Discrimination Connect to Cultural Heritage and Identity?
Hair discrimination attacks textured hair heritage, undermining identity and cultural expression through historical bias and ongoing societal pressure.

How Did Jim Crow Era Policies Impact Black Hair Care?
Jim Crow policies compelled Black individuals to alter natural hair for survival, deeply impacting textured hair heritage and fostering self-sufficient beauty culture.

How Did Historical Perceptions of Textured Hair Shape Discriminatory Workplace Policies?
Historical perceptions, rooted in colonial biases, deemed textured hair unprofessional, shaping policies that suppressed Black hair heritage in workplaces.

School Policy
Meaning ❉ School Policy, in the context of textured hair, represents institutional norms and regulations impacting identity, cultural expression, and well-being.

In What Ways Do Modern Policies Address Hair Discrimination Rooted in Heritage?
Modern policies address hair discrimination by legally protecting natural hair textures and protective styles, affirming their cultural significance rooted in textured hair heritage.

What Historical Policies Shaped Perceptions of Black Hair Heritage?
Historical policies profoundly shaped perceptions of Black hair heritage by devaluing natural textures and promoting Eurocentric beauty standards.

Hair Discrimination Legislation
Meaning ❉ Legal frameworks safeguarding individuals from discrimination based on natural hair textures and protective styles linked to racial heritage.

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Policies like Tignon Laws Resonate in Modern Textured Hair Experiences?
Historical hair policies like Tignon Laws resonate in modern textured hair experiences by shaping beauty standards, influencing self-perception, and inspiring ongoing cultural reclamation of ancestral hair heritage.

Boarding School Hair
Meaning ❉ Boarding School Hair describes the historical and ongoing challenges textured hair faces in educational institutions, reflecting cultural suppression and the enduring fight for hair autonomy.

Cultural Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Policies are the societal rules and expectations, both explicit and implicit, governing hair appearance and care within a community, deeply rooted in historical and cultural significance for textured hair.

Historical Policies
Meaning ❉ Historical Policies are the collective societal norms and codified regulations that have shaped the perception and experience of textured hair across generations.

Boarding School Trauma
Meaning ❉ Boarding School Trauma describes the deep, lasting psychological and cultural injuries from residential institutions, significantly impacting textured hair heritage and identity.

Testimonial Injustice
Meaning ❉ Testimonial Injustice is the systemic devaluation of a person's word due to identity-based prejudice, significantly impacting the recognition of textured hair heritage.

Boarding School Policies
Meaning ❉ This entry defines "Boarding School Policies" as the historical, cultural, and societal frameworks that have shaped the experience of textured hair.

Textured Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Policies encompass the formal and informal norms, expectations, and regulations shaping the perception and experience of textured hair across history and cultures.

How Does the CROWN Act Protect Textured Hairstyles in Schools?
The CROWN Act prohibits discrimination against textured hairstyles in schools, honoring Black and mixed-race hair heritage.

How Did Early Policies Impact Textured Hair?
Early policies often mandated conformity to Eurocentric beauty ideals, suppressing natural textured hair and ancestral care practices.

Hair Wellness Policies
Meaning ❉ Hair Wellness Policies define a comprehensive, culturally attuned approach to hair health, deeply rooted in the heritage and unique needs of textured hair.

What Historical Burdens Do Textured Hair Laws Address?
Textured hair laws address historical burdens of racial discrimination, societal control, and the suppression of cultural identity.

School Policies
Meaning ❉ School policies define guidelines, but their application to hair, particularly textured hair, often reflects historical biases and impacts cultural identity.

Cultural Policies
Meaning ❉ Cultural Policies are societal frameworks, both formal and informal, that shape the meaning and expression of shared heritage, particularly evident in textured hair traditions.
Grooming Policies
Meaning ❉ Grooming Policies are structured guidelines for appearance, often revealing societal power dynamics and historical biases against textured hair, particularly for Black and mixed-race communities.

School Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ School Hair Policies are institutional rules governing student hair appearance, often reflecting and perpetuating societal biases against textured hair heritage.

School Regulations
Meaning ❉ School Regulations for textured hair refer to its inherent biological properties and the historical societal rules that have shaped its cultural significance and care.

Black Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Policies define formal and informal rules governing textured hair, reflecting a history of control and cultural resilience.

Boarding School Impact
Meaning ❉ The Boarding School Impact describes the enduring legacy of forced assimilation policies on Indigenous and Black communities, particularly through the suppression of traditional hair practices.

Military Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Military Hair Policies are formal regulations governing hair appearance in armed forces, historically impacting textured hair and evolving towards inclusivity.

What Modern Legislation Acknowledges Textured Hair Heritage?
Modern legislation like the CROWN Act protects textured hair and traditional styles, affirming their deep connection to racial and cultural heritage.

Colonial Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Colonial Hair Policies refer to historical impositions of Eurocentric hair standards on colonized populations, undermining ancestral hair heritage.

