Racial Recognition
Meaning ❉ Racial Recognition is the societal process of categorizing individuals based on visible traits, particularly hair texture, profoundly shaping identity and belonging.

Racial Recognition Law
Meaning ❉ Racial Recognition Law acknowledges and addresses discrimination based on racial characteristics like textured hair, ensuring equity and cultural affirmation.

Can Historical Hair Discrimination Inform Current International Law?
Historical hair discrimination, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage, provides crucial insights for strengthening international law to protect cultural identity.

Afro-Chilean Experience
Meaning ❉ The Afro-Chilean Experience defines the enduring historical, cultural, and social journey of people of African descent in Chile.

How Did the Tignon Law Reshape Public Appearance?
The Tignon Law compelled Black women to cover their hair, yet they transformed mandated wraps into bold, personal expressions of cultural heritage.

In What Ways Do Contemporary Legal Efforts Acknowledge Hair as a Racial Characteristic?
Contemporary laws acknowledge hair texture as a racial characteristic, protecting textured hair heritage and its cultural expressions.

Curl Pattern Recognition
Meaning ❉ Curl Pattern Recognition is the discerning of hair's natural formations, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and cultural identity across textured hair communities.

Cultural Property Law
Meaning ❉ Cultural Property Law protects collective expressions and knowledge, including textured hair traditions, as vital components of cultural identity and heritage.

Hair Heritage Law
Meaning ❉ The Hair Heritage Law legally protects individuals from discrimination based on hair texture and cultural styles, affirming identity and ancestral practices.

Racial Classifications
Meaning ❉ Racial classifications are social constructs that historically used hair texture to categorize people, influencing identity and systemic oppression.

Patent Law History
Meaning ❉ Patent Law History traces the evolution of recognizing and protecting inventive ideas, deeply interwoven with cultural heritage and hair traditions.

Cultural Appropriation Law
Meaning ❉ Cultural Appropriation Law safeguards heritage by addressing the unacknowledged and often commercialized adoption of cultural elements from originating communities.

Traditional Knowledge Law
Meaning ❉ Traditional Knowledge Law safeguards intergenerational wisdom, practices, and innovations of communities, particularly for textured hair heritage.

Patent Law
Meaning ❉ Patent Law provides exclusive rights for novel inventions, navigating a complex intersection with textured hair heritage and traditional knowledge.

International Law Principles
Meaning ❉ International Law Principles define the global framework for state interactions and universal human rights, significantly impacting the protection of textured hair heritage and cultural identity.

International Law
Meaning ❉ International Law is a framework of norms and principles guiding states and other entities, increasingly extending to cultural identity and ancestral heritage.
Racial Hair Stereotypes
Meaning ❉ Racial hair stereotypes are biased assumptions linking hair characteristics to perceived racial identity, leading to prejudice and discrimination rooted in historical power imbalances.

Social Recognition
Meaning ❉ Social Recognition is the profound communal acknowledgment of identity, status, and worth, deeply rooted in the historical and cultural expressions of textured hair.
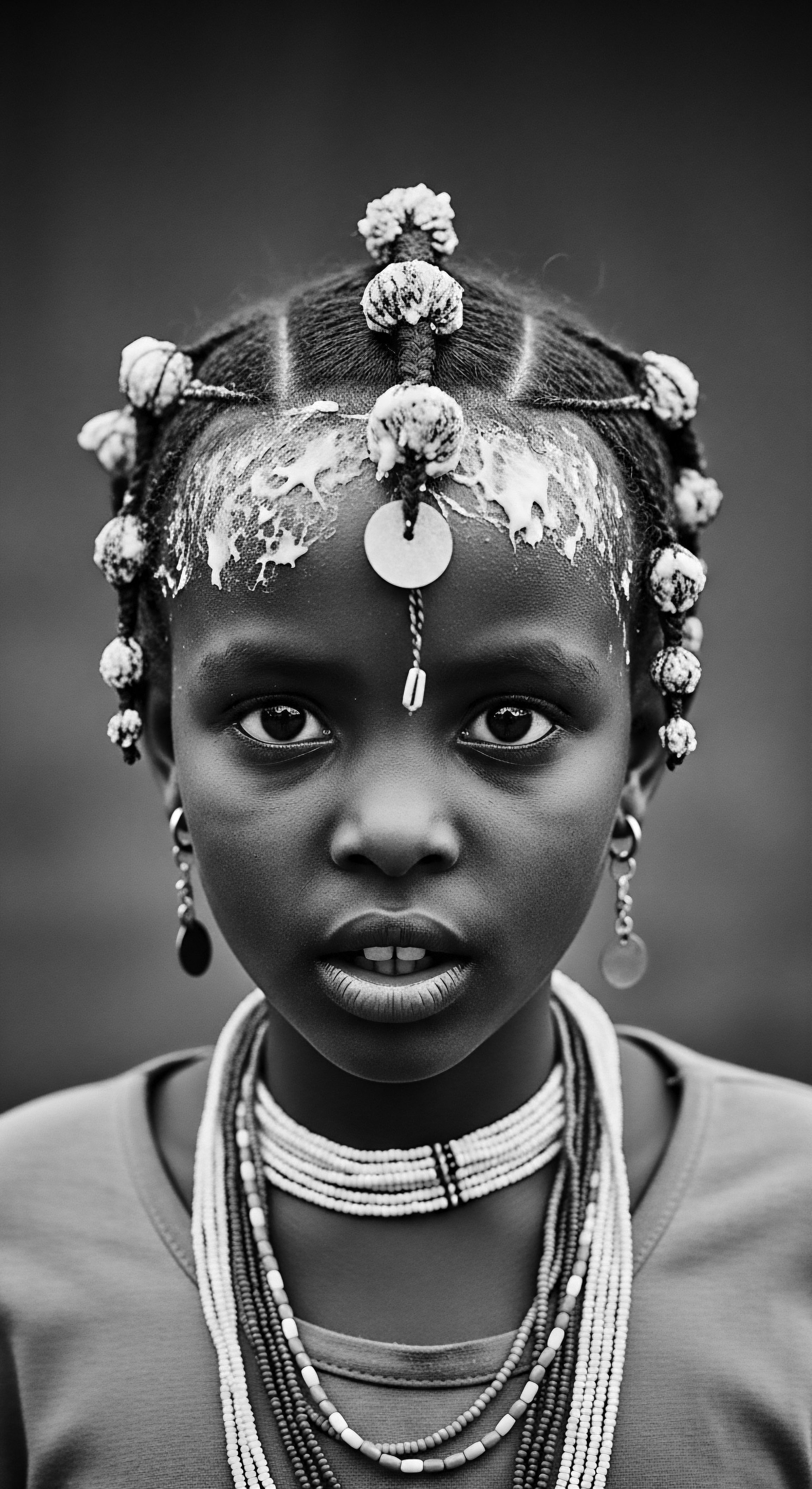

Racial Capital
Meaning ❉ Racial Capital is the societal value attributed to racial identity, often devalued through hair, yet powerfully reclaimed through heritage and cultural affirmation.
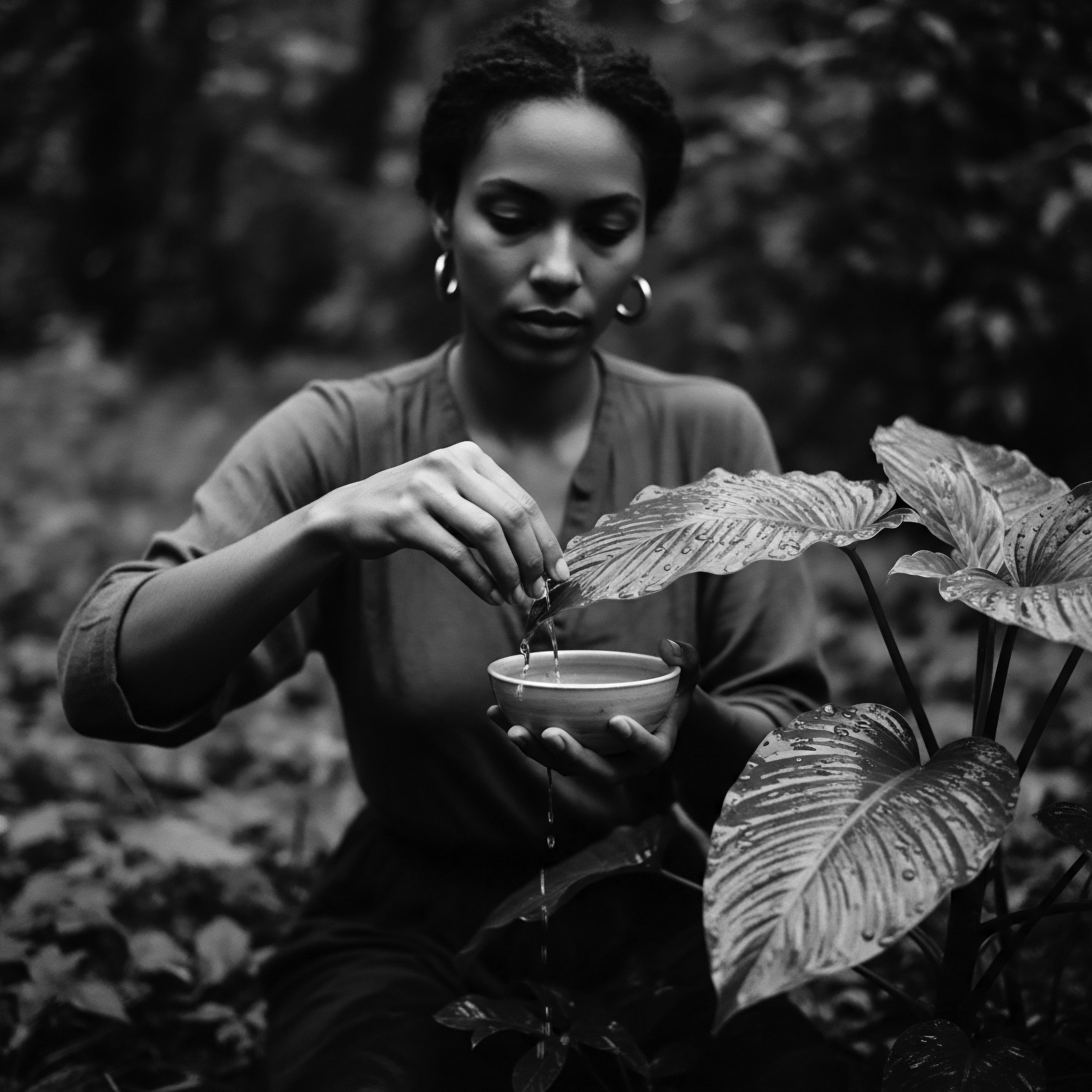

How Did Textured Hair Heritage Influence Resistance to the Tignon Law?
Textured hair heritage inspired defiant adornment of tignons, transforming a symbol of oppression into cultural pride.

How Did Free Women of Color Transform the Tignon Law’s Oppressive Mandate?
Free women of color transformed the Tignon Law's headwrap mandate into elaborate, defiant statements of enduring cultural heritage and identity.
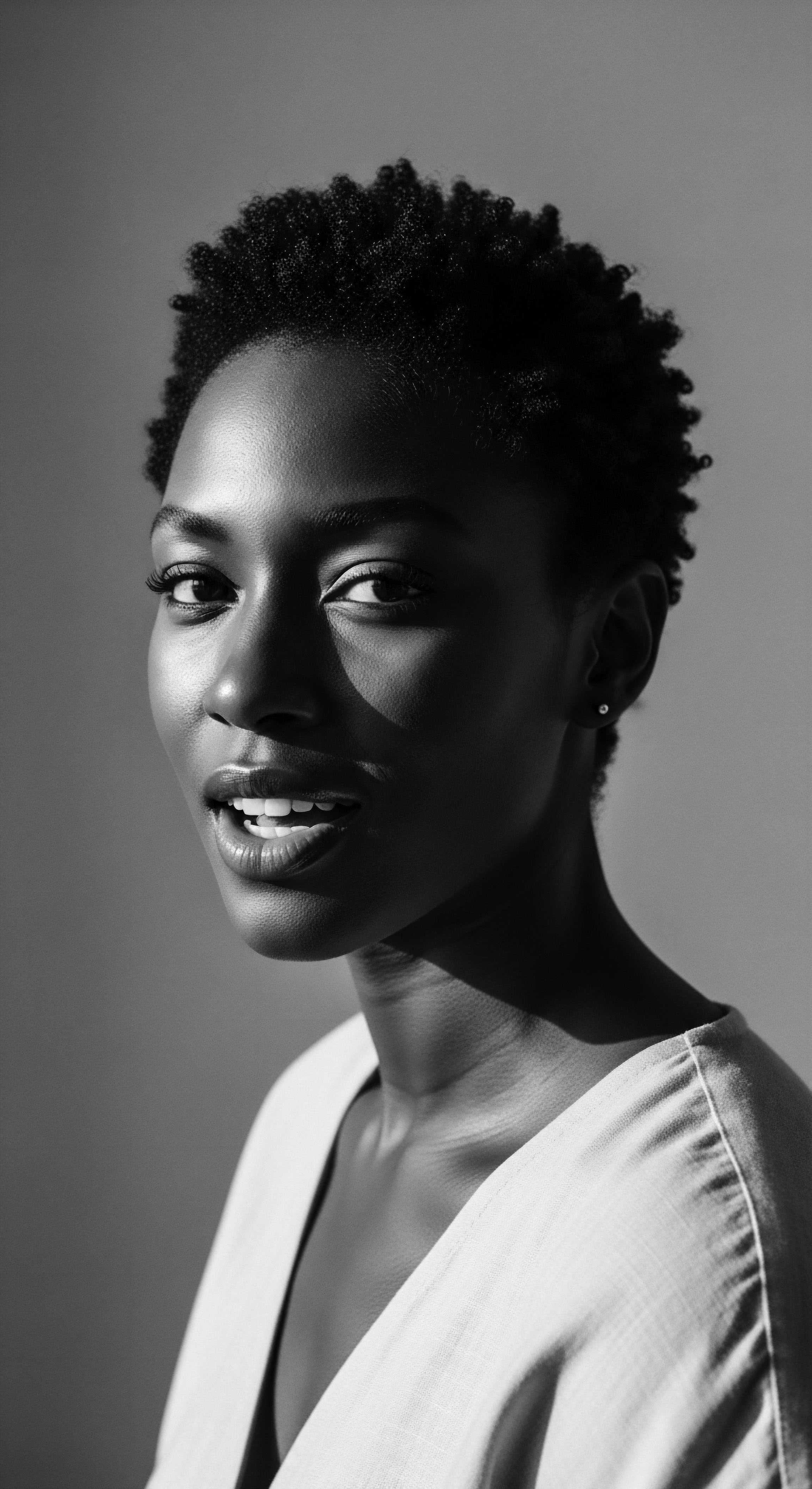

In What Ways Does Legal Recognition of Hair Heritage Promote Cultural Equity?
Legal recognition of hair heritage directly promotes cultural equity by validating diverse textured hair expressions, affirming identity.

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Laws like the Tignon Law Continue to Shape Textured Hair Experiences Today?
Historical hair laws like the Tignon Law continue to shape textured hair experiences through lingering biases and the powerful reclamation of heritage.
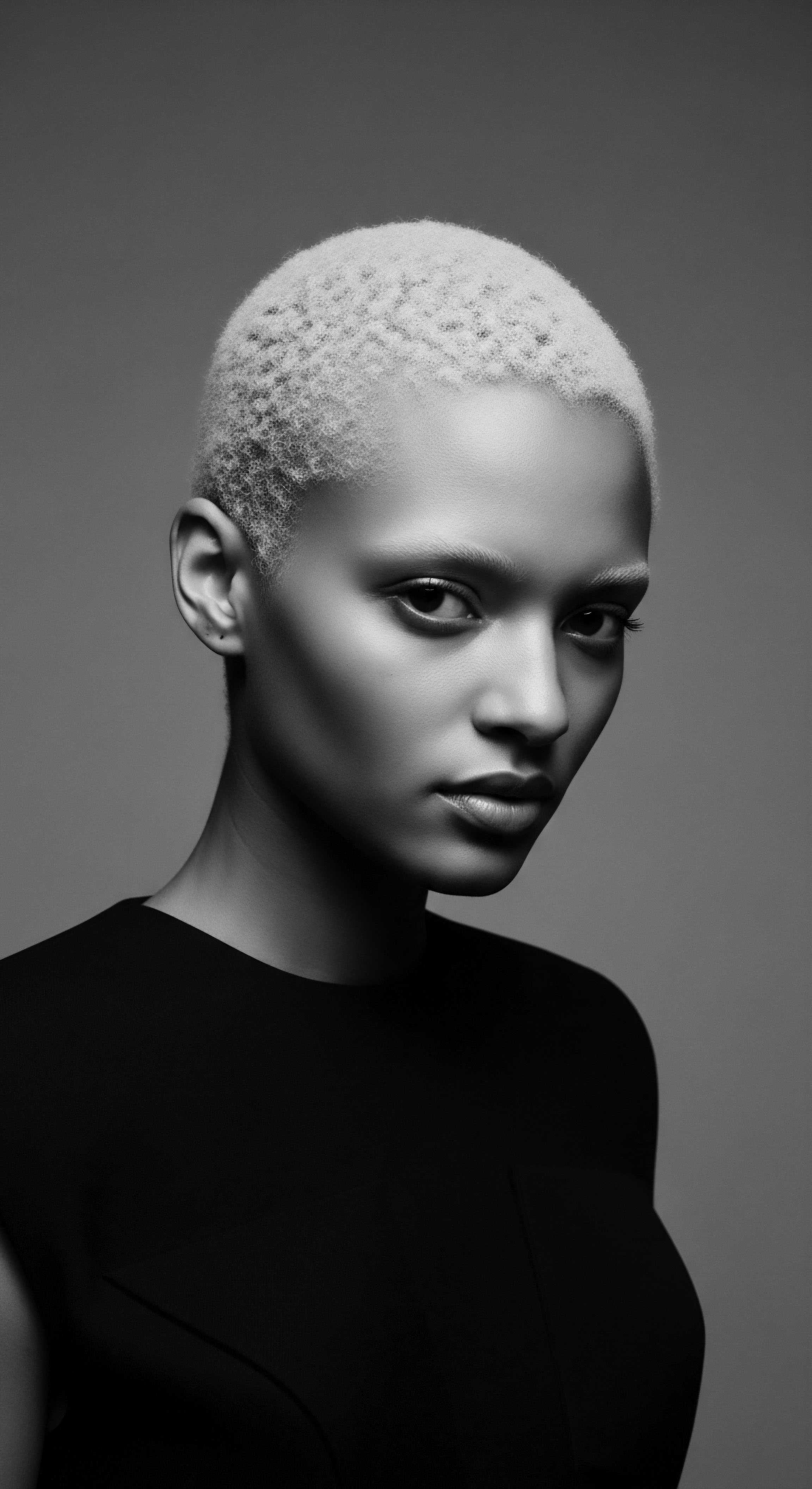

How Did the Tignon Law Affect Hair Care?
The Tignon Law forced free Black women to cover their hair, but they transformed wraps into defiant expressions of cultural heritage.
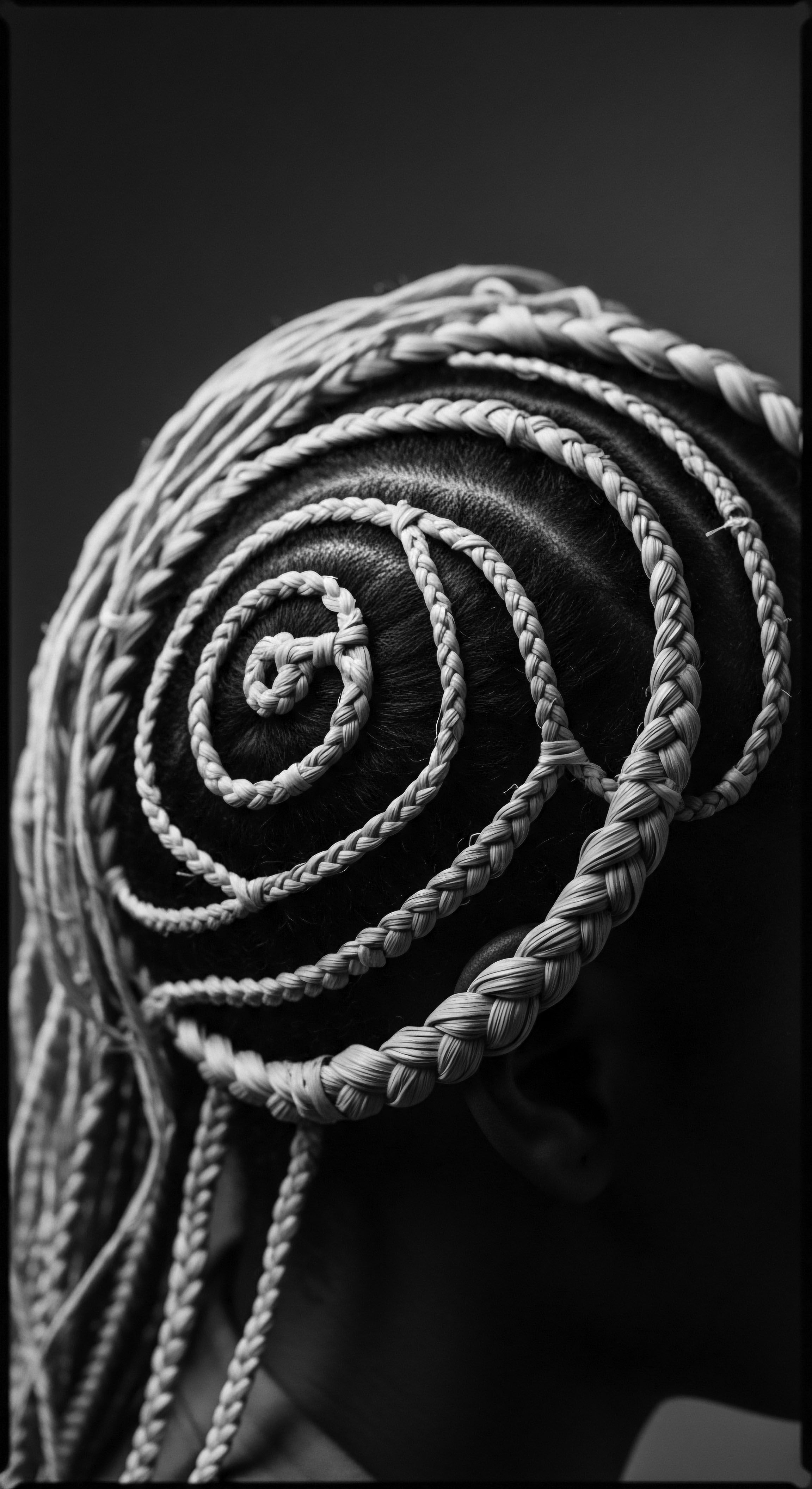

What Ancestral Hair Traditions Are Protected by Modern Law?
Modern laws, such as the CROWN Act, protect ancestral hair traditions by prohibiting race-based discrimination against textured hair and its protective styles.
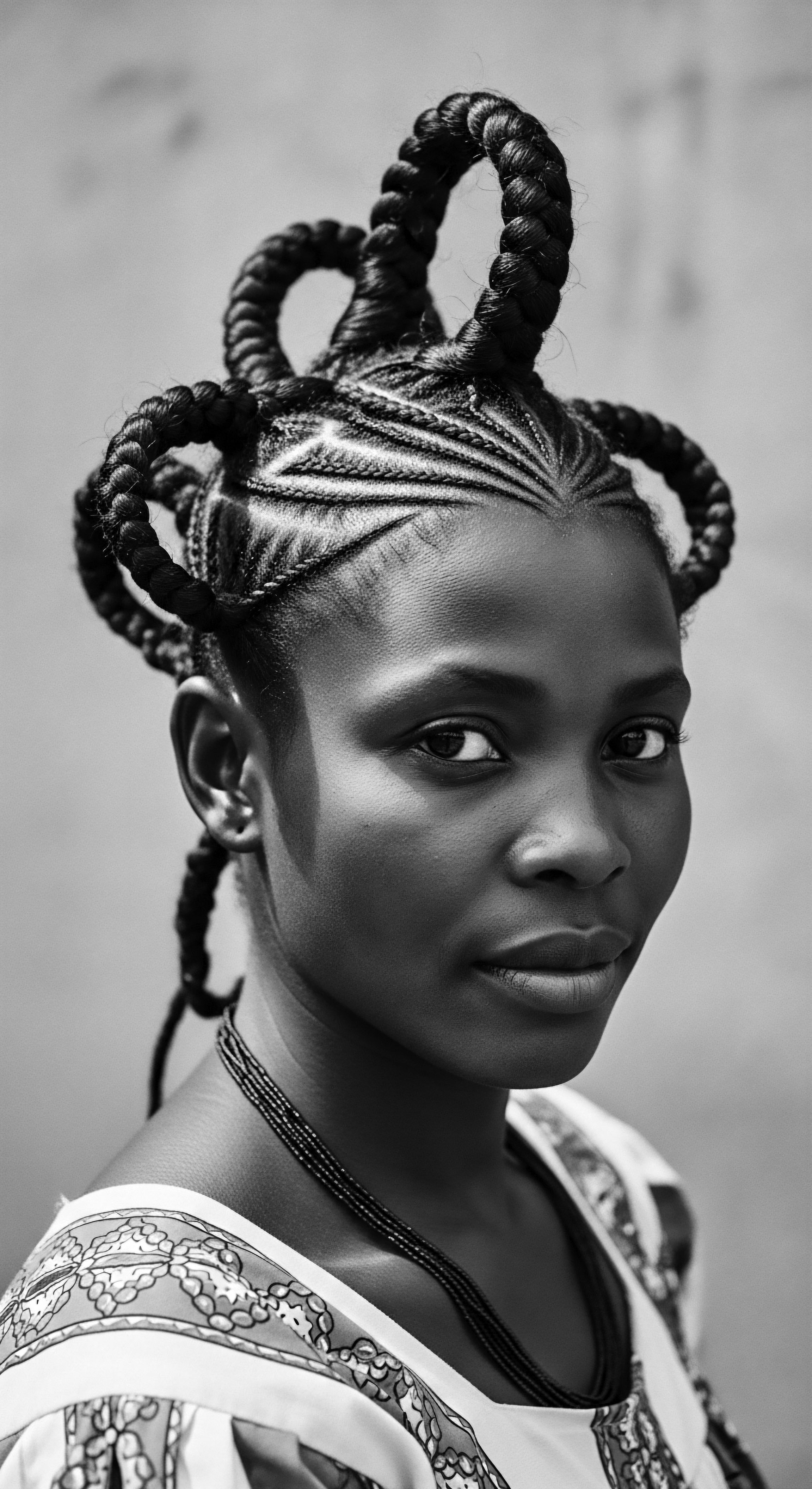

Sumptuary Law History
Meaning ❉ Sumptuary laws are historical regulations that controlled personal appearance, notably hair, often to maintain social hierarchy and suppress cultural expression.

Racial Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Racial Hair Control designates societal systems, legal actions, and biases that historically and presently impose Eurocentric beauty standards on textured hair.
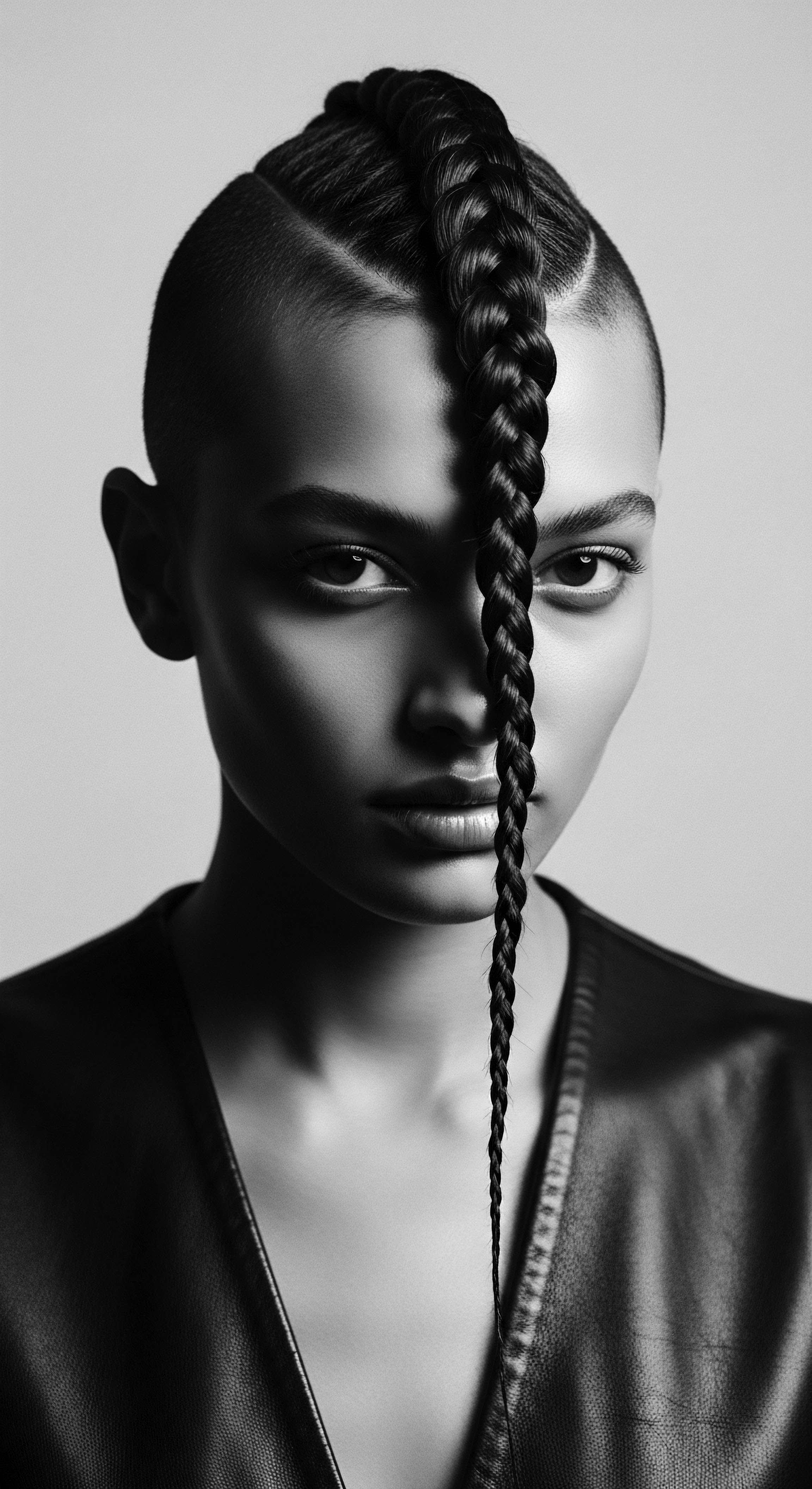

What Impact Does Heritage Recognition Have on Legal Protections for Textured Hair?
Heritage recognition provides a foundation for legal protections by affirming textured hair's profound cultural and racial significance.

How Does Modern Law Address Textured Hair Discrimination?
Modern law addresses textured hair discrimination by enacting legislation, particularly the CROWN Act, which protects natural and protective hairstyles as expressions of racial heritage.

