
Spiritual Labor
Meaning ❉ Spiritual Labor is the ancestral, emotional, and energetic investment transforming textured hair care into an act of profound identity and heritage.

Post-Slavery Migration
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Migration details the profound movements of African peoples after emancipation, shaping textured hair identity and care.

Colonial Labor Systems
Meaning ❉ Colonial Labor Systems structured work through coercion and exploitation, profoundly impacting textured hair as a site of identity and enduring resistance.

Caribbean Indenture
Meaning ❉ Caribbean Indenture describes a post-slavery labor system profoundly shaping Caribbean identities and enduring hair heritage through diverse migrations.

Post-Slavery Hair Impact
Meaning ❉ The Post-Slavery Hair Impact details how historical subjugation reordered perceptions and care of textured hair, influencing identity and opportunity.

Chinese Labor History
Meaning ❉ Chinese Labor History examines the work, migrations, and enduring heritage of Chinese communities globally, revealing subtle links to textured hair care traditions.

Cultural Labor
Meaning ❉ Cultural Labor defines the persistent, often unseen, efforts to sustain identity and heritage through textured hair care and cultural practices.

How Did Eurocentric Beauty Standards Influence Post-Slavery Hair Practices and Textured Hair Health?
Eurocentric beauty standards post-slavery led to harmful straightening practices, altering textured hair health and challenging ancestral identity.
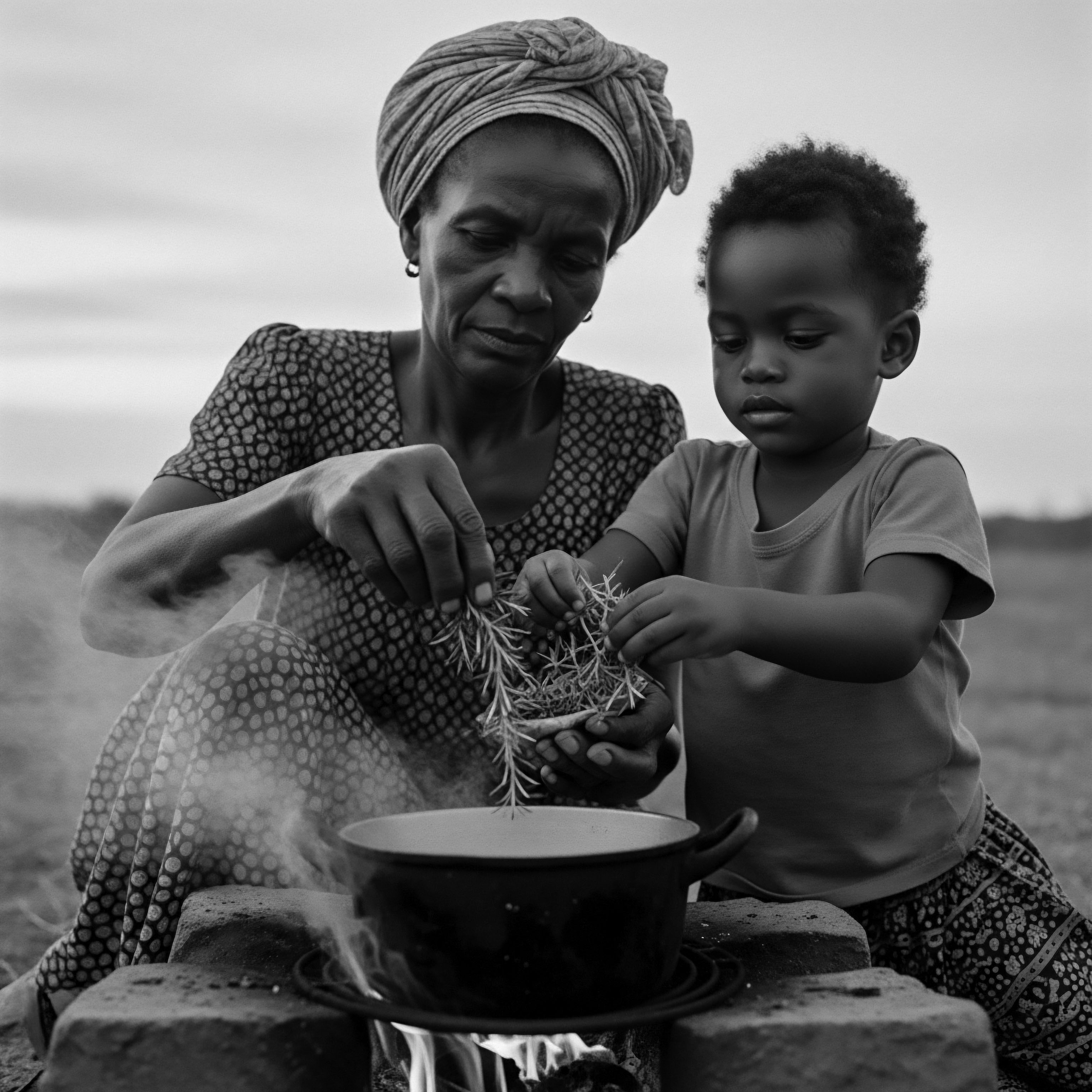

African American Labor
Meaning ❉ African American Labor, in hair care, is generations of work to cultivate, maintain, and imbue textured hair with cultural and economic meaning.

Chinese Indentured Labor
Meaning ❉ Chinese Indentured Labor was a system of coerced migration and exploitation, profoundly impacting global demographics and cultural hair heritage.

How Did Hair Care Rituals Preserve Heritage during Slavery?
Hair care rituals during slavery served as vital, covert anchors of cultural heritage and identity for enslaved African communities.

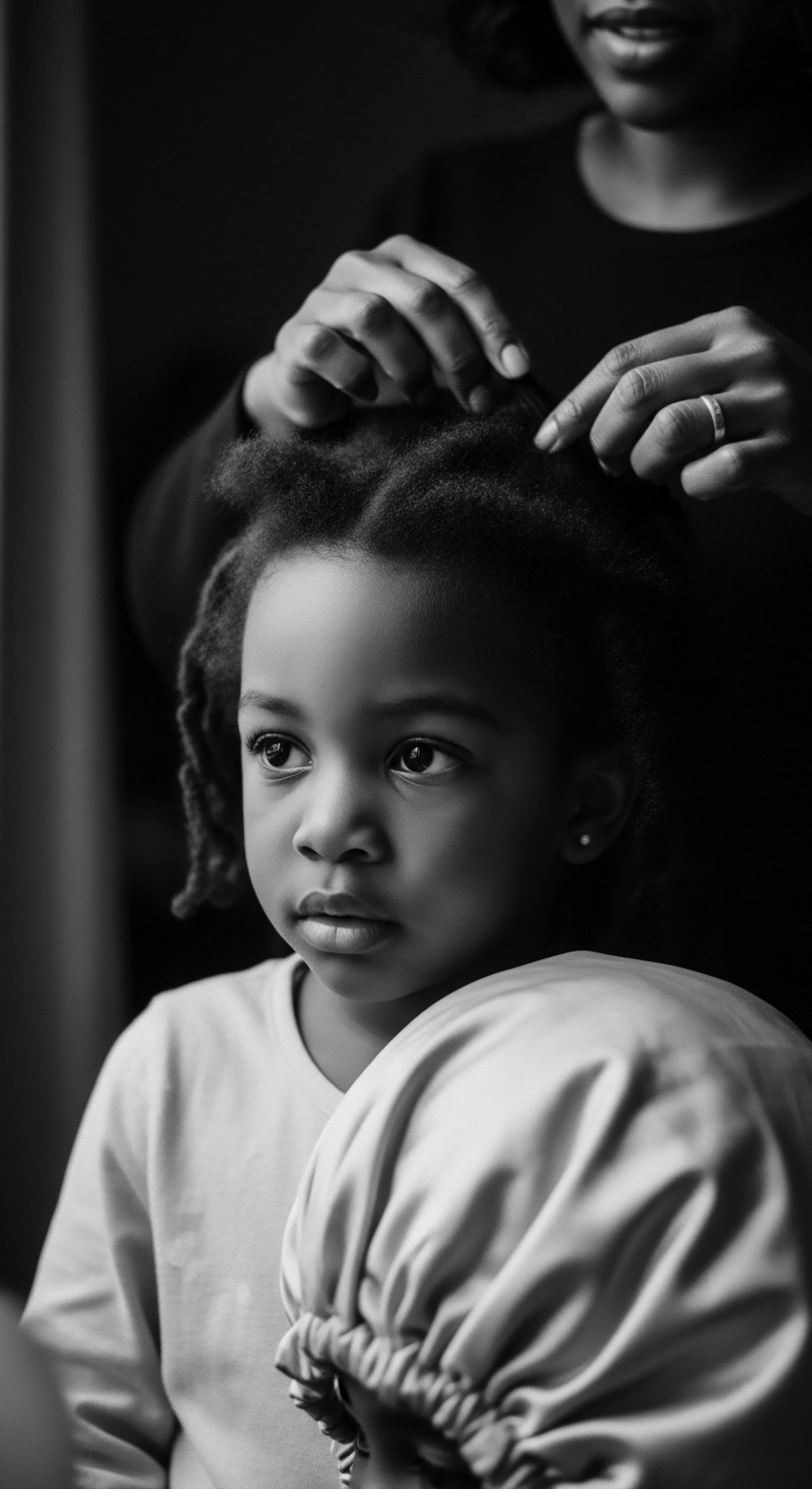
Post-Slavery Labor
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Labor delineates the enduring systems of work and racialized socioeconomic structures that emerged following emancipation, profoundly impacting Black and mixed-race communities and shaping their hair heritage.

How Did Slavery Disrupt Black Hair Care Heritage?
Slavery shattered ancestral Black hair care by stripping identity and access, forcing harmful adaptations that shaped enduring textured hair heritage.

Indentured Legacy
Meaning ❉ The Indentured Legacy details the ongoing historical, cultural, and personal impacts of indentured labor on identity and hair heritage.

Why Did Hair Care Become a Heritage Practice during Slavery?
Hair care became a heritage practice during slavery as a means of survival, covert communication, and resistance, deeply connecting to textured hair identity.

Slavery Hair Impact
Meaning ❉ The Slavery Hair Impact explains the historical oppression and profound cultural transformation of textured hair due to slavery.

Chinese Indentured Servitude
Meaning ❉ Chinese Indentured Servitude describes a 19th-century contractual labor system for Chinese migrants, often mirroring slavery's harsh conditions.

Indentured Labor History
Meaning ❉ This definition unpacks Indentured Labor History through the lens of textured hair heritage, revealing its profound impact on identity and cultural preservation.

Post-Genocide Identity
Meaning ❉ Post-Genocide Identity describes the profound shifts in self-perception and cultural connection following systematic attempts to obliterate a group's heritage.
In What Ways Did Braiding Communicate Heritage and Resistance during Slavery?
Braiding transformed textured hair into a discreet language, conveying heritage and vital messages of resistance for enslaved individuals.
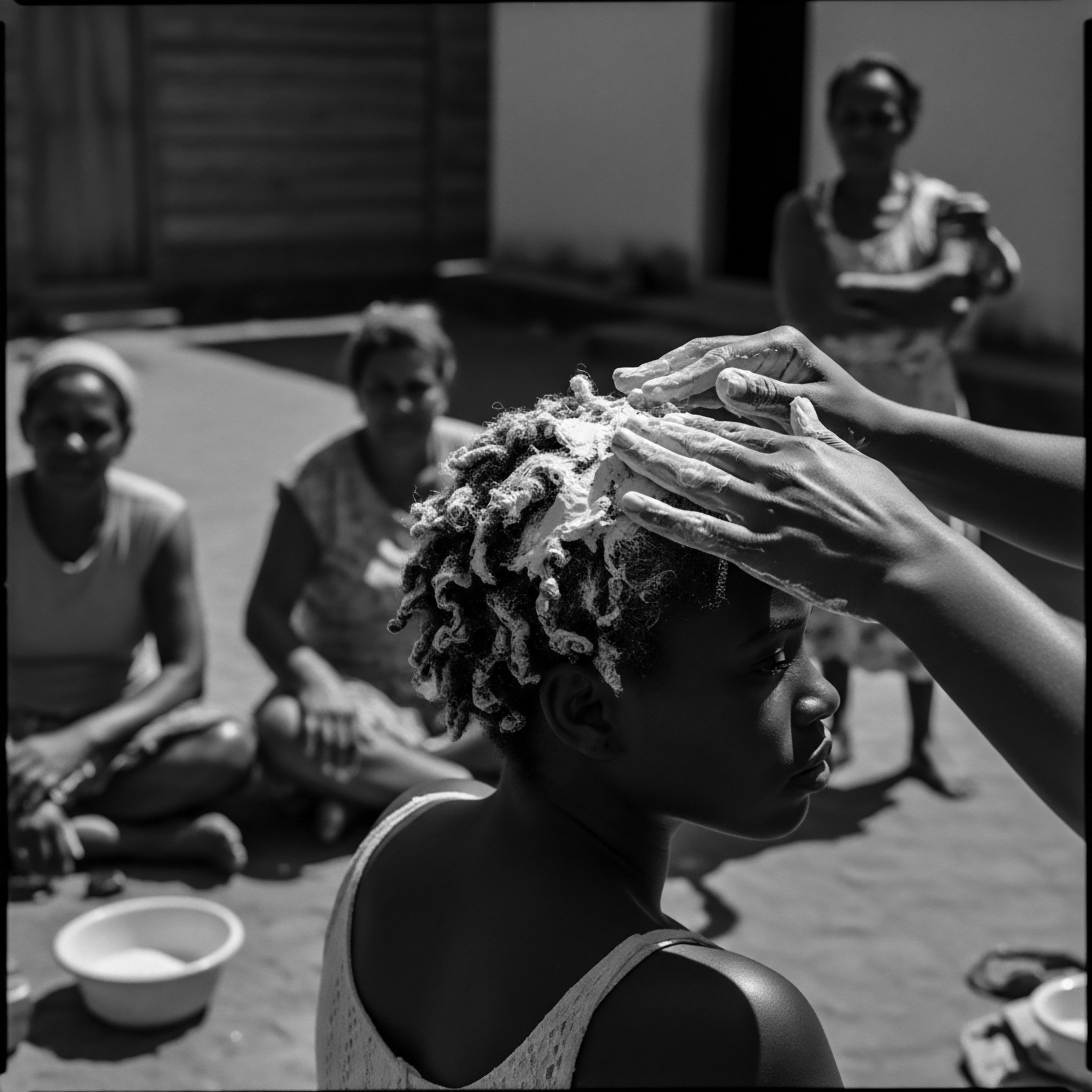

How Did Slavery Affect Black Hair Heritage?
Slavery disrupted but could not erase Black hair heritage, transforming care rituals into acts of resistance and identity preservation.

Indentureship
Meaning ❉ Indentureship defines a historical labor system involving contract-bound migration, profoundly shaping cultural identity and hair heritage in diasporic communities.

How Did Textured Hair Styling Serve as Resistance during Slavery?
Textured hair styling during slavery became a covert language and survival tool, deeply rooting acts of resistance within Black hair heritage.

Trans-Pacific Slavery
Meaning ❉ Trans-Pacific Slavery refers to the forced movement and subjugation of peoples across the Pacific, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and identity.

How Did Textured Hair Heritage Influence Acts of Defiance during Slavery?
Textured hair heritage served as a powerful, covert means of defiance during slavery, providing coded communication and preserving cultural identity.
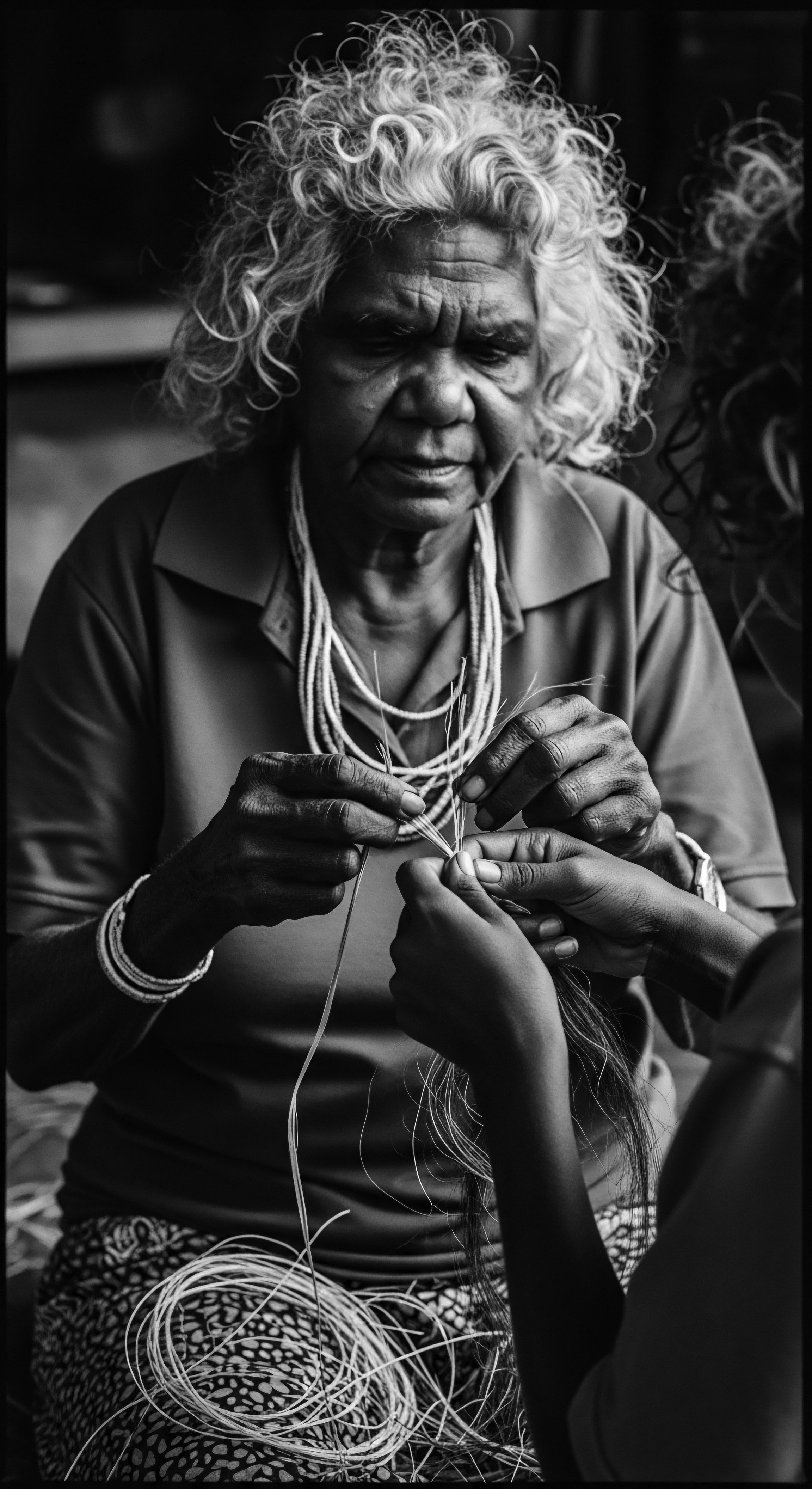

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Serve as a Symbol of Resistance during Slavery?
Textured hair served as a silent yet potent symbol of resistance during slavery, enabling hidden communication, preserving identity, and fostering communal bonds, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

Emotional Labor
Meaning ❉ Emotional Labor is the unseen emotional and psychological effort of managing one's self-presentation, particularly hair, to navigate societal expectations and biases rooted in heritage.
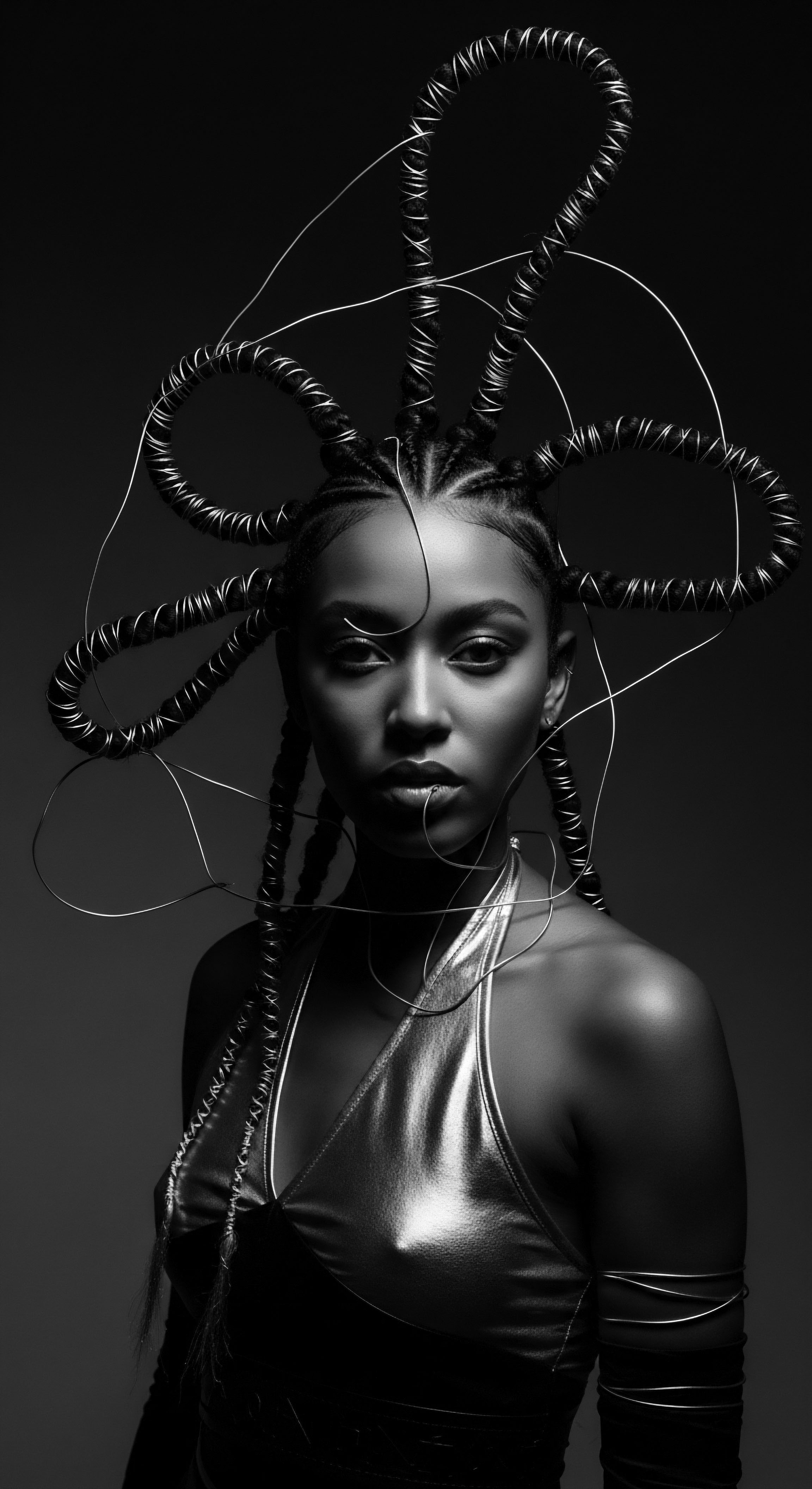

Post-Colonial Hair Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Hair Aesthetics examines how communities redefine hair beauty and care after colonialism, reclaiming ancestral practices and asserting identity.
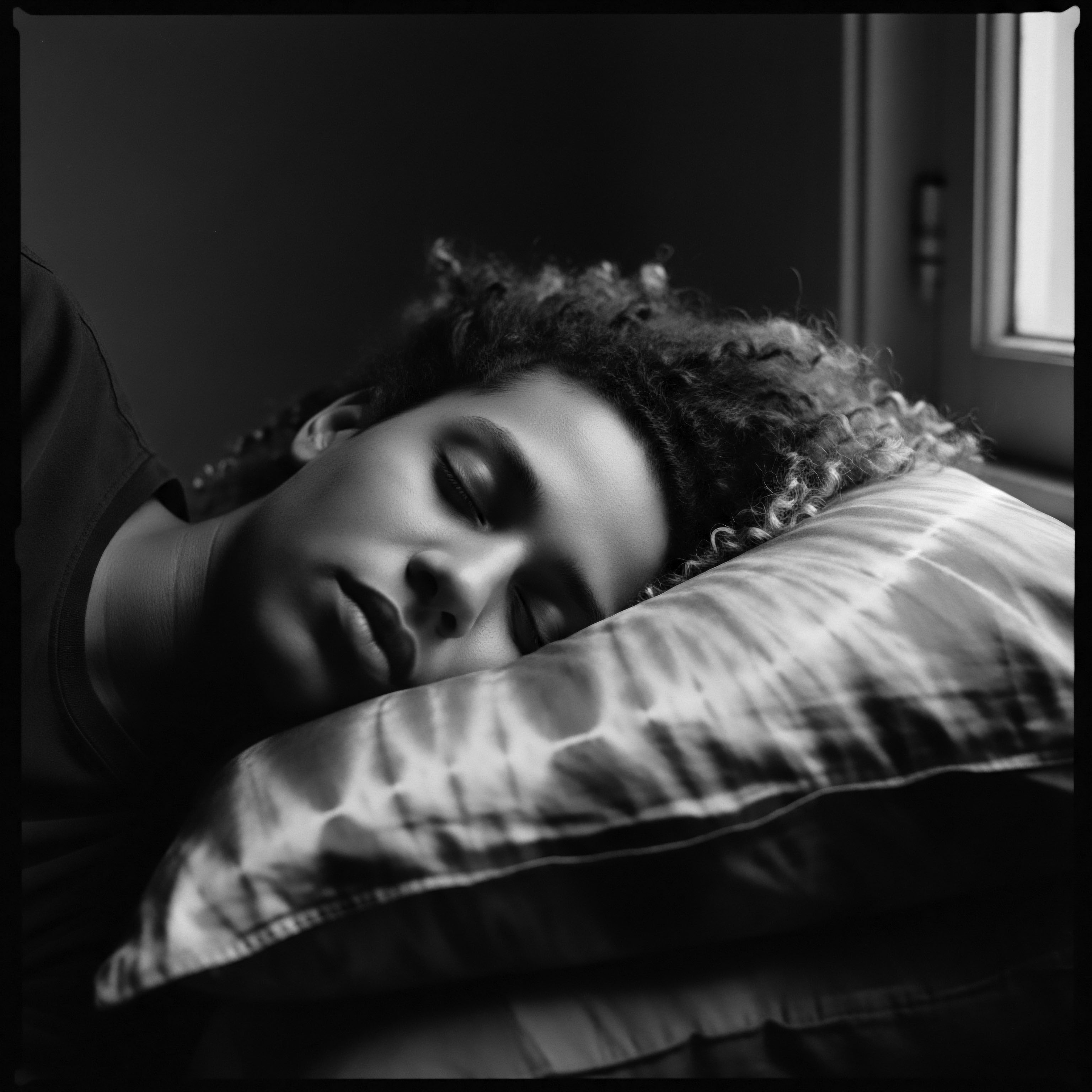

What Impact Did Slavery Have on Black Hair Cleansing Heritage?
Slavery severely disrupted Black hair cleansing heritage, forcing improvisation with limited resources while fostering communal care and eventual reclamation of ancestral practices.

