
Post-Slavery Economic Control
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Economic Control details the systemic economic restrictions on Black communities, profoundly influencing hair culture, consumption, and self-determination.

Post-Civil War Hair
Meaning ❉ Post-Civil War Hair denotes the transformative period where Black hair became a profound symbol of identity, economic agency, and cultural resilience.

Post-Emancipation Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Post-Emancipation Aesthetics defines the evolving beauty ideals and hair practices of African diasporic communities after slavery, marking a profound reclamation of identity and heritage.

Post Traumatic Slave Syndrome
Meaning ❉ Post Traumatic Slave Syndrome details the enduring psychological and behavioral impacts of chattel slavery and systemic racism on African-descended communities.

How Did Hair Care Rituals Preserve Cultural Heritage during Slavery?
Hair care rituals during slavery preserved cultural heritage, ancestral knowledge, and identity through acts of communal care and symbolic styling.

Slavery Identity
Meaning ❉ Slavery Identity describes the enduring impact of enslavement on the self-perception and cultural practices surrounding Black and mixed-race textured hair.

How Did Oil Use in Slavery Preserve Black Hair Heritage?
Oil use during slavery provided essential moisture, protection, and a vital link to ancestral hair care practices, preserving Black hair heritage.

Post-Slavery Exploitation
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Exploitation describes the systematic re-establishment of racialized oppression and economic control over Black communities after formal emancipation.

Post-Civil War Control
Meaning ❉ Post-Civil War Control defines the enduring societal imposition of Eurocentric beauty standards on Black hair, extending racialized control beyond slavery.

How Did Headwraps Become Symbols of Resistance during Slavery?
Headwraps, initially imposed as marks of servitude, transformed through creative defiance into potent symbols of cultural heritage and resistance during slavery.

In What Ways Did Nighttime Hair Rituals Serve as Cultural Resistance during Slavery?
Nighttime hair rituals during slavery served as vital acts of cultural preservation and self-affirmation, embodying deep textured hair heritage.
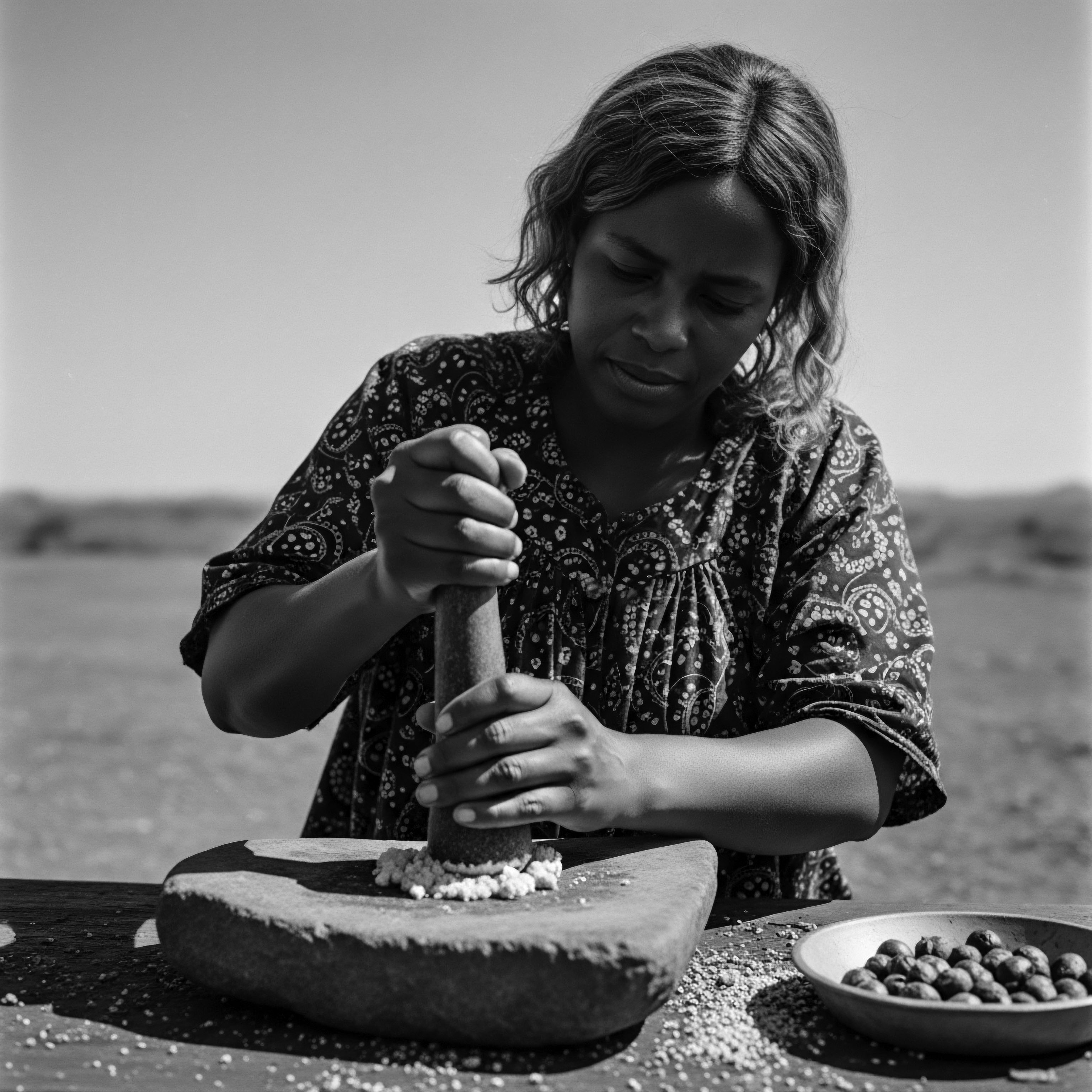

What Historical Role Did Hair Tools Play in Resistance during Slavery?
Hair tools served as instruments of covert resistance during slavery, allowing for hidden communication and survival through textured hair heritage.

How Did Cornrows Serve as a Tool for Resistance during Slavery?
Cornrows served as covert maps and carriers of ancestral knowledge, a resilient expression of textured hair heritage amidst enslavement.

Post-Slavery Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Post-Slavery Hair Heritage denotes the complex and evolving legacy of hair practices, beliefs, and identity for people of African descent.

How Did Ancestral Hair Care Traditions Persist through Slavery?
Ancestral hair care traditions persisted through slavery as vital acts of cultural preservation and quiet resistance.

How Did Plant-Based Care Preserve Hair Heritage during Slavery?
Plant-based care preserved textured hair heritage during slavery through adapted botanical knowledge and secret styling rituals.

Post-Slavery Migration
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Migration details the profound movements of African peoples after emancipation, shaping textured hair identity and care.

Post-Slavery Hair Impact
Meaning ❉ The Post-Slavery Hair Impact details how historical subjugation reordered perceptions and care of textured hair, influencing identity and opportunity.

How Did Eurocentric Beauty Standards Influence Post-Slavery Hair Practices and Textured Hair Health?
Eurocentric beauty standards post-slavery led to harmful straightening practices, altering textured hair health and challenging ancestral identity.

How Did Hair Care Rituals Preserve Heritage during Slavery?
Hair care rituals during slavery served as vital, covert anchors of cultural heritage and identity for enslaved African communities.

Post-Slavery Labor
Meaning ❉ Post-Slavery Labor delineates the enduring systems of work and racialized socioeconomic structures that emerged following emancipation, profoundly impacting Black and mixed-race communities and shaping their hair heritage.

How Did Slavery Disrupt Black Hair Care Heritage?
Slavery shattered ancestral Black hair care by stripping identity and access, forcing harmful adaptations that shaped enduring textured hair heritage.

Why Did Hair Care Become a Heritage Practice during Slavery?
Hair care became a heritage practice during slavery as a means of survival, covert communication, and resistance, deeply connecting to textured hair identity.

Slavery Hair Impact
Meaning ❉ The Slavery Hair Impact explains the historical oppression and profound cultural transformation of textured hair due to slavery.

Post-Genocide Identity
Meaning ❉ Post-Genocide Identity describes the profound shifts in self-perception and cultural connection following systematic attempts to obliterate a group's heritage.
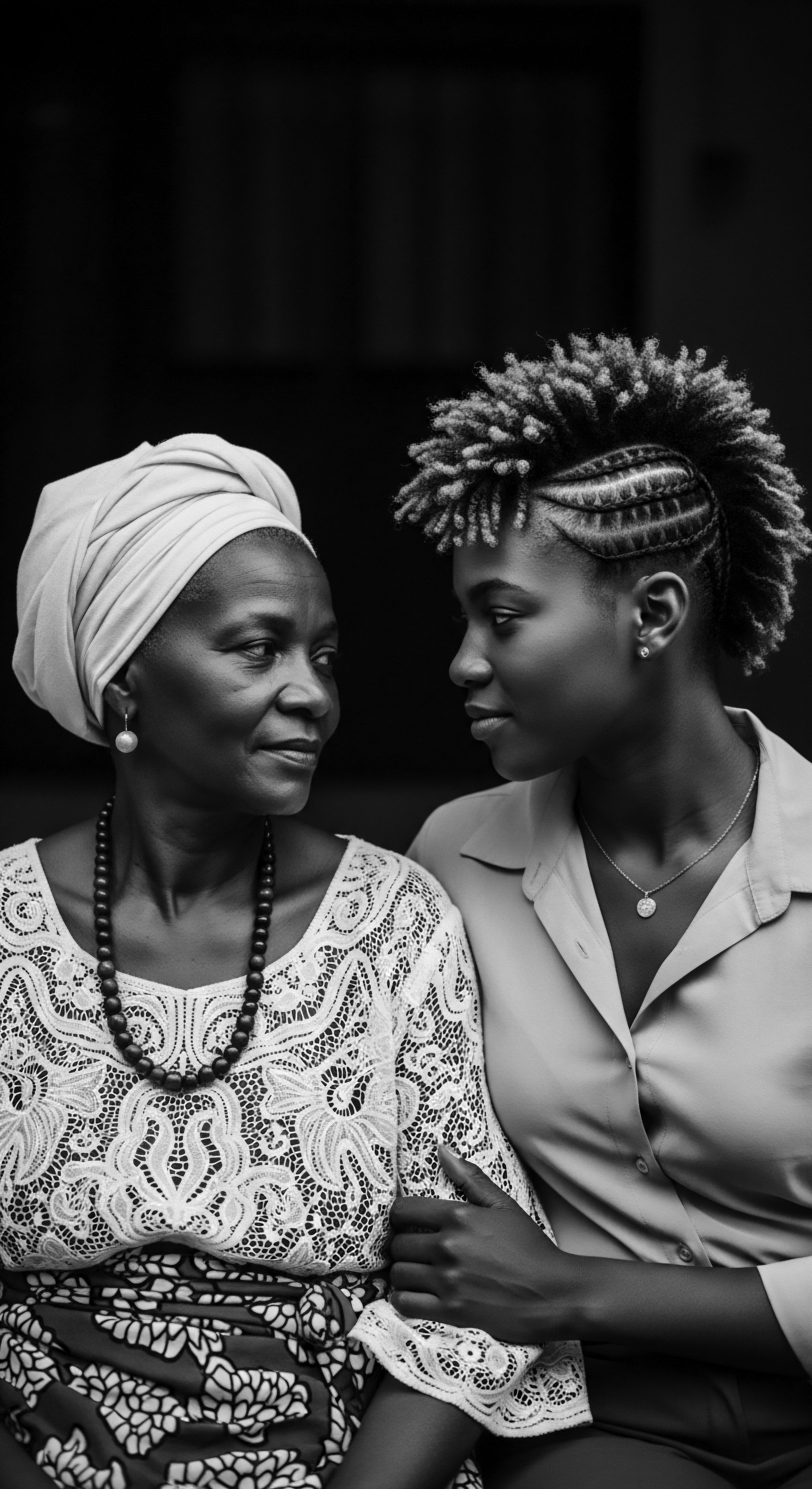
In What Ways Did Braiding Communicate Heritage and Resistance during Slavery?
Braiding transformed textured hair into a discreet language, conveying heritage and vital messages of resistance for enslaved individuals.
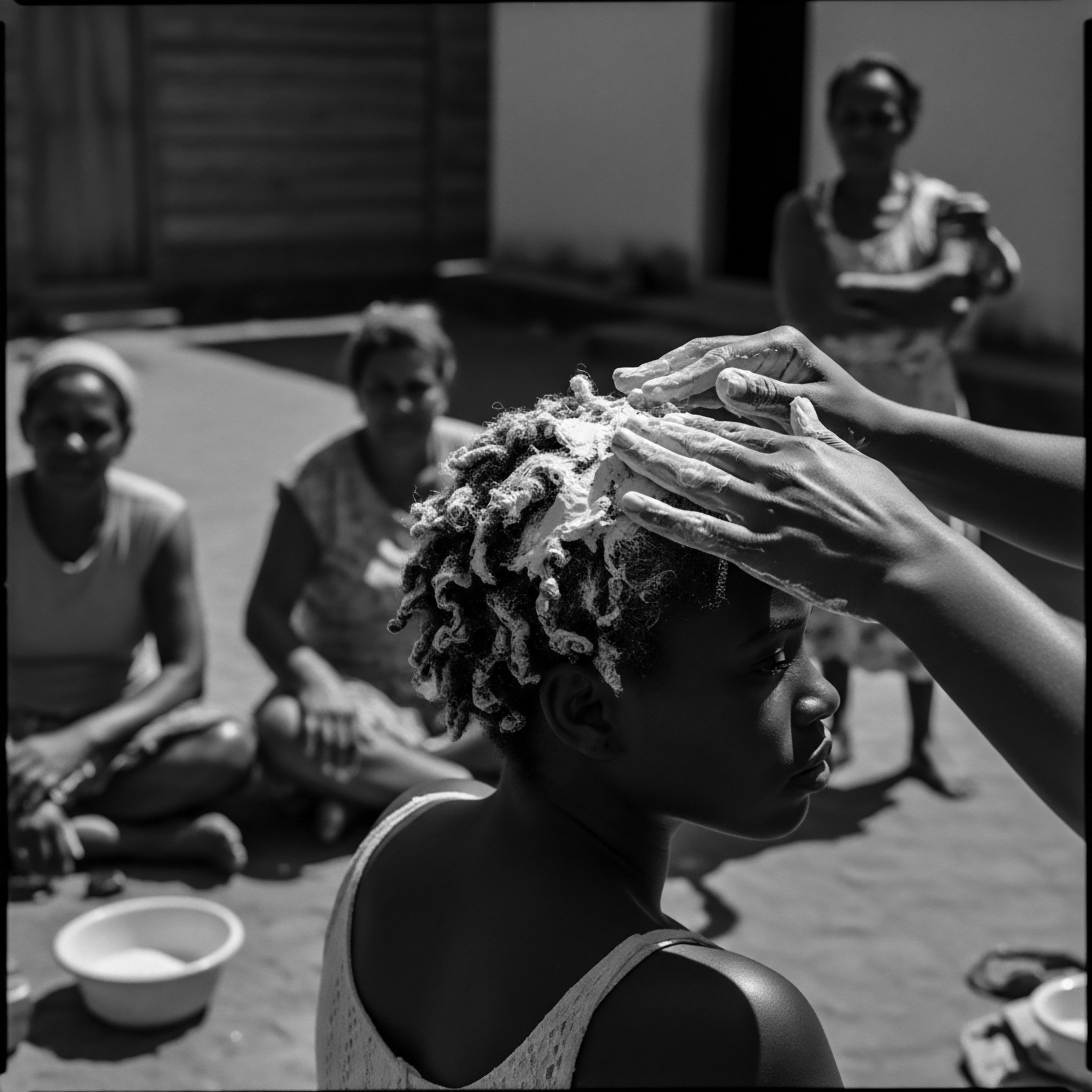

How Did Slavery Affect Black Hair Heritage?
Slavery disrupted but could not erase Black hair heritage, transforming care rituals into acts of resistance and identity preservation.

How Did Textured Hair Styling Serve as Resistance during Slavery?
Textured hair styling during slavery became a covert language and survival tool, deeply rooting acts of resistance within Black hair heritage.

Trans-Pacific Slavery
Meaning ❉ Trans-Pacific Slavery refers to the forced movement and subjugation of peoples across the Pacific, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage and identity.

