
What Modern Legislation Acknowledges Textured Hair Heritage?
Modern legislation like the CROWN Act protects textured hair and traditional styles, affirming their deep connection to racial and cultural heritage.

How Did Textured Hair Become a Symbol of Civil Rights?
Textured hair became a symbol of civil rights through acts of self-acceptance, defiance against oppression, and a return to ancestral pride.

How Does Legislation Address Hair Discrimination and Cultural Heritage?
Legislation now affirms textured hair as a cultural heritage, countering historical discrimination and protecting ancestral expressions.

How Did the Civil Rights Movement Impact Textured Hair Traditions?
The Civil Rights Movement spurred a powerful reclamation of textured hair heritage, transforming it into a symbol of Black pride and identity.

Civil Rights Impact
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Impact refers to the profound effects of the Civil Rights Movement on the recognition, acceptance, and celebration of textured hair heritage.

Post-Colonial Hair Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Hair Aesthetics examines how communities redefine hair beauty and care after colonialism, reclaiming ancestral practices and asserting identity.
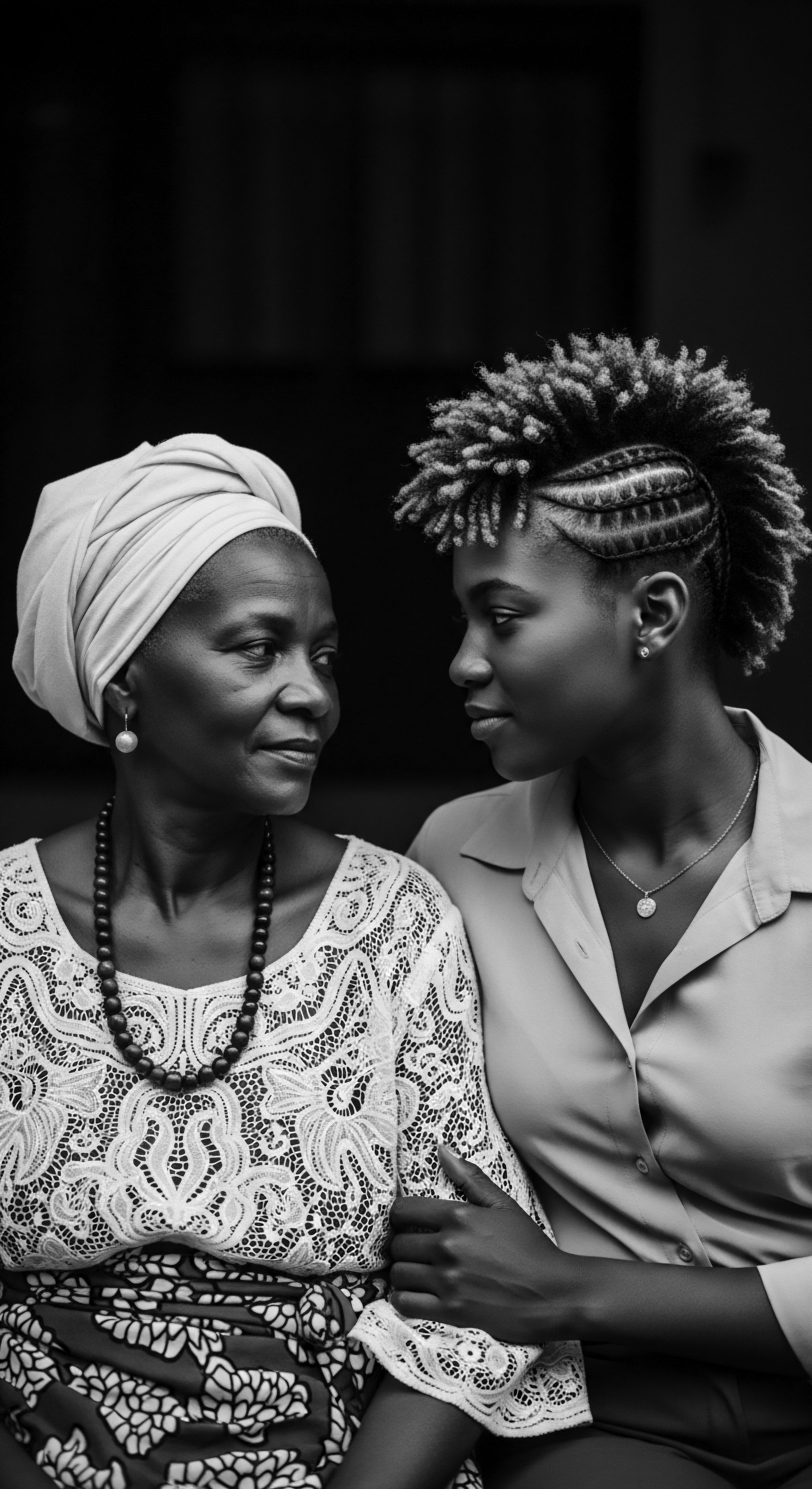
What Impact Did the Civil Rights Movement Have on Textured Hair Acceptance?
The Civil Rights Movement fostered a powerful embrace of natural textured hair, reclaiming it as a symbol of Black identity and heritage.

How Did the Civil Rights Movement Influence Textured Hair’s Cultural Identity?
The Civil Rights Movement shifted textured hair from a site of imposed conformity to a powerful expression of Black heritage and liberation.

How Did the Civil Rights Movement Reshape Textured Hair’s Cultural Meaning?
The Civil Rights Movement transformed textured hair's meaning by affirming its beauty, rejecting assimilation, and reclaiming it as a powerful symbol of Black pride and heritage.

Civil Rights Legacy
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Legacy is the enduring fight for dignity and equity, particularly through the reclamation of textured hair heritage.

Post-Colonial Hair Identity
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Hair Identity signifies the profound journey of reclaiming and redefining selfhood and ancestral dignity through textured hair in the aftermath of colonial influence.

In What Ways Did the Civil Rights Movement Alter Textured Hair’s Cultural Standing?
The Civil Rights Movement significantly altered textured hair's cultural standing by fostering Black pride, leading to a widespread embrace of natural styles and ancestral care practices.

Anti-Discrimination Legislation
Meaning ❉ Anti-Discrimination Legislation safeguards individuals from prejudice based on protected characteristics, notably protecting textured hair as a vital aspect of identity.

Post-Apartheid Identity
Meaning ❉ A complex, evolving sense of self for South Africans, profoundly shaped by the legacy of apartheid and the reclamation of textured hair heritage.

How Does Modern Legislation Protect Natural Hair Heritage?
Modern legislation safeguards natural hair, protecting textured hair heritage and cultural identity against discrimination.

What Historical Biases against Textured Hair Does Current Legislation Challenge?
Current legislation confronts historical biases against textured hair by affirming its cultural significance and protecting ancestral styles.

Post-Colonial Identity
Meaning ❉ The Post-Colonial Identity describes the evolving selfhood of individuals and societies shaped by imperial rule, profoundly influencing textured hair heritage.

Post-Colonial Hair Politics
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Hair Politics examines how historical colonial beauty standards continue to shape perceptions and experiences of textured hair.

How Does Legislation like the CROWN Act Address Hair Discrimination and Heritage?
The CROWN Act addresses hair discrimination by legally protecting natural and protective hairstyles, affirming their deep connection to textured hair heritage.

Post-Colonial Beauty Standards
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Beauty Standards denote the lasting influence of colonial aesthetics on hair and appearance within formerly colonized and diasporic communities.

How Does Modern Legislation Protect Textured Hair Heritage?
Modern legislation protects textured hair heritage by prohibiting discrimination based on hair texture and culturally significant styles.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Symbolize Resistance during the Civil Rights Era?
Textured hair symbolized resistance during the Civil Rights era by visibly asserting Black pride, rejecting Eurocentric beauty norms, and reconnecting with ancestral heritage.

What Modern Legislation Protects Textured Hair Expression and Ancestral Styles?
Modern legislation safeguards textured hair expression and ancestral styles by explicitly defining race to include hair texture and protective hairstyles, affirming cultural heritage.

Post-Emancipation Hair
Meaning ❉ Post-Emancipation Hair describes the historical and ongoing impact of liberation on textured hair identity and practices within the African diaspora.

In What Ways Did the Civil Rights Movement Reshape Views on Black Hair Heritage?
The Civil Rights Movement reshaped Black hair views by affirming natural texture as a symbol of pride and heritage, rejecting imposed Eurocentric norms.

Post-Colonial Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Aesthetics defines the re-evaluation and celebration of textured hair, reclaiming ancestral beauty narratives from colonial impositions.

Civil Rights Era
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Era was a pivotal period where Black Americans asserted their rights, transforming societal norms and reclaiming identity through hair heritage.

Post-Colonial Hair
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Hair signifies the historical impact of colonial beauty standards on textured hair and the ongoing reclamation of ancestral hair traditions.

Post-Colonial Economics
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Economics, within Roothea's library, is the economic impact of colonial legacies on textured hair practices, perceptions, and commercial landscapes.

