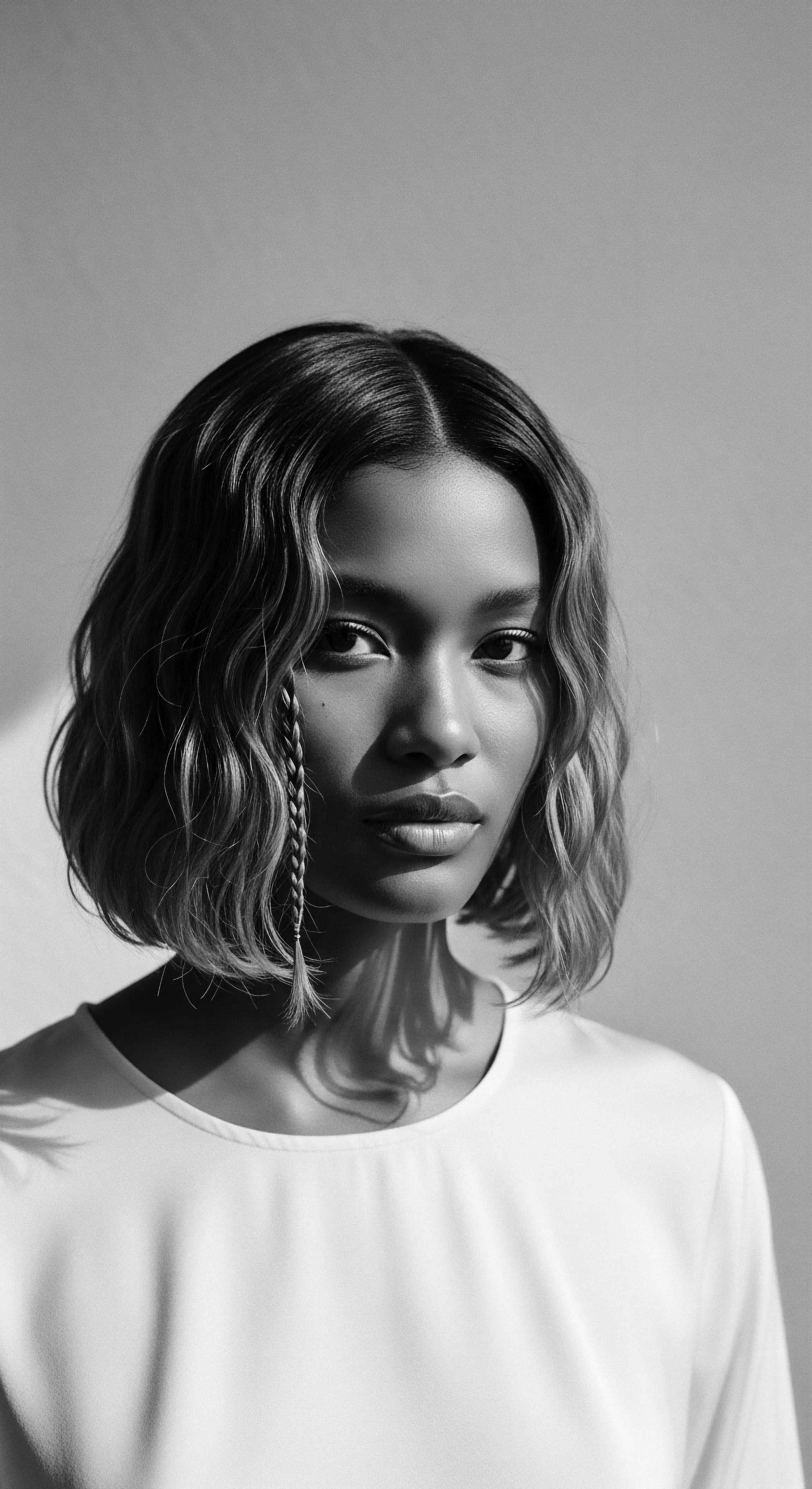

Textured Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Control is the deep, heritage-rooted understanding and intentional management of coiled hair through traditional and evolving cultural practices.

Post-Colonial Resilience
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Resilience is the enduring capacity of formerly colonized peoples to reclaim and uphold their distinct cultural identity through practices like hair heritage.
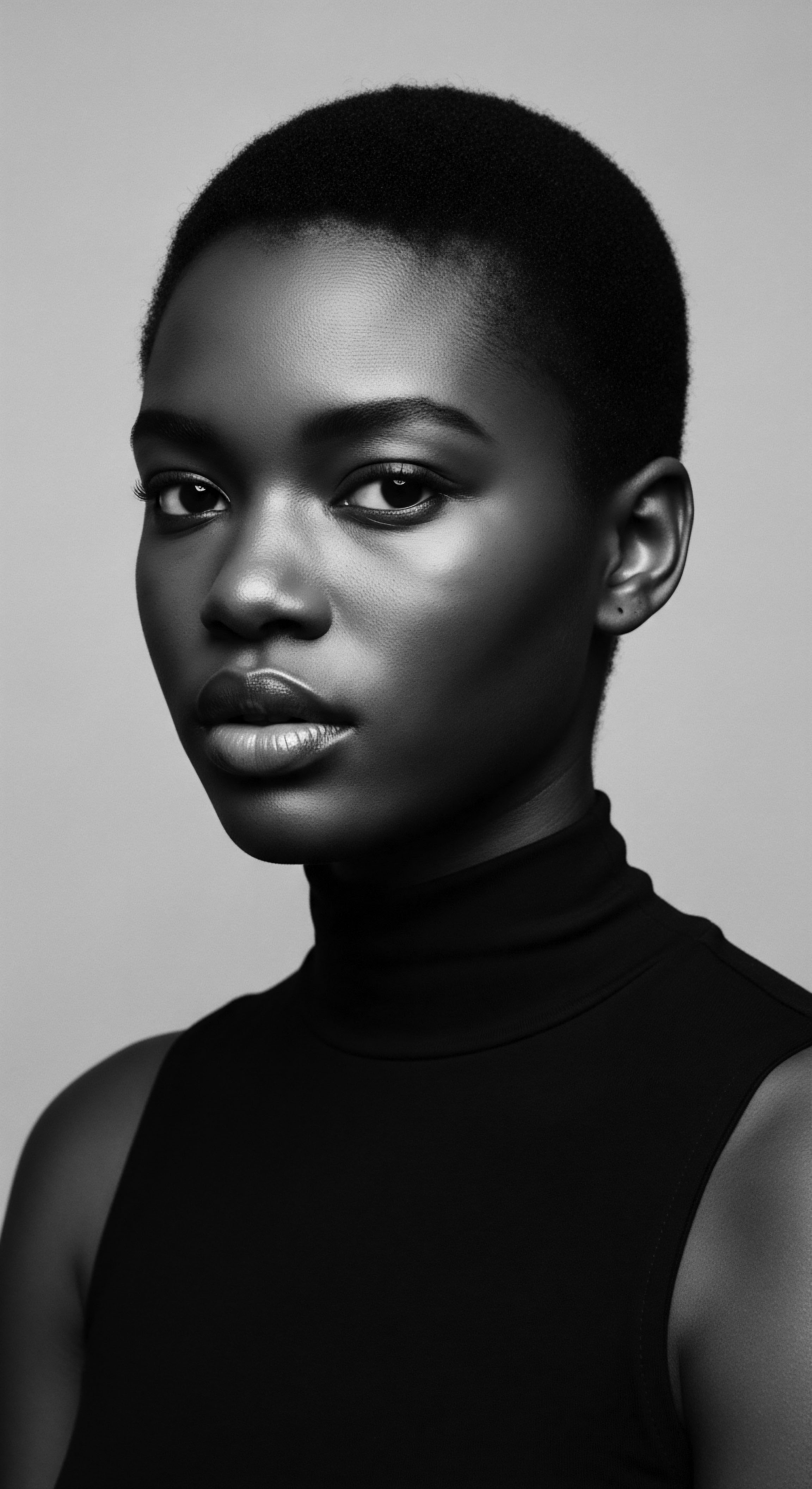

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Become a Political Statement during the Civil Rights Movement?
Textured hair became a political statement by embodying self-acceptance, challenging Eurocentric beauty standards, and visibly asserting Black pride and heritage during the Civil Rights Movement.
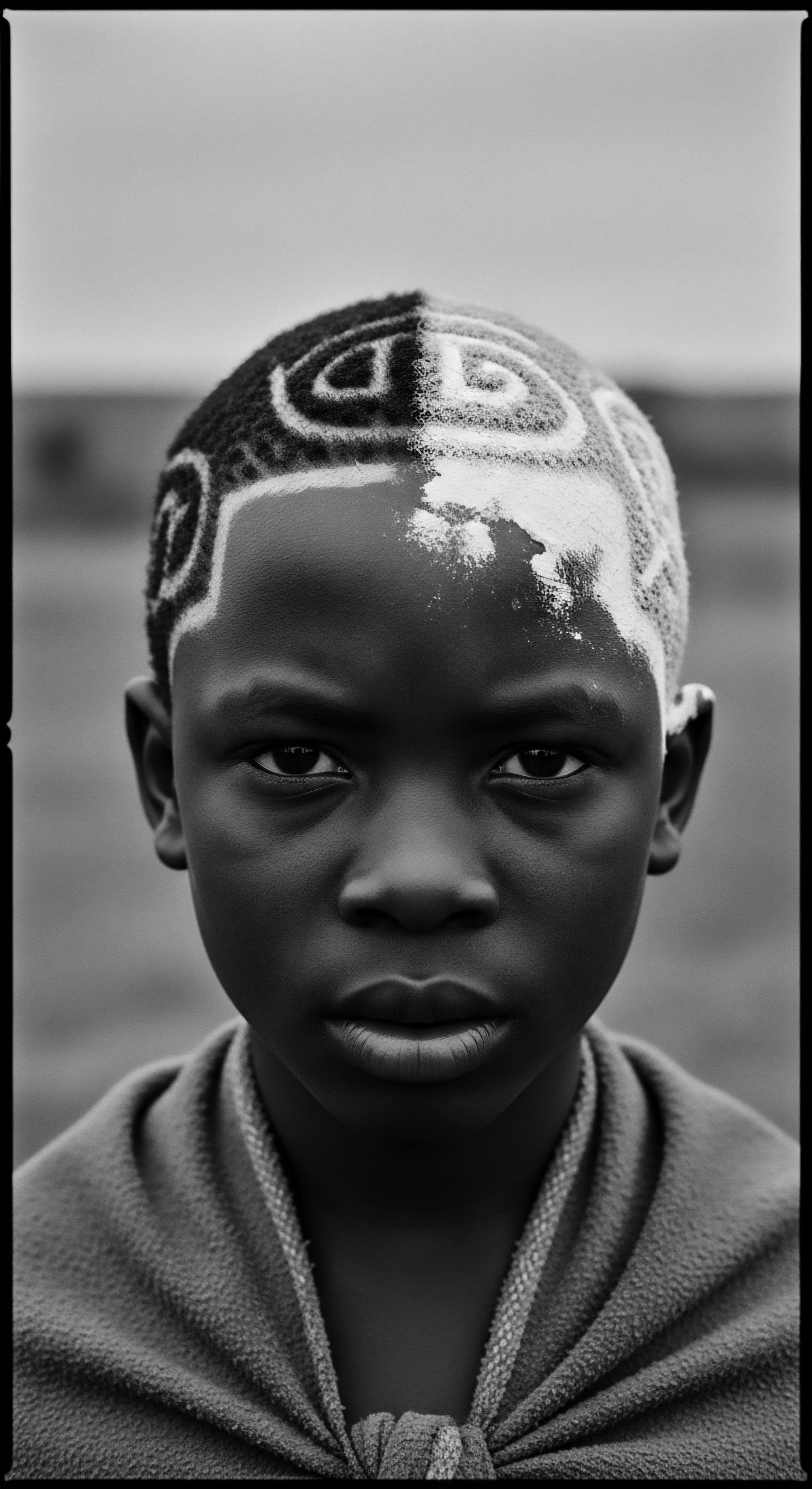

Slave Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Slave Hair Control denotes the systematic subjugation and dehumanization of Black people through the forced manipulation and devaluation of their hair.

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Hair and Why?
Historical laws aimed to control Black hair as a means of social subordination, inadvertently strengthening textured hair heritage through resilience.
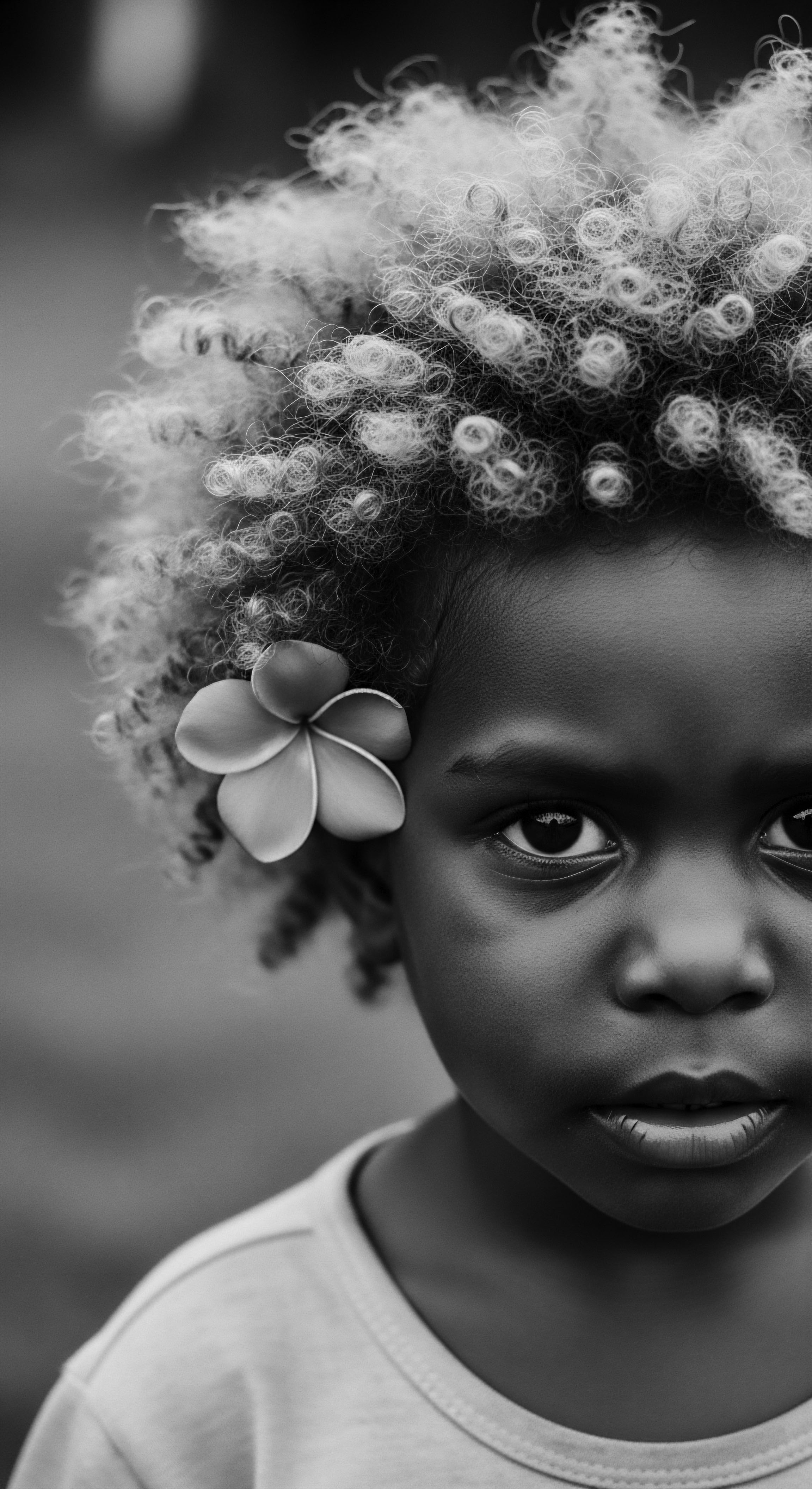

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Hair Identity?
Historical laws aimed to control Black hair, most notably the Tignon Laws, served to suppress identity and enforce social hierarchy.

What Historical Laws Attempted to Control Black Hair Expression?
Historical laws attempted to control Black hair expression by forcing conformity, but textured hair heritage consistently found avenues for powerful resistance.
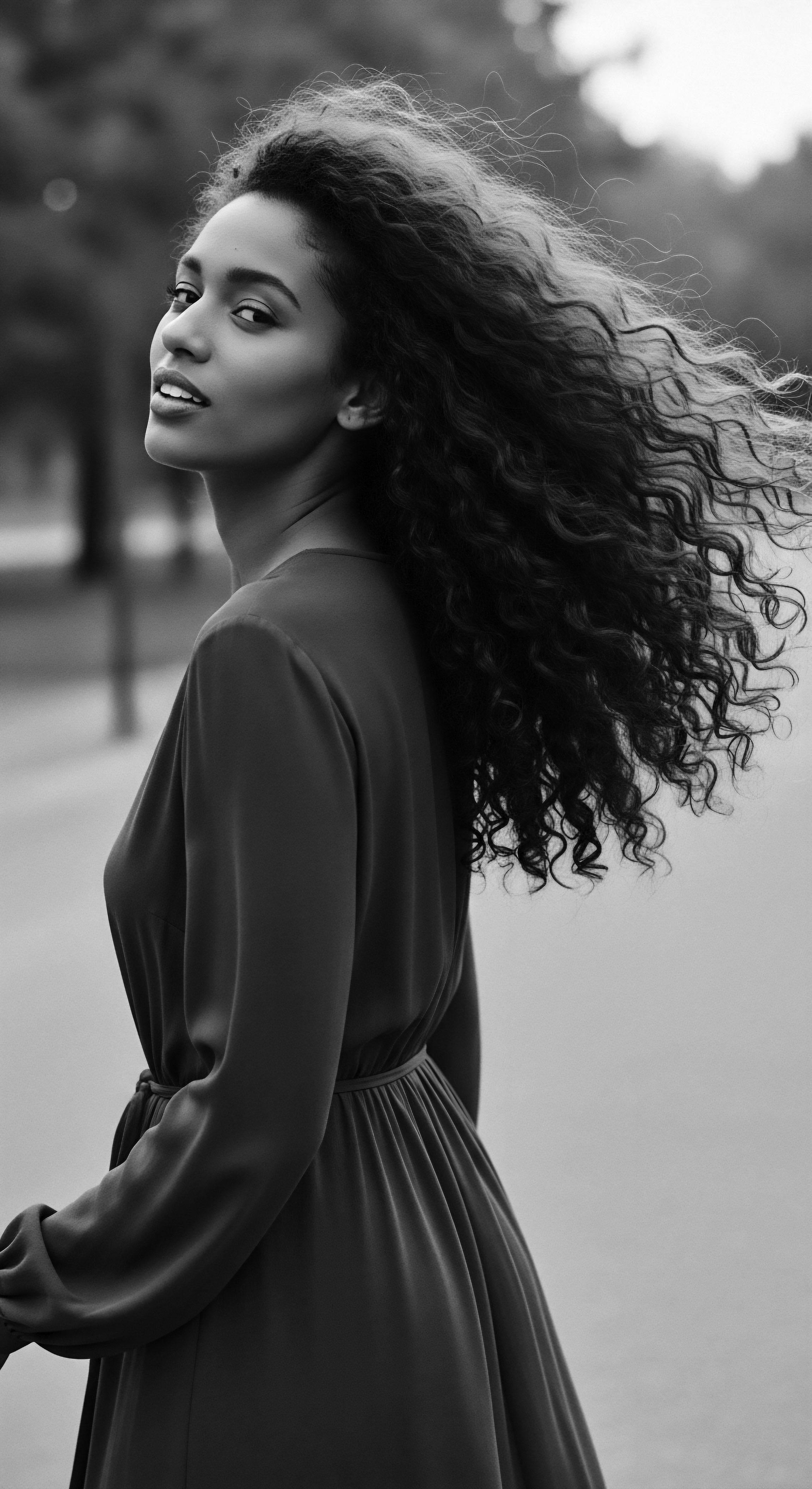

Civil Rights Barbershops
Meaning ❉ Civil Rights Barbershops were pivotal community centers for Black men, blending hair care with vital political strategy and cultural affirmation during segregation.
How Did Hair Defy Colonial Control?
Textured hair defied colonial control by serving as a profound vessel for ancestral knowledge, cultural identity, and enduring self-expression.

Civil Rights Identity
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Identity manifests as the inherent right to selfhood and authentic expression, particularly through textured hair heritage, against systemic discrimination.

How Did Textured Hair Become a Symbol of Identity during Civil Rights?
Textured hair transformed into a powerful identity symbol during Civil Rights by rejecting imposed norms and embracing authentic ancestral heritage.

What Ancestral Hair Practices Persisted during Slavery and Civil Rights?
Ancestral hair practices persisted through slavery and Civil Rights by adapting to harsh conditions and serving as powerful symbols of Black and mixed-race heritage.

What Historical Laws Sought to Control Black Women’s Hair?
Historical laws sought to control Black women's hair by devaluing natural styles, forcing conformity, and suppressing cultural heritage.

Post-Colonial Beauty
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Beauty defines the reclamation of indigenous hair traditions as a powerful act of identity and resistance against colonial impositions.

How Did Ancient Hair Practices Resist Colonial Control?
Ancient hair practices preserved textured hair heritage by embodying cultural identity, self-sufficiency, and continuous defiance against colonial control.

How Did Historical Laws Attempt to Control Black Women’s Hair?
Historical laws sought to diminish Black women's beauty and social standing by regulating their textured hair, a profound attack on heritage.

Post-Colonial Trauma
Meaning ❉ Post-Colonial Trauma is the enduring psychological and cultural impact of colonial oppression, deeply affecting textured hair heritage and identity.

What Was the Role of Textured Hair during the Civil Rights Era?
Textured hair during the Civil Rights era became a profound symbol of Black pride and heritage, defying Eurocentric beauty standards.

Racial Hair Control
Meaning ❉ Racial Hair Control designates societal systems, legal actions, and biases that historically and presently impose Eurocentric beauty standards on textured hair.
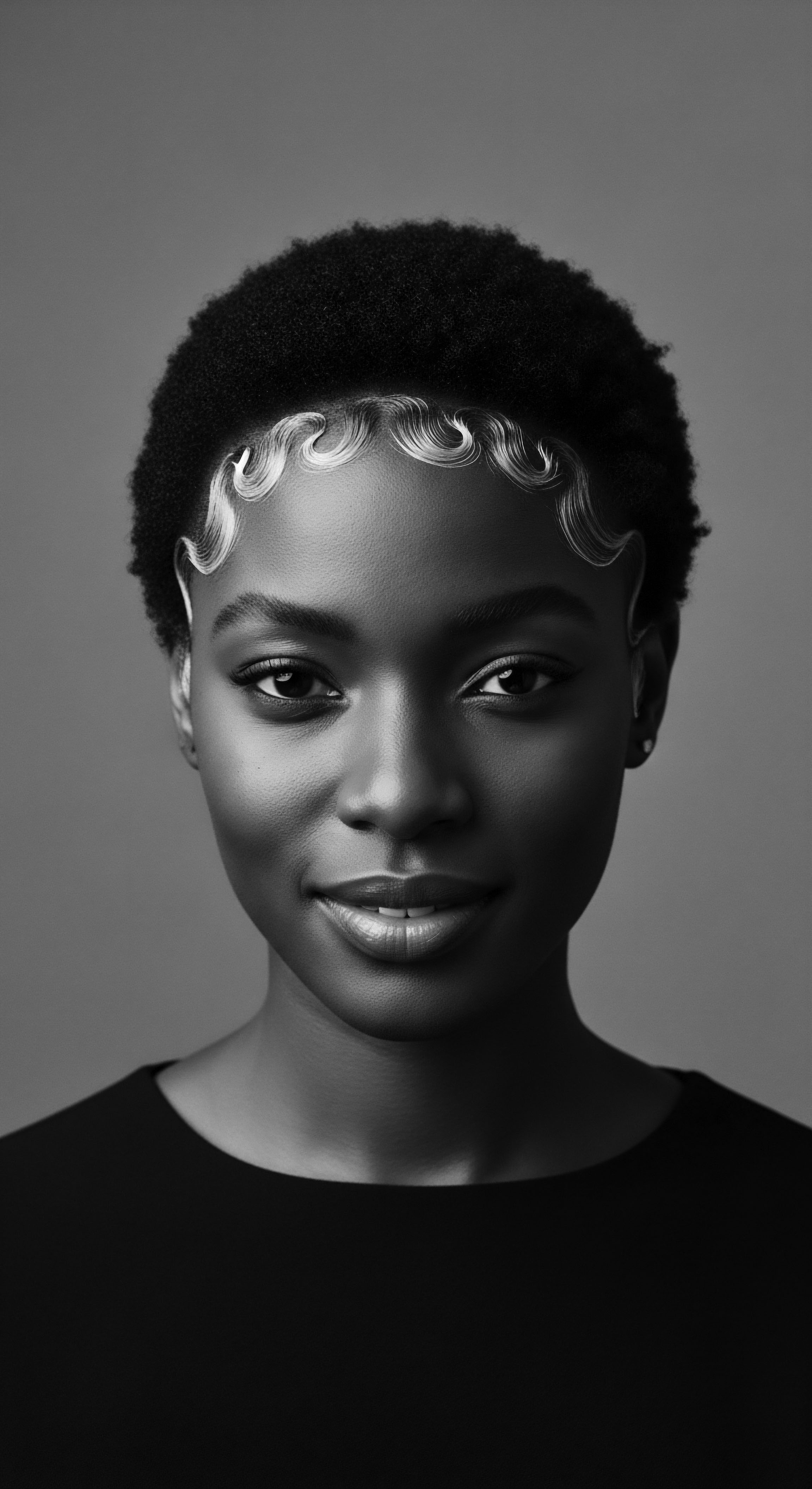

Post-Apartheid Hair
Meaning ❉ A multifaceted phenomenon reflecting liberation, identity reclamation, and the enduring heritage of textured hair in post-apartheid South Africa.

Civil Rights Legislation
Meaning ❉ Civil Rights Legislation safeguards fundamental liberties, increasingly encompassing protection against discrimination based on textured hair and cultural hairstyles.

Identity Control Theory
Meaning ❉ Identity Control Theory explains how individuals strive to align internal self-conceptions with external social perceptions to maintain a coherent sense of self.

Systemic Racial Control
Meaning ❉ Systemic Racial Control defines the pervasive societal mechanisms historically devaluing and policing textured hair, influencing identity and opportunity.

Post-Civil War Exploitation
Meaning ❉ Post-Civil War Exploitation describes the systematic subjugation of Black Americans through economic, social, and cultural mechanisms, profoundly impacting their hair heritage.

Civil Rights Era Legislation
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Era Legislation represents a transformative legal framework that sought to dismantle systemic discrimination, profoundly impacting Black hair heritage and identity.

Identity Control
Meaning ❉ Identity Control refers to the ongoing process of aligning one's internal sense of self with external perceptions, often expressed powerfully through hair and heritage.

What Historical Mandates Sought to Control Afro-Descendant Hair Styles?
Historical mandates sought to control Afro-descendant hair, aiming to suppress identity and uphold racial hierarchies, yet sparking powerful acts of cultural resilience.
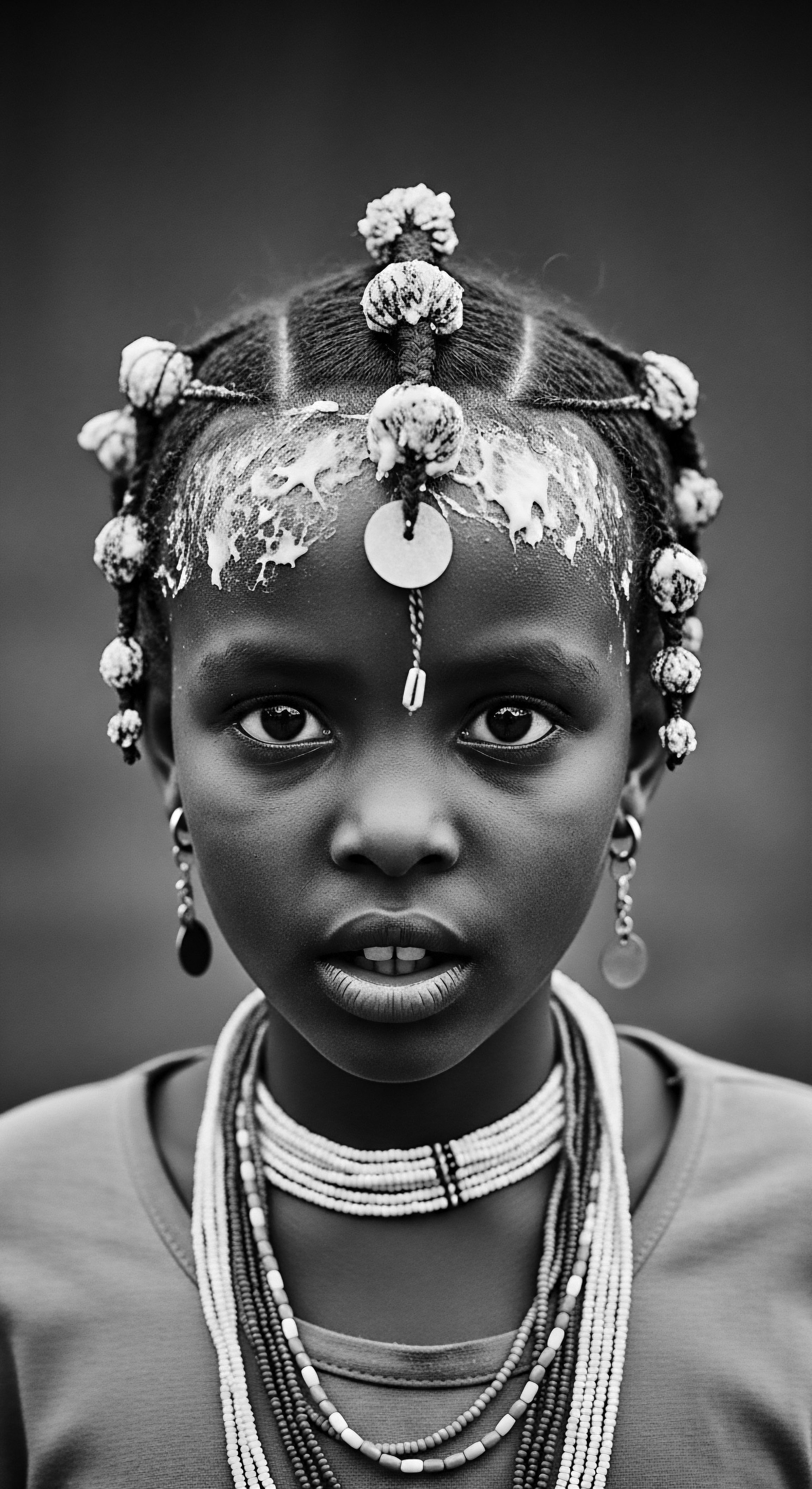

How Did Tignon Laws Control Black Women’s Appearance?
The Tignon Laws aimed to control Black women's appearance by forcing head coverings, yet they sparked powerful expressions of textured hair heritage.

Post-Emancipation Identity
Meaning ❉ Post-Emancipation Identity signifies the complex reconstruction of selfhood and cultural expression for formerly enslaved people, deeply tied to hair heritage.

