What Traditional Nighttime Rituals Supported Textured Hair Health and Heritage?
Traditional nighttime rituals for textured hair involved protective styling and natural balms, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage for health and preservation.

Can Traditional Nighttime Rituals Truly Protect Textured Hair from Moisture Loss?
Ancestral nighttime rituals, deeply rooted in heritage, offer profound moisture protection for textured hair through careful techniques and materials.

Can Modern Science Validate Ancestral Nighttime Hair Practices for Textured Hair?
Modern science confirms ancestral nighttime hair practices protect textured hair by reducing friction and retaining moisture, honoring a rich heritage of care.

What Is the Historical Link between Head Wraps and Protective Styling for Textured Hair?
Head wraps and protective styles connect directly to textured hair heritage by safeguarding strands through generations, from ancient necessity to cultural expression.

What Ancestral Nighttime Rituals Preserved Textured Hair’s Hydration?
Ancestral nighttime rituals for textured hair hydration centered on protective coverings and natural emollients, preserving moisture and cultural heritage.

How Did Nighttime Rituals Shield Heritage Hair?
Nighttime rituals shielded heritage hair by reducing friction and retaining moisture, preserving strands with ancestral wisdom.

How Does Silk Preserve Textured Hair Moisture?
Silk preserves textured hair moisture by reducing friction and not absorbing hydration, honoring ancestral protective care.

Do Traditional Nighttime Rituals Still Protect Textured Hair Today?
Traditional nighttime rituals remain fundamental for textured hair, their protective principles validated across centuries and scientific advancements.

What Materials Were Traditionally Favored for Nighttime Hair Protection in Heritage Communities?
Heritage communities primarily favored silk and satin for nighttime hair protection to preserve moisture and reduce friction for textured strands.
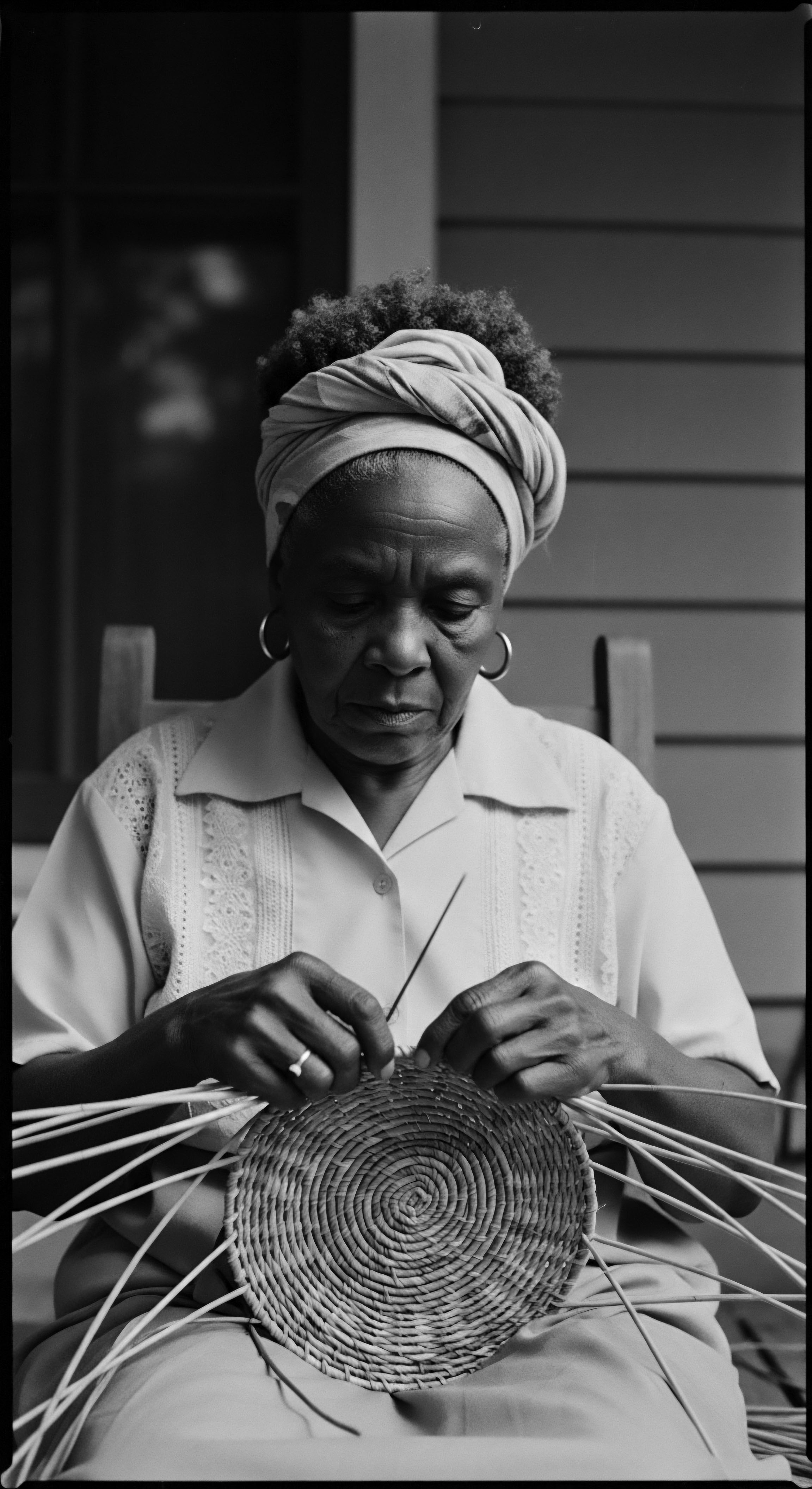

What Is the Historical Significance of Nighttime Hair Protection in Heritage Communities?
Nighttime hair protection in heritage communities is a profound act of safeguarding textured hair’s health and identity, rooted in ancestral resilience.

What Ancestral Wisdom Guides Current Textured Hair Nighttime Care?
Ancestral wisdom guides textured hair nighttime care through practices of protection, moisture sealing, and gentle styling, rooted in cultural heritage.

How Do Plant-Based Nighttime Rituals Connect to Textured Hair Heritage?
Plant-based nighttime rituals deeply connect to textured hair heritage by preserving ancestral knowledge of botanical care and cultural identity.

How Did Ancestral Practices Protect Textured Strands Overnight?
Ancestral practices protected textured strands overnight through specialized styling, head coverings, and natural emollients, preserving hair's structural and cultural integrity.

What Historical Significance Does Nighttime Hair Protection Hold for Textured Strands?
Nighttime hair protection for textured strands signifies a powerful, enduring heritage of resilience and self-care.
What Ancestral Knowledge Guided the Nighttime Preservation of Textured Hair?
Ancestral knowledge guided nighttime textured hair preservation through protective coverings, natural emollients, and communal rituals rooted in profound respect for its unique heritage.

In What Ways Do Traditional Nighttime Hair Rituals Align with Modern Scientific Understanding for Textured Hair?
Traditional nighttime hair rituals protect strands and retain moisture, echoing modern scientific understanding through ancestral wisdom.

Why Does Textured Hair Need Nighttime Moisture?
Nighttime moisture is crucial for textured hair to counter natural dryness and friction, honoring ancestral care and preserving its heritage of vitality.

In What Ways Do Modern Routines Reflect African Hair Heritage?
Modern hair care practices for textured hair deeply reflect African hair heritage through ancient techniques, ingredients, and the powerful symbolism of identity and protection.

In What Ways Do Oils Protect Textured Hair Overnight?
Oils shield textured hair overnight by sealing in moisture and reducing friction, a protective practice deeply rooted in ancestral care traditions.
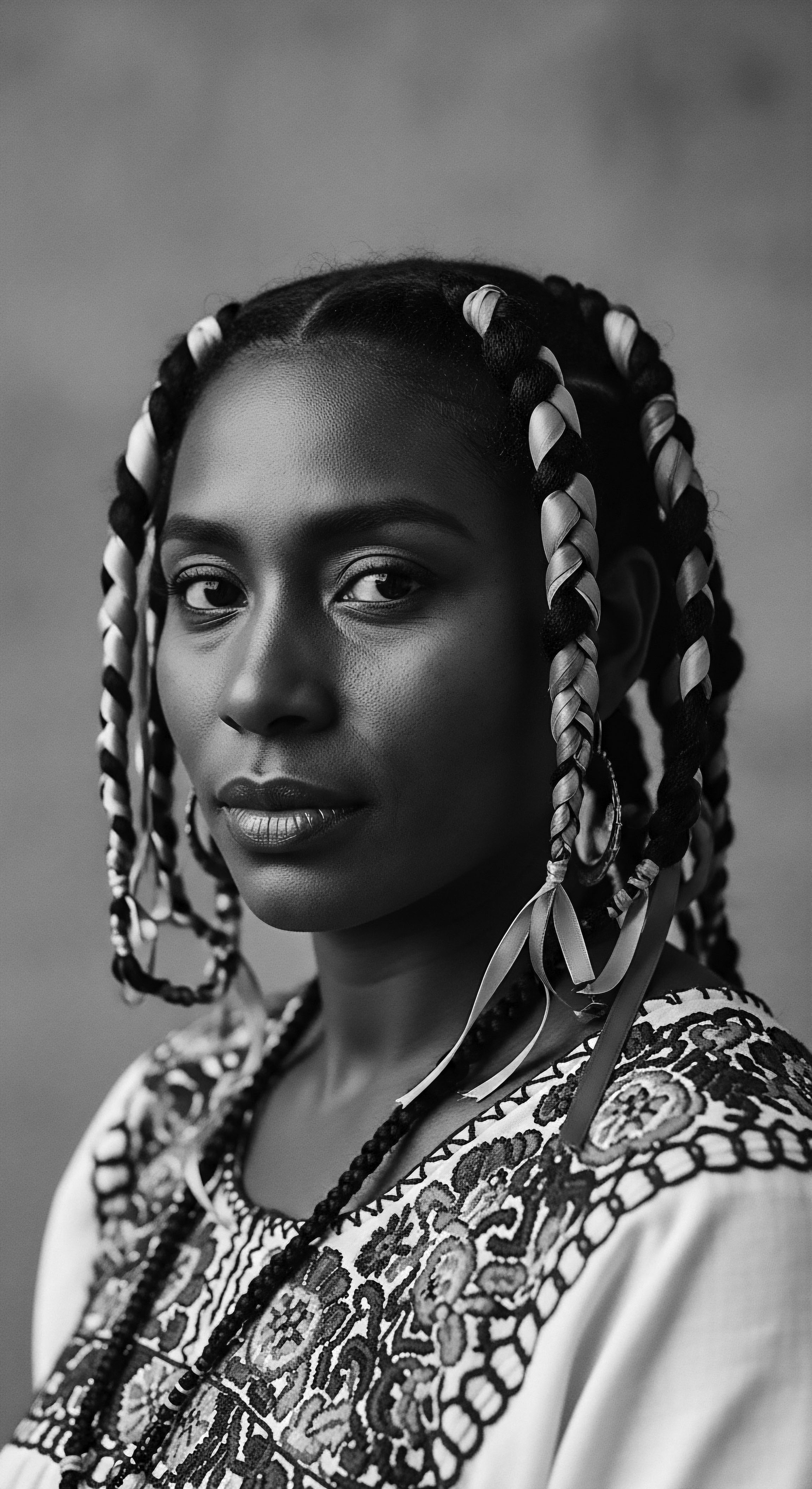

In What Ways Did Ancestral Nighttime Hair Protection Influence Current Practices for Textured Hair?
Ancestral nighttime hair protection, primarily through wraps and braids, laid the foundation for modern textured hair care.

What Ancestral Practices Influence Modern Nighttime Hair Routines for Textured Hair?
Modern nighttime hair routines for textured hair directly descend from ancestral practices, preserving cultural heritage and protecting strands.

Why Is Nighttime Care Essential for Textured Hair?
Nighttime care preserves textured hair by minimizing friction and locking in moisture, echoing centuries of ancestral wisdom and cultural resilience.
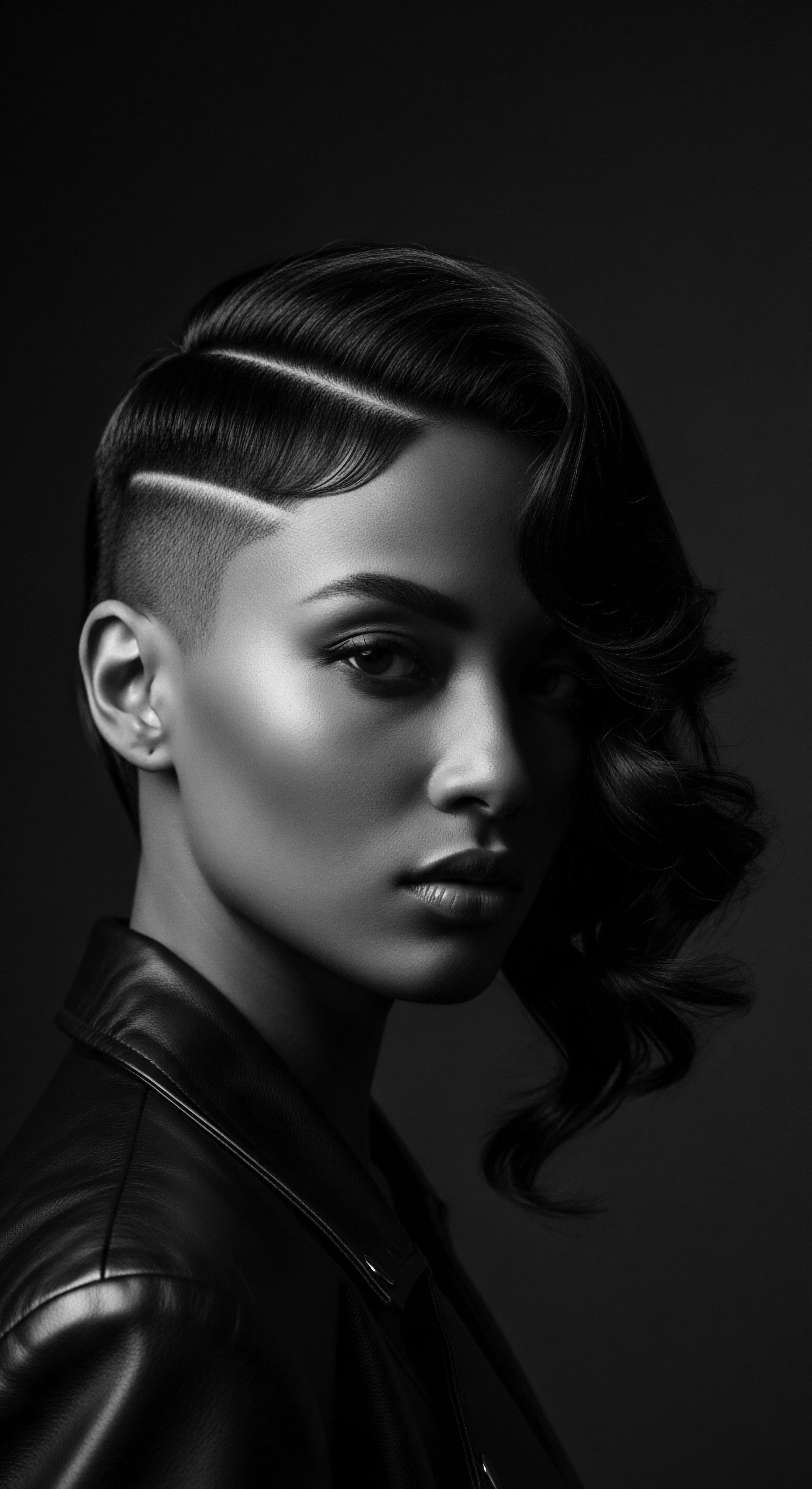

How Does Textured Hair Lineage Inform Modern Nighttime Care Choices?
Textured hair lineage informs modern nighttime choices by extending ancestral practices of protection, moisture retention, and cultural reverence.
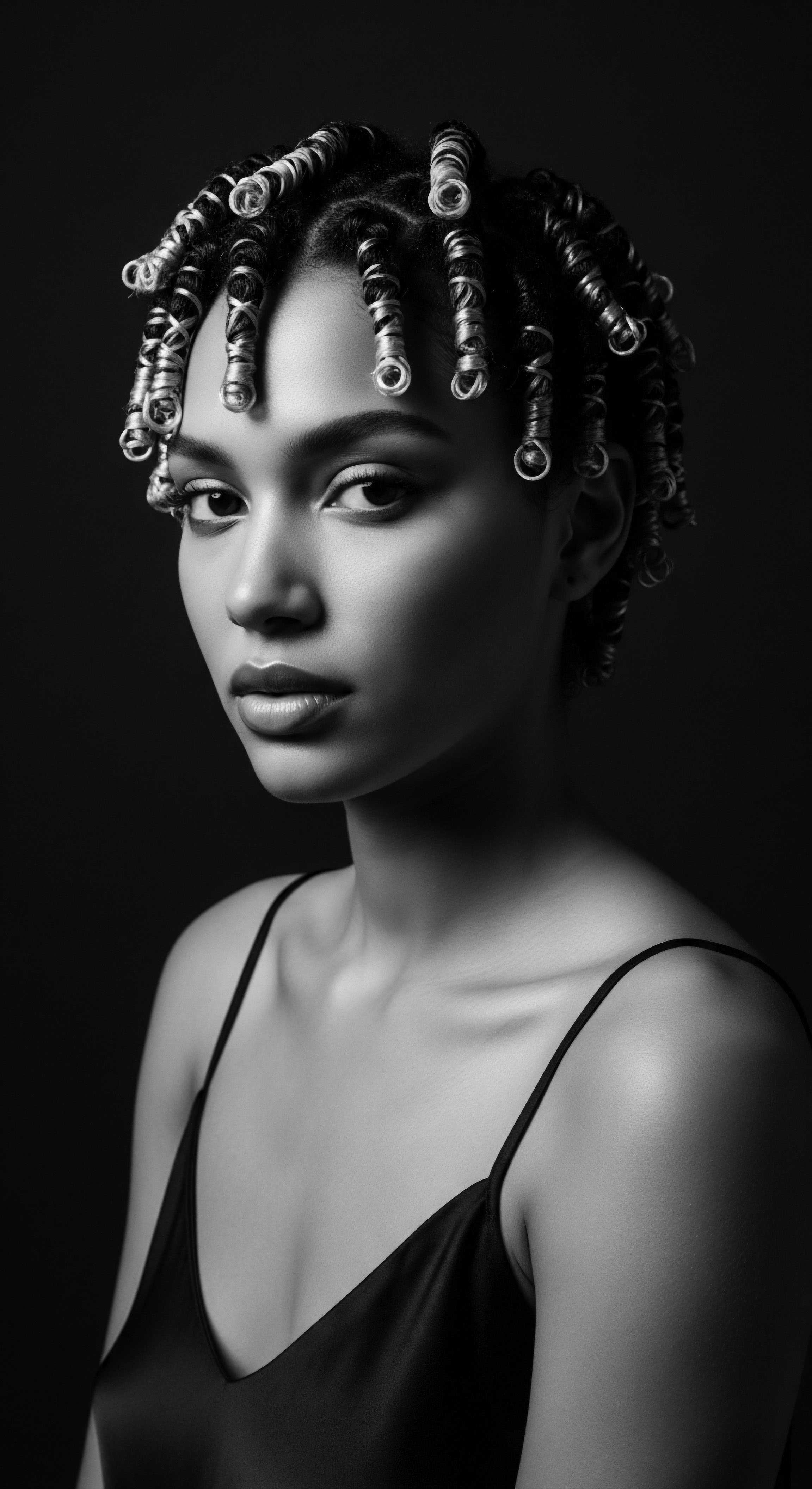

Why Is Moisture Preservation Vital for Textured Hair during Sleep?
Moisture preservation is vital for textured hair during sleep to guard against dryness and breakage, a practice deeply rooted in ancestral safeguarding methods.

