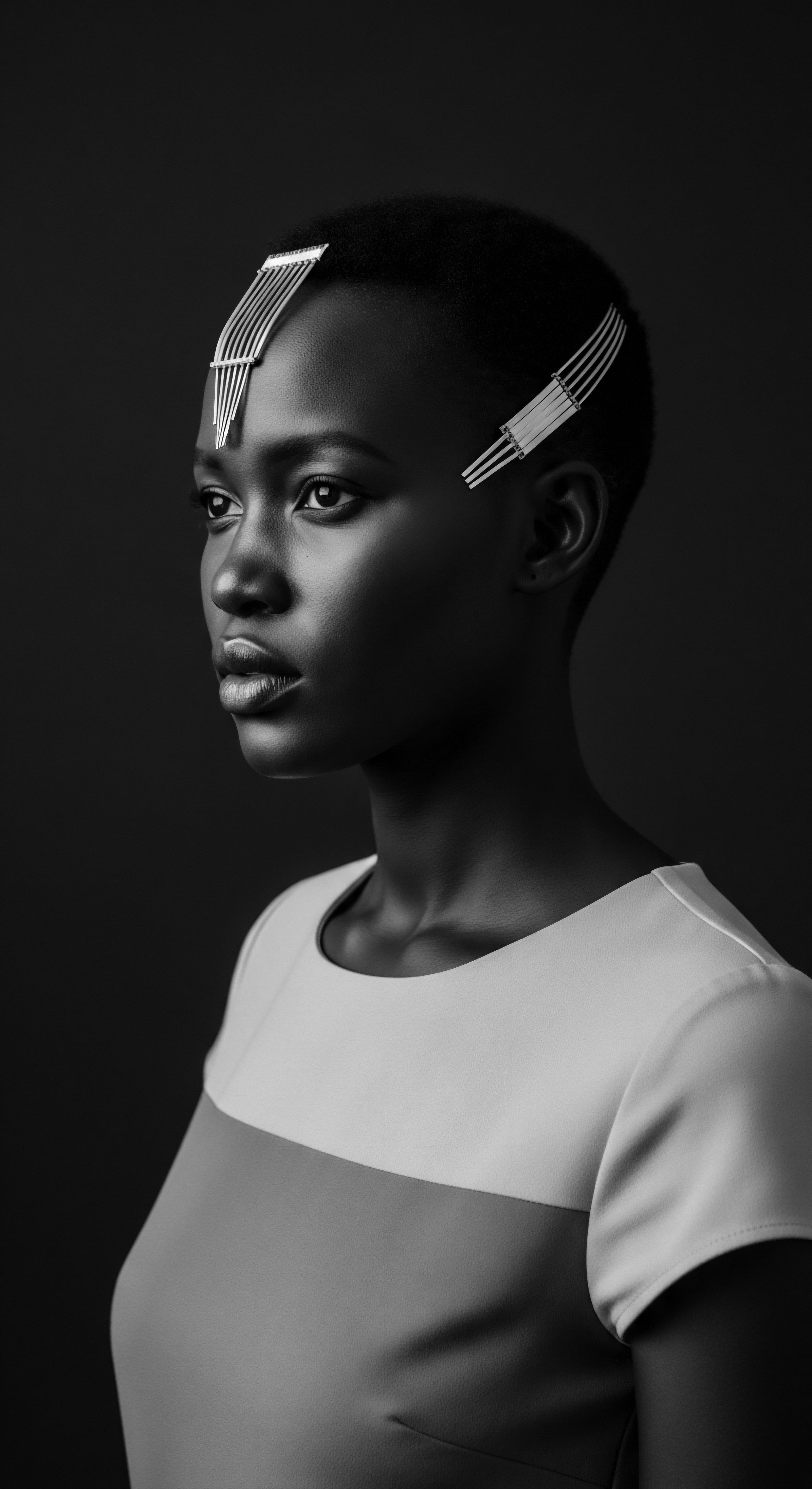
What Cultural Practices Protected Hair in African Societies?
African cultural practices safeguarded hair through protective styling, natural ingredients, and deeply rooted communal rituals, preserving textured hair heritage.
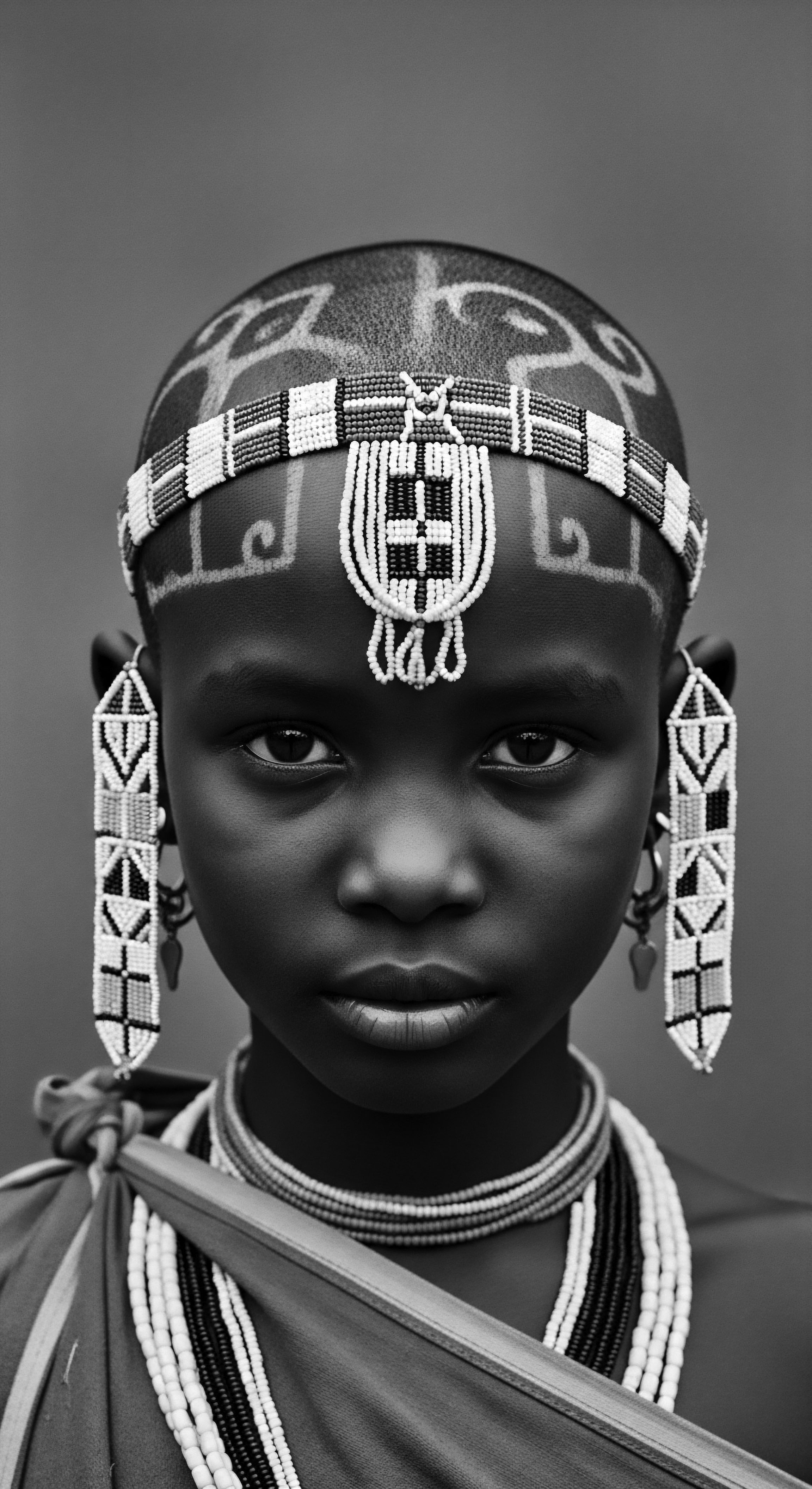

What Historical Significance Did Hair Hold in African Societies?
Hair in African societies held deep communal, spiritual, and social significance, a vibrant record of textured hair heritage.

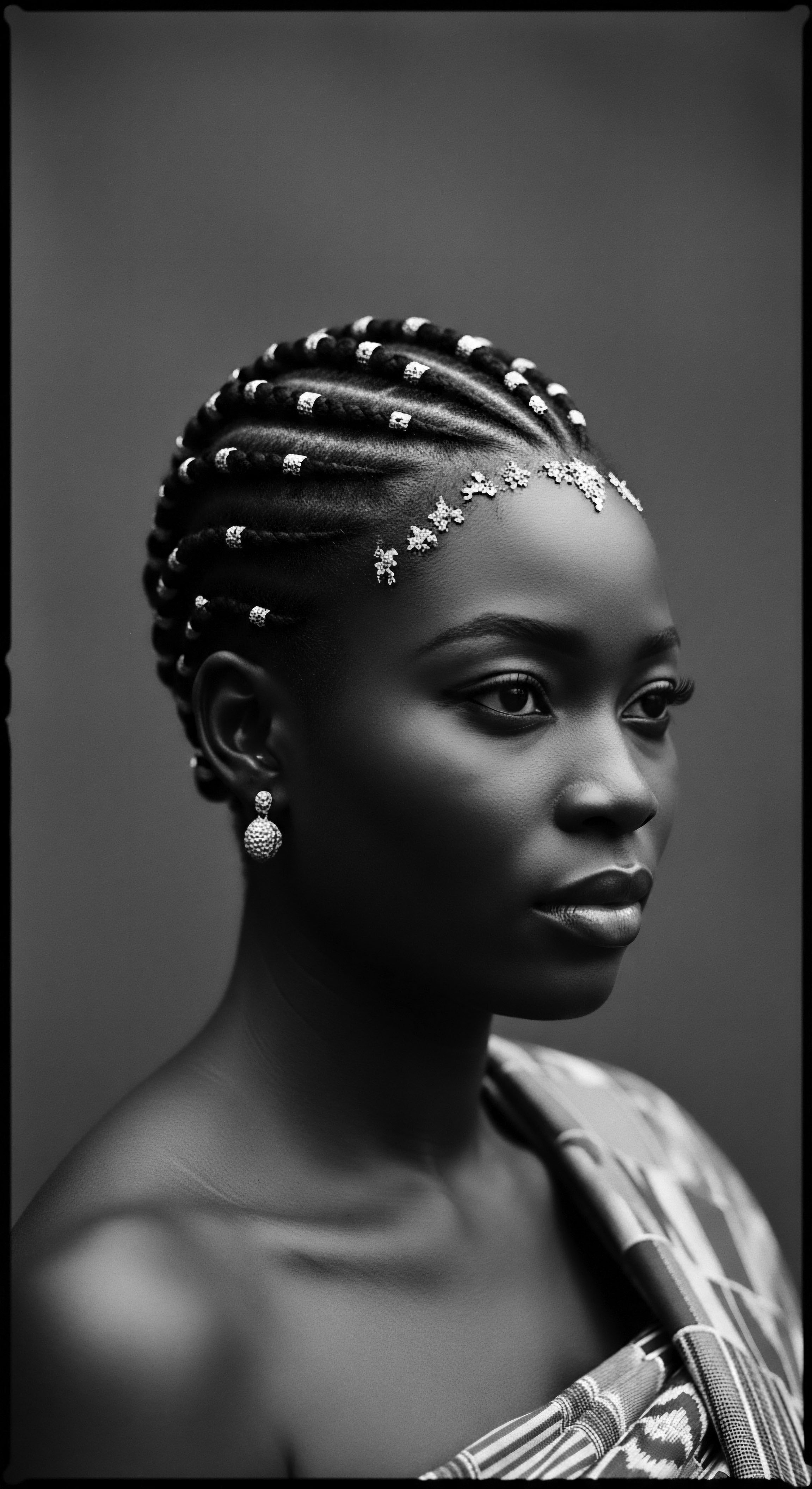
How Did Historical Hair Adornments Convey Identity in African Societies?
Historical African hair adornments conveyed age, social standing, marital status, and tribal affiliation, deeply connecting individuals to their textured hair heritage.
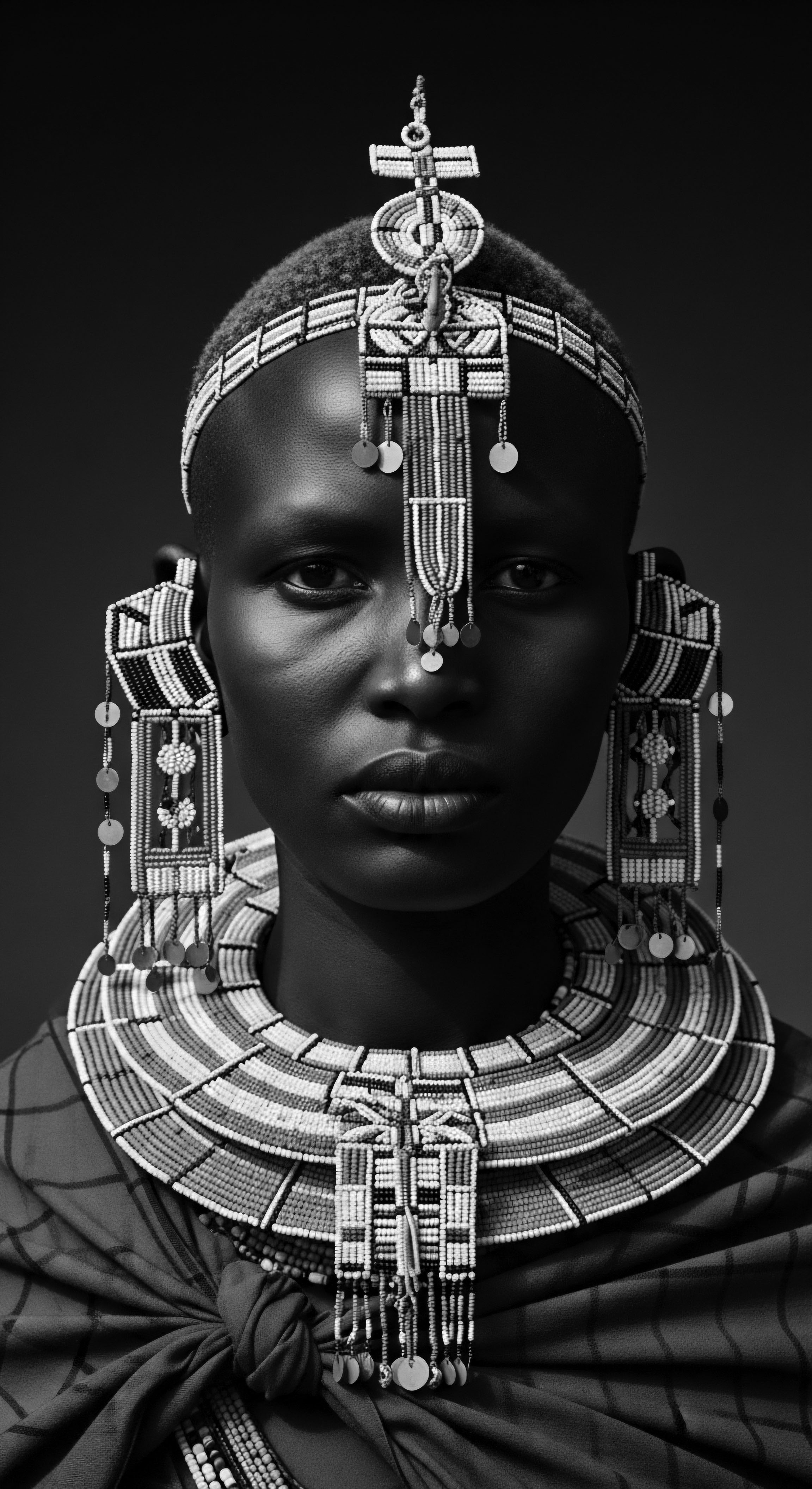

In What Ways Did Hair Symbolize Identity and Status in Ancient Societies across the Globe?
Hair in ancient societies, especially textured hair, profoundly symbolized identity and status through styling, adornment, and ritual practices.

How Did Pre-Colonial African Societies Honor Hair Heritage?
Pre-colonial African societies honored hair heritage as a spiritual conduit, social map, and artistic expression.

How Did Ancient Societies Protect Hair?
Ancient societies protected textured hair through natural oils, protective styling, and head coverings, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.
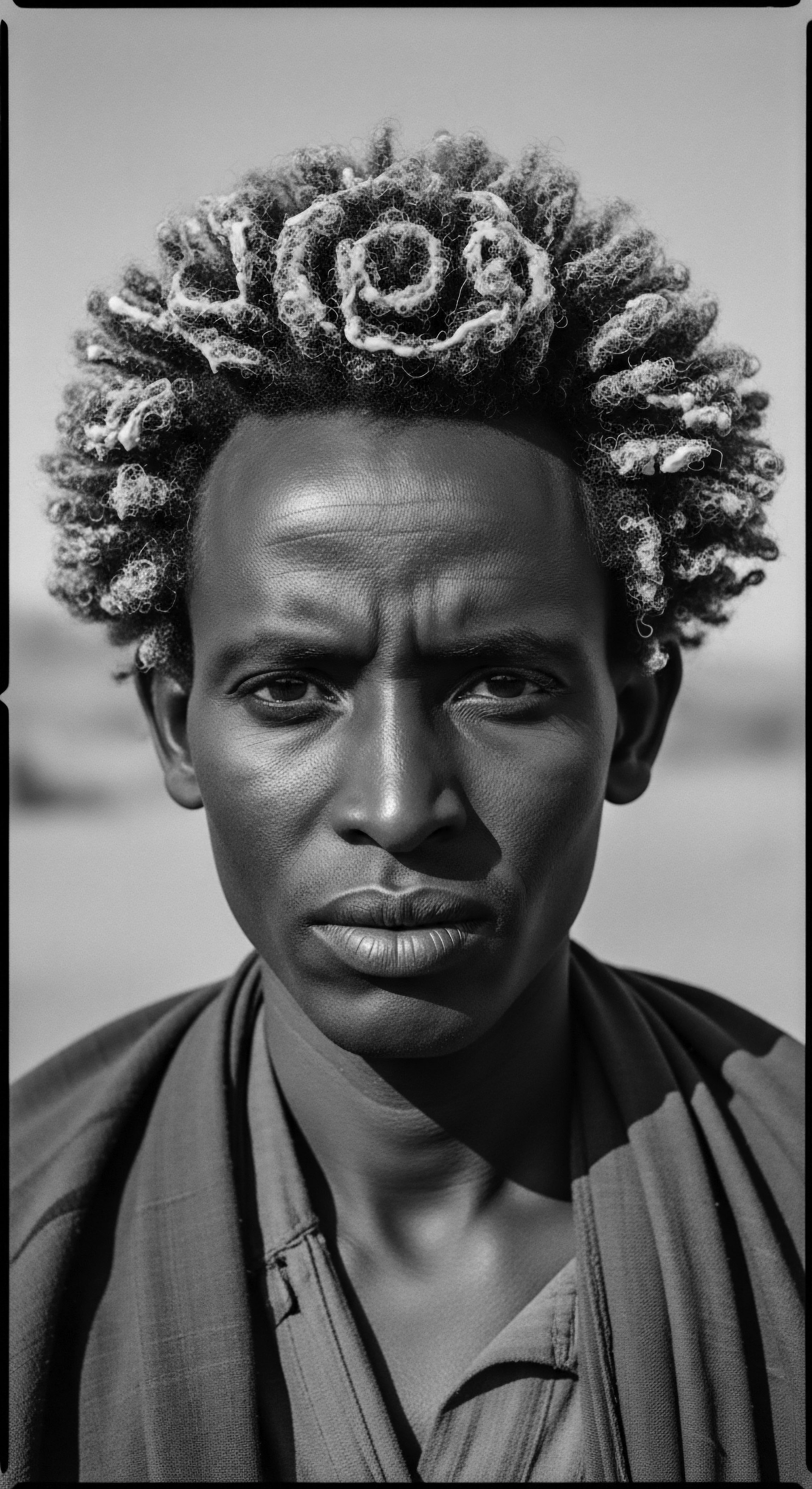

How Did Hair Communicate Status in Ancient African Societies?
Ancient African hair communicated status through intricate styles, adornments, and communal rituals, reflecting deep textured hair heritage.
How Did Ancient African Societies Use Hairstyles to Communicate?
Ancient African societies used intricate hairstyles as a visual lexicon, communicating complex details of identity, status, and spiritual connection.

Why Did Certain Societies Regulate Textured Hair?
Societies regulated textured hair to enforce social hierarchies, suppress cultural identity, and dismantle ancestral heritage.
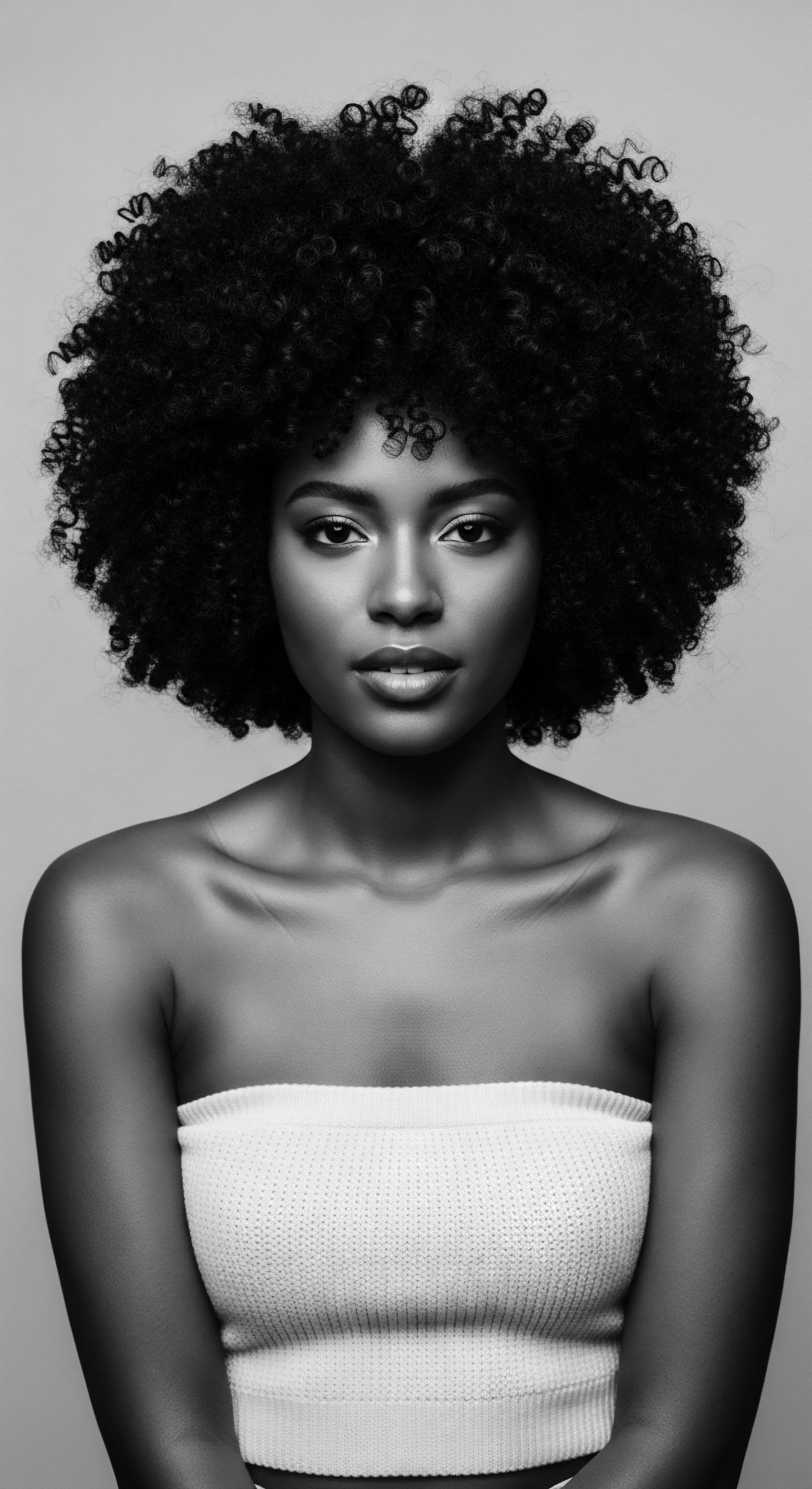

How Did Ancient Societies Identify Textured Hair?
Ancient societies identified textured hair through visual cues, tactile understanding, and by integrating its unique properties into cultural practices and spiritual beliefs, deeply shaping their heritage.
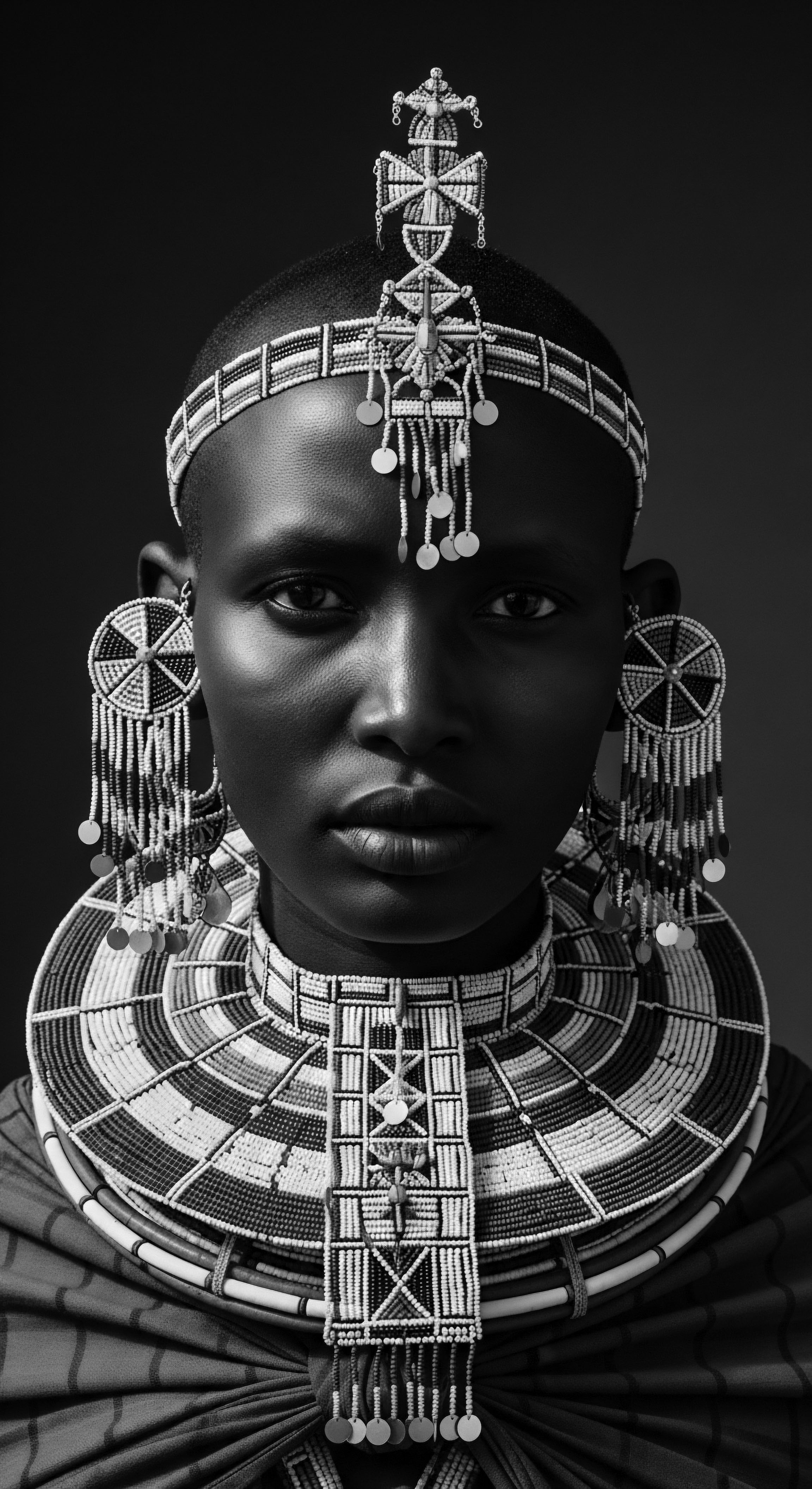

What Ancestral Rituals Honored Textured Hair in Ancient Societies?
Ancestral rituals honored textured hair through spiritual practices, social communication, and meticulous protective care deeply rooted in heritage.

How Did Ancient Societies Cleanse Textured Hair with Plant Materials?
Ancient societies cleansed textured hair using diverse plant materials rich in natural saponins, connecting ancestral botanical wisdom to hair heritage.

What Historical Laws Regulated Textured Hair in Colonial Societies?
Colonial laws regulating textured hair aimed to impose racial hierarchy and erase cultural identity, a deep affront to textured hair heritage.

What Cultural Significance Did Hair Hydration Practices Hold in past Societies?
Past societies understood hair hydration as a vital cultural practice, intrinsically tied to identity and communal heritage.

What Is the Ancestral Meaning of Textured Hair in African Societies?
Textured hair in African societies represents a heritage of identity, spiritual connection, and communal storytelling.

How Did Ancient African Societies Honor Hair?
Ancient African societies honored textured hair as a profound symbol of identity, social standing, and spiritual connection, deeply integrated into their heritage.

How Did Early Societies Treat Textured Hair?
Early societies revered textured hair, using natural resources and communal practices to style and care for it, reflecting status and spiritual connection.
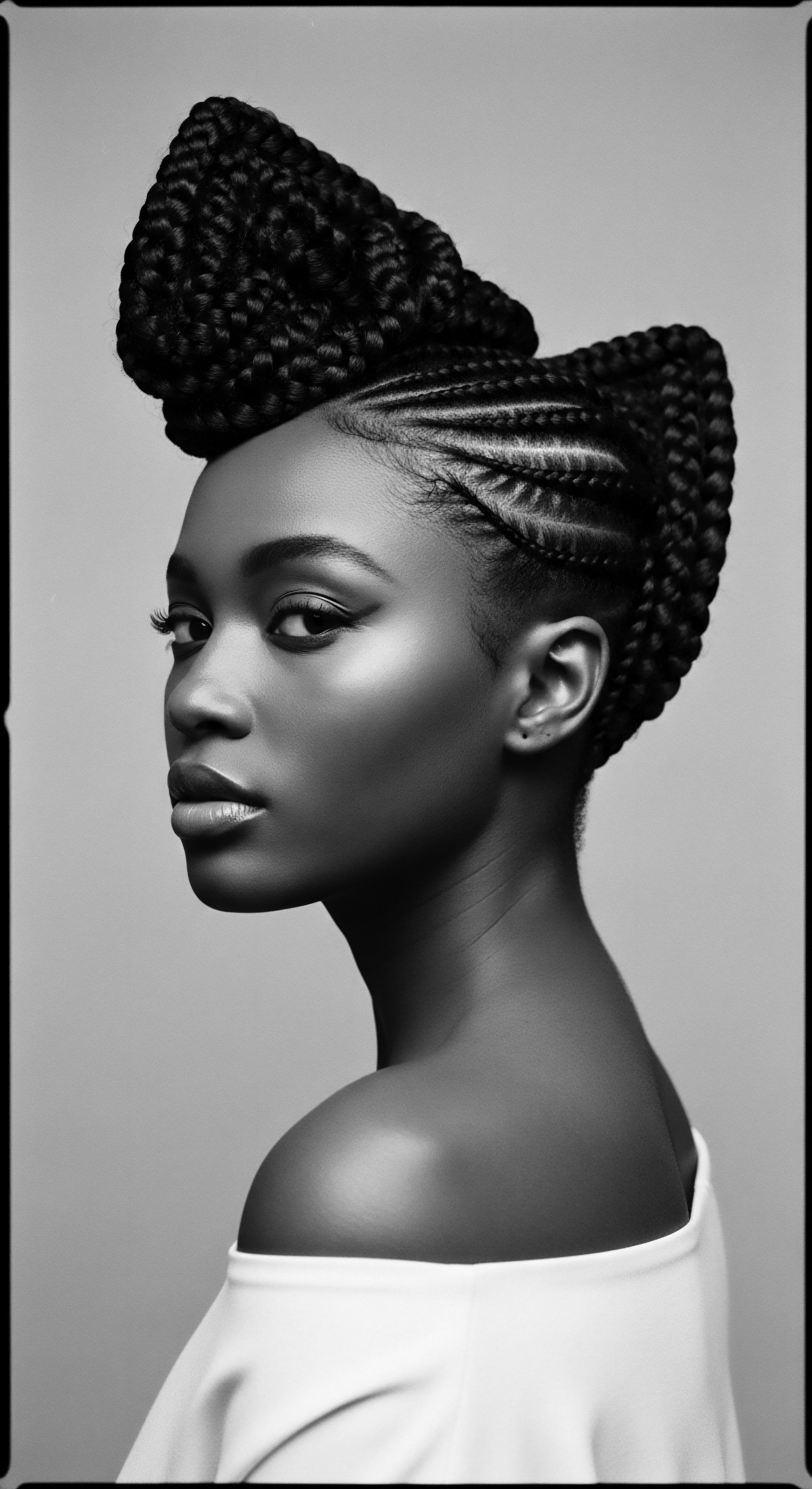

Why Did Ancestral Societies Wash Textured Hair Less Often?
Ancestral societies washed textured hair less often due to its biology, water scarcity, and to preserve intricate, culturally significant styles.

How Did Clay Benefit Textured Hair in Early Societies?
Clay provided cleansing, mineral nourishment, and styling support for textured hair in early societies, deeply connected to heritage.

How Did African Societies Care for Textured Hair?
African societies cared for textured hair through intricate protective styling and rituals, deeply linking it to heritage, status, and holistic wellness.
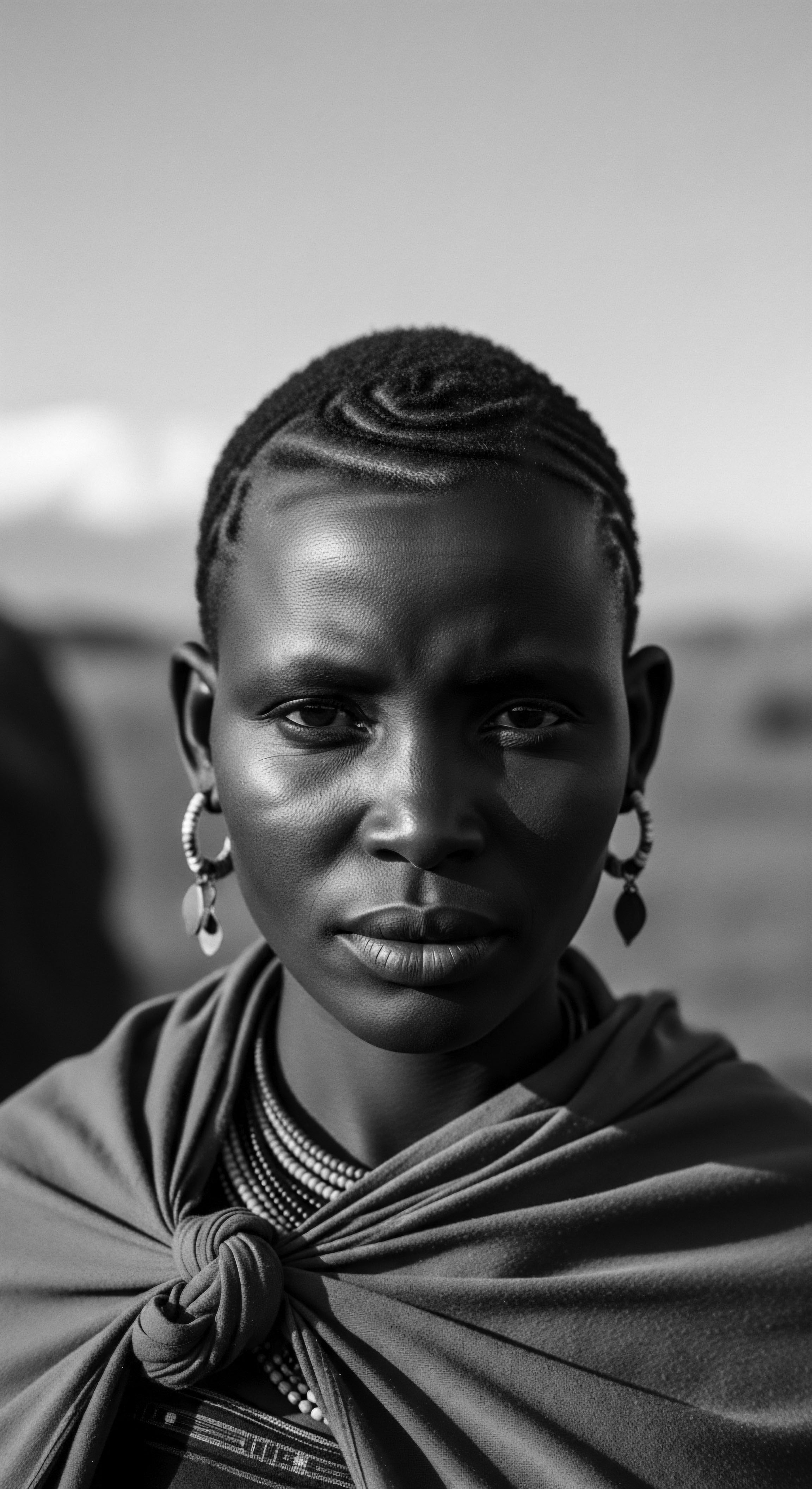

What Natural Ingredients Did Ancient Societies Use for Textured Hair?
Ancient societies nurtured textured hair with indigenous plant oils, clays, and herbal infusions, preserving its vitality and cultural symbolism.

What Roles Did Textured Hair Play in Ancient Societies?
Textured hair in ancient societies served as a powerful visual language, reflecting identity, status, spirituality, and communal heritage.
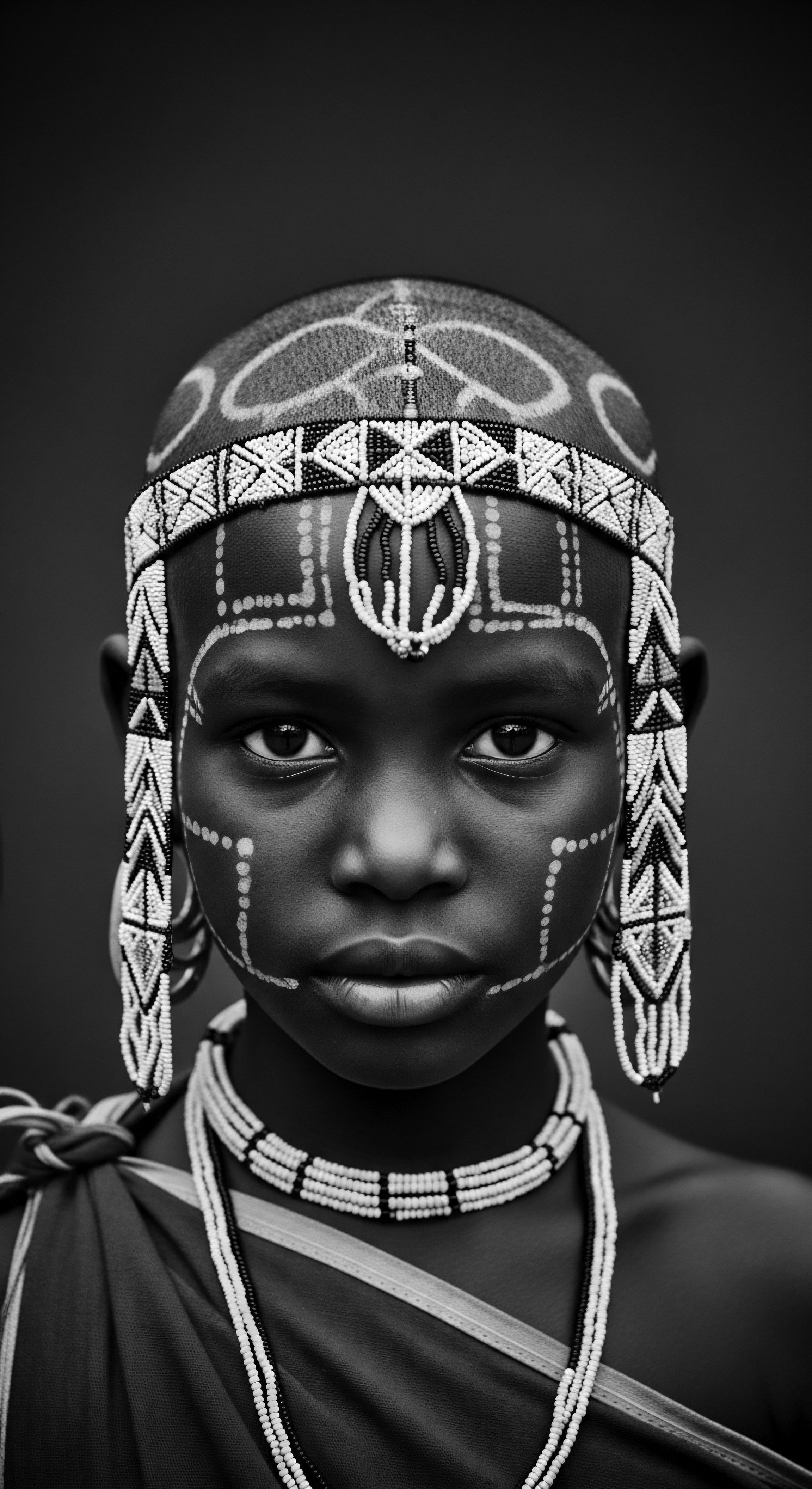

How Did Ancient Societies Adorn Textured Hair?
Ancient societies adorned textured hair through intricate styles and natural elements, signifying identity, status, and spiritual connection within their rich heritage.

What Natural Ingredients Did Ancient Societies Use for Textured Hair Health and What Is Their Heritage?
Ancient societies cherished textured hair with natural ingredients like oils, herbs, and resins, reflecting a deep heritage of care and identity.
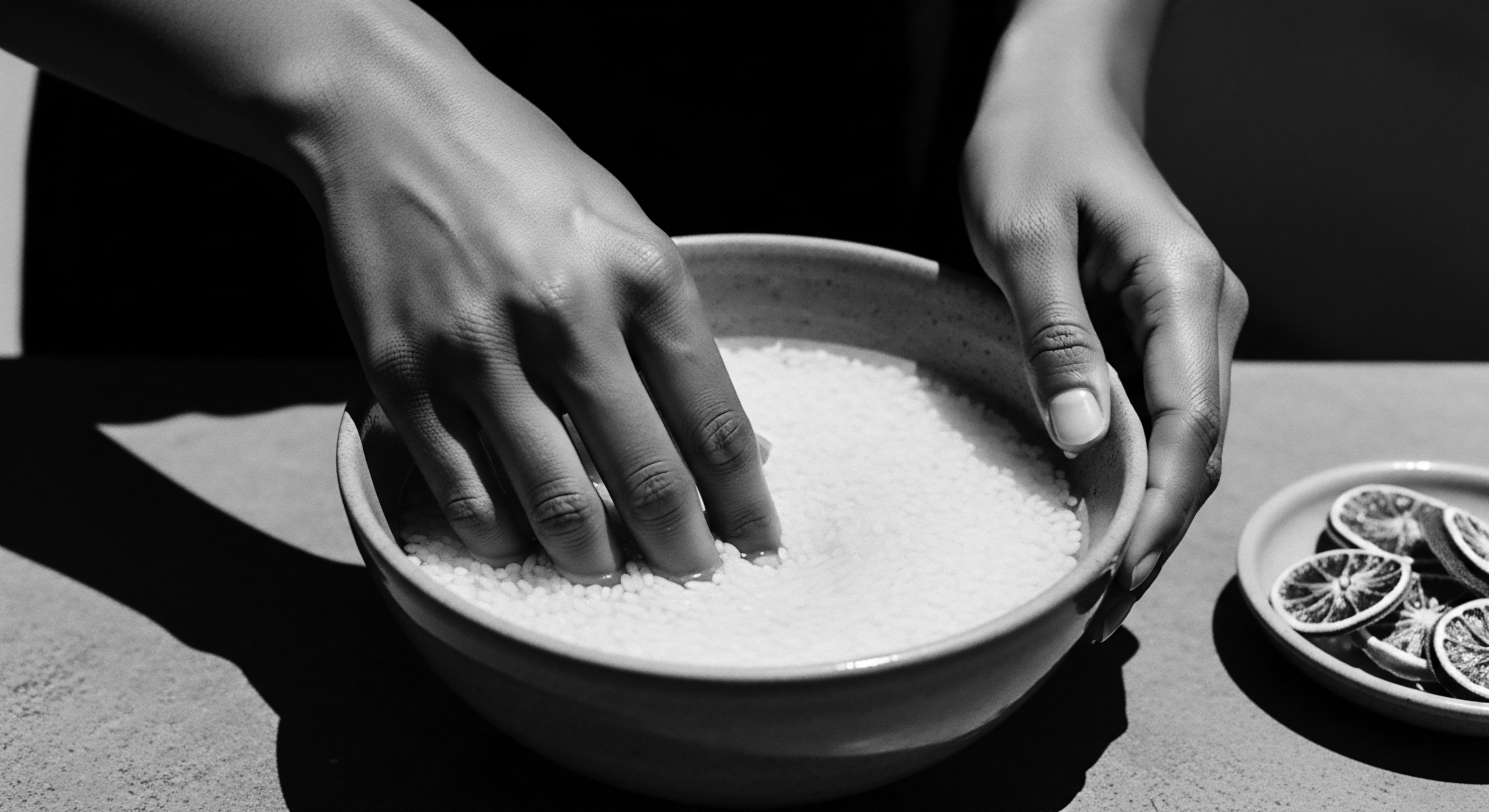

In What Ways Did Ancient Societies Care for Textured Hair with Natural Elements?
Ancient societies cared for textured hair using natural elements like plant oils, clays, and herbal infusions, practices deeply rooted in cultural heritage and ancestral wisdom.
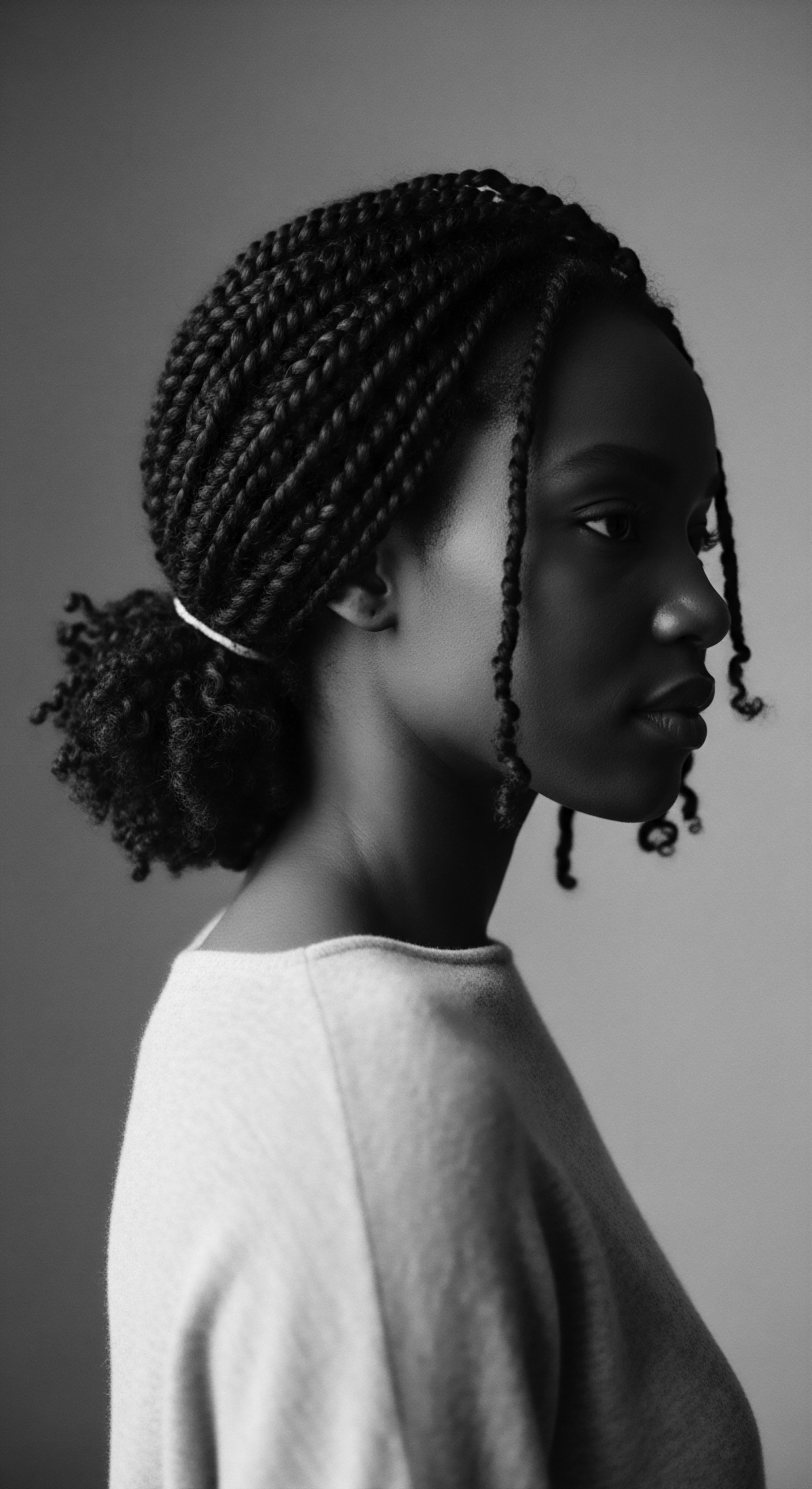

How Did Early Societies View Textured Hair Care?
Early societies regarded textured hair care as a vital cultural practice deeply intertwined with identity, spirituality, and communal heritage.

What Historical Significance Did Textured Hair Hold in African Societies?
Textured hair in African societies was a profound cultural language, signaling identity, spiritual connection, and social standing through centuries of heritage.
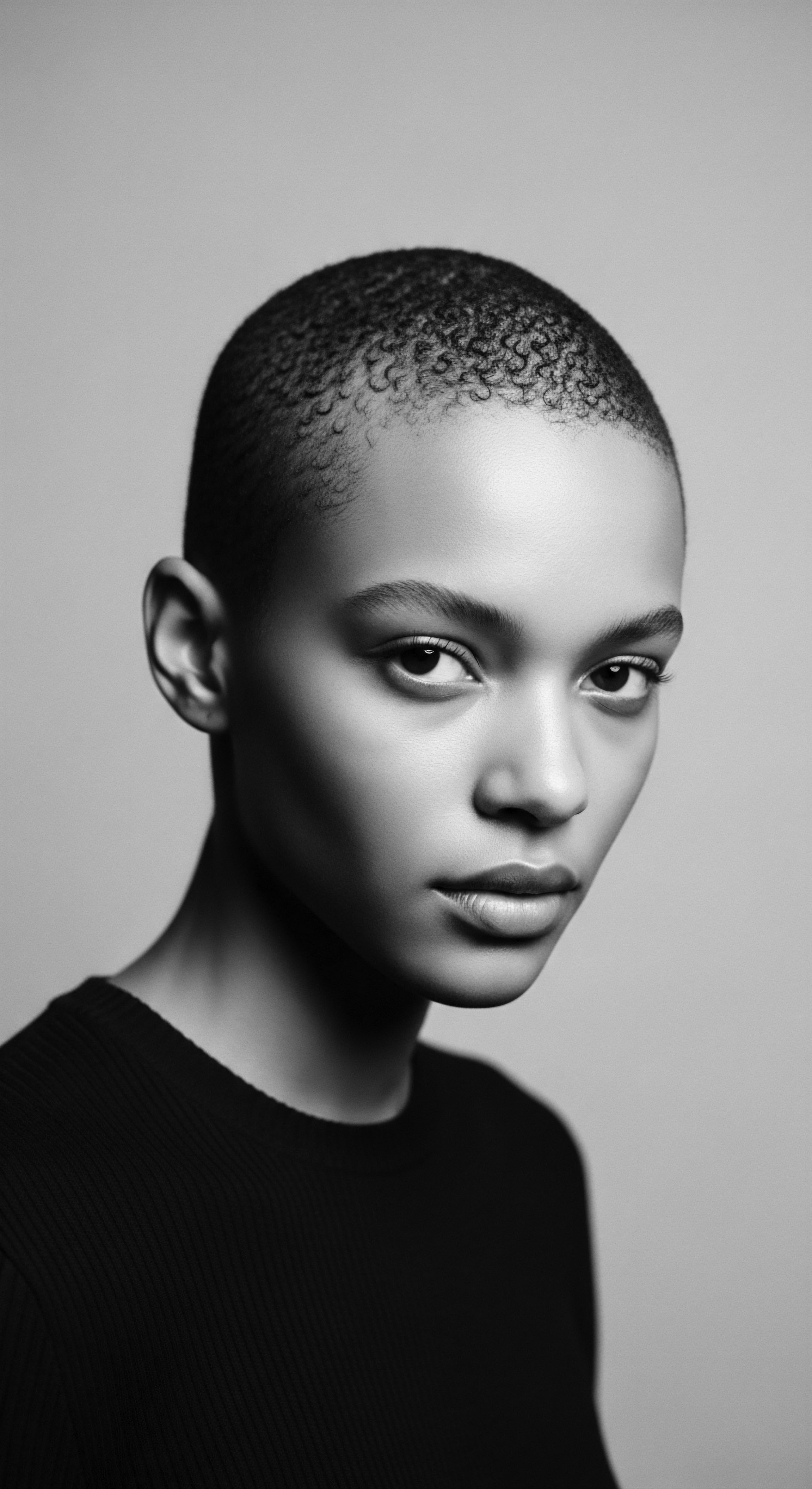

In What Ways Did Pre-Colonial African Societies View Hair as a Marker of Heritage?
Pre-colonial African societies viewed hair as a powerful heritage marker, communicating identity, social rank, and spiritual connection.

How Do Societies Perceive Graying in Textured Hair Heritage?
Societies often perceive graying in textured hair through a complex lens of historical bias, cultural reverence, and personal reclamation.

