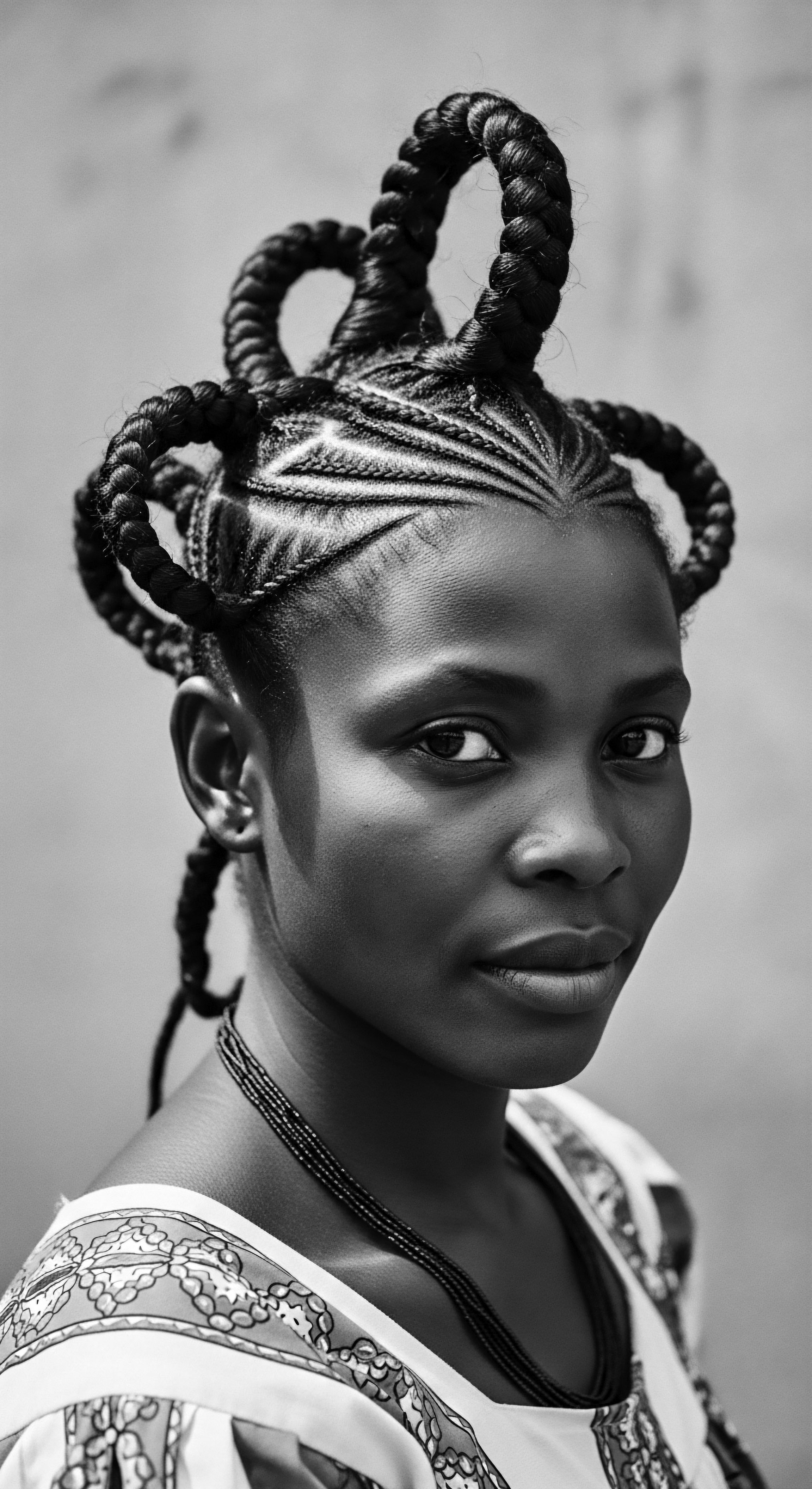
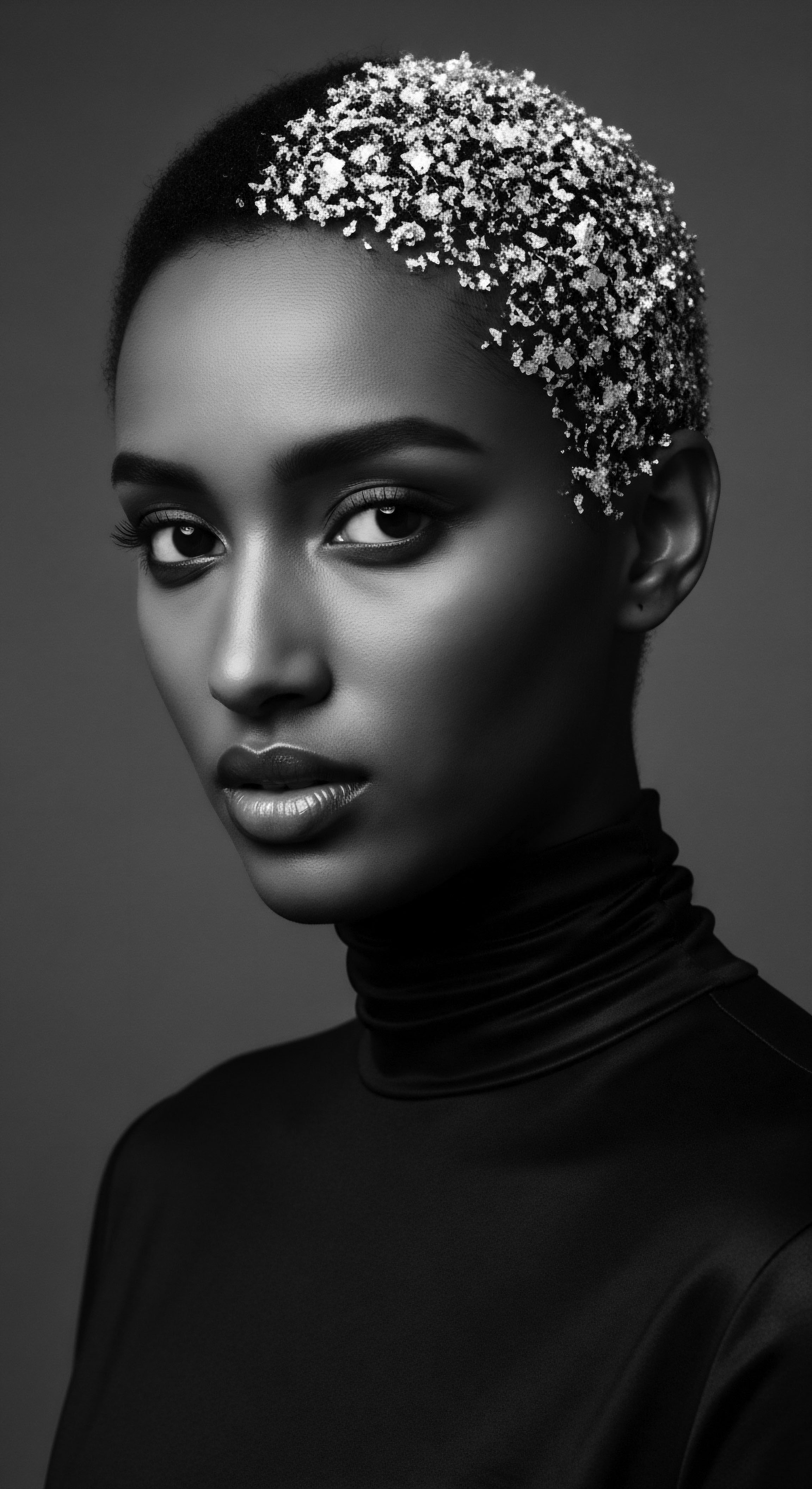
What Historical Laws Sought to Suppress Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical laws sought to suppress textured hair heritage by imposing Eurocentric beauty standards and controlling public appearance, notably through acts like the Tignon Laws.

How Did Jim Crow Era Policies Impact Black Hair Care?
Jim Crow policies compelled Black individuals to alter natural hair for survival, deeply impacting textured hair heritage and fostering self-sufficient beauty culture.
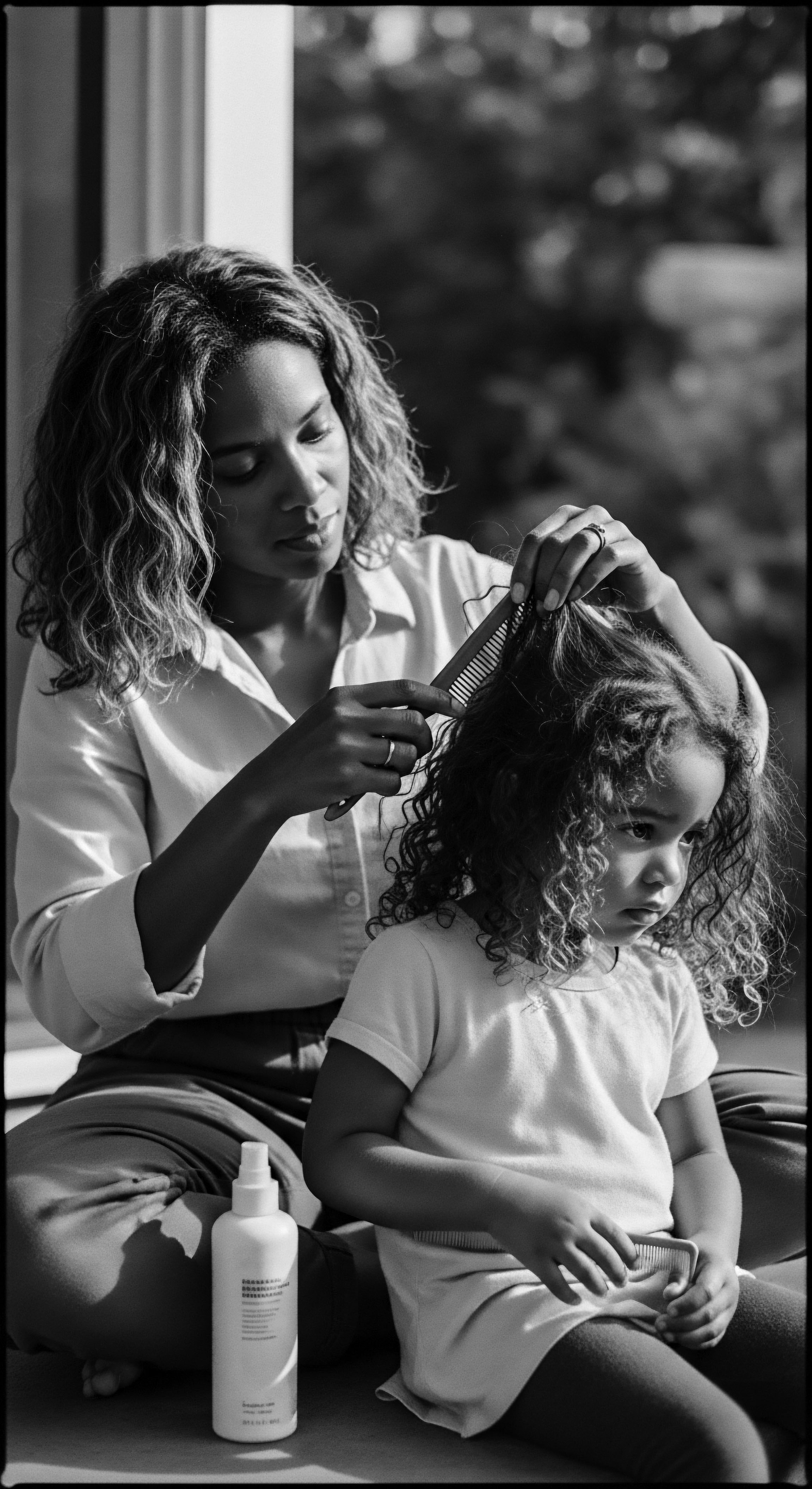

How Did Hair Tools during the Civil Rights Era Express Identity and Heritage?
Hair tools during the Civil Rights era expressed identity by enabling styles that defied oppressive norms and asserted Black heritage.

What Enduring Heritage Does Textured Hair Represent in the Modern Era of Self-Acceptance?
Textured hair represents a living heritage of resilience, identity, and ancestral wisdom in the modern era of self-acceptance.

Madam C.J. Walker
Meaning ❉ Madam C.J. Walker was a pioneering entrepreneur who built a hair care empire that empowered Black women economically and affirmed their beauty heritage.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Symbolize Defiance during the Black Power Era?
Textured hair symbolized defiance during the Black Power era by reclaiming ancestral aesthetics and asserting Black identity against Eurocentric beauty standards.

Jim Crow Era
Meaning ❉ The Jim Crow Era signifies a period of systemic racial segregation and discrimination in the U.S. profoundly shaping Black hair experiences and cultural identity.
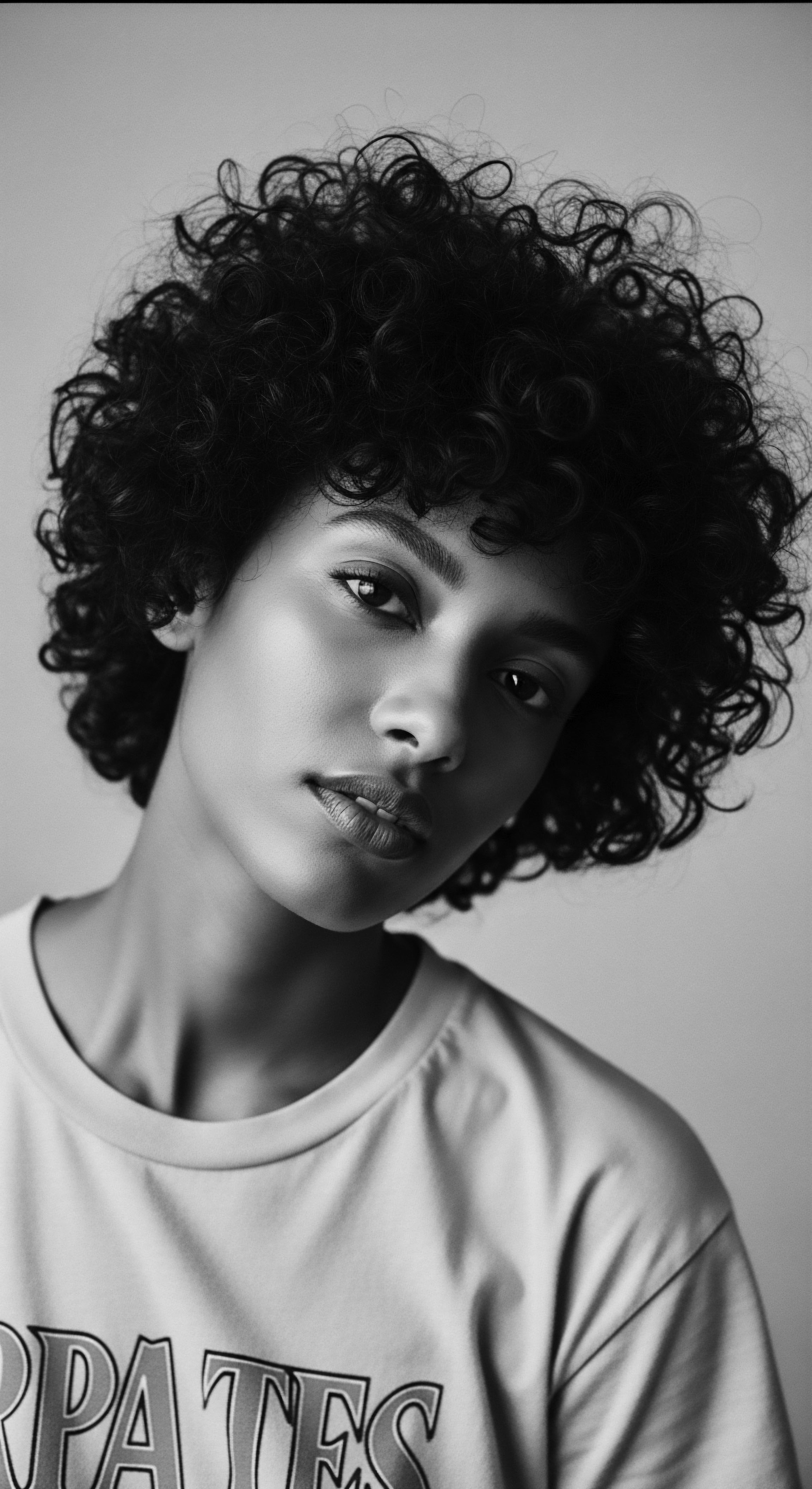

How Did the Civil Rights Era Reshape the Perception of Textured Hair Heritage?
The Civil Rights era reshaped textured hair perception by transforming it from a symbol of inferiority into a powerful declaration of Black pride and cultural heritage.

Kitchen Beauticians
Meaning ❉ Kitchen Beauticians are informal home-based hair care providers, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race communities, preserving textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Do Modern Bonnets Reflect the Legacy of Black Hair Care Heritage?
Modern bonnets preserve textured hair's moisture and style, directly reflecting ancestral practices of protection and cultural self-care.

What Historical Forces Shaped Textured Hair Styling Traditions?
Historical forces shaped textured hair styling traditions through ancestral cultural practices, colonial oppression, and resilient acts of identity reclamation.

Civil Rights Era
Meaning ❉ The Civil Rights Era was a pivotal period where Black Americans asserted their rights, transforming societal norms and reclaiming identity through hair heritage.

Hair Salon History
Meaning ❉ The Hair Salon History is a profound cultural narrative of spaces where textured hair care, community, and identity converge across generations.

What Role Did Textured Hair Play during the Era of Enslavement?
Textured hair served as a vital tool for communication, resistance, and the preservation of cultural heritage amidst the dehumanizing conditions of enslavement.

Jim Crow Era Hair
Meaning ❉ Jim Crow Era Hair refers to the forced conformity and cultural adaptation of Black hair practices under racial segregation, deeply impacting textured hair heritage.

Slave Era Hair
Meaning ❉ Slave Era Hair defines the resilient hair practices and cultural adaptations of enslaved Africans, showcasing heritage and identity against systemic oppression.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Symbolize Resistance during the Civil Rights Era?
Textured hair symbolized resistance during the Civil Rights era by visibly asserting Black pride, rejecting Eurocentric beauty norms, and reconnecting with ancestral heritage.

Enslavement Era
Meaning ❉ The Enslavement Era signifies a period of profound historical trauma and cultural resilience, particularly impacting textured hair heritage through forced assimilation and persistent ancestral practices.

Slave Era Resistance
Meaning ❉ Slave Era Resistance, through textured hair, embodies the defiant preservation of identity and cultural practices amidst oppression.

Jim Crow Hair
Meaning ❉ "Jim Crow Hair" denotes the societal pressures and discriminatory practices during the Jim Crow era that compelled Black and mixed-race individuals to alter their natural hair textures to conform to Eurocentric beauty standards for social acceptance and economic survival.

Enslavement Era Hair
Meaning ❉ Enslavement Era Hair refers to the adaptive hair care practices and cultural significations of textured hair during chattel slavery, symbolizing resilience and ancestral memory.

What Historical Struggles Shaped Textured Hair Care Traditions?
Historical struggles, from enslavement to discrimination, profoundly shaped textured hair care, making it a powerful symbol of identity and heritage.

How Does Hair Connect Black Heritage?
Hair is a living link to Black heritage, embodying ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity through its unique texture and historical care practices.

Apartheid Era Hair
Meaning ❉ Apartheid Era Hair refers to the systemic control and devaluation of textured hair in South Africa, a key marker for racial classification.
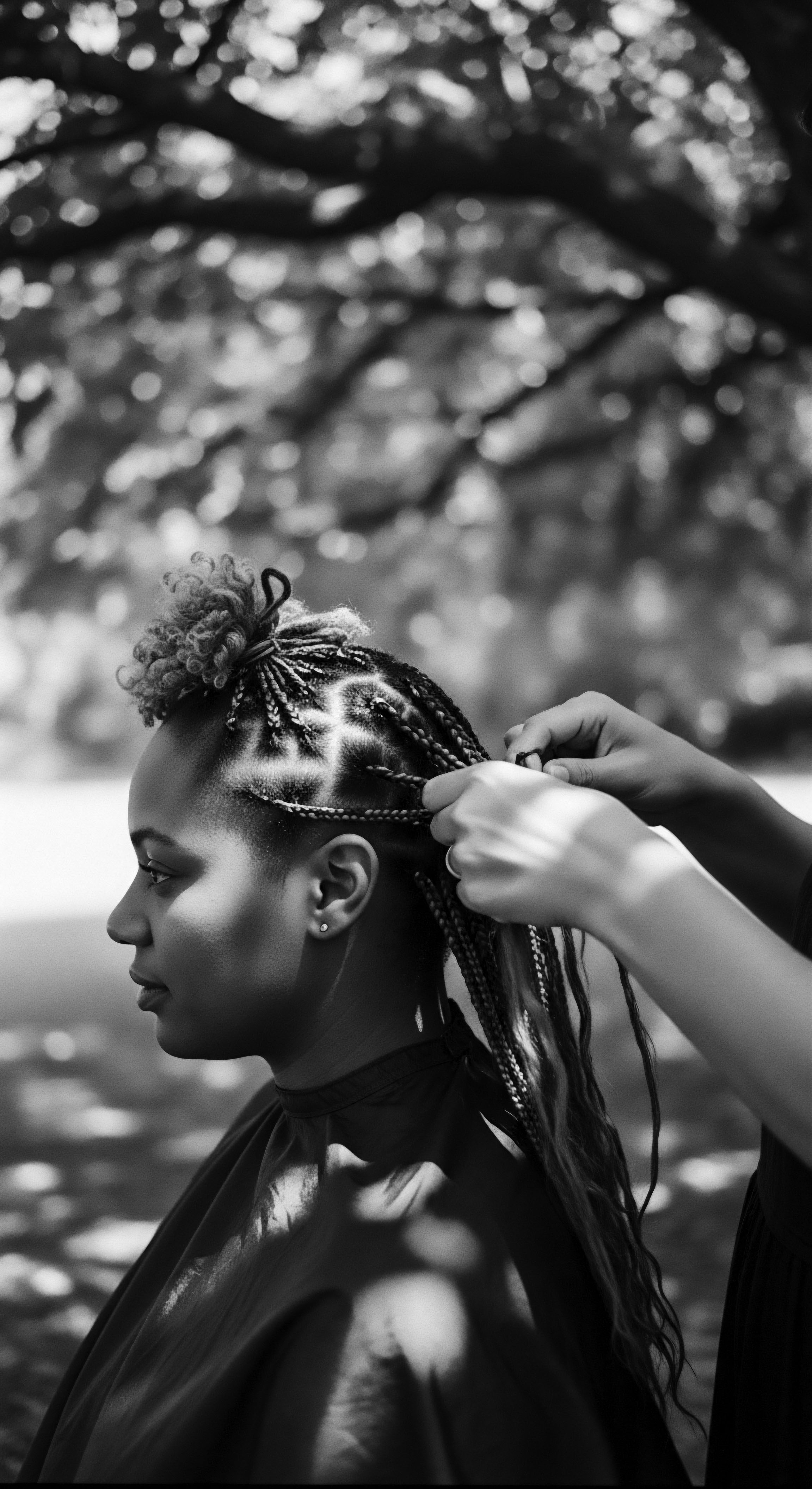
Annie Malone
Meaning ❉ Annie Malone was a pioneering Black entrepreneur who founded Poro, a hair care empire and college, empowering Black women economically and culturally.

Annie Malone Legacy
Meaning ❉ The Annie Malone Legacy embodies the profound impact of Black entrepreneurship on hair care, community building, and economic empowerment.

Hair Care Professionals
Meaning ❉ Hair Care Professionals are guardians of follicular health and cultural heritage, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and the unique needs of textured hair.

Poro College Heritage
Meaning ❉ Poro College Heritage embodies the enduring legacy of Annie Turnbo Malone's pioneering institution, which redefined Black hair care and fostered economic autonomy.

