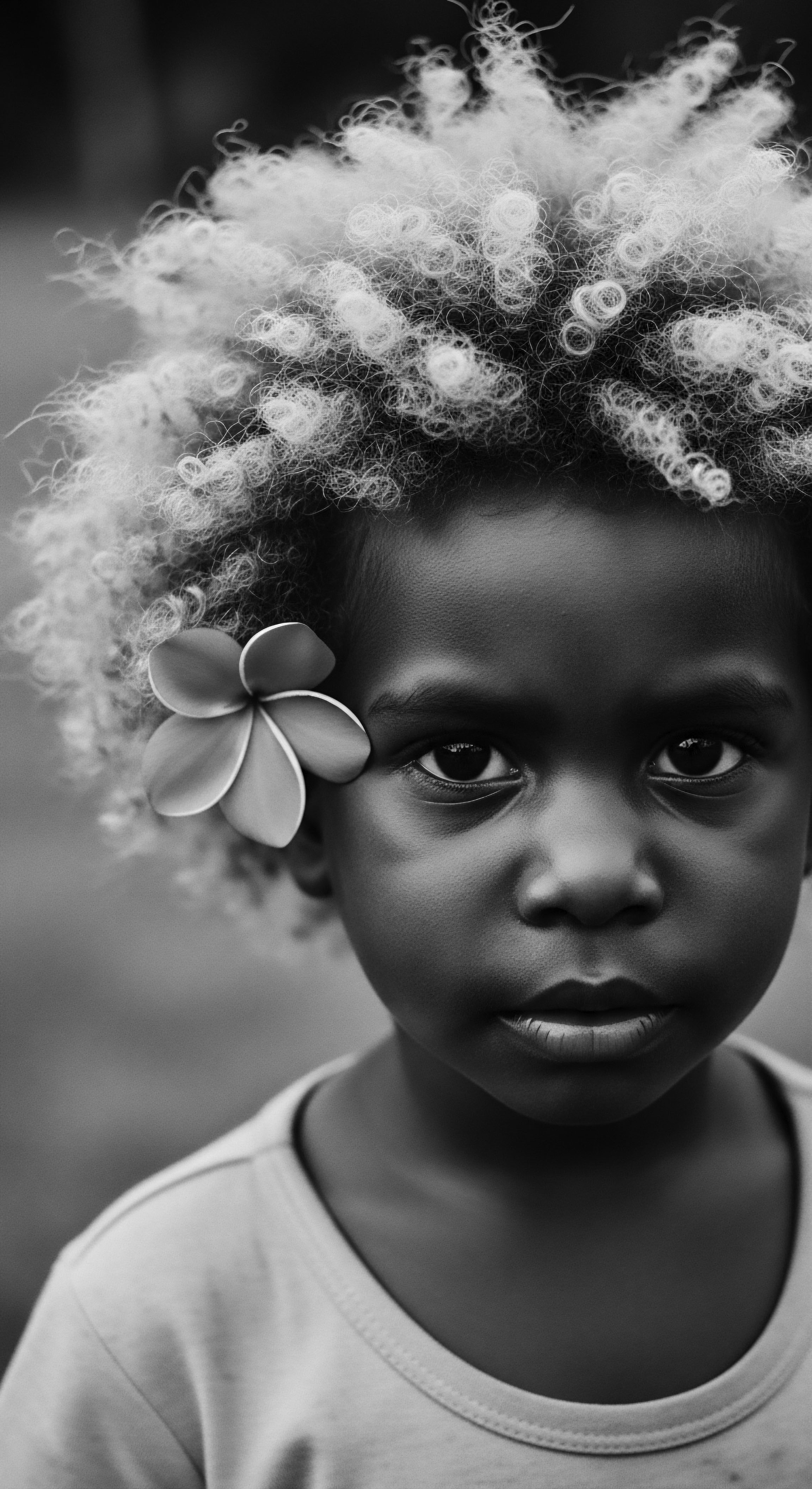
How Did Ancestral Oils Benefit Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils provided textured hair with essential moisture, protection, and structural integrity, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.
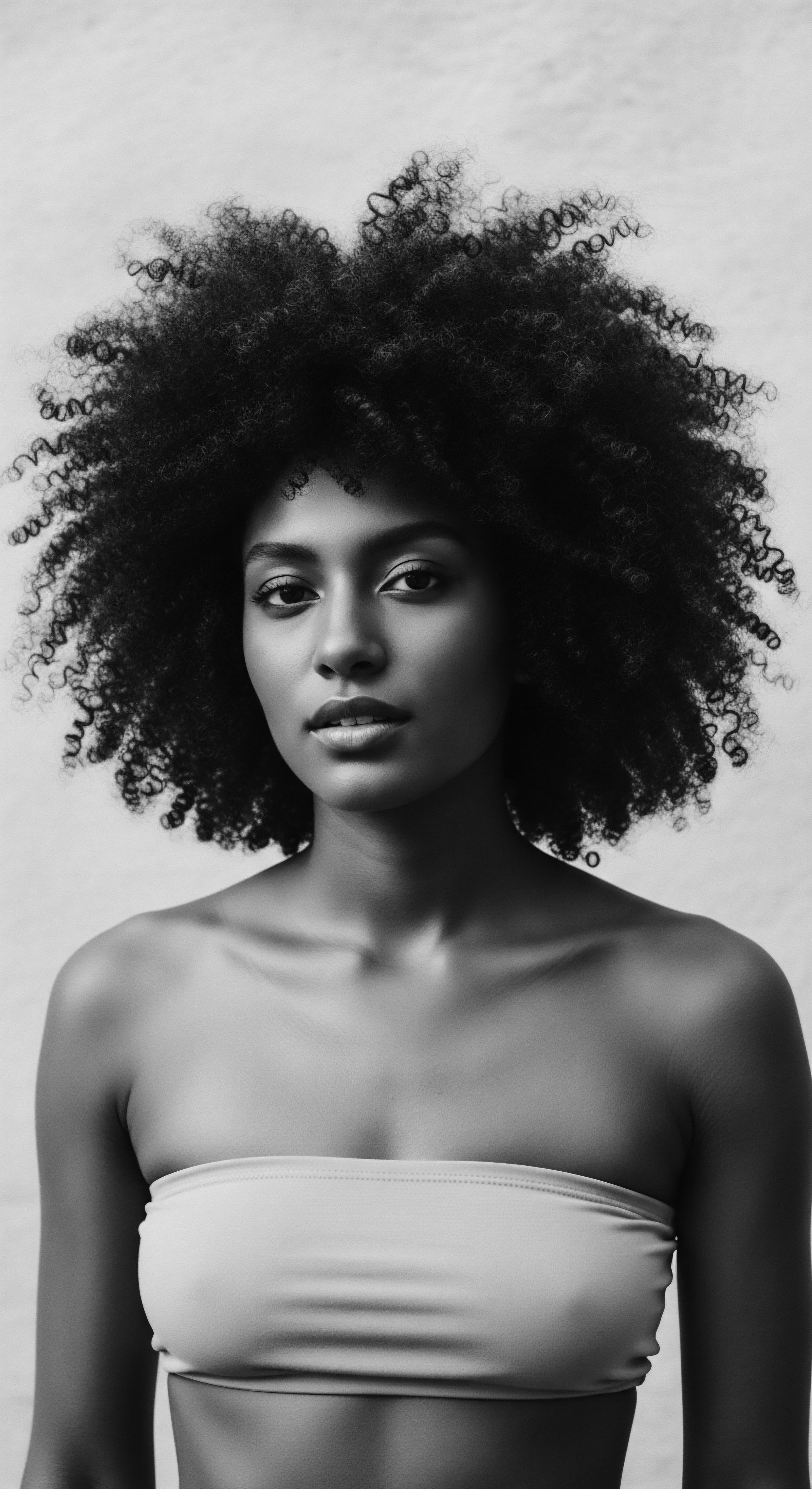

Plant-Based Oils
Meaning ❉ This editorial defines Plant-Based Oils through their deep historical and cultural significance in textured hair care, especially within Black and mixed-race heritage.

How Does Textured Hair’s Structure Relate to Traditional Oiling?
Textured hair's coiled structure benefits from traditional oiling, a heritage practice that seals moisture and strengthens delicate strands.

Botanical Practices
Meaning ❉ Botanical Practices involve using plant materials for textured hair care, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural identity.

Traditional African Hair Remedies
Meaning ❉ Traditional African Hair Remedies are ancestral practices and natural ingredients for textured hair, embodying centuries of cultural heritage and holistic well-being.

Indigenous Plant Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Plant Wisdom is the ancestral knowledge of botanical properties and their applications for holistic well-being, especially for textured hair.

How Do Ancestral Oils Benefit Modern Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils nourish modern textured hair by providing deep moisture, protection, and cultural connection, reflecting a rich heritage of care.
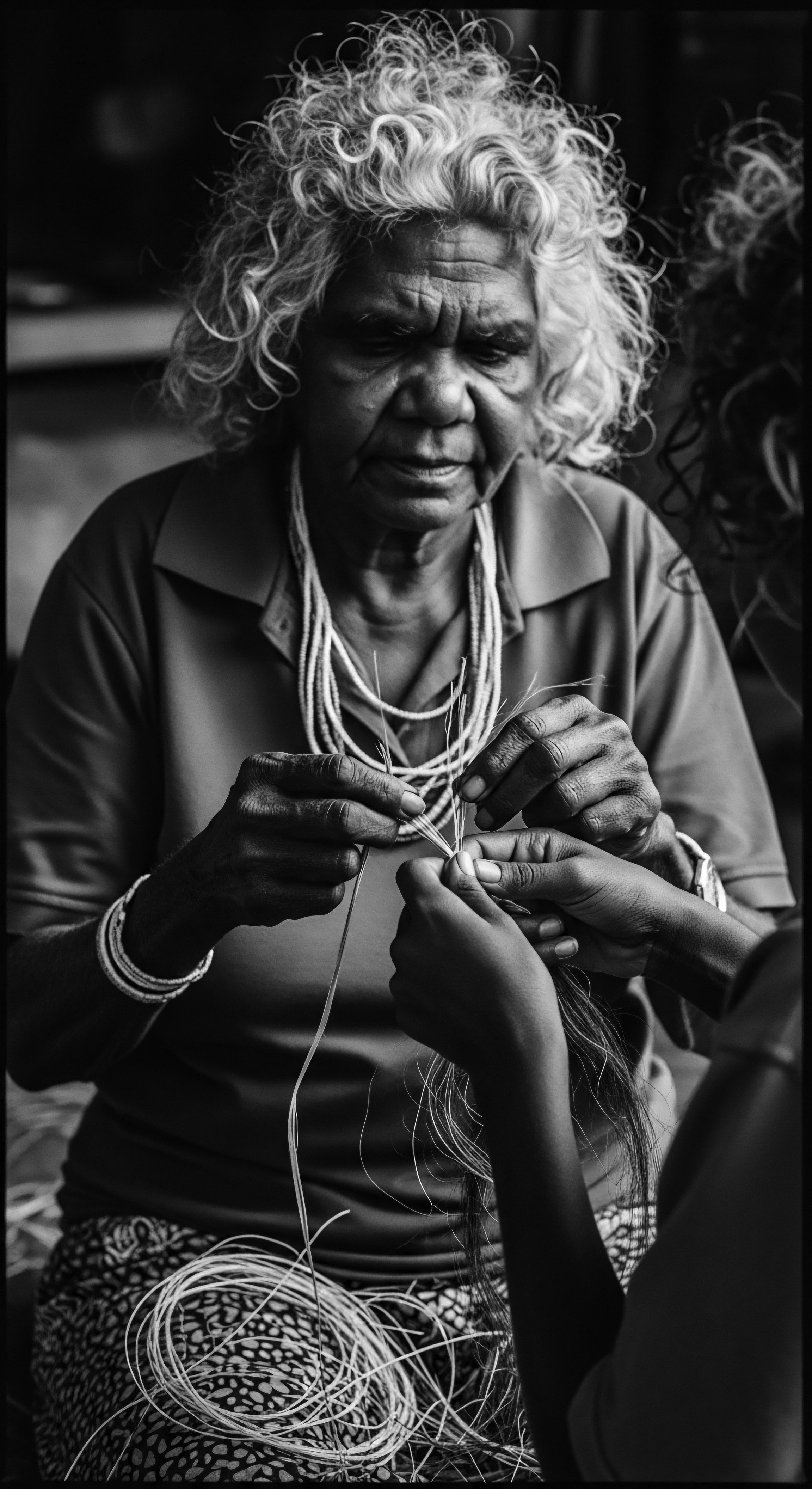

How Do Indigenous Practices Inform the Use of Amazonian Oils for Textured Hair?
Indigenous Amazonian practices deeply inform textured hair care through ancestral oil use, a legacy of natural protection and profound cultural connection.

In What Ways Does Ancestral Wisdom Influence the Science of Hair Products for Textured Hair?
Ancestral wisdom profoundly influences modern textured hair product science by offering foundational knowledge of hair structure, ingredient efficacy, and holistic care rooted in heritage.

What Ancestral Cleansers Shaped Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral cleansers for textured hair, like saponin-rich plants, clays, and plant ashes, prioritized gentle purification and honored cultural heritage.

Hair Health Plants
Meaning ❉ Hair Health Plants are botanicals historically and presently revered for nurturing textured hair, embodying ancestral wisdom and cultural continuity.

Which Traditional Plants Support Scalp Health for Textured Hair?
Traditional plants like shea, neem, and Chebe offer historical wisdom for textured hair scalp health, connecting to ancestral care.

Traditional Botanical Knowledge
Meaning ❉ Traditional Botanical Knowledge is the inherited wisdom and practices of using plants for holistic textured hair care and cultural identity.

What Ancestral Plants Shaped Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral plants like shea, baobab, neem, fenugreek, and black seed profoundly shaped textured hair care, offering hydration, strength, and scalp wellness rooted in enduring heritage.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Plant-Based Hydration in Textured Hair Heritage?
Plant-based hydration is a core cultural pillar, connecting textured hair to ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity across generations.

Can Ancestral Plant Remedies Explain Contemporary Textured Hair Product Effectiveness?
Ancestral plant remedies, rooted in generations of cultural heritage, explain contemporary textured hair product effectiveness by providing naturally potent compounds for moisture, strength, and scalp health.

Can Traditional African Ingredients Provide Modern Solutions for Textured Hair Concerns?
Traditional African ingredients offer effective modern solutions for textured hair concerns by providing deep moisture, protection, and nourishment, rooted in centuries of ancestral heritage and natural wisdom.

Botanical Legacy
Meaning ❉ The Botanical Legacy is the enduring relationship between botanical resources and the cultural heritage of textured hair care practices.
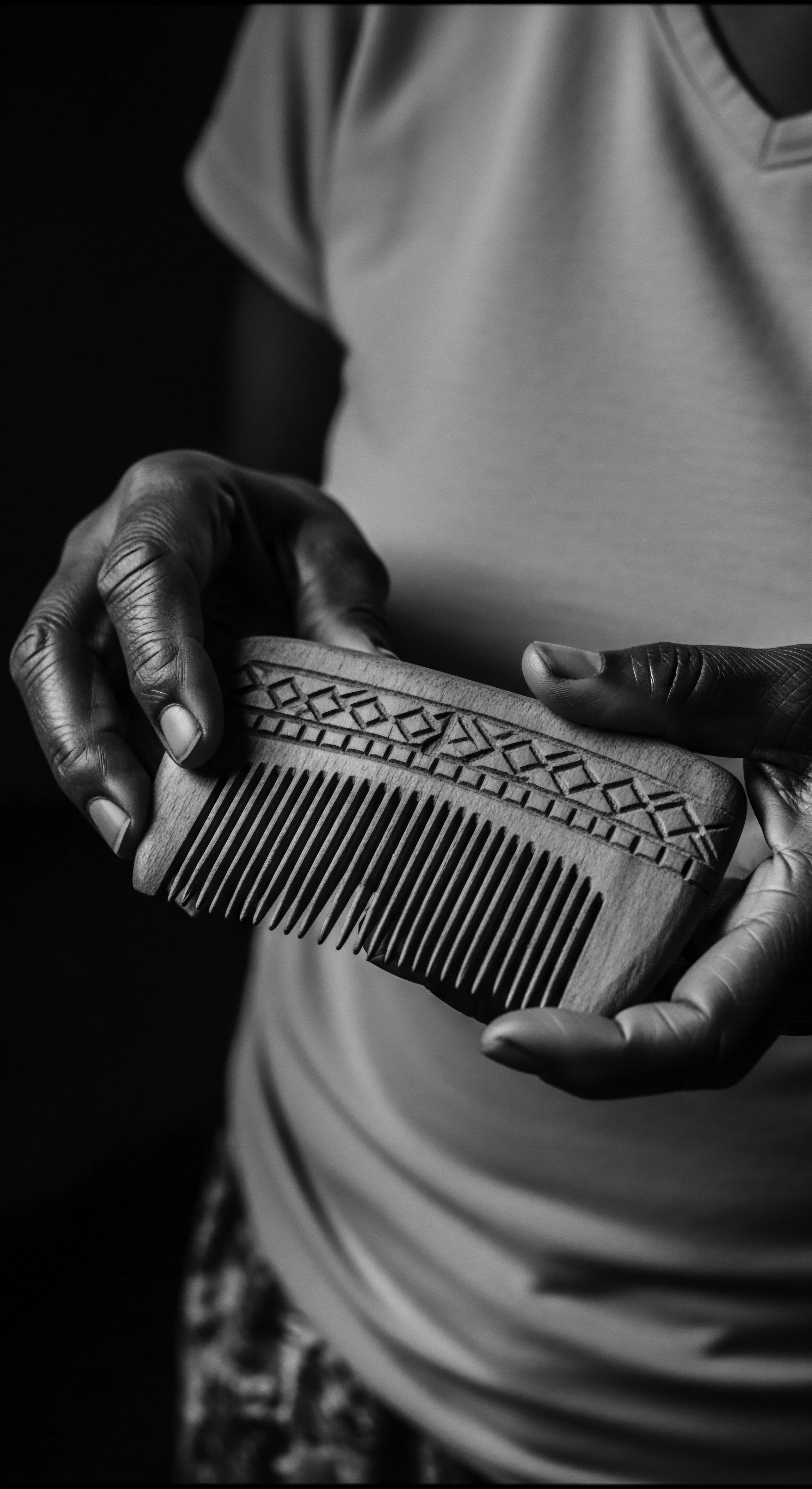

Traditional Black Soap
Meaning ❉ Traditional Black Soap is a heritage-rich, plant-based cleanser from West Africa, vital for textured hair care and cultural identity.

Scalp Microbiome
Meaning ❉ The Scalp Microbiome is a complex ecosystem of microorganisms on the scalp, deeply connected to textured hair heritage and ancestral care practices.

Amazonian Ethnobotany
Meaning ❉ Amazonian Ethnobotany is the study of rainforest plant uses for textured hair care, deeply rooted in Black and Indigenous ancestral wisdom.

Cupuaçu Butter
Meaning ❉ Cupuaçu Butter is a revered Amazonian botanical lipid, offering profound hydration and protection for textured hair, rooted in centuries of ancestral wisdom.
Ancient Beauty
Meaning ❉ Ancient Beauty is the inherent, ancestral strength and cultural significance embodied in textured hair, viewed as a living archive of heritage.

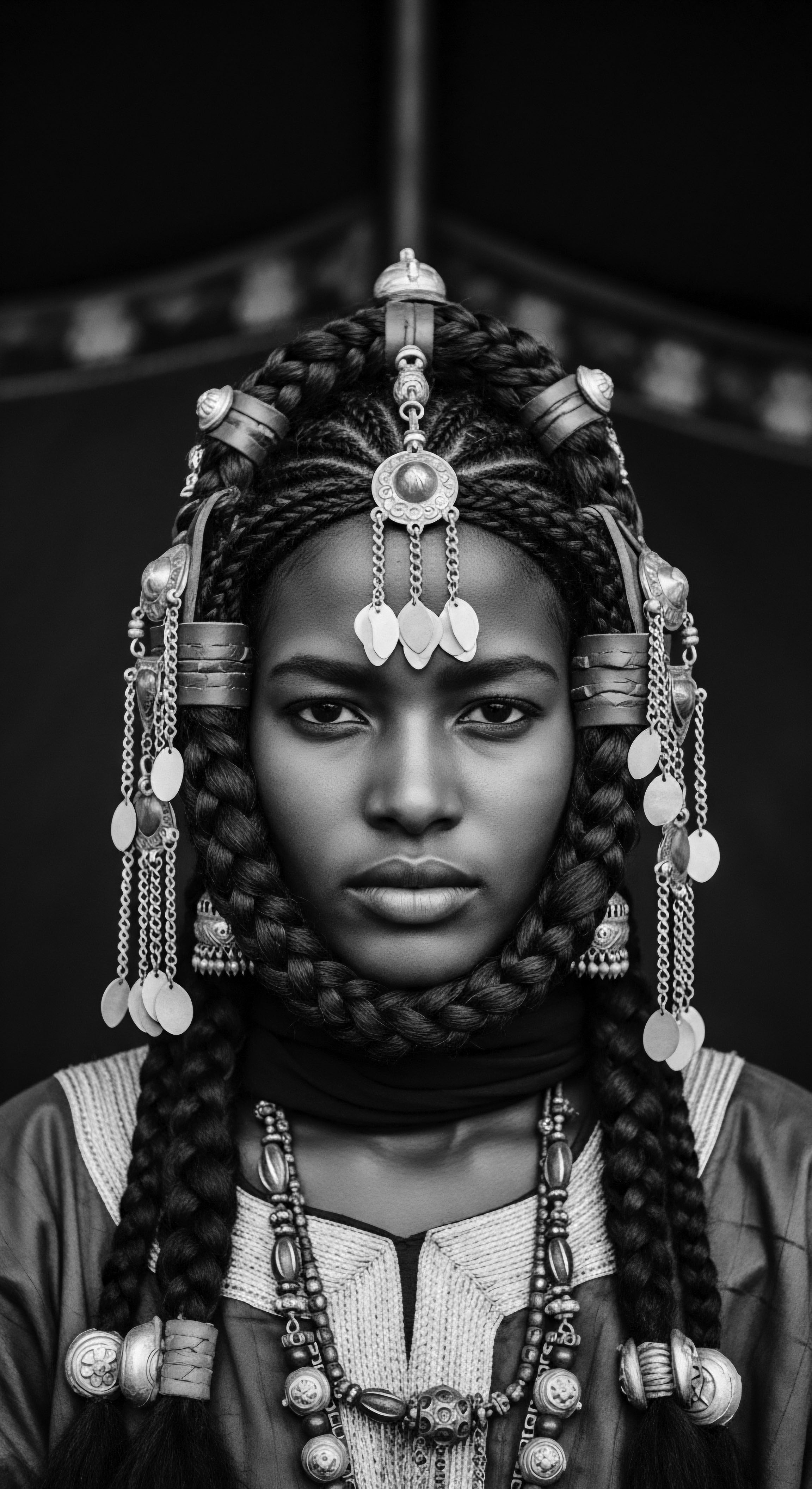
How Do Himba Hair Traditions Relate to Broader African Heritage?
Himba hair traditions, through otjize and intricate styling, symbolize deep identity, social status, and ancestral connection to broader African textured hair heritage.

What Ancient Practices Connected Amazonian Plant Use to Black Hair Heritage?
Ancient Amazonian plant use, particularly botanical oils, connected to Black hair heritage through resilient knowledge transfer and cultural adaptation across the diaspora.

What Historical Examples Reveal the Effectiveness of Plant-Based Hair Care Heritage?
Historical examples reveal plant-based hair care heritage effectively sustained textured hair through ancestral wisdom, ritual, and natural botanicals.

Can Modern Science Validate the Efficacy of Traditional Botanical Hair Purifiers from Textured Hair Heritage?
Modern science confirms traditional botanical hair purifiers work through natural compounds, validating centuries of textured hair heritage wisdom.

Slippery Elm
Meaning ❉ Slippery Elm is a revered botanical known for its mucilaginous inner bark, historically used by diverse communities for soothing and conditioning textured hair.

Amazonian Botanicals
Meaning ❉ Amazonian Botanicals represent ancient flora from the Amazon, embodying ancestral wisdom for nourishing textured hair and preserving cultural heritage.

