
What Ancestral Cleansing Traditions Benefit Textured Hair?
Ancestral cleansing traditions for textured hair use natural ingredients and mindful rituals to honor hair's unique heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Inform Modern Textured Hair Routines?
Ancestral practices inform modern textured hair routines through holistic care, protective styling, and natural ingredient use, rooted in deep heritage.

In What Ways Do Ancient Hair Rituals Continue to Shape Modern Care Practices for Textured Hair?
Ancient hair rituals continue to shape modern textured hair care by emphasizing profound moisture, protective styling, and communal well-being, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom.

Overnight Routines
Meaning ❉ Overnight Routines for textured hair are pre-sleep practices deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, designed to protect, nourish, and preserve strands.
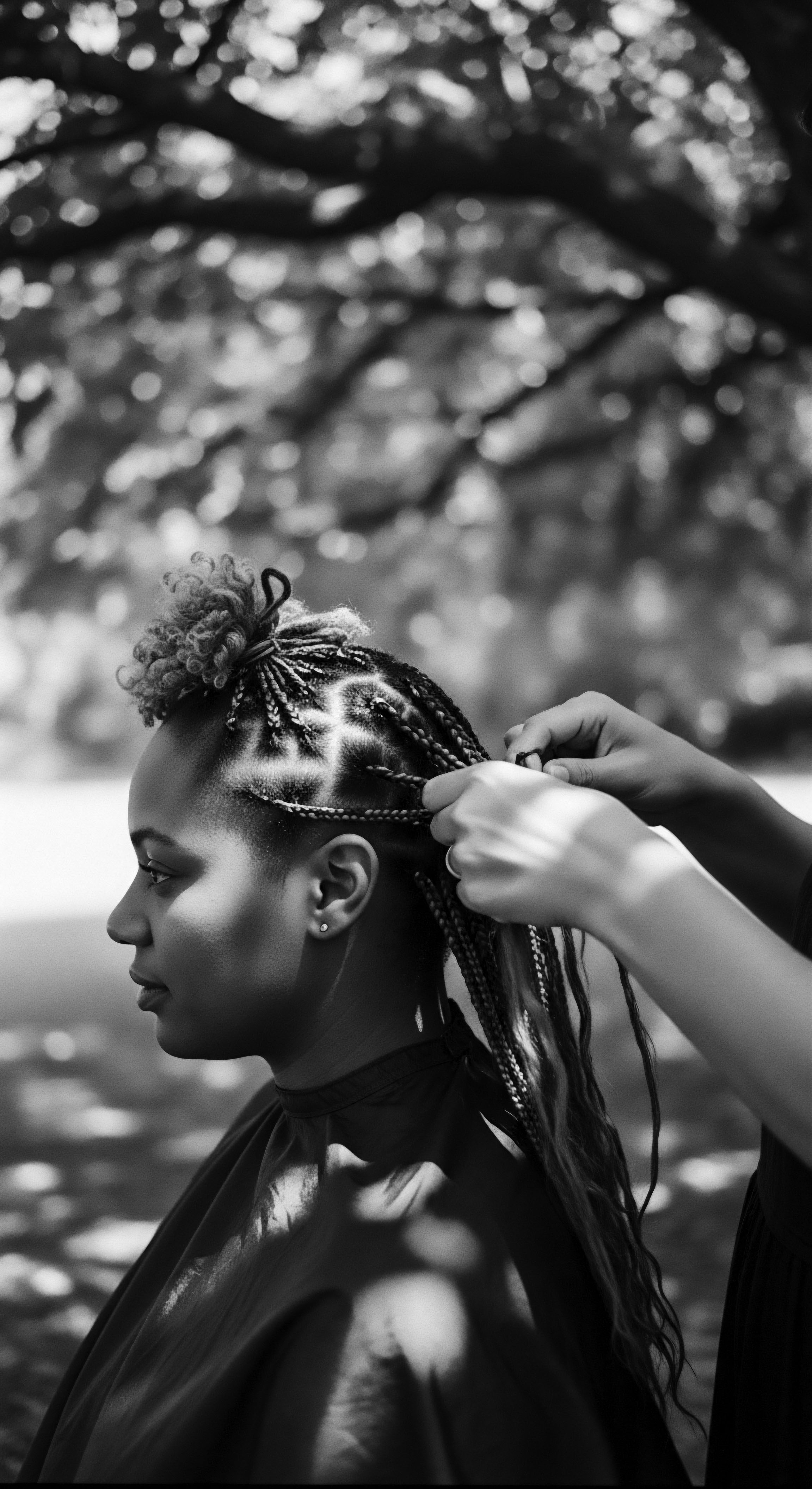
How Do Textured Hair Practices Connect to Ancestral Wisdom?
Textured hair practices are deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, embodying cultural identity, spiritual connection, and historical resilience.

What Ancestral Rituals Honored Textured Hair in Ancient African Cultures?
Ancestral African rituals honored textured hair as a sacred, communicative extension of self, interwoven with identity, spirituality, and community heritage.

What Lessons from Historical Textured Hair Care Traditions Apply to Modern Wellness?
Historical textured hair traditions offer profound lessons in holistic wellness, emphasizing ancestral wisdom and cultural connection in modern care.

How Did Ancient Combs Safeguard Textured Hair?
Ancient combs safeguarded textured hair through designs that respected natural curl patterns, reducing breakage and promoting health, a heritage of care.

Can Ancient Hair Practices Truly Enhance Contemporary Textured Hair Routines?
Ancient hair practices offer a heritage-rich blueprint for enhancing contemporary textured hair routines with profound wisdom.

Can Ancestral Plant Practices Provide Guidance for Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancestral plant practices offer timeless wisdom for modern textured hair regimens by upholding a heritage of moisture, protection, and holistic self-care.

How Did Ancient African Practices Influence Textured Hair Care?
Ancient African practices shaped textured hair care by focusing on natural ingredients, protective styles, and communal rituals, honoring hair as a symbol of identity and heritage.
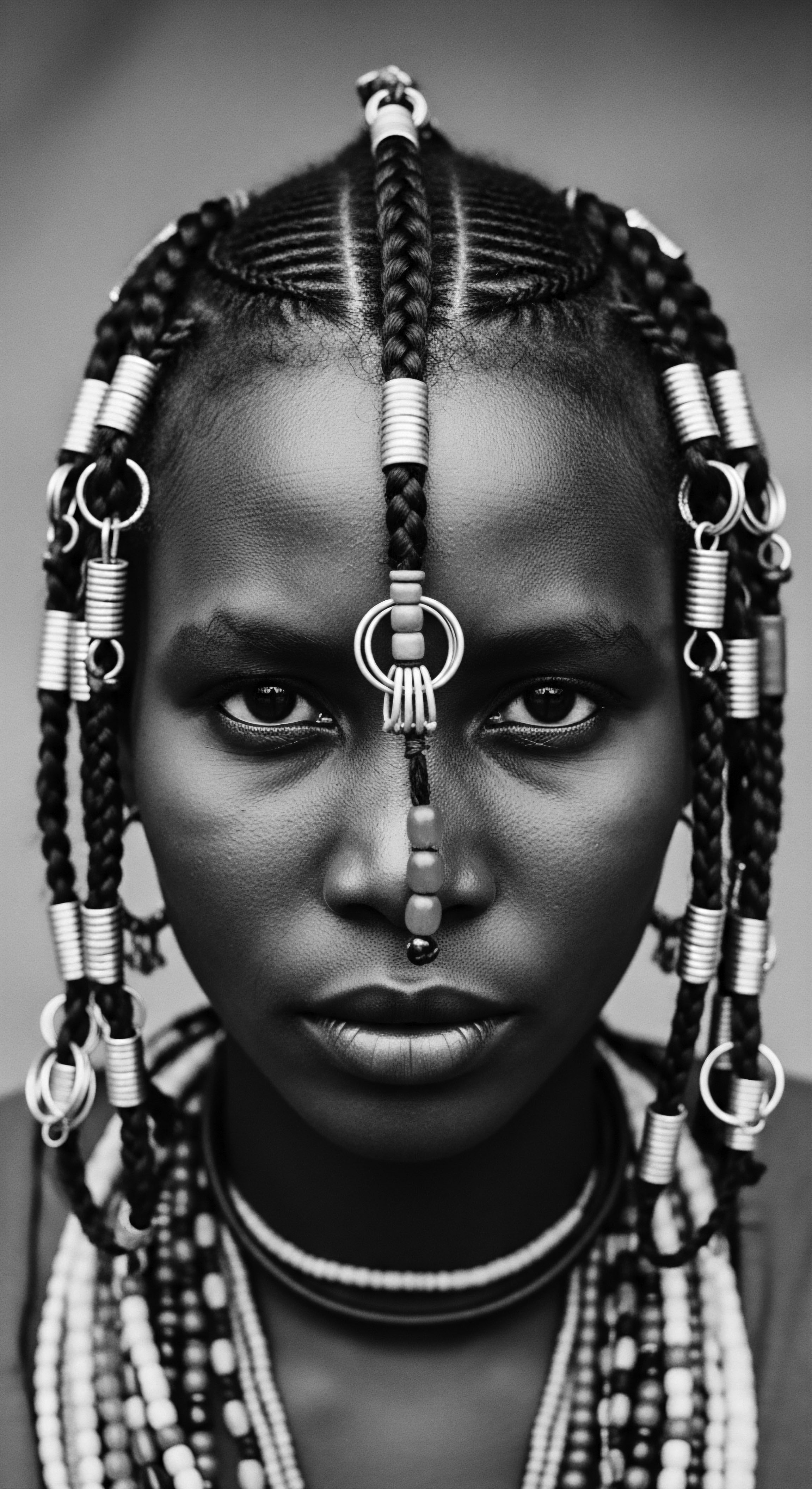

How Did Ancestral Hair Rituals Preserve Textured Hair’s Moisture?
Ancestral hair rituals preserved textured hair moisture through intuitive use of natural emollients, protective styles, and gentle, consistent care, deeply rooted in heritage.

African Hair Technologies
Meaning ❉ African Hair Technologies encompass ancestral knowledge, practices, and scientific understandings for textured hair, rooted in cultural identity.

Pomegranate Oil
Meaning ❉ Pomegranate Oil is a botanical extract celebrated for its unique fatty acid profile, deeply rooted in historical hair care traditions for nourishing textured hair.

What Are the Enduring Cultural Meanings of Hair Length and Strength in African Heritage?
Hair length and strength in African heritage convey deep meanings of identity, spirituality, and communal ties, profoundly shaping textured hair legacy.

Early Black Business
Meaning ❉ Early Black Business signifies enterprises by African descendants, vital for community provision and cultural identity, especially in textured hair care.

How Do Ancestral Hair Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Health?
Ancestral hair practices significantly influence modern textured hair health by providing a heritage of protective styling and natural nourishment.
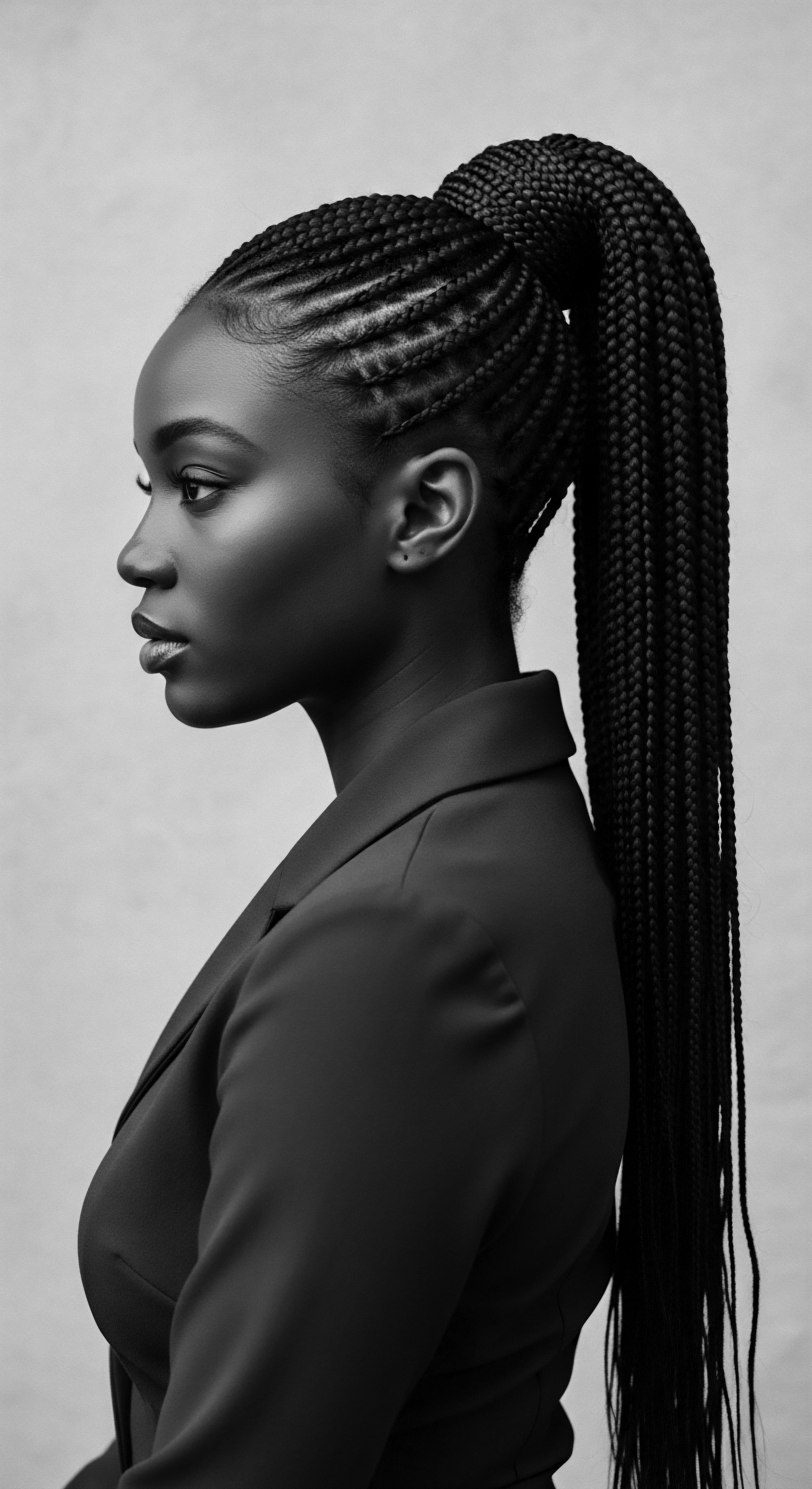

Kanuri Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Kanuri Hair Practices are profound cultural expressions of identity, social status, and life's passages, rooted in ancestral West African traditions.

How Did Historical Cultures View Textured Hair’s Unique Properties?
Historical cultures viewed textured hair as a profound marker of identity, status, and spiritual connection, leveraging its unique properties for communication and protection.

How Do Ancient Hair Practices Inform Modern Care for Textured Hair?
Ancient hair practices illuminate modern textured hair care by offering a heritage of intuitive scientific understanding, cultural expression, and holistic well-being.

What Scientific Principles Confirm the Benefits of Traditional African Plant Ingredients for Textured Hair?
Ancestral plant wisdom, validated by science, deepens understanding of textured hair care heritage.

Cultural Hair Adversity
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Adversity describes systemic pressures devaluing textured hair, rooted in historical oppression and impacting identity.

How Did Headwraps Sustain Textured Hair?
Headwraps sustained textured hair by offering physical protection and acting as symbols of enduring cultural heritage and self-determination.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Textured Hairstyles?
Textured hairstyles serve as a living chronicle, profoundly reflecting the enduring identity, resilience, and ancestral heritage of Black and mixed-race communities.

What Traditional Care Principles Inform Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Traditional care principles, steeped in heritage, inform modern textured hair regimens through a deep understanding of hair's unique biology and historical practices.

Can Traditional Textured Hair Care Connect Generations?
Traditional textured hair care connects generations by transmitting ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and resilient practices.
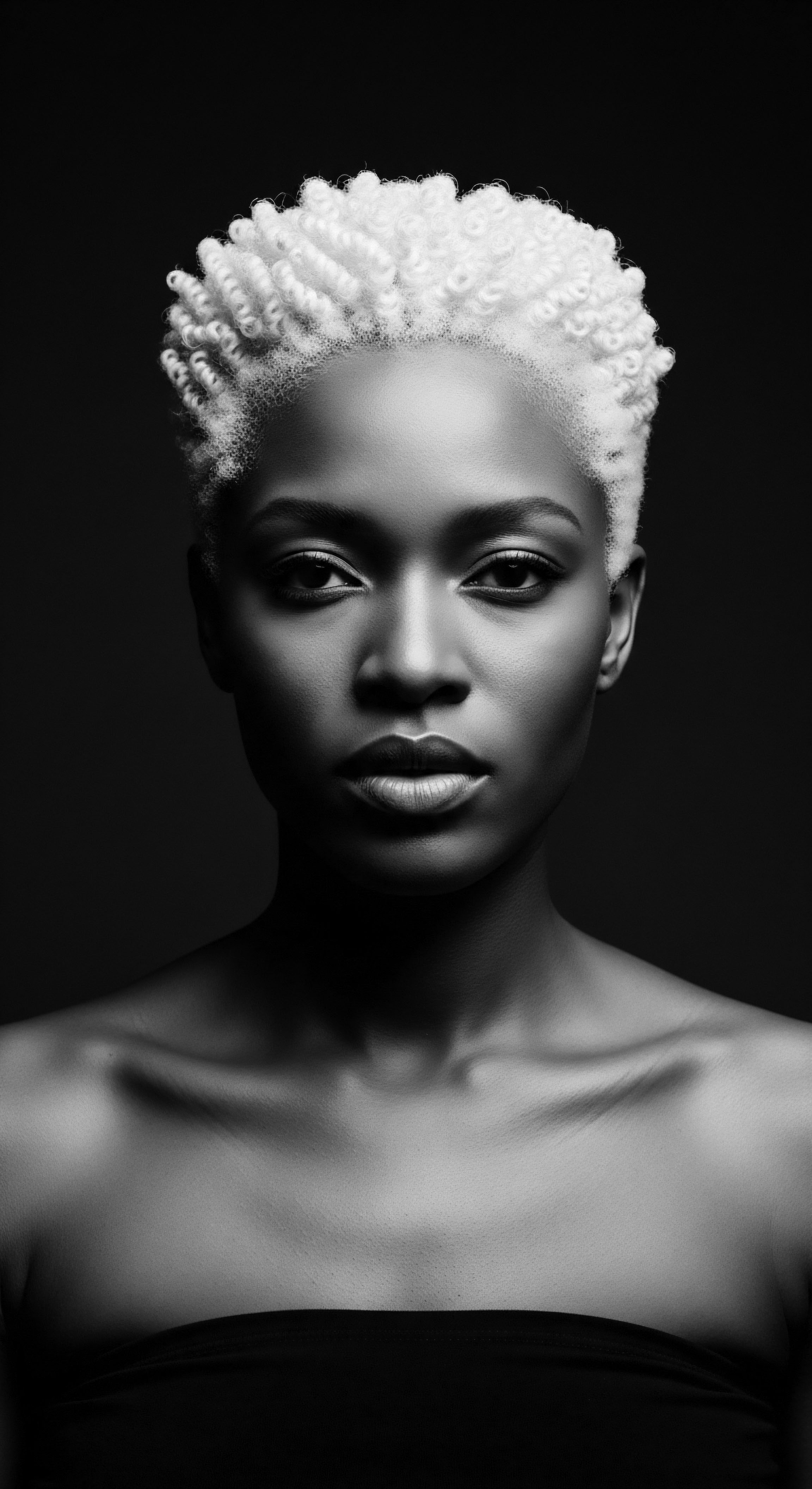

What Is the Historical Significance of Protective Styles in African Heritage?
Protective styles hold historical significance as ancient African heritage expressions, communicating identity, and safeguarding textured hair.
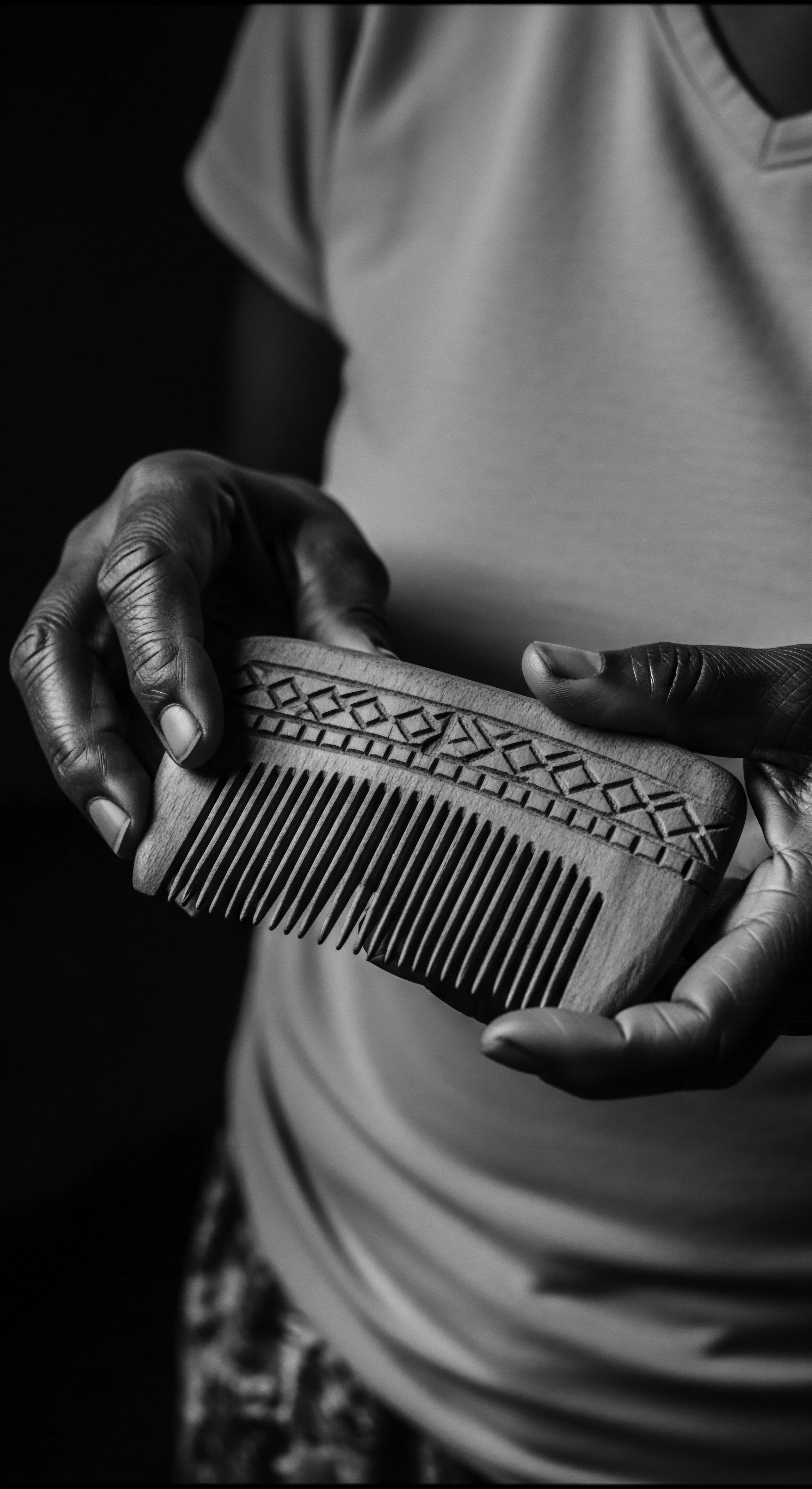

What Ancestral Ingredients Enhance Textured Hair Health with Oiling?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter, coconut, and castor oil profoundly enhance textured hair health by drawing on a rich heritage of purposeful oiling.
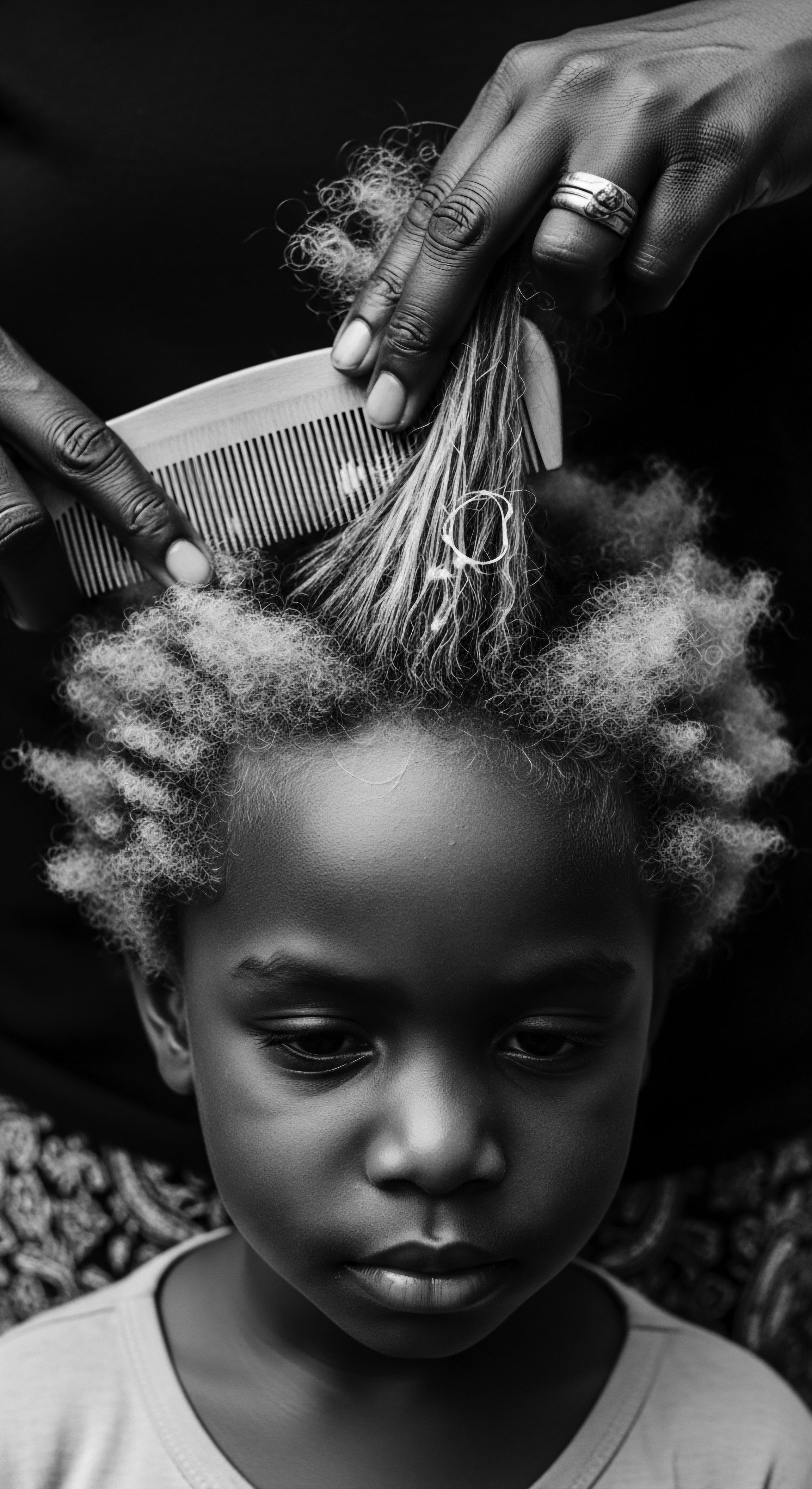

What Is the Enduring Cultural Connection to Natural Textured Hair?
The enduring cultural connection to natural textured hair resides in its deep heritage as a symbol of identity, communication, and resilience.

