
How did ancient communities classify different hair textures?
Ancient communities often classified hair through its role in identity, status, and spiritual beliefs, deeply embedding it in textured hair heritage.

What enduring legacy do traditional plant oils hold for textured hair heritage?
Traditional plant oils form a vital, enduring legacy for textured hair heritage, preserving ancestral care rituals and strengthening cultural identity.

What historical evidence confirms castor oil’s role in hair rituals?
Historical accounts confirm castor oil's enduring role in textured hair rituals, especially for its deeply nourishing and protective qualities across diverse ancestral practices.

What is the historical significance of protective styles in diaspora communities?
Protective styles signify resilience and identity, anchoring diaspora communities to their textured hair heritage and ancestral practices.

In what ways do historical hair rituals connect to cultural identity and community resilience?
Historical hair rituals, especially for textured hair, served as powerful affirmations of cultural identity and anchors for community resilience.

In what ways did ancestral knowledge inform the scientific understanding of textured hair?
Ancestral knowledge intuitively guided the understanding and care of textured hair, informing practices now validated by modern science.

How is textured hair a living ancestral record?
Textured hair is a biological blueprint and cultural chronicle, preserving genetic heritage and the ancestral wisdom of Black and mixed-race communities.

How did pre-colonial African societies honor hair heritage?
Pre-colonial African societies honored hair heritage as a spiritual conduit, social map, and artistic expression.

What ancient African practices preserve textured hair’s legacy?
Ancient African practices preserve textured hair's legacy through sacred rituals, botanical remedies, and intricate styling, symbolizing deep cultural identity.

How does Chebe powder traditionally strengthen textured hair?
Chebe powder traditionally fortifies textured hair by coating strands, minimizing breakage, honoring ancestral hair care heritage.

What traditional practices influenced modern hair care rituals?
Ancient practices and ancestral wisdom, especially from Black and mixed-race communities, profoundly shaped modern textured hair care rituals.

What is the role of traditional West African oils in preserving hair heritage?
Traditional West African oils protect textured hair, embody ancestral wisdom, and preserve a rich heritage of identity and communal care.

How do traditional African hair care ingredients align with modern hair science?
Traditional African hair care ingredients align with modern science through shared principles of moisture retention, scalp wellness, and hair strength, rooted deeply in textured hair heritage.
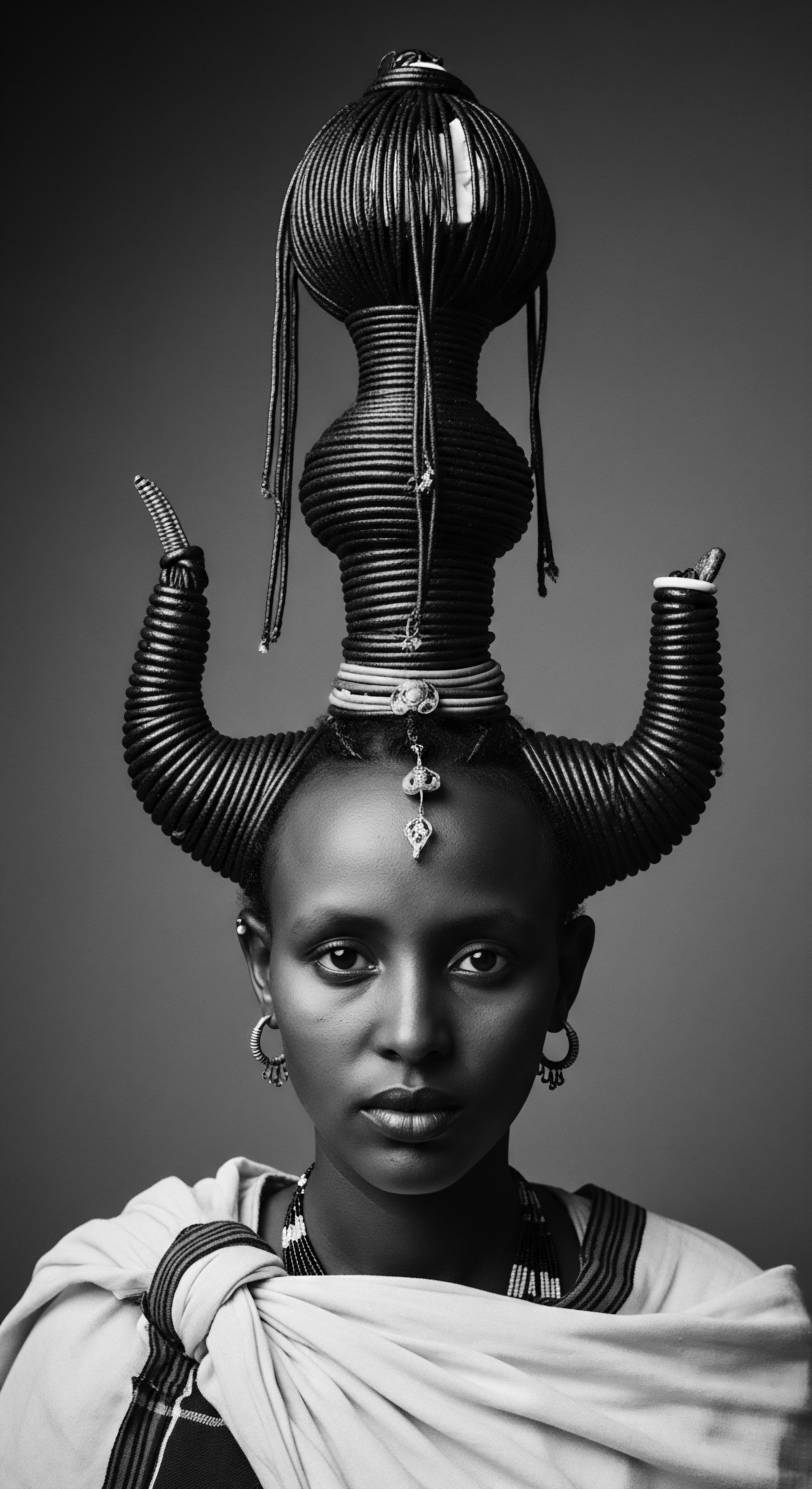

What is the ancestral meaning of adornments?
Ancestral adornments for textured hair convey identity, status, and spiritual connection, acting as a living record of heritage.

What ancestral oils are traditionally used for Black hair care?
Ancestral plant-based oils like shea butter, castor oil, and palm oil were traditionally used for Black hair care, forming a vital part of textured hair heritage.

What traditional practices influenced Black hair?
Traditional practices influenced Black hair through symbolic meaning, communal rituals, protective styles, and natural ingredient use, all rooted in heritage.
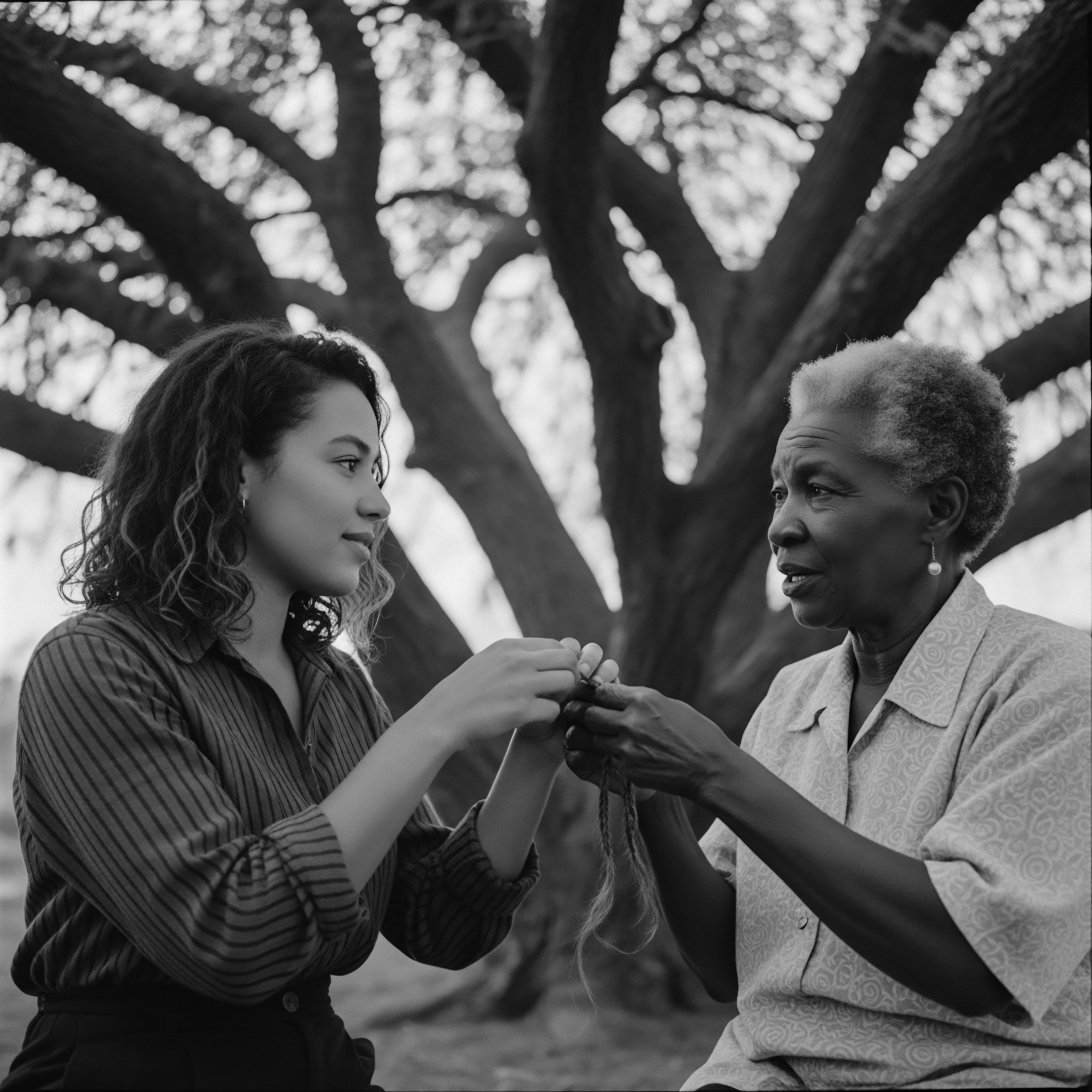

What ancestral hair care ingredients supported braiding traditions?
Ancestral hair care ingredients like shea butter, coconut oil, and plant-based cleansers provided nourishment and strength for textured hair braiding traditions.

What spiritual connections does hair hold?
Textured hair holds spiritual connections as an ancestral conduit, signifying identity, power, and sacred heritage across Black and Indigenous cultures.
How does modern hair care connect to the enduring wisdom of traditional Black hair rituals?
Modern textured hair care deeply mirrors traditional Black hair rituals by prioritizing heritage, protection, and identity.

What traditional oils benefit coiled hair?
Traditional oils like shea butter and castor oil deeply nourish coiled hair, echoing ancestral wisdom for moisture and protection.

What traditional African ingredients were used for hair purification?
Traditional African hair purification used earth-derived elements like black soap, qasil powder, and mineral-rich clays, honoring textured hair heritage.

How do hair rituals strengthen family bonds?
Hair rituals, through shared touch and knowledge passed across generations, forge profound familial bonds rooted in textured hair heritage.

How has textured hair care expressed cultural belonging?
Textured hair care expresses belonging through inherited ancestral practices that celebrate identity and community.

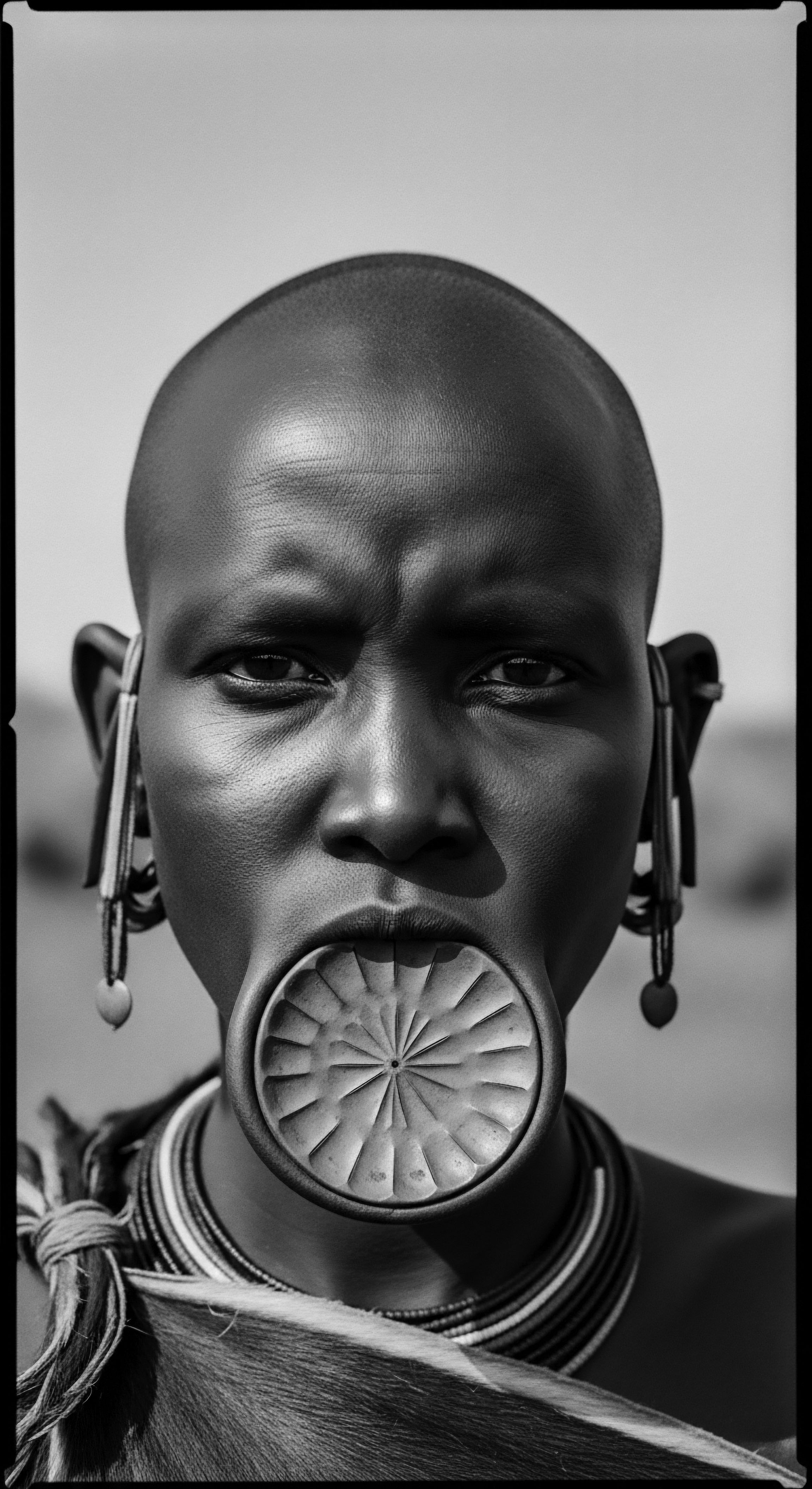
How did ancestral oiling methods change?
Ancestral oiling methods evolved from earth-sourced communal rituals to individual heritage acts, adapting through cultural shifts.

How did ancient societies protect hair?
Ancient societies protected textured hair through natural oils, protective styling, and head coverings, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

Can hair practices today connect to ancestral Black hair care heritage?
Modern textured hair practices profoundly connect to ancestral Black hair care heritage through shared principles of protection, holistic wellness, and identity.

Why is hair oiling considered a cultural practice for textured hair?
Hair oiling is a cultural practice for textured hair rooted in ancestral wisdom, providing moisture, protection, and a deep connection to heritage.

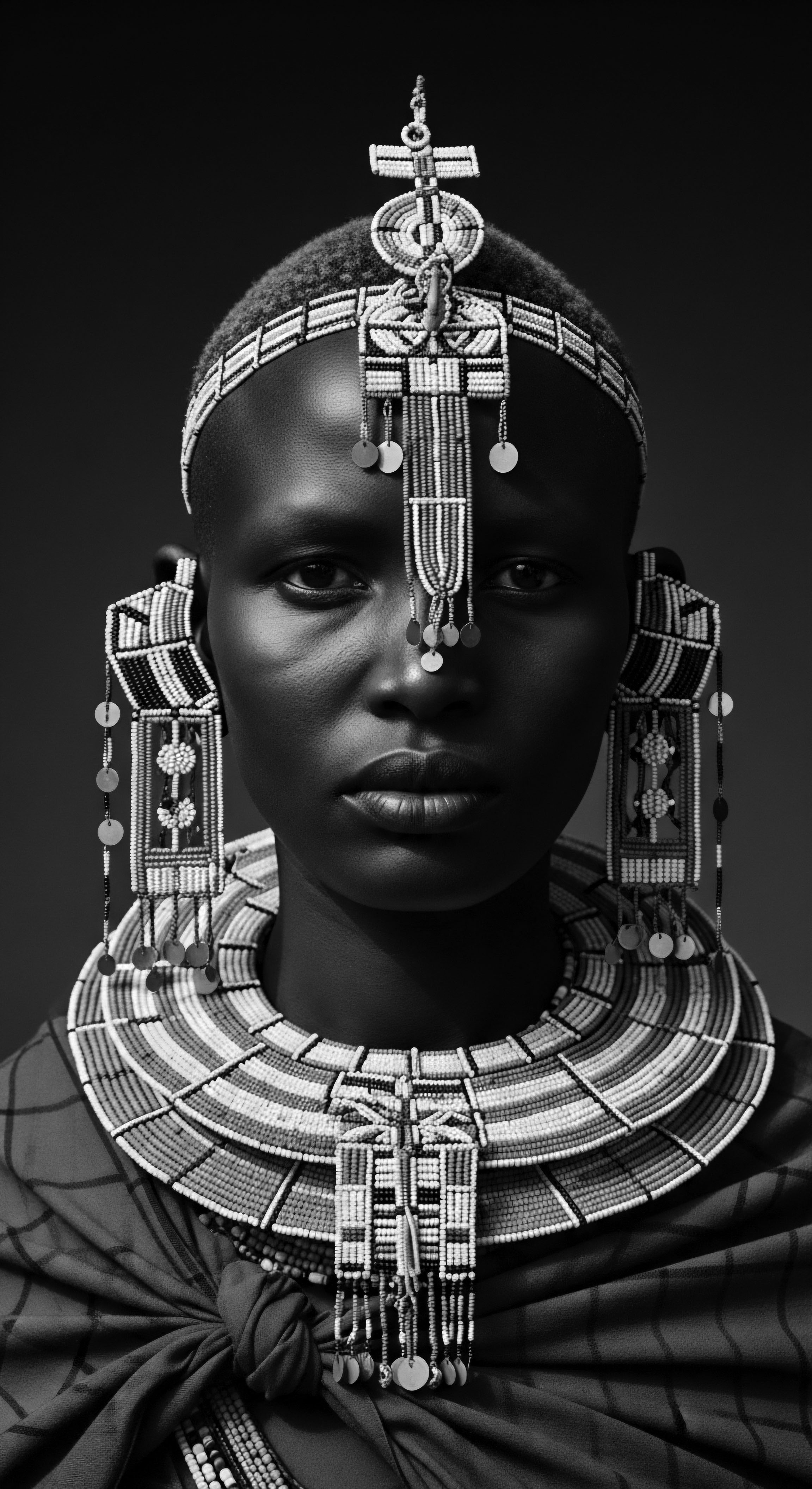
How did traditional African hair practices communicate identity and status?
Traditional African hair practices were a vibrant language, communicating identity, social status, and spiritual beliefs through specific styles and adornments, reflecting a deep textured hair heritage.

How do traditional plant oils care for textured strands?
Traditional plant oils care for textured strands by deeply moisturizing and protecting the hair shaft, a practice rooted in diverse ancestral heritage and validated by modern science.

