
How Do Plant Uses Moisturize Textured Hair?
Plant uses moisturize textured hair by providing natural lipids and humectants, a heritage-rich practice passed through generations.

In What Ways Do Contemporary Textured Hair Practices Reflect Ancestral Knowledge?
Contemporary textured hair practices directly reflect ancestral wisdom, preserving identity and culture through inherited care rituals and styling methods.

What Ancestral Oils Are Still Important for Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils, rich in heritage, remain vital for textured hair by providing deep moisture and protection rooted in historical traditions.

How Does Ancient Hair Knowledge Connect to Black Heritage?
Ancient hair knowledge connects to Black heritage through ancestral care rituals, symbolic styling, and tools that honored identity and community.

Can Clay Truly Define and Prepare Textured Hair for Ancestral Styles?
Clay, an ancient earth mineral, can define and prepare textured hair for ancestral styles by cleansing, protecting, and enhancing natural curl patterns through rich heritage practices.

What Is the Ancestral Connection to Modern Textured Hair Care?
The ancestral connection to modern textured hair care lies in inherited wisdom regarding structure, protective styling, and natural ingredient use.

Which Ancestral Earths Cleanse Textured Hair?
Ancestral earths like rhassoul, bentonite, and kaolin cleanse textured hair by drawing impurities while honoring its inherent moisture, a heritage of mindful care.

What Is the Biological Reason for Varied Textured Hair?
Varied textured hair stems from inherited follicle shapes and protein distribution, a biological legacy shaped by ancestral adaptation.

Can Traditional Head Coverings Prevent Textured Hair Damage?
Yes, traditional head coverings offer crucial protection for textured hair by reducing friction, maintaining moisture, and shielding from environmental elements, a practice deeply rooted in heritage.

What Ancestral Materials Shaped Early Textured Hair Tools?
Ancestral materials like wood, bone, and early metals formed diverse tools that honor textured hair heritage.

Can Ancient Oiling Rituals Inform Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancient oiling rituals deeply inform modern textured hair care by providing a heritage of protection, hydration, and cultural connection.
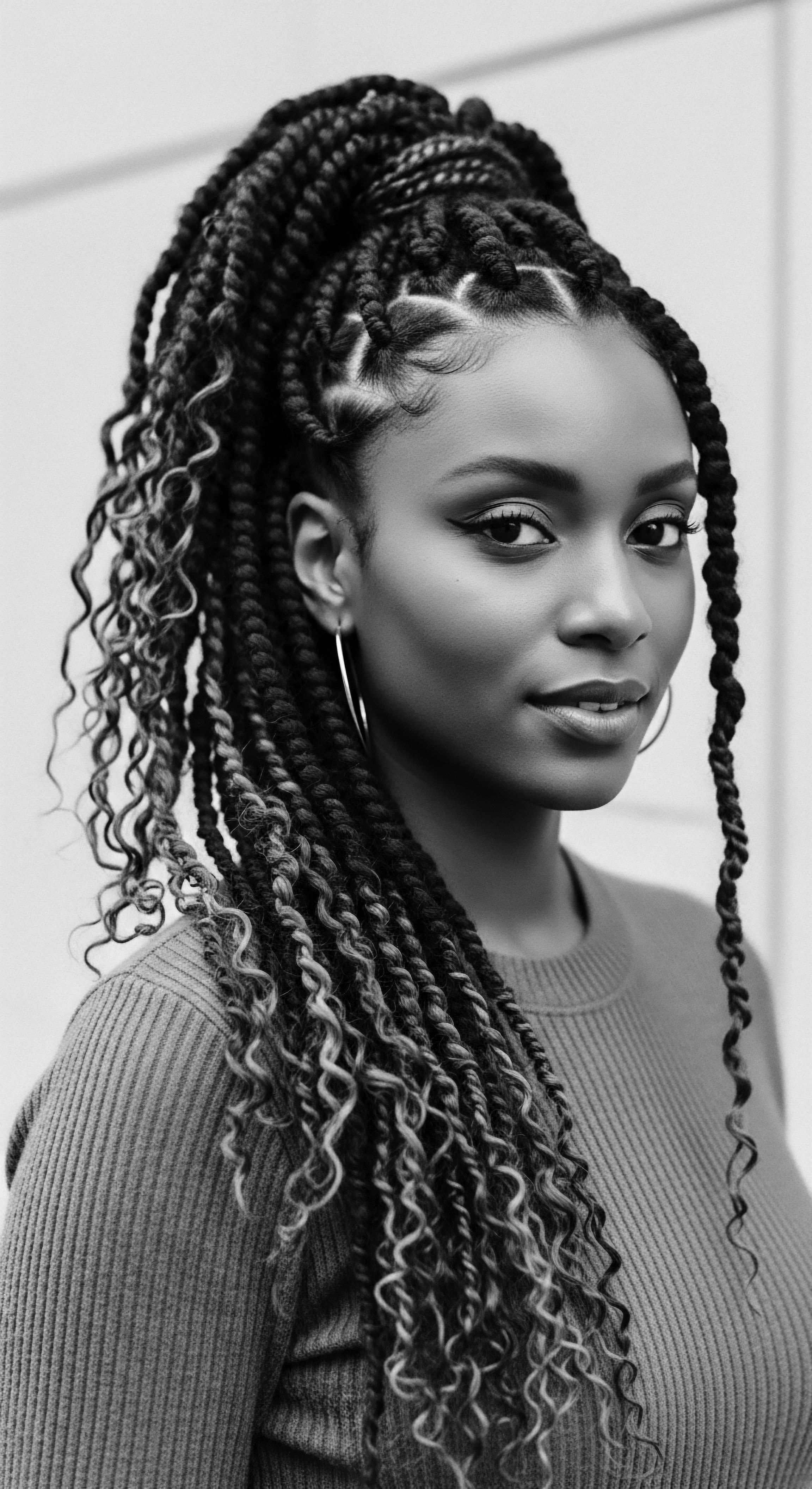
How Did Historical Cultures Protect Textured Hair during Rest?
Historical cultures protected textured hair during rest through smooth coverings, protective styles, and natural oils, honoring its unique heritage and preserving its health.

How Did Cleansing Traditions Shape Textured Hair Identity?
Cleansing traditions shaped textured hair identity by rooting care in ancestral wisdom, communal rituals, and a deep reverence for natural beauty.

How Does Clay Chemically Benefit Textured Hair Historically?
Clay historically cleanses and nourishes textured hair through mineral exchange, deeply rooted in ancestral care and heritage.

How Did Ancestral Oils Care for Textured Scalps?
Ancestral oils nourished textured scalps by protecting, moisturizing, and supporting hair growth, deeply rooted in Black hair heritage.

What Historical Ingredients Influenced Textured Hair’s Ph?
Historical ingredients like alkaline plant ash and acidic fruit rinses shaped textured hair's pH, reflecting ancestral wisdom in hair heritage.

What Traditions Connected Textured Hair to Ancestral Practices?
Textured hair traditions connected ancestral practices by serving as vital cultural markers, spiritual conduits, and ingenious forms of communication and resistance.

Why Was Traditional Clay Cleansing Ideal for Textured Hair’s Unique Structure?
Traditional clay cleansing suited textured hair by gently purifying and enriching strands with heritage minerals.

Water Hair Science
Meaning ❉ Water Hair Science explores how water interacts with hair's structure and behavior, especially for textured hair, informed by ancestral practices.

What Is the Scientific Basis for Ancient Textured Hair Cleansing Ingredients?
Ancient textured hair cleansing ingredients often rely on natural compounds like saponins and mineral clays, aligning with modern science to gently purify while preserving hair's inherited qualities.

Did Ancestral Practices Preserve Textured Hair from Sun Damage?
Ancestral practices preserved textured hair from sun damage through inherent hair structure, protective styling, and natural emollients and pigments.

Do Natural Oils Truly Hydrate Textured Hair?
Natural oils primarily seal moisture into textured hair, deeply rooted in ancestral practices for care and resilience.

How Can Science Validate Traditional Textured Hair Rituals of the Diaspora?
Science affirms that ancestral textured hair rituals optimize hair health through methods rooted in deep historical heritage.

What Historical Purposes Did Hair Oiling Serve for Textured Hair?
Hair oiling historically nourished, protected, and styled textured hair, while also symbolizing deep cultural identity and ancestral connection.

What Historical Ingredients Guarded Textured Hair from Sun and Wind?
Ancestral textured hair care, deeply rooted in heritage, employed natural oils, butters, and strategic styling to shield strands from environmental stressors.

What Historical Significance Do Hair Oiling Practices Hold for Textured Strands?
Hair oiling for textured strands signifies a heritage of protective care, cultural connection, and enduring ancestral wisdom.

How Does Historical Hair Oiling Inform Modern Regimens for Textured Hair?
Historical hair oiling informs modern textured hair regimens by grounding care in ancestral wisdom and the biological needs of coiled strands, offering a deep connection to heritage.

What Oils Did Ancient Cultures Use for Textured Hair?
Ancient cultures used diverse oils like castor, olive, coconut, shea, and sesame to nourish and protect textured hair, upholding a rich heritage of care.

How Do Traditional African Ingredients Benefit Textured Hair Wellness?
Traditional African ingredients nourish textured hair wellness by deeply moisturizing and fortifying strands, continuing a rich ancestral heritage.

