
What Is the Cultural Significance of Head Coverings in Textured Hair Heritage?
Head coverings hold deep cultural significance in textured hair heritage, acting as symbols of identity, protection, and resistance across generations.

How Do African Oils Connect to Black Hair Heritage?
African oils connect to Black hair heritage through centuries of ancestral practices, providing essential nourishment and cultural identity for textured strands.

What Is the Cultural Heritage of Textured Hair Care?
The cultural heritage of textured hair care is a rich chronicle of ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity, woven into the very structure of Black and mixed-race hair.

What Role Did Historical Oils Play in the Cultural Expression of Black Hair Heritage?
Historical oils served as essential emollients, protective agents, and cultural symbols, deeply woven into textured hair heritage.

What Plant Oils Sustained Textured Hair through History?
Ancestral plant oils like shea butter, coconut oil, and castor oil sustained textured hair through history, providing moisture, protection, and cultural connection.

What Ancestral Ingredients Nourish Textured Hair Today?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and castor oil nourish textured hair by providing moisture, protection, and strength, reflecting a rich heritage of care.

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Practices Continue to Inform Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical hair practices profoundly inform modern textured hair care by providing foundational knowledge of hair structure, traditional ingredients, protective styling, and holistic wellness, all rooted in ancestral heritage.

What Botanical Wisdom Supported Textured Hair’s Moisture Balance Historically?
Botanical wisdom from textured hair heritage used plant butters and oils to seal moisture, reflecting deep ancestral knowledge of hair's needs.

How Did Ancestral Hair Care Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Health?
Ancestral hair care practices profoundly influence modern textured hair health by providing foundational wisdom on ingredients, protective styling, and holistic wellness.

Can Traditional Oils Genuinely Benefit Textured Hair Health, Drawing from Ancestral Wisdom and Current Understanding?
Traditional oils genuinely benefit textured hair health by providing deep moisture and protection, rooted in centuries of ancestral wisdom.

In What Ways Do Historical Practices Continue to Influence Modern Textured Hair Care Routines?
Historical practices profoundly influence modern textured hair care through ancestral techniques, tools, and cultural significance.
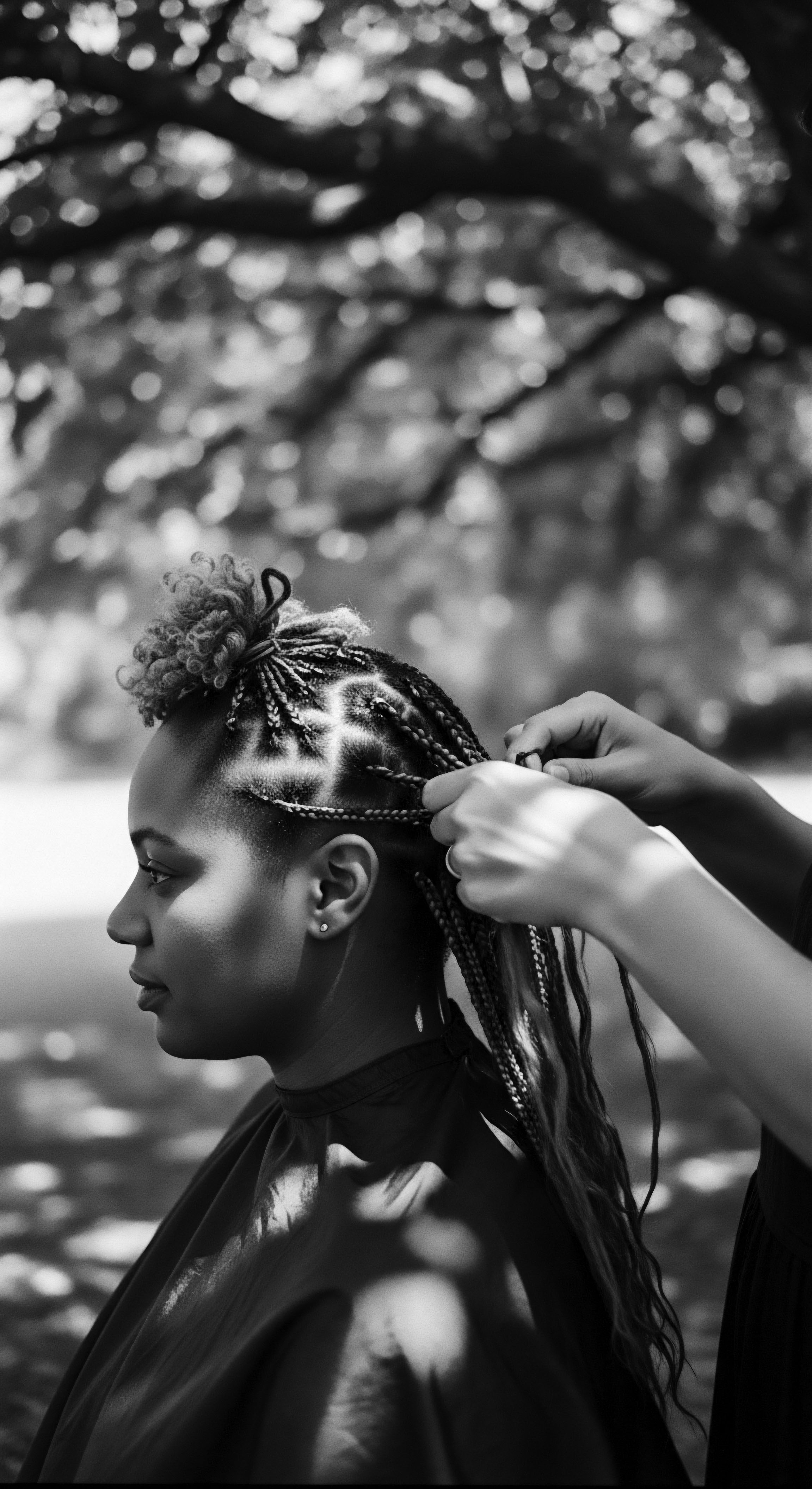
What Historical Styles Protected Textured Hair from Dryness?
Historical styles like braids, twists, and headwraps, alongside natural oils, protected textured hair from dryness by sealing in moisture and reducing environmental exposure.

In What Ways Does Cultural Heritage Shape Textured Hair Wellness Practices?
Cultural heritage deeply shapes textured hair wellness practices, grounding modern care in ancestral wisdom, historical rituals, and profound identity.
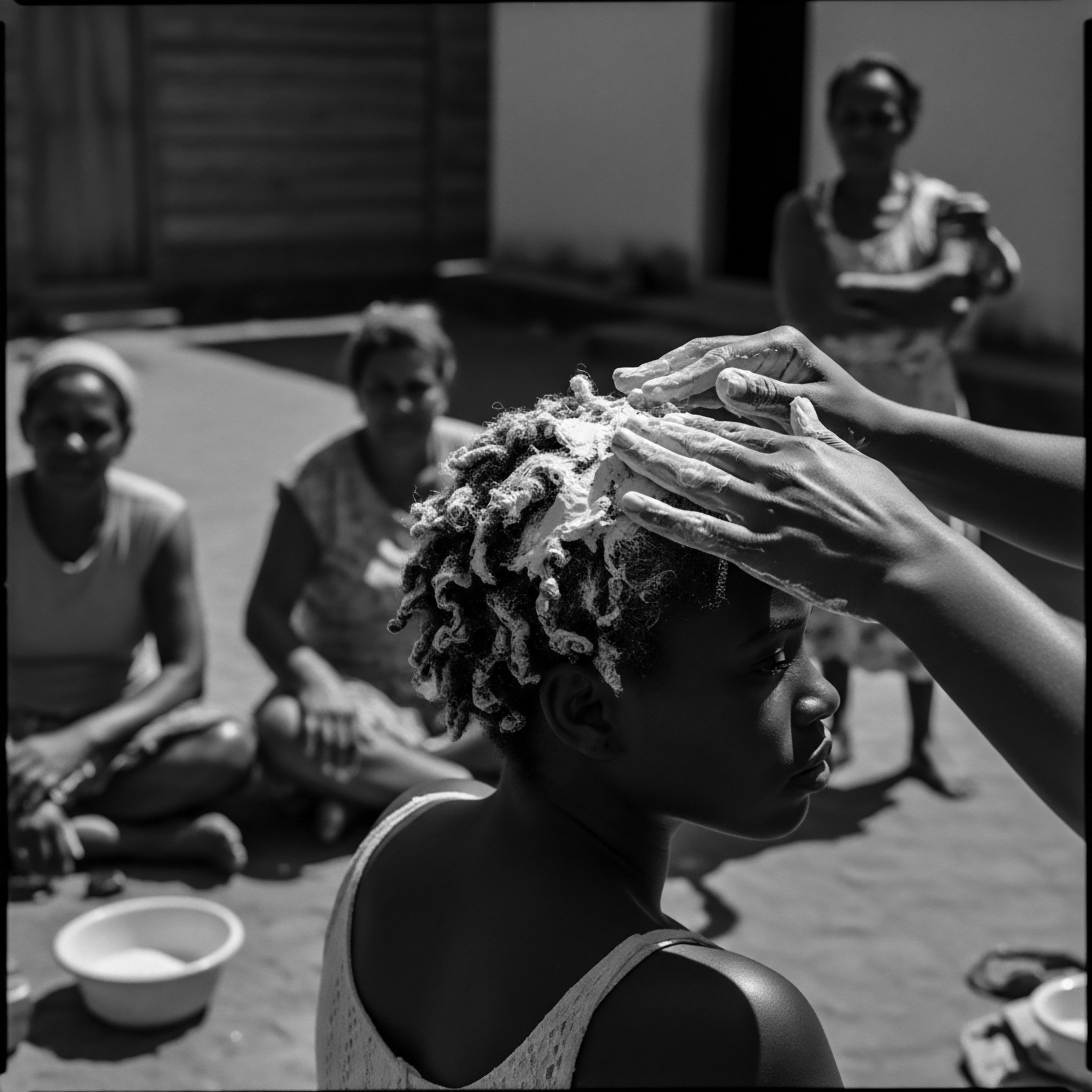

How Does Ancestral Hair Care Connect to Black Cultural Identity and Heritage?
Ancestral hair care profoundly connects to Black cultural identity by serving as a living record of heritage, resilience, and communal wisdom.

Saharan Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Saharan Hair Practices define ancestral hair care wisdom from the Sahara and Sahel, emphasizing textured hair heritage, natural ingredients, and cultural identity.

How Did Traditional Oils Signify Cultural Identity in African Heritage?
Traditional oils in African heritage signify cultural identity by anchoring hair care in ancestral wisdom, communal rituals, and resilience.

In What Ways Do Ancestral Practices Influence Contemporary Textured Hair Care Philosophies?
Ancestral practices deeply inform contemporary textured hair care by providing foundational knowledge of hair structure, traditional ingredients, and styling methods, all steeped in cultural heritage.

Textured Hair Mechanics
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Mechanics is the study of inherent properties and behaviors of curly, coily, and wavy hair, rooted in ancestral wisdom and scientific understanding.

Afro Pick Significance
Meaning ❉ The Afro pick signifies a cultural tool embodying ancestral heritage, Black identity, and resilience in textured hair care.

In What Ways Do Adornments Symbolize Resilience in Textured Hair Heritage?
Adornments in textured hair heritage represent resilience through historical identity, resistance against oppression, and continuous cultural affirmation.

In What Ways Do Contemporary Hair Care Materials Respect Ancestral Practices for Textured Strands?
Contemporary hair care materials honor ancestral practices by mimicking traditional ingredients, replicating protective styling principles, and validating age-old wisdom through scientific understanding.

Gulf Cultural Hair
Meaning ❉ Gulf Cultural Hair signifies the inherited wisdom and distinctive hair traditions of textured strands, particularly within Black and mixed-race communities across Gulf regions.

What Historical Cleansing Ingredients Continue to Influence Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical cleansing ingredients, from clays to plant saponins, continue to shape modern textured hair care by honoring ancestral wisdom and gentle purification.

What Ancestral Tools Influenced Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral combs, natural fibers, and protective head coverings profoundly shaped modern textured hair care, connecting current practices to a rich heritage.

In What Ways Did Hair Rituals Preserve Cultural Heritage across the Diaspora?
Hair rituals served as a vital means of cultural preservation, transmitting identity, knowledge, and resilience across the textured hair diaspora.

Can Textured Hair Care Practices Truly Influence Self-Perception and Cultural Continuity?
Textured hair care practices deeply influence self-perception and cultural continuity by preserving ancestral wisdom, fostering community bonds, and serving as a symbol of resistance and identity.

How Does the Heritage of Textured Hair Influence Modern Beauty Rituals and Identity?
Textured hair heritage profoundly shapes modern beauty rituals by grounding them in ancestral practices of care, communal bonding, and identity expression.

What Traditional Ingredients Support Textured Hair Health through Heritage?
Traditional ingredients, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, supported textured hair health by providing natural moisture, strength, and protection, honoring a rich heritage.

Asian Hair Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Asian Hair Wisdom is a comprehensive system of traditional hair care practices and philosophies, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and natural ingredients.

