
What Is the Historical Origin of Specific Protective Styles?
Protective styles originated from ancient African civilizations, evolving as essential methods for textured hair health, cultural expression, and ancestral connection.
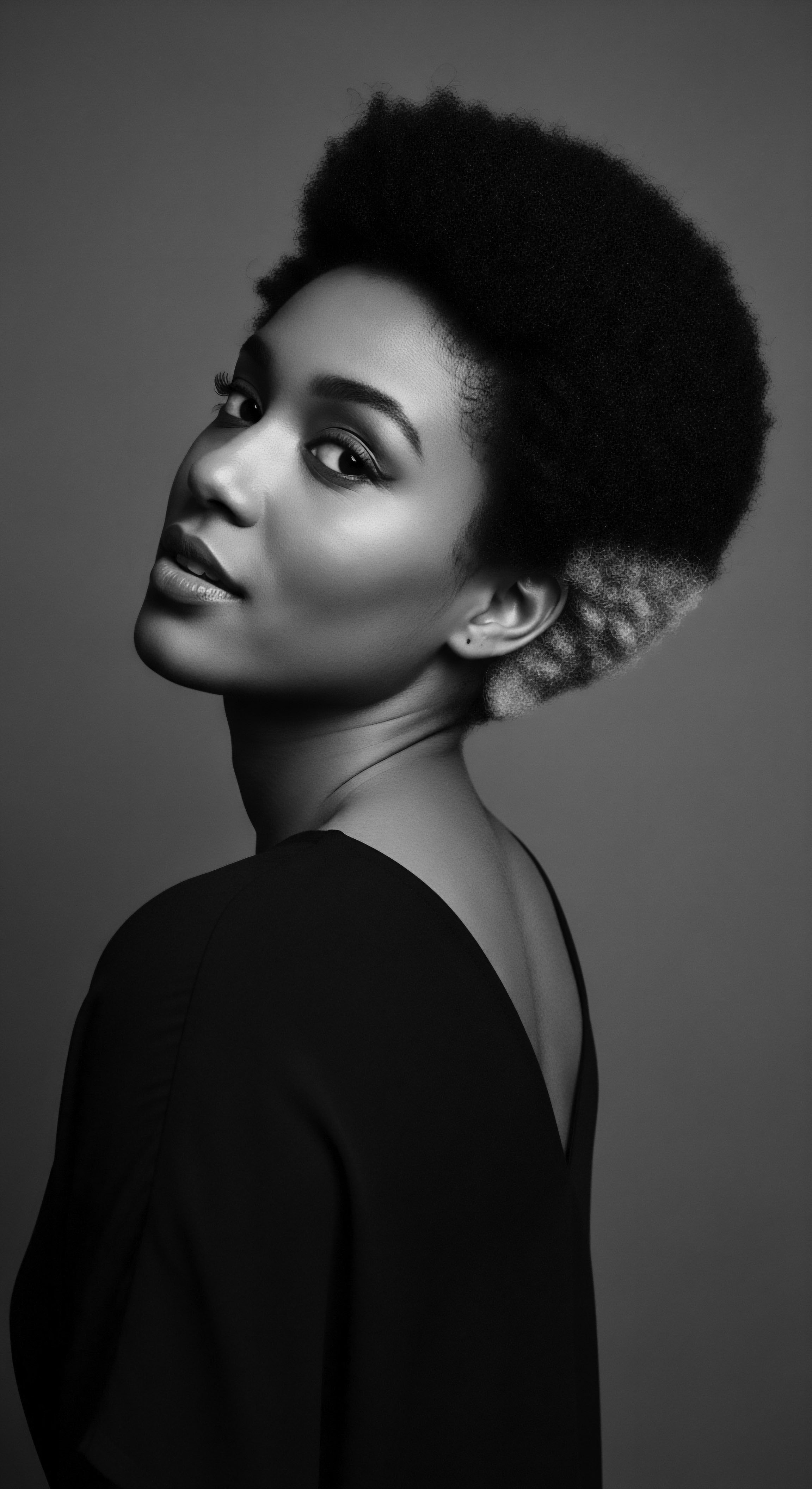

What Ancestral Practices for Hair Are Validated by Science?
Ancestral practices for textured hair, from oiling to protective styles, are validated by science as methods for moisture retention and reduced breakage, deeply linked to heritage.

What Cultural and Scientific Insights Explain the Enduring Relevance of Traditional Oils for Coiled Hair?
Traditional oils for coiled hair endure through cultural heritage, scientific efficacy, and deeply ingrained ancestral practices.

What Historical Examples Show Hair as a Symbol of Resistance?
Textured hair has historically served as a potent symbol of resistance, embodying cultural identity and defiance against oppression within Black and mixed-race heritage.
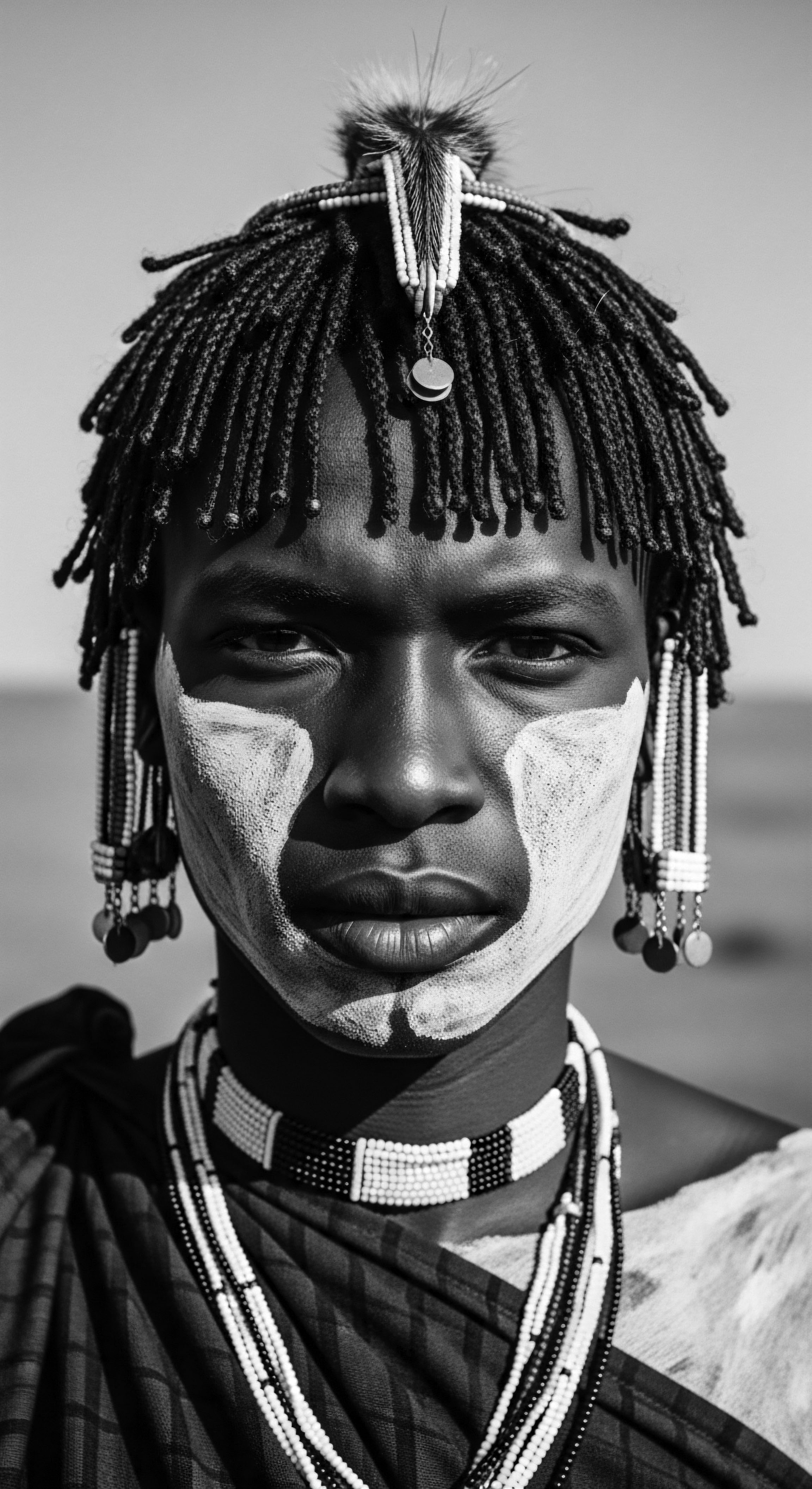

How Do Ancestral Hair Care Practices Influence Modern Beauty Standards?
Ancestral hair practices profoundly shape modern beauty standards by preserving the heritage, rituals, and profound identity woven into textured hair care.
How Do Headwraps Connect Modern Care to Historical Heritage?
Headwraps connect modern textured hair care to historical heritage by serving as protective coverings, cultural markers of identity, and symbols of resilience against oppressive norms.

What Is the Scientific Basis for Hair Bonnets in Heritage Care?
Hair bonnets reduce friction and maintain moisture, scientifically preserving textured hair’s health, a practice deeply rooted in ancestral care.

Potassium Carbonate
Meaning ❉ Potassium Carbonate is a foundational alkaline salt, historically derived from wood ash, crucial for ancient hair cleansing, texture modification, and cultural practices in textured hair heritage.
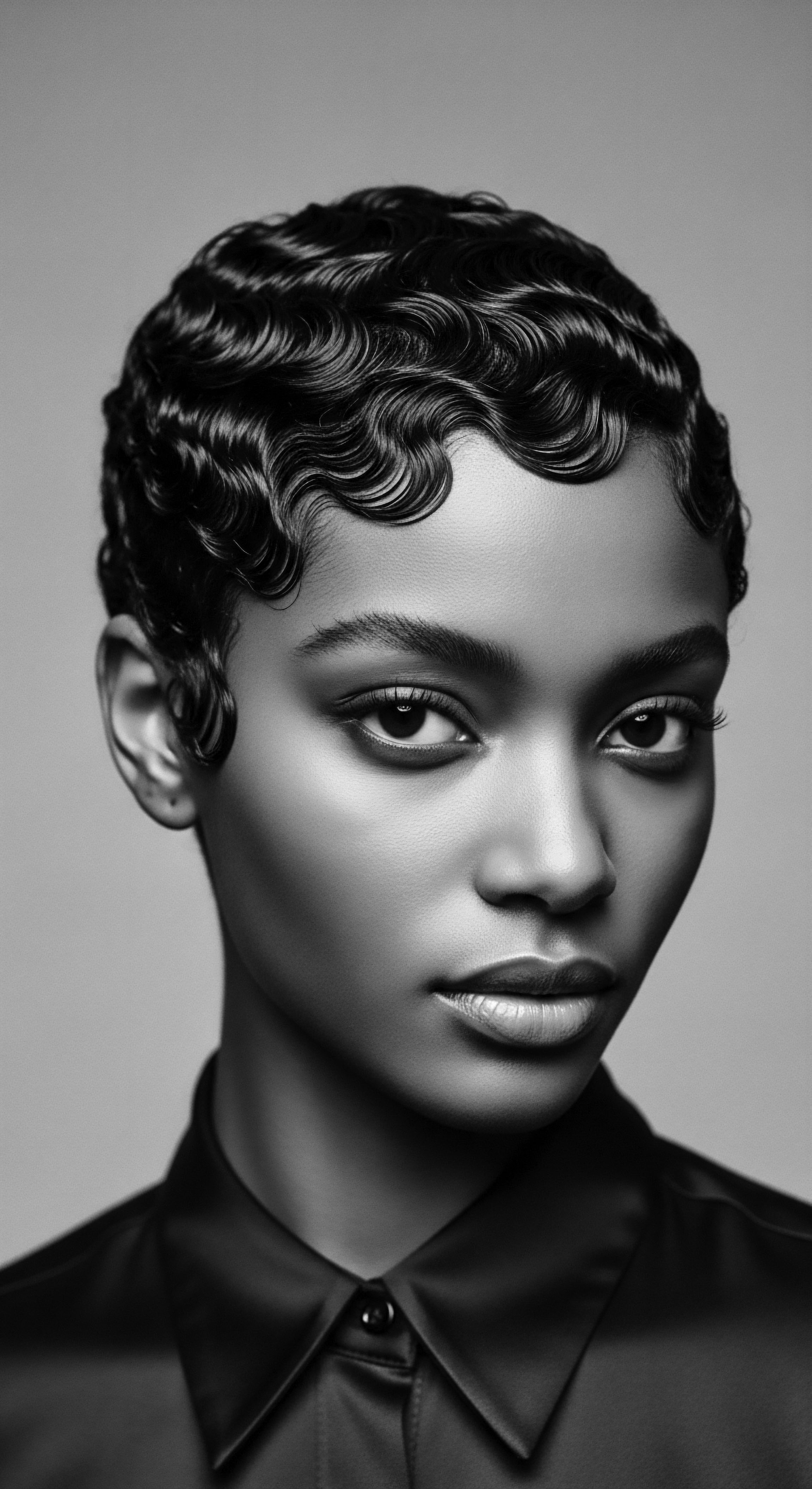

What Ancestral Materials Formed Early Textured Hair Combs?
Early textured hair combs were crafted from abundant natural materials like wood, bone, ivory, and shell, reflecting a profound heritage.

What Is Heritage Hair Care?
Heritage hair care is the ancestral wisdom and cultural practices nurturing textured hair, connecting past traditions to present well-being.

How Do Plant-Based Ingredients Benefit Textured Hair?
Plant-based ingredients deeply benefit textured hair by delivering ancestral moisture and strength, honoring a rich heritage of care.

What Are the Oldest Textured Hair Care Practices?
The oldest textured hair care practices are deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, utilizing natural ingredients and communal rituals for health and identity.
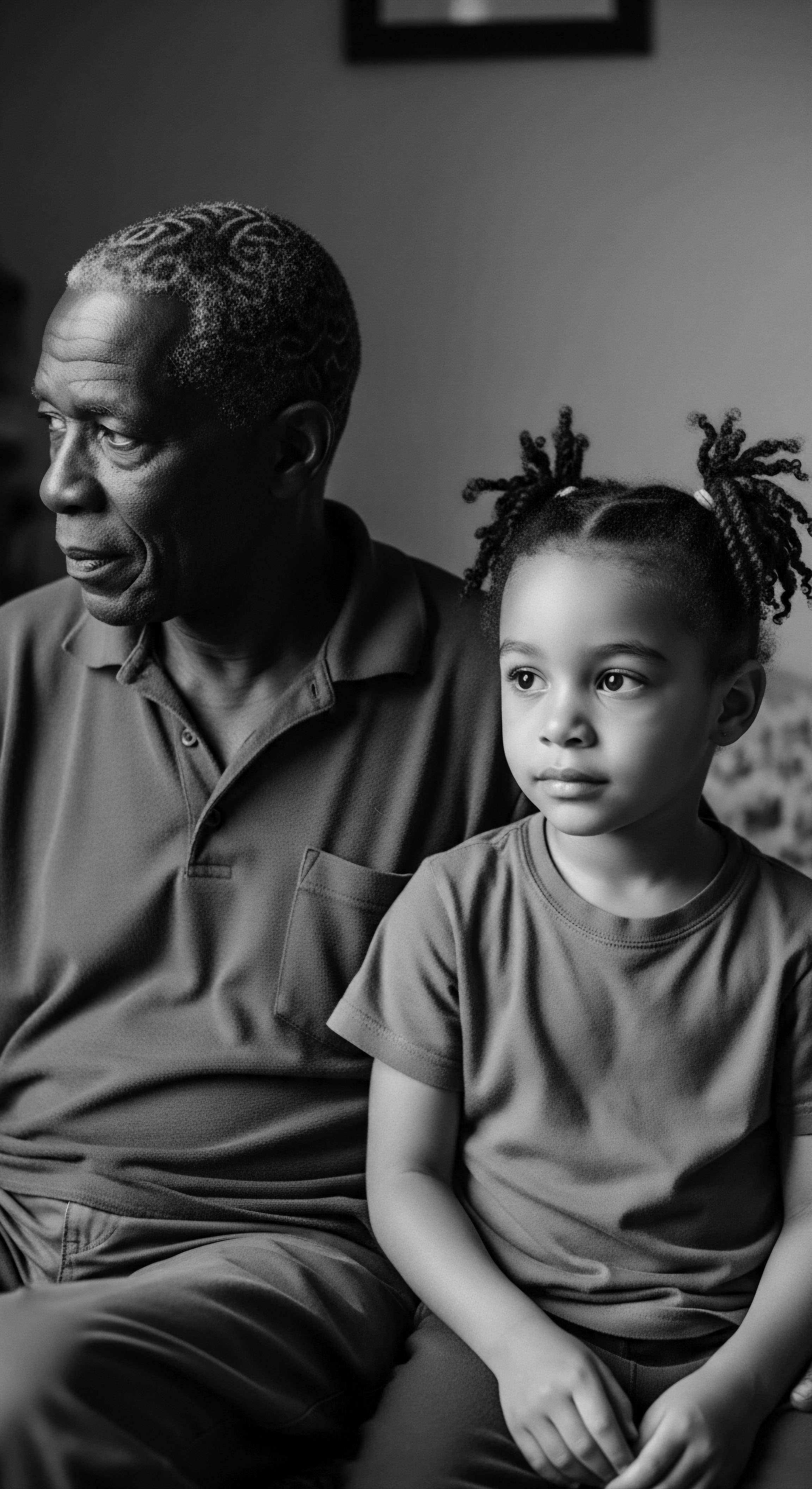

Can Historical Hair Care Traditions Teach Us about Textured Hair Health Today?
Historical hair care practices offer crucial insights into textured hair health by revealing a deep, intuitive science rooted in ancestral heritage.

What Botanical Compounds Help Textured Hair?
Botanical compounds assist textured hair by drawing from ancient ancestral practices that hydrate, strengthen, and protect, deeply connecting to heritage.
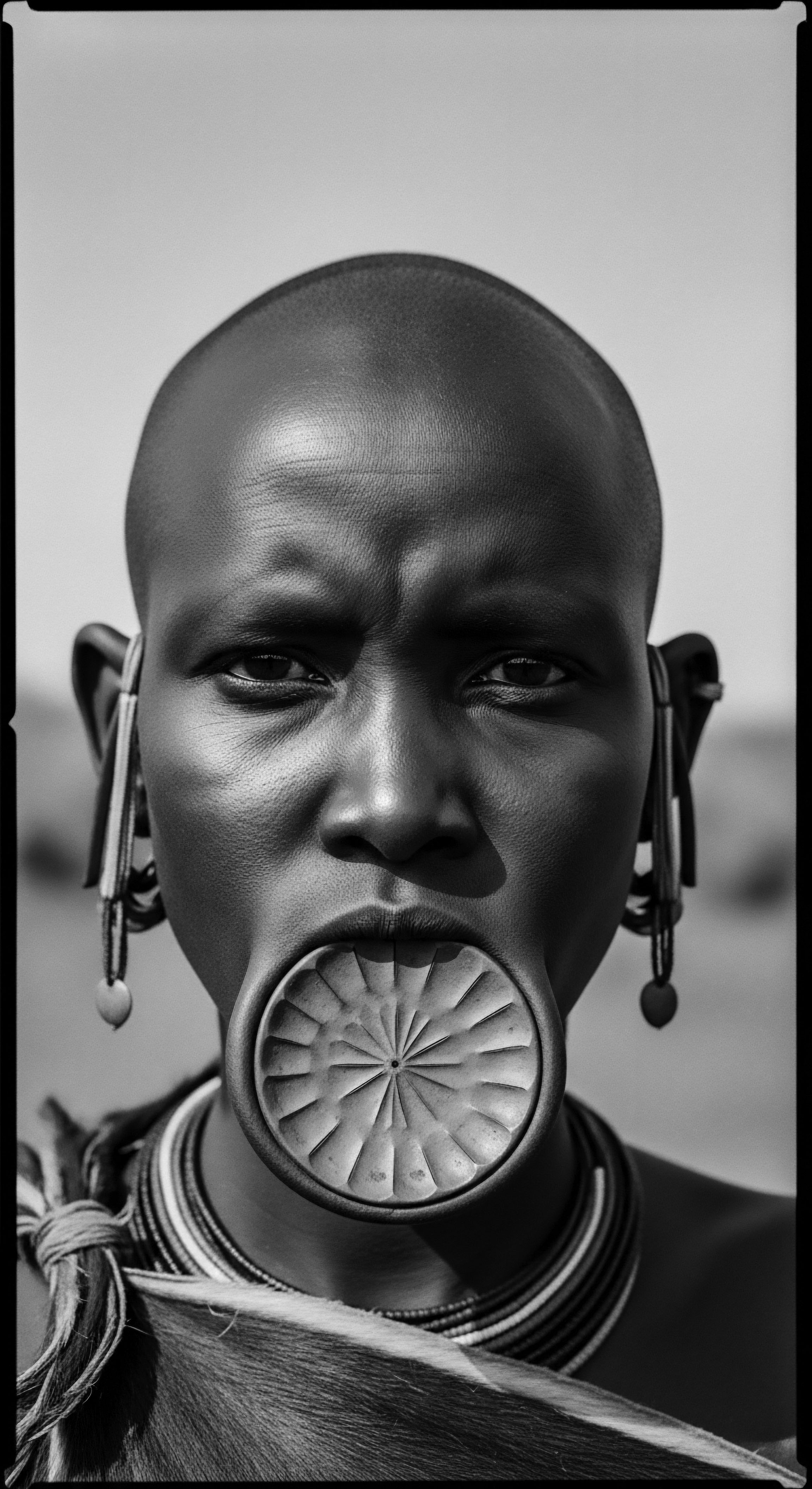

How Has Textured Hair Identified Social Status Historically?
Textured hair historically signaled social status through intricate styles, adornments, and communal rituals, reflecting deep cultural heritage.

What Scientific Properties Validate Historical Textured Hair Oiling Practices?
Historical textured hair oiling practices are scientifically validated by their deep nourishment, friction reduction, and cuticle protection.

How Do Historical Hair Practices Validate Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical hair practices provide empirical and cultural validation for modern textured hair care, deeply rooted in heritage and ancestral wisdom.

What Traditional African Ingredients Cleansed Textured Hair Historically?
Traditional African ingredients like plant ash-based soaps and mineral-rich clays historically cleansed textured hair, honoring ancestral wisdom and preserving cultural heritage.

How Did Heritage Impact Hair Care?
Textured hair heritage deeply guides care through ancestral wisdom, resilient practices, and cultural resistance, shaping modern approaches.

Do Digital Spaces Truly Preserve Hair Heritage?
Digital spaces amplify hair heritage, offering wide access to traditions while challenging us to preserve the lived, embodied experience.

What Historical Sources Document the Use of Specific Oils in Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical sources reveal specific oils, like shea, palm, and castor, were essential for nourishing textured hair heritage across African and diaspora communities.
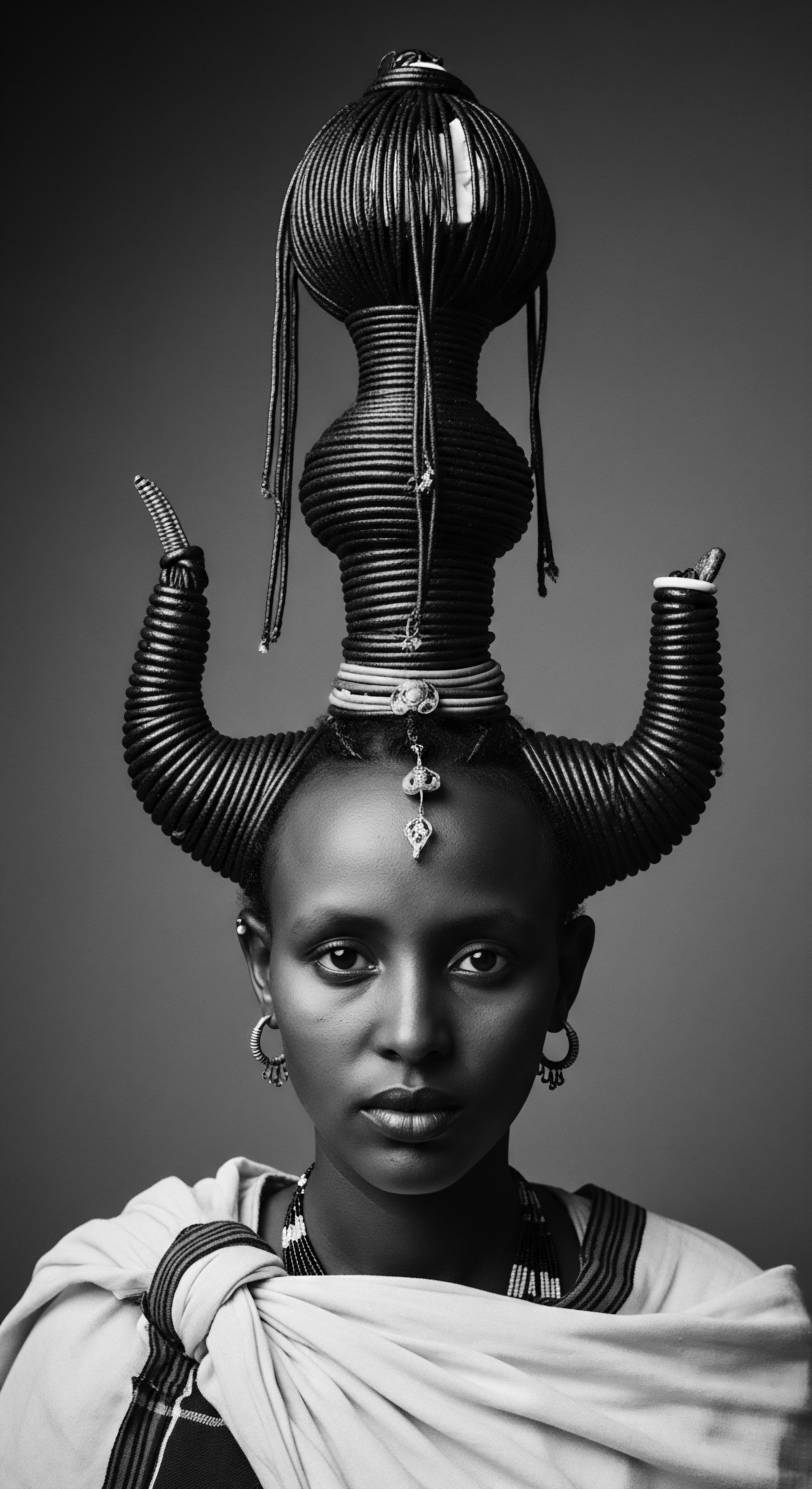

What Historical Significance Do Hair Care Rituals Hold for Textured Hair Communities?
Hair care rituals for textured hair communities are living archives of identity, defiance, and communal wisdom, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Shaped Ancient Egyptian Textured Hair Care?
Ancient Egyptians maintained textured hair with natural oils, elaborate braids, and wigs for hygiene, status, and spiritual connection.
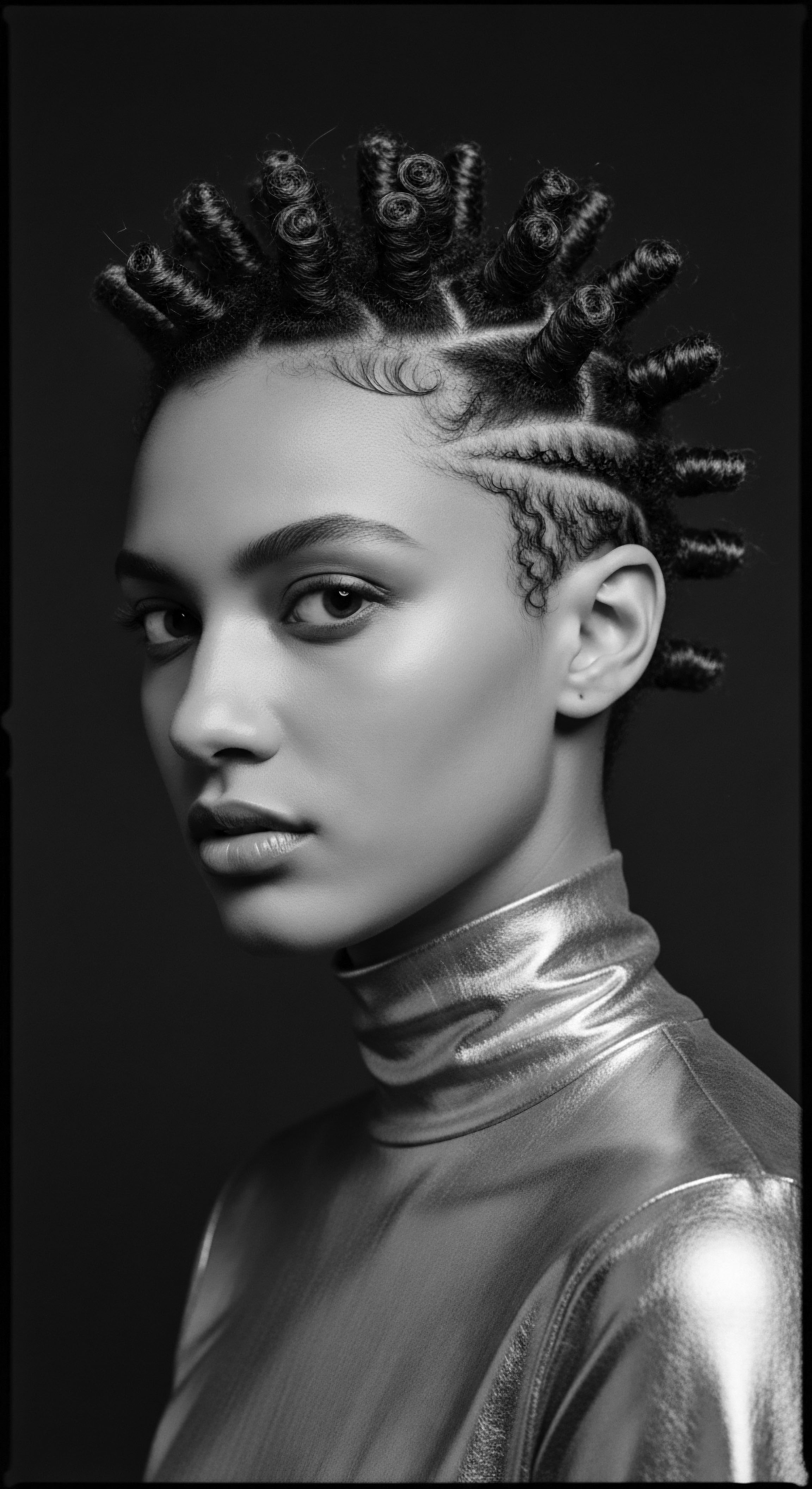

Heavy Metal Contamination
Meaning ❉ Heavy metal contamination refers to the unwanted presence of dense metallic elements in hair, often rooted in historical exposures affecting textured hair heritage.

How Did Hot Combs Influence Heritage?
The hot comb deeply shaped textured hair heritage, reflecting complex interplay of identity, cultural adaptation, and enduring resilience.

Can Ancient Hair Tools Improve Contemporary Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancient hair tools, rooted in ancestral knowledge, offer profound insights for contemporary textured hair care, fostering a deeper connection to heritage.

How Can Modern Practices Honor Heritage Hair Care?
Modern practices honor textured hair heritage by recognizing ancestral wisdom, adapting traditional care, and valuing cultural significance.

What Is the Biological Reason for Textured Hair’s Unique Needs?
Textured hair’s unique needs stem from its elliptical follicle and coiled structure, impacting moisture retention and fragility, shaping care rituals rooted in ancestral heritage.

How Did Textured Hair Traditions Reflect Social Standing?
Textured hair traditions historically conveyed status, wealth, marital standing, and communal role through style and adornment.

