How Does Cultural Heritage Influence Modern Textured Hair Care Science?
Cultural heritage deeply influences modern textured hair care science by grounding scientific inquiry in ancestral practices, revealing time-tested methods for strand vitality.

Which Ancestral Oils Best Shielded Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, coconut oil, and castor oil best shielded textured hair by forming protective barriers and offering deep nourishment rooted in heritage.

Hair Retraction
Meaning ❉ Hair Retraction is the inherent elasticity of textured hair to recoil into its natural, tighter pattern, signifying health and cultural meaning.

How Did Tignon Laws Reshape Heritage?
Tignon Laws sought to diminish free Black women's public presence, but they transformed mandated head coverings into symbols of cultural heritage.

What Cultural Legacy Does Textured Hair Carry through History?
Textured hair’s legacy signifies identity, spiritual connection, and enduring cultural resistance across generations.

Can Science Explain Traditional Textured Hair Care Wisdom?
Science validates that traditional textured hair care wisdom, rooted in ancestral practices, protects unique hair structure and preserves moisture, enhancing its heritage.
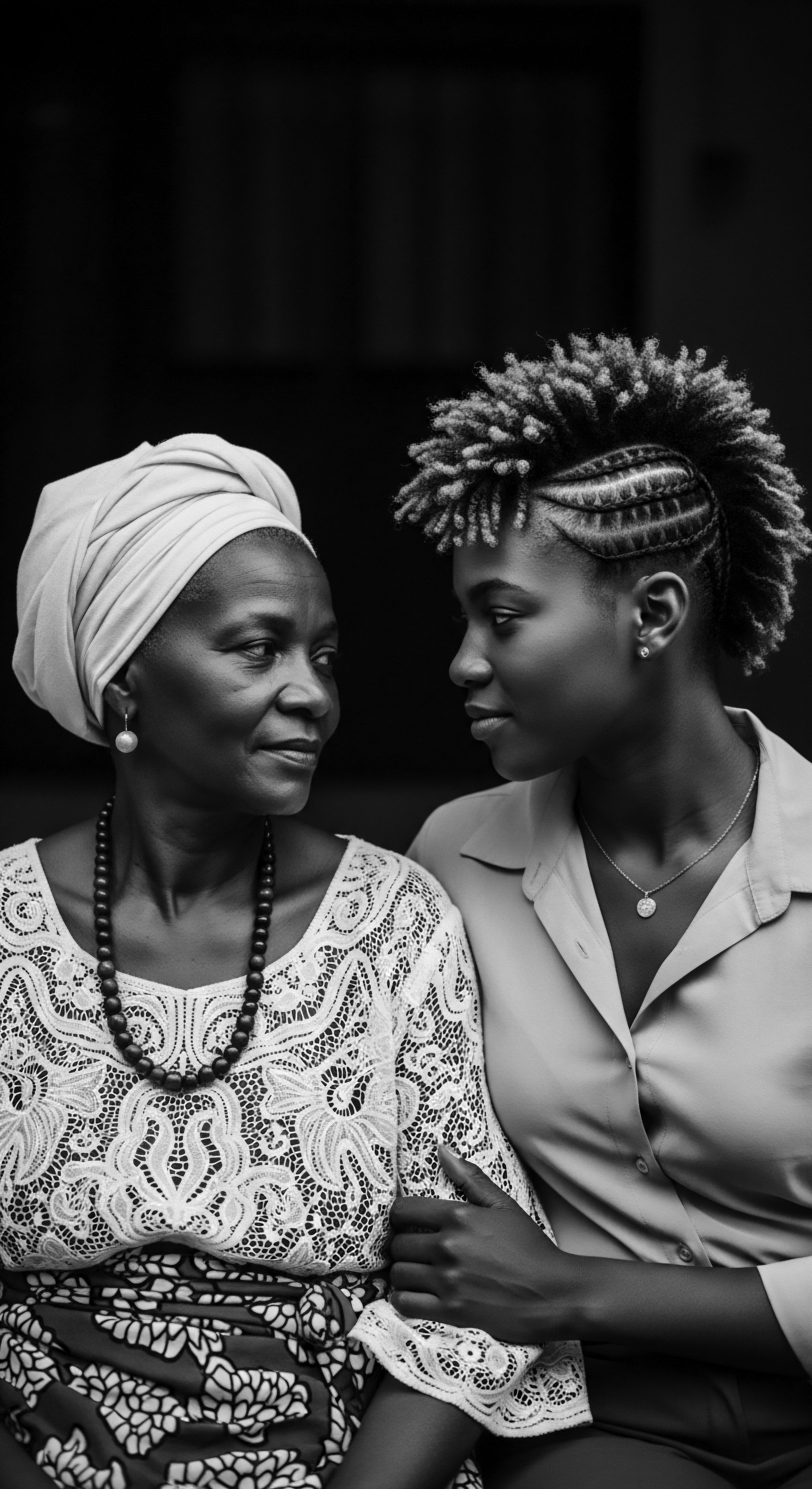
What Ancestral Knowledge Guides Contemporary Textured Hair Care Practices?
Ancestral knowledge guides contemporary textured hair care by emphasizing natural ingredients, protective styling, and holistic well-being, rooted in deep heritage.

Why Does Textured Hair Require More Moisture?
Textured hair requires more moisture due to its unique coiled structure hindering natural oil distribution, and its ancestral heritage of adapting to arid climates.

How Did Historical Cultural Practices Preserve Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical cultural practices preserved textured hair heritage through spiritual reverence, coded styling, and natural care systems.

How Do Historical Styling Practices Impact Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical styling practices for textured hair inform modern care by carrying forward ancestral knowledge of structure, protection, and identity.

What Is the Enduring Cultural Significance of Textured Hair Today?
Textured hair signifies a profound connection to ancestral practices, resilience, and the evolving identity of Black and mixed-race communities.

Braiding Science
Meaning ❉ Braiding Science is the study of textured hair's properties and its cultural manipulation for protection, expression, and historical preservation.

What Historical Tools Reflect the Unique Needs of Textured Hair?
Historical tools for textured hair, from wide-toothed combs to headwraps, reflect ancient ingenuity and cultural resilience in preserving ancestral hair care traditions.

What Ancestral Elements Shape Modern Textured Hair Products?
Modern textured hair products are shaped by ancestral elements, drawing deeply from historical ingredients and traditional care rituals.

Can Ancient Hair Protection Methods Offer Scientific Benefits for Contemporary Textured Hair?
Ancient hair protection methods offer scientific benefits for textured hair by minimizing manipulation, retaining moisture, and utilizing nourishing botanicals, rooted deeply in cultural heritage.

What Historical Evidence Supports Shea Butter’s Benefits for Textured Hair?
Historical evidence, rooted in West African ancestral practices, validates shea butter’s efficacy for textured hair's unique hydration needs.

Why Is Textured Hair More Prone to Dryness and Breakage?
Textured hair's unique structure, paired with historical disconnections from ancestral care, makes it naturally prone to dryness and breaking.

How Do Historical Braiding Practices Protect Textured Hair?
Historical braiding practices protect textured hair by containing strands, reducing manipulation, and preserving ancestral heritage.

How Does Ancient Hair Knowledge Shape Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancient hair knowledge provides the foundation for modern textured hair care, weaving ancestral practices into contemporary routines.

How Does Textured Hair Connect to Ancestral Identity and Community?
Textured hair is a living historical record, connecting individuals to ancestral identity and community through its biological structure, traditional practices, and symbolic significance.

How Does Ancestral Knowledge Guide Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancestral knowledge guides modern textured hair regimens by grounding care in historical practices of moisture, protection, and holistic well-being.

Can Old Plant-Based Remedies Still Condition Textured Hair?
Yes, old plant-based remedies, steeped in centuries of heritage, provide powerful conditioning for textured hair.

What Ancestral Knowledge Guides Hydrating Textured Hair?
Ancestral knowledge guides hydrating textured hair through protective styles, plant-based remedies, and holistic well-being.
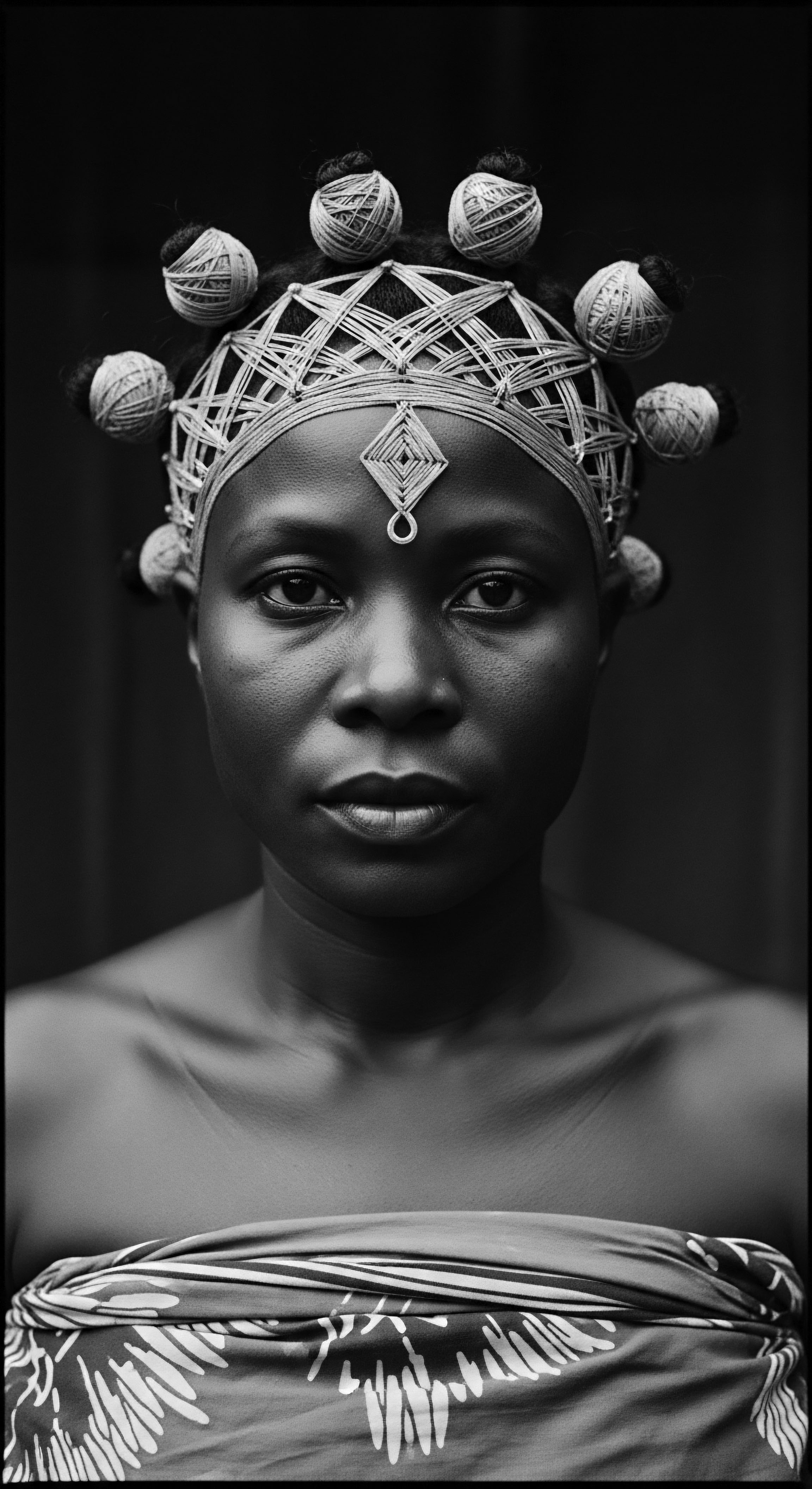

What Is the Historical Significance of Textured Hair in Cultural Strength?
Textured hair signifies cultural strength by embodying historical resistance, identity, and profound ancestral connection.

What Traditional Ingredients Provided Protective Care for Textured Hair across Cultures?
Traditional care for textured hair across cultures relied on natural ingredients like shea butter, coconut oil, and chebe powder for moisture and protection.

Corporate Professionalism
Meaning ❉ Corporate Professionalism refers to societal expectations for conduct and appearance in work settings, significantly shaped by historical and cultural norms around textured hair.

Porosity Heritage
Meaning ❉ Porosity Heritage defines the inherited relationship between textured hair's biological porosity and ancestral care wisdom across Black and mixed-race communities.

What Is the Historical Power of Textured Hair as Identity?
Textured hair historically signifies identity, status, and spiritual connection, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race ancestral heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Inform Textured Hair Care Laws?
Ancestral practices inform textured hair care laws by shaping deep cultural norms, sustainable ingredient choices, and protective styling techniques rooted in heritage.

