
How Did Ancient Communities Safeguard Textured Hair from Environmental Challenges?
Ancient communities safeguarded textured hair using ancestral knowledge, protective styling, natural ingredients, and communal care rooted in heritage.
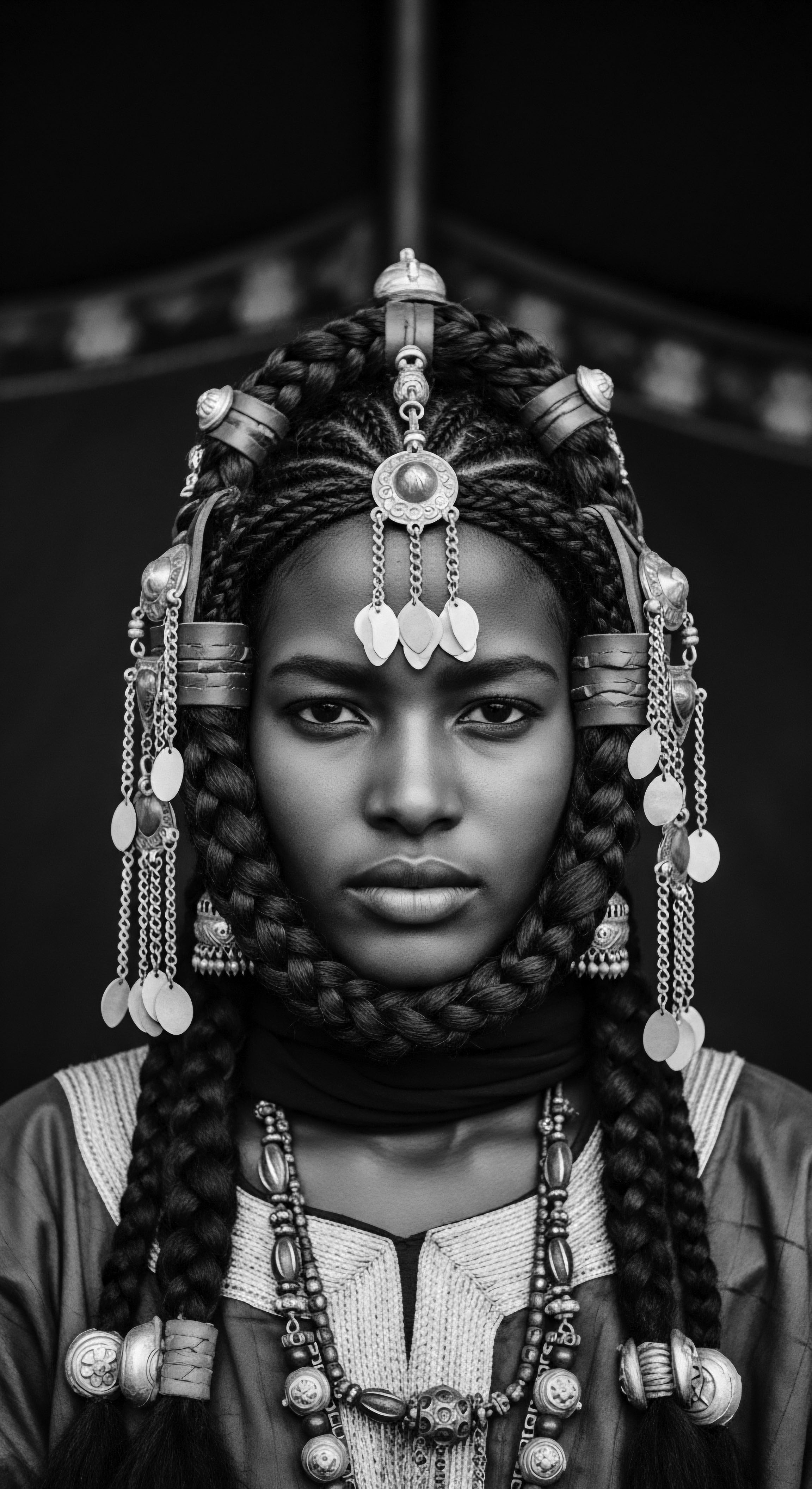

Which Ancestral Ingredients Underpin Today’s Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter, castor oil, and Chebe powder ground today's textured hair care in rich cultural heritage and wisdom.
What Is the Ancestral Significance of Beeswax in Textured Hair Traditions?
Beeswax holds ancestral significance in textured hair traditions as a protective, styling, and preserving agent rooted in heritage.

What Is Multani Mitti’s Heritage in Hair Care?
Multani Mitti, a versatile clay, carries a deep heritage in hair care through its ancestral use in South Asia for cleansing and balancing textured hair.

What Cultural Significance Do Textured Hair Tools Hold across Generations?
Textured hair tools embody ancestral wisdom, identity, and cultural continuity across generations, linking past practices to present-day care.

Can Historical Hair Rituals Inform Modern Approaches to Textured Hair Care and Heritage?
Historical hair rituals offer ancestral wisdom informing modern textured hair care with timeless techniques and ingredients, deepening heritage connections.

What Cultural Practices Surrounded the Use of Natural Butters for Textured Hair Heritage?
Cultural practices surrounding natural butters for textured hair connect ancestral wisdom, community ritual, and self-expression.

How Do Traditional Protective Hairstyles Protect Textured Hair?
Traditional protective styles safeguard textured hair by minimizing manipulation and environmental exposure, a practice rooted in ancestral wisdom.

How Does Traditional Hair Oiling Connect to Modern Textured Hair Product Formulations?
Traditional hair oiling connects to modern textured hair products by providing a heritage-rich blueprint for moisturizing ingredients and holistic care philosophies.

What Ancestral Wellness Philosophies Support Textured Hair Vitality Today?
Ancestral wellness philosophies support textured hair vitality through holistic practices deeply rooted in cultural heritage and natural care.

How Do Genetics Shape Textured Hair?
Genetics shapes textured hair through follicle design and protein bonding, a legacy celebrated in diverse cultural heritages.

What Is the Scientific Basis for Botanical Gentleness on Textured Hair?
Botanical gentleness on textured hair is rooted in ancient practices, using plant compounds that hydrate, strengthen, and protect the unique hair structure, honoring heritage.

How Does Chebe Powder Impact the Structural Integrity of Textured Hair?
Chebe powder strengthens textured hair by forming a protective, friction-reducing coating, a practice rooted in ancestral Chadian hair care heritage.

What Minerals in Clays Benefit Textured Hair Heritage?
Minerals in clays, historically used in textured hair heritage, strengthen, detoxify, and nourish strands through deep earth connection.

Why Does Textured Hair Face Societal Bias?
Societal bias against textured hair stems from historical dehumanization and imposed Eurocentric beauty standards, often ignoring rich cultural heritage.

What Traditional Plants Support Textured Hair?
Traditional plants, rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer deep nourishment and protection for textured hair, honoring a rich cultural heritage.

What Ancient African Practices Protected Textured Hair from Environmental Damage?
Ancient African practices protected textured hair through natural emollients, botanical shields, and intricate styling that valued heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Countered Textured Hair Dryness for Generations?
Ancestral practices countered textured hair dryness through traditional oils, butters, protective styles, and gentle handling, deeply rooted in heritage.

What Cultural Significance Do Ancient Cleansing Methods Hold for Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancient cleansing methods for textured hair embody a heritage of self-care, communal bonding, and deep connection to natural wisdom.

Do Traditional Indian Practices Align with Textured Hair Needs?
Traditional Indian practices offer deep alignment with textured hair needs, rooted in ancestral wisdom and proven by science.

Hair Heritage Neglect
Meaning ❉ Hair Heritage Neglect describes the disengagement from ancestral hair care practices and the cultural meanings of textured hair.

How Did Ancient Cultures Use Clay for Textured Hair?
Ancient cultures used clay for textured hair for cleansing, protection, styling, and cultural identity, connecting ancestral practices with hair well-being.

How Does Oil Composition Help Textured Hair Retain Moisture?
Oil composition, through fatty acid profiles, protects and deeply hydrates textured hair, reflecting centuries of ancestral wisdom.

Why Is Silk Protein Beneficial for Textured Hair Hydration?
Silk protein deeply hydrates textured hair by binding to keratin and attracting water, honoring ancestral moisture-retention practices.

What Specific Botanical Elements Strengthen Textured Hair from Historical Practices?
Historical botanical elements, such as shea butter and chebe powder, strengthen textured hair by providing deep moisture, structural protection, and scalp nourishment derived from ancestral wisdom.

Can Ancient Plant Knowledge Inform Modern Textured Hair Care Regimens?
Ancient plant knowledge deeply informs modern textured hair care by offering time-tested botanical insights for strong, healthy strands, honoring our heritage.

What Ancestral Butters Moisturized Textured Hair?
Ancestral butters like shea, cocoa, and mafura provided essential moisture and protection, honoring textured hair heritage.

What Ancestral Botanicals Boost Textured Hair Vitality?
Ancestral botanicals like shea butter, Chebe powder, and aloe vera have nourished textured hair vitality through centuries of heritage practices.

What Is the Ancestral Significance of Using Natural Clays on Textured Hair?
Natural clays hold profound ancestral significance for textured hair, serving as foundational cleansers, protectors, and cultural markers of heritage.

