African Social Organization
Meaning ❉ African Social Organization defines the communal bonds and ancestral practices that shape identity and care, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

Water Effects
Meaning ❉ Water Effects denote the multifaceted interaction of water with textured hair, influencing its structure, care, and cultural significance.

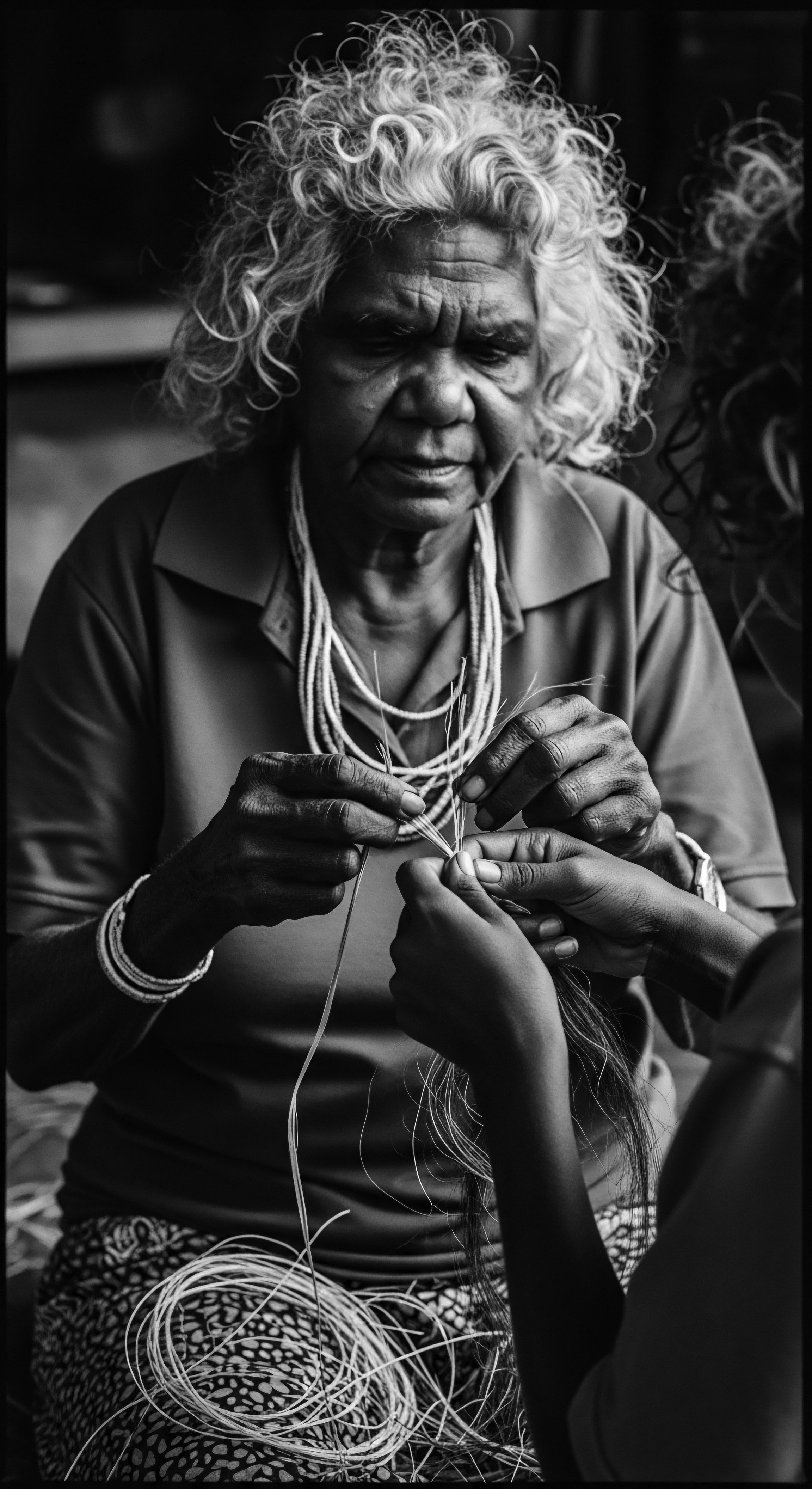
How do ancestral plant uses shape modern hair care?
Ancestral plant uses shape modern hair care by providing a heritage of natural ingredients and practices that honor and protect textured hair.

What is Himba otjize?
Himba otjize is a deeply symbolic paste of butterfat and red ochre, embodying centuries of textured hair heritage for protection and identity.

Civil Rights Salons
Meaning ❉ Civil Rights Salons were intimate, informal communal spaces in Black communities where hair care rituals intertwined with vital discussions on racial justice and identity.
What is the historical role of hair in Black community identity?
Textured hair's historical role is a profound connection to ancestral heritage, serving as a powerful symbol of identity, communication, and resilience.

What scientific principles validate traditional hair oiling?
Traditional hair oiling validates scientific principles of moisture retention and cuticle protection for textured hair heritage.
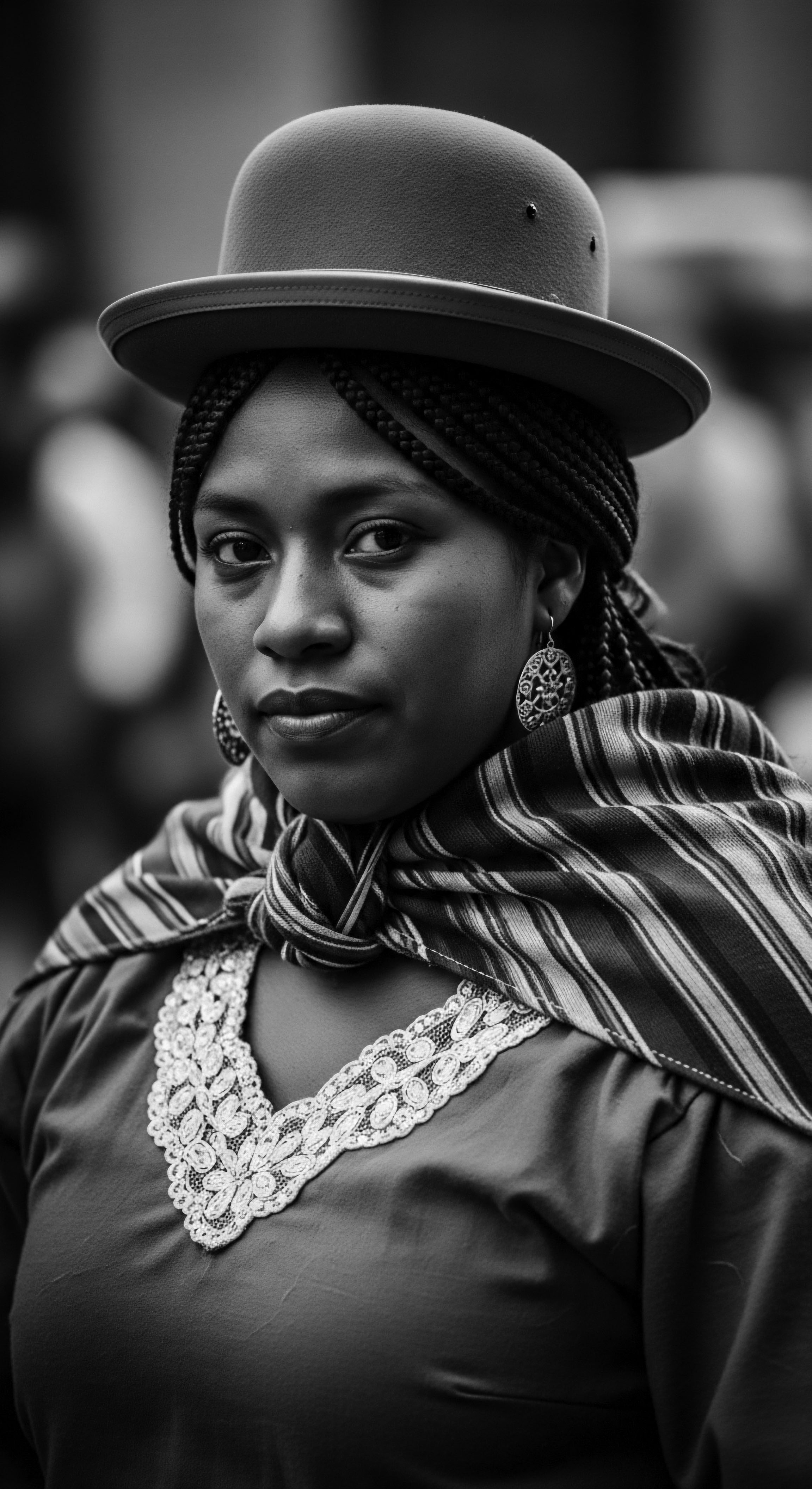

What historical role did hair play in resistance?
Textured hair played a vital historical role in resistance as a symbol of identity, a tool for communication, and a defiant assertion of cultural heritage.

How did ancient hairstyles signal status?
Ancient hairstyles, especially textured ones, were profound visual languages signaling status, wealth, and spiritual connection within ancestral communities.

Chemical Sensitivities
Meaning ❉ Chemical sensitivities signify the body's unique response to substances at low levels, profoundly influencing textured hair care due to historical chemical exposures.
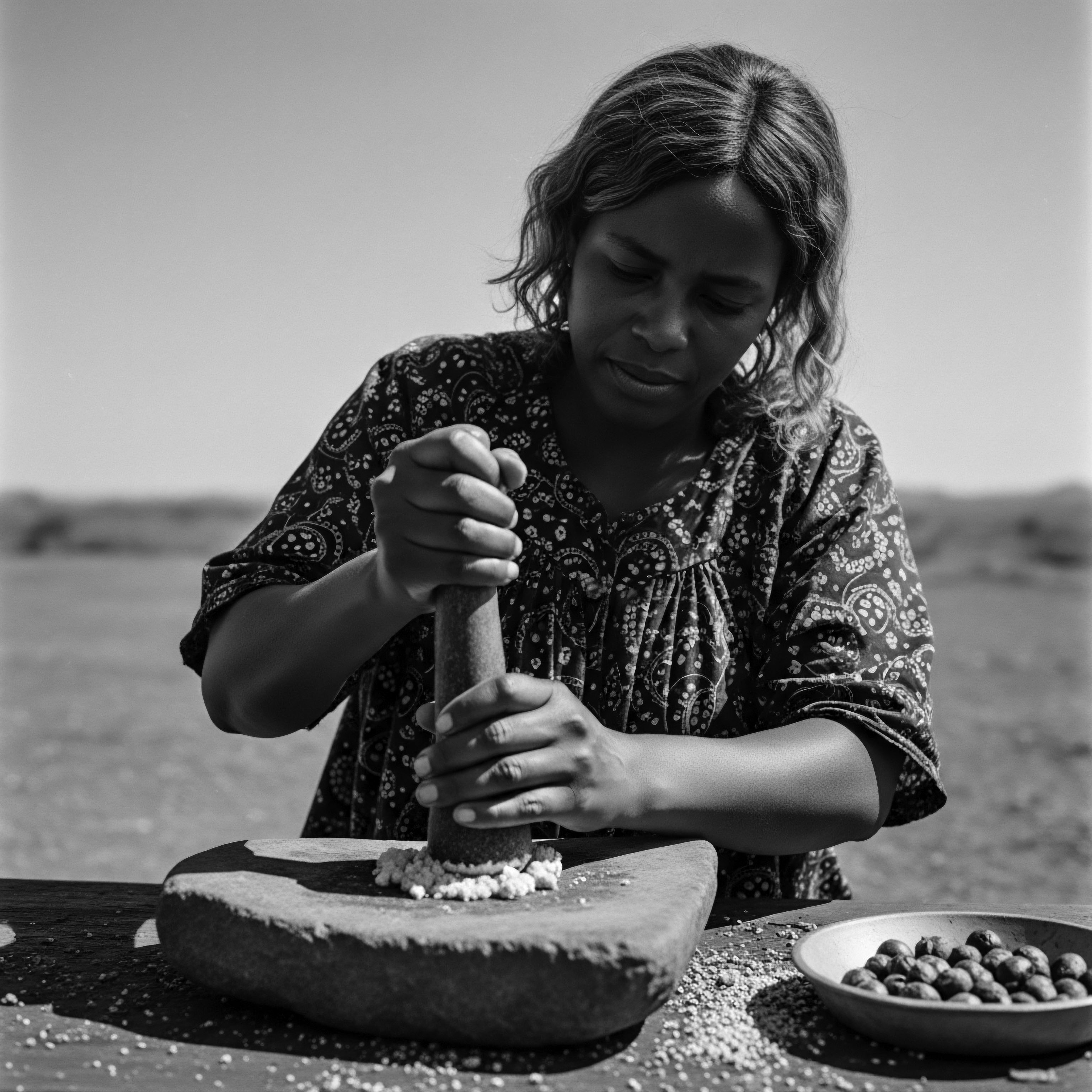

How do ancient hair rituals shape modern care practices?
Ancient hair rituals, steeped in heritage, provide the timeless blueprint for modern textured hair care, preserving identity and resilience.

Can ancient African hair tools shape modern sustainable beauty?
Ancient African hair tools inform modern sustainable beauty by prioritizing natural materials, gentle care, and a deep connection to textured hair heritage.

Can Mongongo oil’s benefits for textured hair be scientifically explained?
Mongongo oil nourishes textured hair by sealing moisture and protecting strands, scientifically validating ancestral practices.

Can traditional protective hairstyles reduce sun damage to coils and kinks?
Traditional protective hairstyles for coils and kinks, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, reduce sun damage by physically covering the hair and scalp, and by working with hair's inherent melanin protection.

What historical traditions surround Chebe powder use?
Chebe powder, from Chad's Basara women, is an ancestral blend used to strengthen textured hair and promote length retention through traditional protective methods.

Vitiligo Identity
Meaning ❉ Vitiligo Identity explores the intersection of depigmentation on textured hair and its profound cultural and personal significance within Black and mixed-race heritages.

What scientific evidence supports the protective qualities of traditional African hair oils?
Traditional African hair oils provide protective benefits for textured hair, supported by scientific evidence of their moisturizing and strengthening properties.

In what ways does African diaspora heritage shape today’s hair identity?
African diaspora heritage profoundly shapes today's textured hair identity through ancestral practices, enduring cultural symbolism, and resilience against historical challenges.

In what ways do ancient hair rituals connect to holistic well-being?
Ancient hair rituals deeply connect to holistic well-being through their historical emphasis on communal care, spiritual alignment, and identity preservation within textured hair heritage.

PPD Allergy
Meaning ❉ PPD allergy signifies an immune response to para-phenylenediamine, a chemical common in permanent hair dyes, impacting textured hair communities significantly.

How do ancient styling methods shape modern hair care?
Ancient styling methods deeply influence modern textured hair care, validating ancestral wisdom and emphasizing heritage, protection, and community.

Can traditional African oils influence future hair care philosophies rooted in legacy?
Traditional African oils offer a profound legacy for textured hair care, informing future philosophies with their heritage of holistic well-being and natural efficacy.

How did ancestral practices shape black soap’s heritage?
Ancestral practices shaped black soap's heritage through meticulous ingredient selection and communal ritual, deeply connecting it to textured hair care and cultural identity.

What specific botanicals nourished African hair historically?
Historically, African hair was nourished by botanicals such as shea butter, chebe powder, aloe vera, castor oil, and marula oil, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

In what ways do historical hair care rituals shape modern beauty practices?
Historical hair rituals deeply shape modern textured hair practices, preserving ancestral wisdom and cultural identity across generations.

How does traditional hair care validate ancestral wisdom and modern science?
Traditional hair care validates ancestral wisdom and modern science by preserving textured hair heritage through proven techniques and ingredients.

What specific oils were commonly used in historical African hair care traditions?
Historical African hair care prioritized oils like shea, palm, and castor for textured hair's unique hydration and protective needs, honoring ancestral wisdom.

Generational Hair Impact
Meaning ❉ Generational Hair Impact defines hair's inherited traits, ancestral care knowledge, and its evolving cultural meaning through generations.

What specific styles became symbols of resistance during historical oppression?
Specific textured hair styles became covert communication tools and visual declarations of pride, asserting identity and cultural heritage during periods of oppression.

