
How did forced hair cutting impact Indigenous identity and heritage?
Forced hair cutting profoundly assaulted Indigenous identity, severing spiritual ties and disrupting a rich textured hair heritage.

What traditional African oils support hair health and growth?
Traditional African oils like shea, castor, baobab, moringa, and argan offer centuries of proven support for textured hair health and growth.

How did ancestral headwrap traditions preserve hair’s vitality and heritage?
Ancestral headwraps shielded textured hair, preserving its natural vitality and cultural heritage through generations.

Socio-Environmental Factors
Meaning ❉ Socio-Environmental Factors describe the interwoven societal and ecological influences shaping textured hair identity and care practices.

What were the Tignon Laws?
The Tignon Laws, a 1786 mandate in Louisiana, forced free women of color to cover their textured hair, sparking an artful heritage of resistance through headwraps.

What is the ancestral meaning of hair?
The ancestral meaning of hair, especially textured hair, is a living record of heritage, identity, communication, and resilience.

What historical roles did textured hair play in survival?
Textured hair’s historical roles in survival span biological protection, cultural communication, and covert resource storage, underscoring its deep heritage.

What traditional African plants moisturize coils?
Traditional African plants such as shea butter, baobab oil, and Chebe powder naturally hydrate coils, honoring a deep heritage of ancestral care.

How did historical oppression influence early hair care?
Historical oppression profoundly altered early hair care by devaluing textured hair, forcing assimilation, and disrupting ancestral practices and identity.

African Diaspora Spirituality
Meaning ❉ A unique definition of African Diaspora Spirituality, exploring its profound connection to textured hair heritage and ancestral practices.

What is the historical connection between hair tools and social status in ancient cultures?
Hair tools in ancient cultures served as potent symbols of social status, directly connected to textured hair heritage.

Why do textured hair types require unique moisture practices?
Textured hair's distinct structure and heritage require diligent moisture practices to sustain its innate health and resilience.
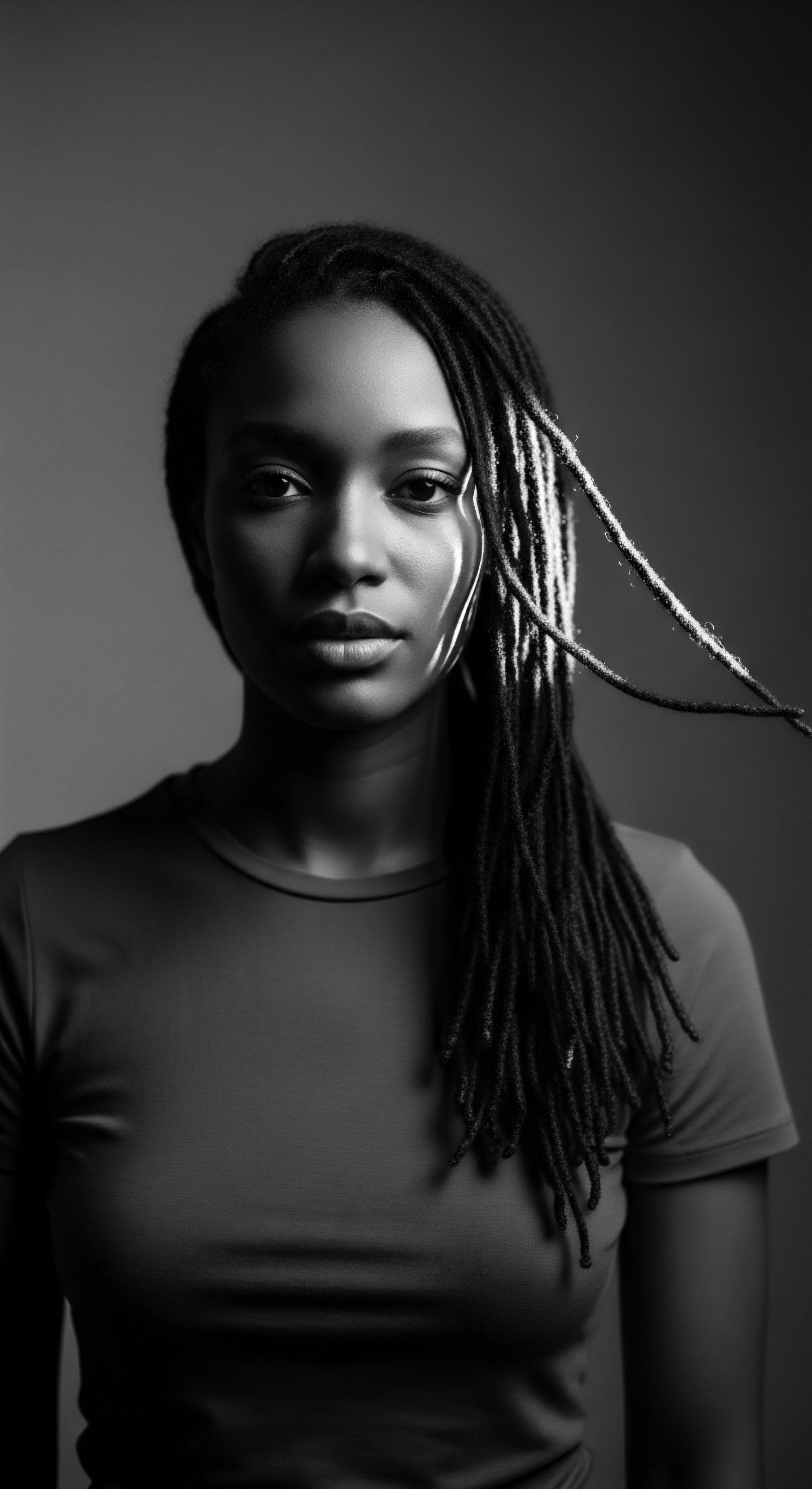
Acts of Resistance
Meaning ❉ Acts of Resistance, in textured hair, signifies a profound declaration of identity, cultural preservation, and defiance against imposed norms.

Socio-economic Factors
Meaning ❉ Socio-economic Factors describe how wealth, status, and opportunity influence textured hair experiences, from ancestral practices to modern discrimination.

What benefits do silk and satin offer for textured hair care?
Silk and satin minimize friction and preserve moisture for textured hair, connecting to centuries of protective heritage.

What socio-economic factors relate to bonnet use in textured hair communities?
The bonnet’s use in textured hair communities is a saga of ancestral protection, economic resilience, and cultural pride.

Can baobab oil help address textured hair challenges?
Baobab oil addresses textured hair challenges by nourishing strands and connecting care practices to enduring ancestral heritage.

What is the cultural significance of ancient African hair practices?
Ancient African hair practices were profound cultural expressions, deeply entwined with identity, social status, spirituality, and ancestral heritage.

How did traditional protective styles influence hair care today?
Traditional protective styles for textured hair, rooted in ancestral practices, significantly shaped modern hair care by emphasizing manipulation reduction, moisture retention, and cultural expression.

Which West African grains have unique amino acid profiles for textured hair?
West African fonio offers unique amino acids like methionine and cysteine crucial for textured hair's strength, reflecting ancient heritage.

What are the enduring benefits of traditional cleansers for **textured hair**?
Traditional cleansers, rooted in ancestral practices, gently purify textured hair while preserving its natural moisture, reinforcing a deep connection to heritage.

What cultural significance did hair combs hold in ancient African societies?
Hair combs in ancient African societies were vital tools for personal adornment, identity, and a profound connection to textured hair heritage.

What is the cultural background of bonnets?
Bonnets protect textured hair by reducing friction and preserving moisture, a practice deeply rooted in ancestral Black hair heritage.

How did head coverings protect ancestral textured hair?
Ancestral head coverings protected textured hair by shielding it from environmental damage and reducing friction, preserving moisture and styles as a heritage practice.

What ancestral practices mirror modern scientific findings on hair health?
Ancestral textured hair practices reveal intuitive wisdom on porosity and protection, echoing modern scientific understanding and cultural heritage.

Why do bonnets matter for textured hair heritage?
Bonnets protect textured hair from friction and moisture loss, preserving its health and continuing a deep ancestral tradition of care.

In what ways do historical materials continue to shape contemporary textured hair care practices?
Historical practices and ancestral ingredients continue to shape contemporary textured hair care through a rich heritage of wisdom.

How do ancestral oils benefit coiled hair?
Ancestral oils nourish coiled hair by sealing moisture and protecting its unique structure, connecting users to a rich heritage of care.

Cell Membrane Complex
Meaning ❉ The Cell Membrane Complex is the vital adhesive structure binding hair cells, dictating hair health and influencing traditional care practices.

