
How do ancestral oils shape modern hair care?
Ancestral oils continue to shape modern hair care by deeply connecting individuals to their textured hair heritage and traditional wellness.

Somatic Resistance
Meaning ❉ Somatic Resistance refers to textured hair's innate ability to reclaim its natural form and the collective cultural resilience embodied by its communities.

In what specific ways does shea butter’s composition benefit diverse textured hair types?
Shea butter’s balanced fatty acids and unique non-saponifiable compounds offer ancestral moisture, shield, and elasticity for diverse textured hair types.

How did Jamaican Black Castor Oil originate?
Jamaican Black Castor Oil originated from ancestral African practices, brought to the Caribbean by enslaved peoples who adapted traditional methods of roasting and boiling castor beans for hair, skin, and medicinal uses, creating a potent oil deeply tied to textured hair heritage.
Hair Abrasion
Meaning ❉ Hair abrasion is the physical wear on the hair shaft's cuticle, often exacerbated by styling and historical practices within textured hair traditions.

How does textured hair reflect ongoing Black identity movements?
Textured hair reflects Black identity movements by embodying centuries of cultural heritage, resistance, and self-acceptance.

What historical biases influenced perceptions of Black hair in work settings?
Historical biases against Black hair in work settings stem from Eurocentric beauty standards that devalued textured hair heritage.

Can modern science explain the traditional Chadian approach to textured hair health?
Modern science confirms the Chadian approach to textured hair health, particularly Chebe, effectively retains length through moisture and strand protection, upholding a rich heritage.
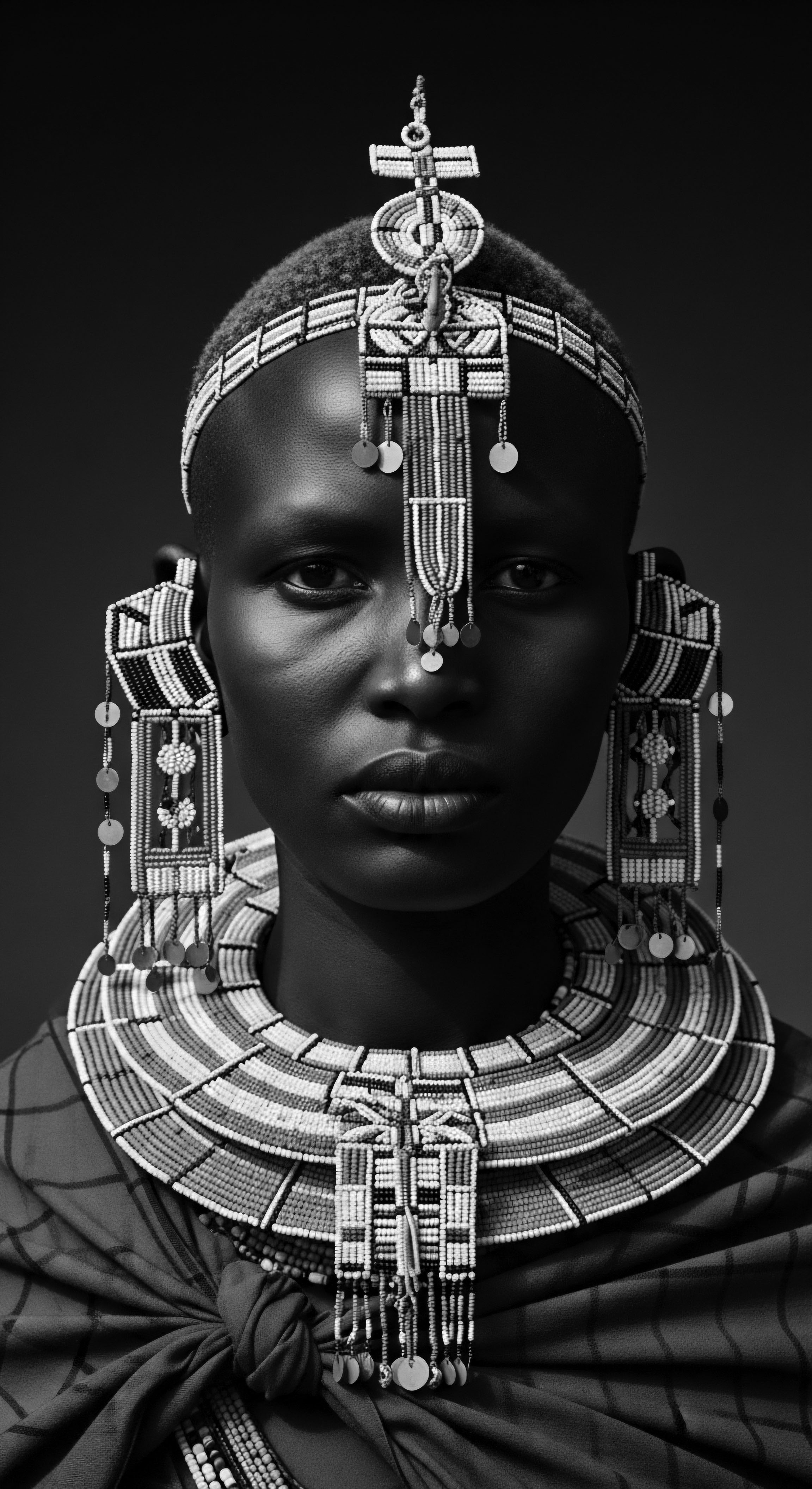

How did adornments signify social standing in ancient hair traditions?
Ancient hair adornments on textured hair conveyed social standing, wealth, and life stages through intricate styles and symbolic materials rooted in heritage.

How does ancestral hair wisdom shape modern textured hair care?
Ancestral hair wisdom shapes modern textured hair care by emphasizing natural ingredients and protective styles rooted in deep cultural heritage.

Discrimination Biomarkers
Meaning ❉ Discrimination Biomarkers describe the physical and structural alterations in textured hair, and related physiological responses, caused by sustained societal pressures and systemic bias.

Historical Resistance
Meaning ❉ Historical Resistance in textured hair signifies the inherent strength and cultural practices asserting identity against oppressive norms.

Can ancient hair protection rituals truly improve modern hair health?
Ancient hair rituals deeply rooted in textured hair heritage truly enhance modern hair health through enduring protective and nourishing methods.

What cultural beliefs shaped ancient African hair care practices and heritage?
Ancient African cultural beliefs imbued hair with spiritual, social, and identity-based meanings, deeply influencing textured hair heritage.

How do protective styles connect to cultural survival?
Protective styles serve as a direct, living link to textured hair heritage, safeguarding both physical strands and cultural identity.

How do traditional hair practices honor heritage?
Traditional hair practices deeply honor heritage by sustaining ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and communal bonds through generations.

Fermented Rice Care
Meaning ❉ Fermented Rice Care defines a deeply traditional and scientifically affirmed practice of using fermented rice water for nurturing textured hair.

How do ancestral hair practices influence modern care?
Ancestral practices shape modern textured hair care by providing foundational principles of protection, moisture, and holistic wellbeing.

How did hair reflect Black pride?
Hair reflects Black pride by revealing deep textured hair heritage, ancestral care, and resilient self-definition against imposed beauty standards.

Which traditional African ingredients condition textured hair historically?
Traditional African ingredients like shea butter, marula oil, and Chebe powder historically conditioned textured hair by providing deep moisture and protection, rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural practices.

What historical significance do botanical oils hold for textured hair heritage?
Botanical oils embody the historical wisdom and enduring resilience central to textured hair heritage.

What historical hair practices are supported by modern science?
Historical hair practices for textured strands are supported by modern science, validating ancestral wisdom regarding hair structure, moisture retention, and botanical applications.

How did traditional hair practices connect to cultural identity?
Traditional hair practices intricately wove cultural identity into textured strands, reflecting ancestral wisdom and community bonds.

In what ways did communal hair rituals preserve moisture knowledge across generations?
Communal hair rituals passed down intuitive moisture knowledge, adapting ancestral wisdom to textured strands through shared practices.

What is hair porosity for textured hair?
Hair porosity describes how textured hair absorbs and holds moisture, deeply rooted in its heritage and care traditions.

What is the historical significance of hair bonnets in Black culture?
Hair bonnets hold profound **heritage** significance, preserving Black textured hair and embodying resilience against historical oppression.

How did ancestral hair practices persist?
Ancestral hair practices persist through resilient cultural knowledge, adapting traditional care and styling to honor textured hair heritage.

How did ancient Africans nourish hair?
Ancient Africans used natural oils, butters, and specific plant powders to nourish hair, honoring textured heritage and community.

Which clays best cleanse textured hair?
Rhassoul and bentonite clays, deeply rooted in ancestral cleansing practices, offer gentle yet effective purification for textured hair.

