Stress Physiology
Meaning ❉ Stress physiology describes the body's response to challenges, profoundly impacting textured hair health through historical and cultural burdens.

How Does the Legacy of Colonial Beauty Standards Affect Textured Hair Today?
Colonial beauty standards distorted the ancestral reverence for textured hair, creating enduring biases and societal pressures that Black and mixed-race individuals continue to navigate and actively redefine.

Cultural Body Marks
Meaning ❉ Cultural Body Marks are deliberate alterations or adornments to textured hair, serving as a visual language of identity, heritage, and communal meaning.
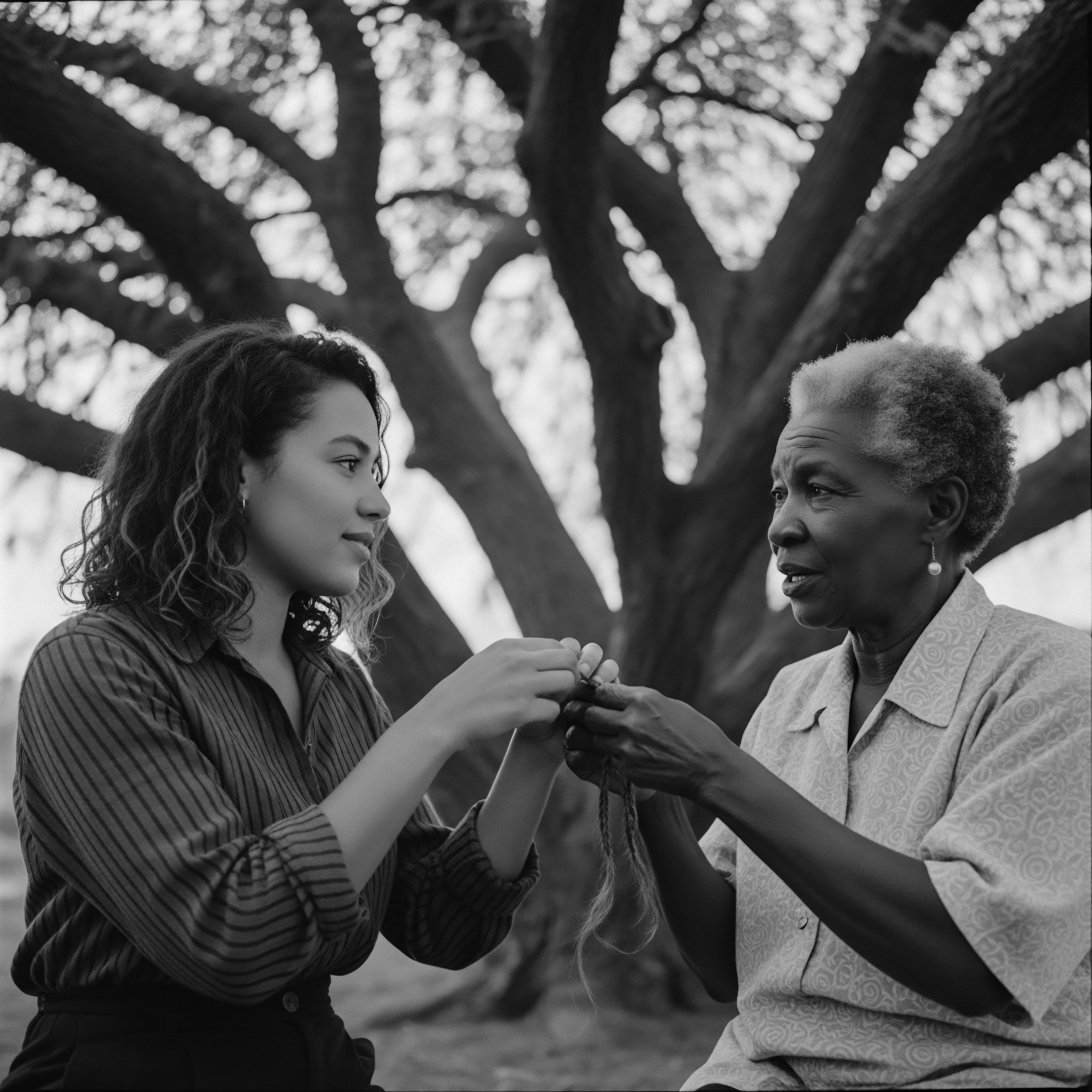

Nyama Hair Connection
Meaning ❉ The Nyama Hair Connection describes the profound, inherent bond between individuals of African descent and their textured hair, deeply rooted in historical and cultural significance.

In What Ways Does Hair Reflect Cultural Identity and Heritage in Black Communities?
Hair in Black communities embodies a profound heritage, reflecting identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom through its unique texture and styling.

Afro-Peruvian Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Afro-Peruvian Heritage embodies the vibrant cultural legacy and resilient identity of people of African descent in Peru, particularly expressed through textured hair.

How Do Societal Perceptions of Textured Hair Impact Self-Esteem?
Societal views on textured hair deeply affect self-esteem, often through historical bias, yet heritage provides resilience.

Biopolitical Hair Narratives
Meaning ❉ Biopolitical Hair Narratives examine how hair, particularly textured hair, is a site where power, identity, and societal control intersect.

How Did Historical Oppression Impact Textured Hair Care Choices?
Historical oppression compelled textured hair care choices towards concealment and alteration, fracturing ancestral practices while sparking enduring reclamation.

Pencil Test History
Meaning ❉ The Pencil Test was a discriminatory historical practice that used hair's ability to hold an object for arbitrary racial classification, particularly during apartheid.

In What Ways Do Legal Shifts Influence Global Textured Hair Acceptance and Ancestral Practices?
Legal shifts reshape textured hair acceptance by validating ancestral practices and cultural identity.

Cultural Journeys
Meaning ❉ Cultural Journeys defines the historical and evolving significance of textured hair as a living archive of heritage, identity, and resilience.

Black Hair Mexico
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Mexico refers to the diverse textured hair of African descendants in Mexico, a profound symbol of their rich, enduring heritage and cultural resilience.

Cultural Attribution
Meaning ❉ Cultural Attribution defines how shared customs and historical contexts assign meaning to textured hair within Black and mixed-race communities.

African Diaspora Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ African Diaspora Hair Heritage is the profound, evolving legacy of textured hair's cultural, historical, and biological significance for people of African descent.

Cultural Wounding
Meaning ❉ Cultural Wounding is a profound, often intergenerational, assault on a group's collective identity and well-being, deeply affecting textured hair heritage.

What Is the Historical Significance of Textured Hair in Mixed-Race Identity?
Textured hair in mixed-race identity reflects a complex heritage, a visible marker of historical classification and enduring cultural pride.

Historical Coverings
Meaning ❉ Historical Coverings represent the enduring cultural and protective practices of adorning textured hair, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race heritage.
Ancestral Hair Justice
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Justice recognizes the inherent worth, cultural significance, and biological integrity of textured hair, honoring its historical lineage and challenging discrimination.

Biracial Hair Identity
Meaning ❉ The Biracial Hair Identity signifies the unique hair characteristics and profound cultural significance arising from mixed racial heritage, particularly its deep connection to textured hair traditions.

Colonial Hair Classifications
Meaning ❉ Colonial Hair Classifications are the imposed systems that racialized hair texture to control populations and reinforce social hierarchies during colonial eras.

Colonialism’s Legacy
Meaning ❉ Colonialism's Legacy in textured hair is the enduring impact of historical colonial practices on Black and mixed-race hair identity and care.

Colonial Casta System
Meaning ❉ The Colonial Casta System was a rigid, race-based social hierarchy in Spanish and Portuguese colonies, using physical traits like hair texture to determine status and enforce European dominance.

What Historical Influences Shaped Textured Hair Care Choices?
Historical influences shaped textured hair care through ancestral wisdom, oppressive forces, and movements reclaiming Black identity.

Eurocentric Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Eurocentric Aesthetics defines beauty through European features, historically devaluing textured hair and influencing societal perceptions and experiences.

Traditional Knowledge Protection
Meaning ❉ Traditional Knowledge Protection is the safeguarding of ancestral practices and wisdom, particularly within textured hair heritage, against exploitation and misrepresentation.

Intersectionality Definition
Meaning ❉ Intersectionality reveals how overlapping identities shape distinct experiences of textured hair, rooted in historical and cultural contexts.

Societal Impact
Meaning ❉ The Societal Impact is the pervasive influence of collective beliefs and historical narratives on individual and communal identity, profoundly shaping the experience of textured hair.

Modern Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Modern Hair Care integrates scientific understanding with ancestral wisdom to nurture textured hair, recognizing its profound significance as a marker of identity and heritage.

