Textured Heritage
Meaning ❉ Textured Heritage is the profound legacy of textured hair, encompassing its biological characteristics, historical significance, and cultural meanings within Black and mixed-race communities.

Hair Community Dynamics
Meaning ❉ Hair Community Dynamics is the intricate interplay of shared heritage, care rituals, and collective identity expressed through textured hair within communities.

Hair Ethics
Meaning ❉ Hair Ethics is the conscious recognition of hair, particularly textured hair, as a living testament to history, identity, and cultural continuity.

What Historical Examples Show the Strength of Textured Hair Heritage?
Textured hair heritage powerfully illustrates resilience and cultural continuity through historical acts of coded communication and identity reclamation.

Cultural Misrecognition
Meaning ❉ Cultural Misrecognition is the societal devaluing of a group's cultural expressions, profoundly impacting textured hair identity and ancestral practices.

Textured Hair Exploitation
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Exploitation describes the systemic devaluation and commodification of textured hair, detaching it from its profound cultural and ancestral heritage.
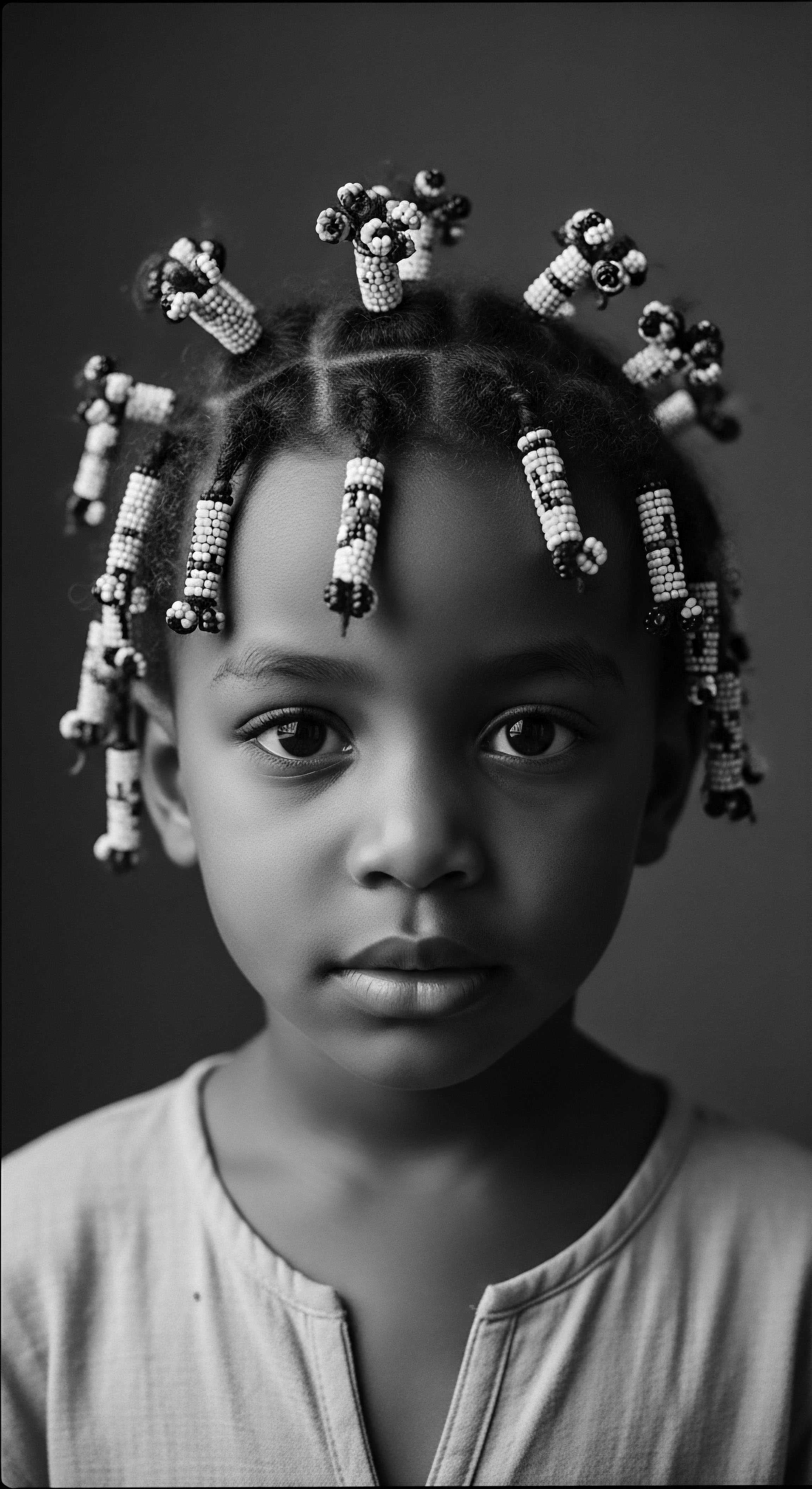

Hair Biology Cultural Context
Meaning ❉ The Hair Biology Cultural Context examines the profound connection between hair's biological traits and its cultural significance across human societies.

African Rituals
Meaning ❉ African Rituals refer to traditional hair practices deeply rooted in cultural identity, ancestral wisdom, and communal significance for textured hair.

Global Hair Care History
Meaning ❉ The Global Hair Care History is a rich chronicle of human hair practices, profoundly shaped by cultural heritage, identity, and resilience.
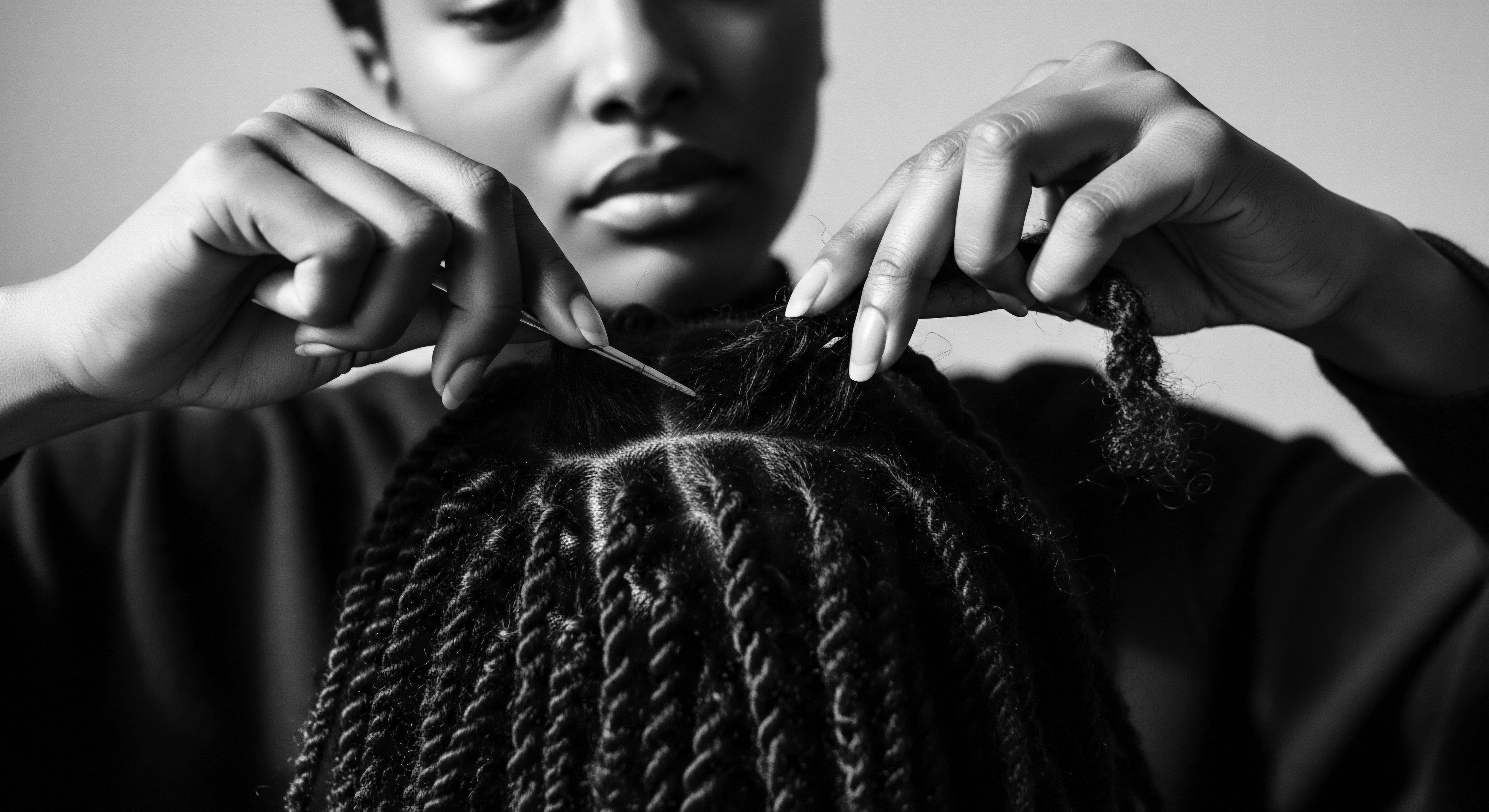

How Did Colonialism Impact the Perception of Black Hair Heritage?
Colonialism reshaped Black hair perception by imposing Eurocentric beauty standards, leading to systemic discrimination and the suppression of ancestral hair heritage.

Holistic Hair Solutions
Meaning ❉ Holistic Hair Solutions is a comprehensive approach to hair and scalp well-being, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and ancestral wisdom.

Racial Health Disparities
Meaning ❉ Racial Health Disparities signify systemic, preventable imbalances in health outcomes disproportionately affecting communities of color, rooted in historical and ongoing societal inequities.

How Has Textured Hair Influenced Expressions of Identity and Heritage Today?
Textured hair profoundly shapes identity and heritage through its ancestral roots, cultural rituals, and ongoing resistance to discrimination.

Hair Dignity
Meaning ❉ Hair Dignity is the inherent worth and cultural significance of hair, particularly textured hair, as an extension of identity and ancestral connection.

How Do Traditional Hair Care Practices from the Diaspora Support Textured Hair Health Today?
Traditional diaspora hair practices, rooted in heritage, provide enduring health benefits for textured hair through natural ingredients and protective styling.

Historical Cleansing
Meaning ❉ Historical Cleansing refers to the systematic suppression and eradication of traditional hair practices and meanings within textured hair heritage.

Healthcare Inequity
Meaning ❉ Healthcare Inequity is a systemic imbalance in health access, quality, and outcomes, profoundly affecting textured hair communities due to historical biases.
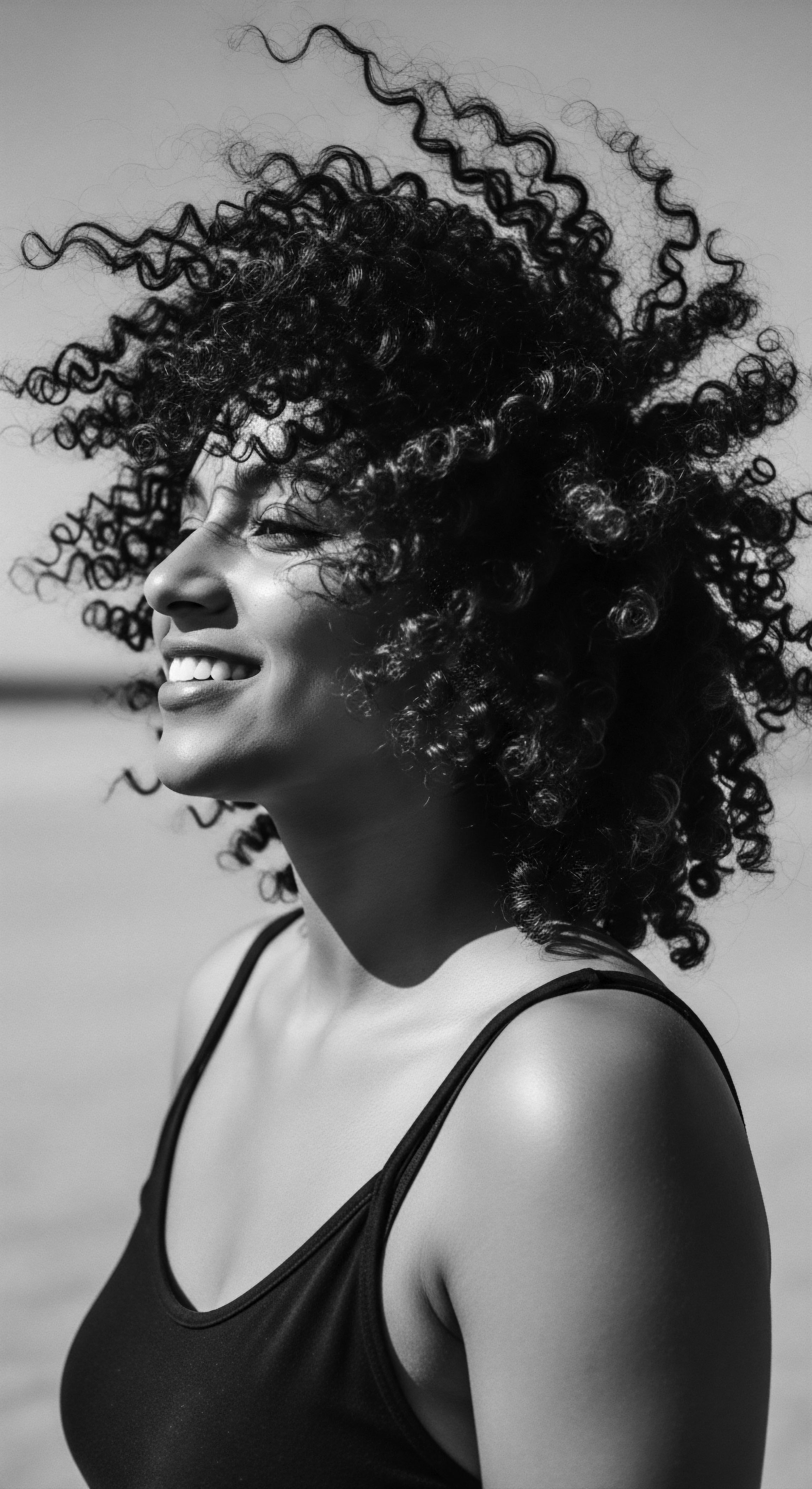

How Does Textured Hair Today Reflect Historical Acts of Resistance?
Textured hair today reflects historical acts of resistance through its enduring heritage, embodying defiance against oppression and a celebration of authentic identity.

Systemic Influences
Meaning ❉ Systemic Influences are the deep, interconnected historical, social, and economic forces shaping textured hair's perception, care, and lived experience.

What Societal Norms Impacted Textured Hair Acceptance Historically?
Societal norms historically impacted textured hair acceptance by devaluing ancestral styles, forcing conformity to Eurocentric ideals, and sparking powerful movements for heritage reclamation.

Regulatory Equity
Meaning ❉ Regulatory Equity is the inherent capacity of textured hair to maintain its natural balance and health, profoundly shaped by its rich cultural heritage.

Cultural Competence
Meaning ❉ Cultural Competence in textured hair care signifies a deep, affirming understanding of its historical, cultural, and biological significance.

Contractual Servitude
Meaning ❉ Contractual Servitude defines the profound, ancestral commitment to nurturing textured hair as a living testament to Black and mixed-race heritage.

Wavy Hair Definition
Meaning ❉ Wavy hair describes hair strands with an S-shaped pattern, a unique texture with deep cultural and historical significance for textured hair heritage.

Colonialism’s Hair Legacy
Meaning ❉ Colonialism's Hair Legacy is the enduring influence of colonial practices on the perception, care, and cultural significance of textured hair, especially within Black and mixed-race communities.

Natural Hair Philosophies
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Philosophies is a profound understanding of hair as an extension of self, deeply rooted in historical lineage and cultural identity.

How Did Textured Hair Symbolize Resistance during Historical Periods?
Textured hair symbolized resistance through ancestral communication, covert acts of defiance, and bold affirmations of identity and heritage.

Micronesian Hair
Meaning ❉ Micronesian Hair is a profound expression of diverse genetic heritage and cultural practices, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and identity.

Community Enterprise
Meaning ❉ A Community Enterprise is a collective endeavor rooted in shared heritage, pooling resources and knowledge for mutual well-being, particularly evident in textured hair care.