Textured Hair Rights
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Rights assert the inherent freedom to wear natural hair without prejudice, recognizing its deep connection to identity and cultural heritage.

Cultural Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Heritage is the enduring collection of knowledge, practices, and meanings associated with hair, particularly textured hair, passed through generations.

Hair Health History
Meaning ❉ Hair Health History explores the evolving biological, cultural, and identity-driven narratives of hair care, profoundly rooted in textured hair heritage and ancestral wisdom.

In What Ways Did Ancestral Hair Practices Influence Black and Mixed-Race Heritage?
Ancestral hair practices shaped Black and mixed-race heritage by imbuing textured hair with profound cultural, spiritual, and social significance.

Social Standing
Meaning ❉ Social Standing, in the context of textured hair, refers to the perceived value and position assigned to individuals or groups based on their hair's cultural, historical, and social significance.

Workplace Inclusion
Meaning ❉ Workplace Inclusion, for textured hair, is the deliberate creation of environments where natural hair and ancestral styles are genuinely welcomed and valued.

Black Hair Legacy
Meaning ❉ The Black Hair Legacy is a living archive of textured hair heritage, care, and identity, rooted in ancestral wisdom and continuous resilience.

Cultural Legacy
Meaning ❉ Cultural Legacy is the inherited wisdom, practices, and meanings of textured hair within Black and mixed-race communities, shaping identity and resilience.
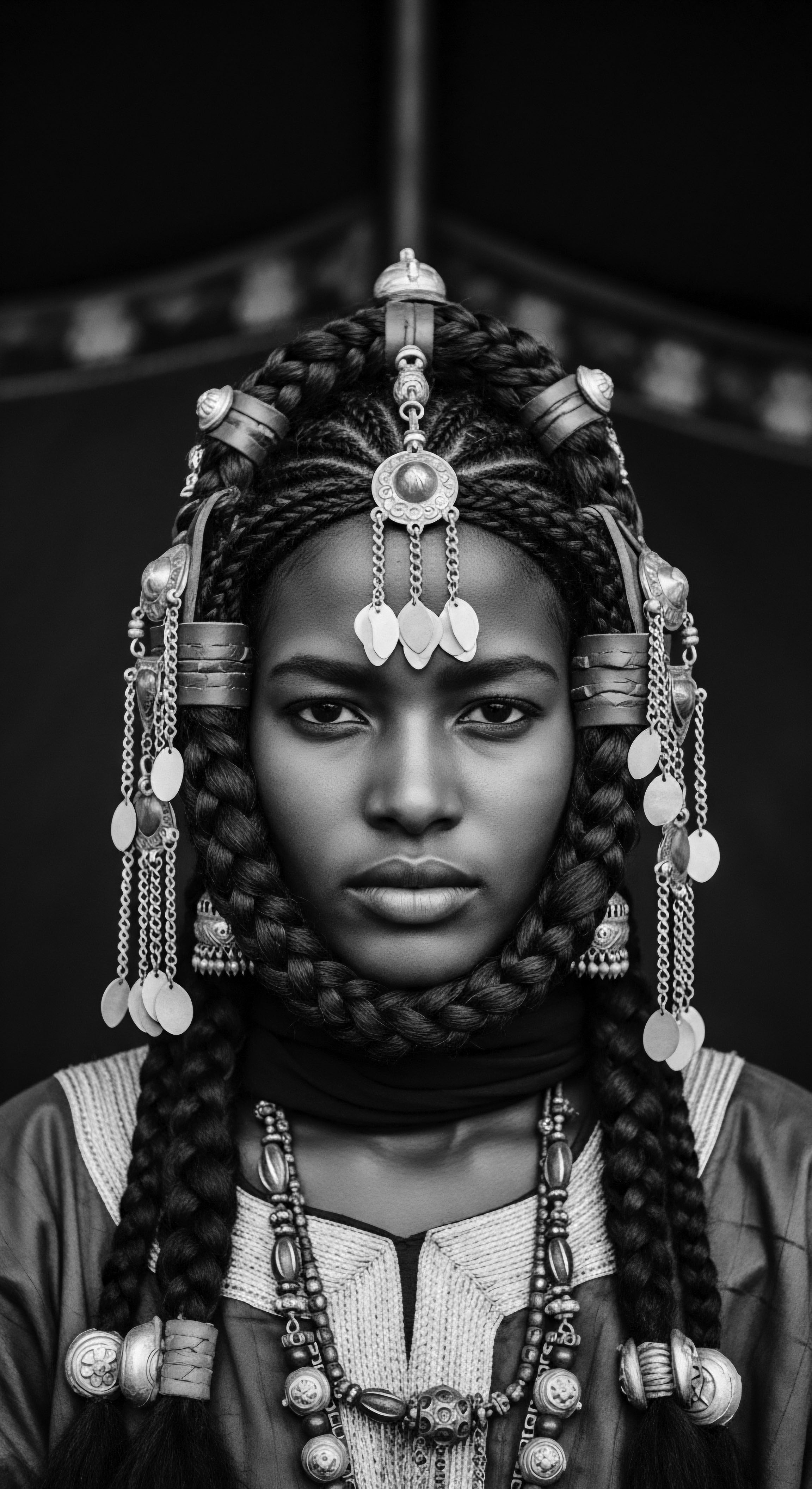

In What Ways Do Protective Styles Embody the Cultural Heritage of Black Communities?
Protective styles embody Black cultural heritage through ancestral wisdom, communal rituals, and acts of identity and resistance.

African Headwraps
Meaning ❉ The African Headwrap is a deeply significant cultural artifact, embodying protection, identity, and a rich heritage for textured hair across the African diaspora.
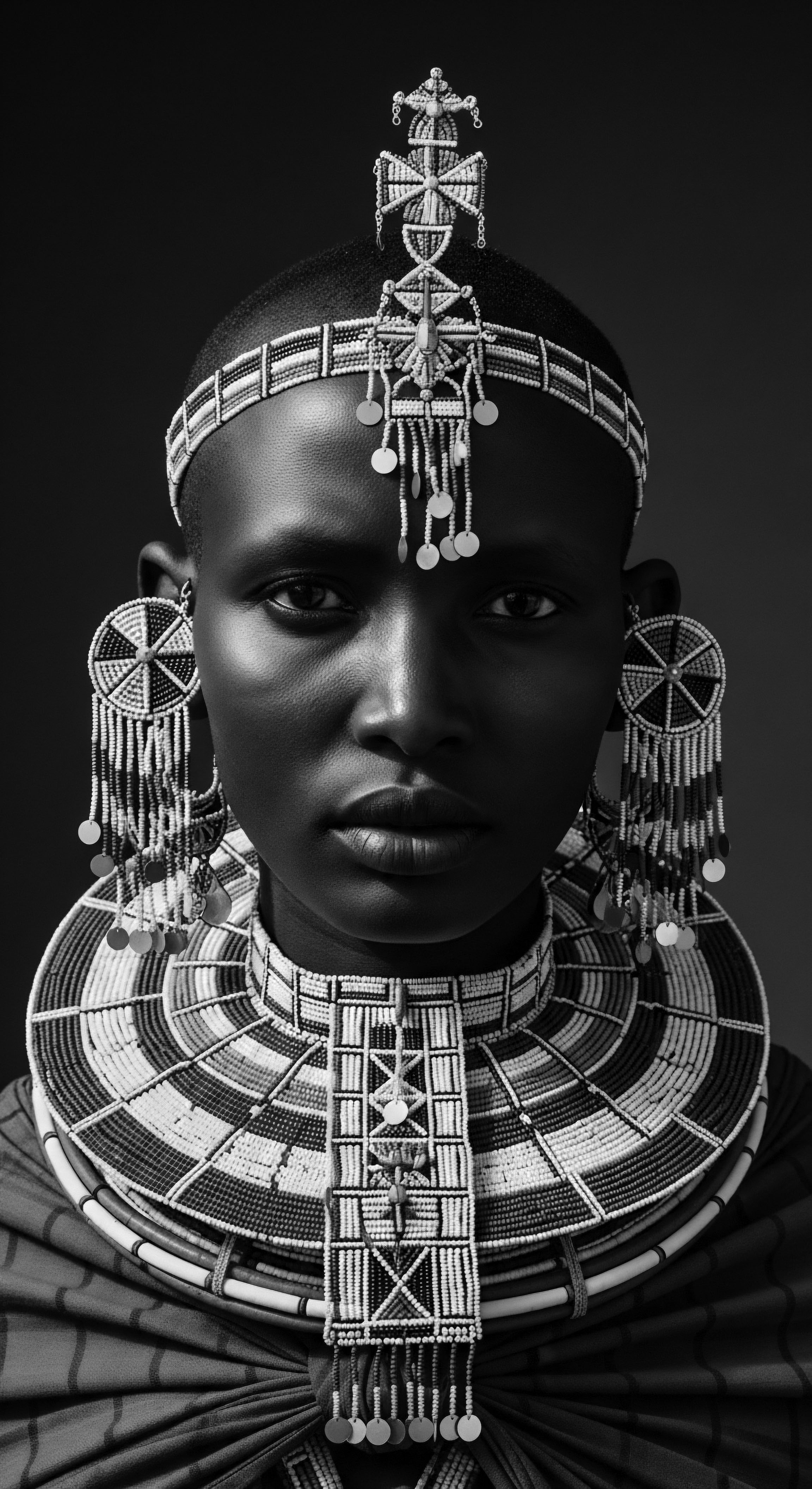

What Is the Historical Link between Hair and African Heritage?
Hair holds a deep historical link to African heritage, serving as a powerful symbol of identity, status, spirituality, and resistance for textured hair communities.
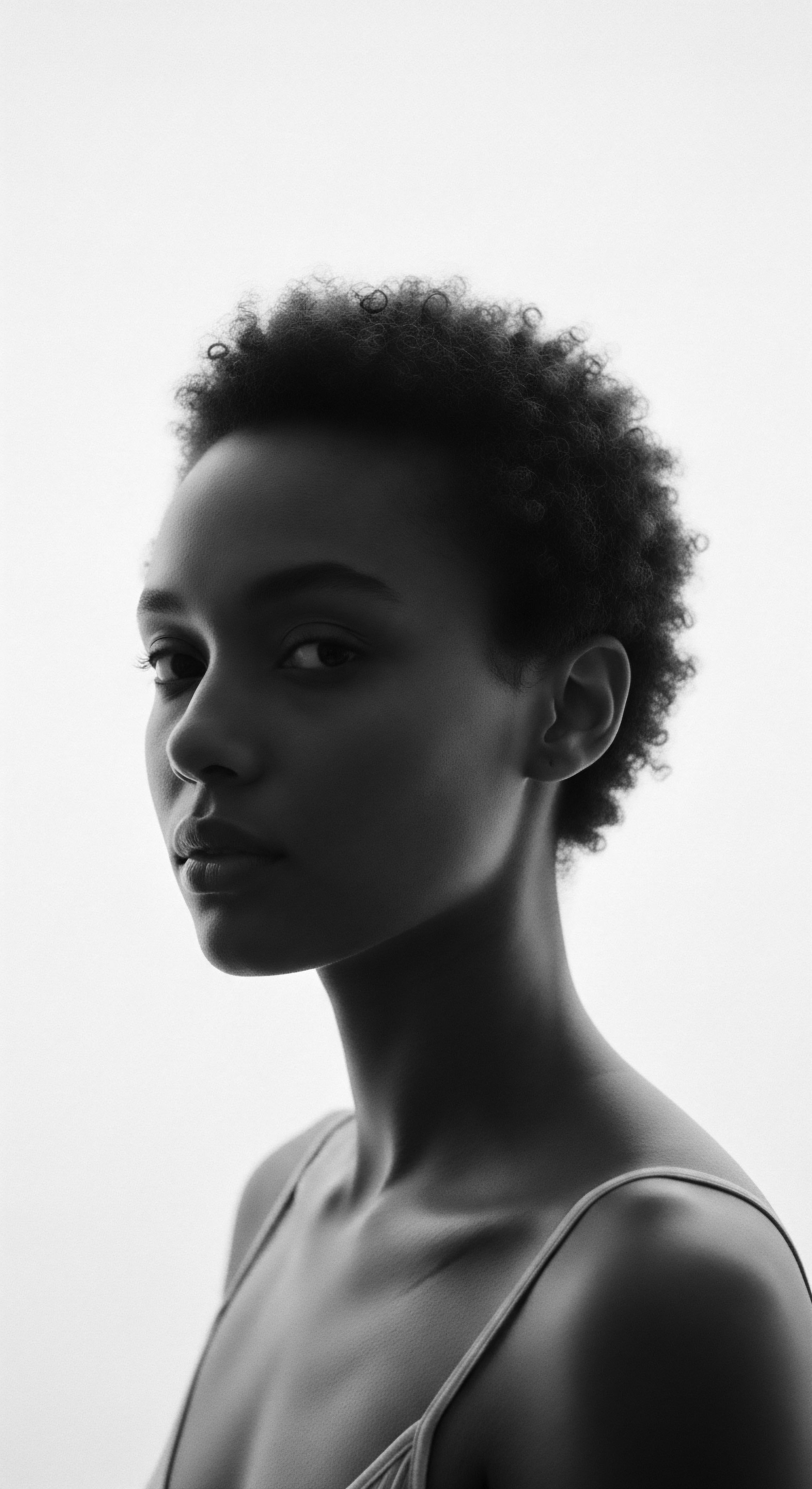

Curl Pattern
Meaning ❉ The curl pattern is the intrinsic shape of a hair strand, a biological trait deeply intertwined with heritage, identity, and cultural care practices.

What Historical Laws Shaped Perceptions of Textured Hair?
Historical laws shaped textured hair perceptions by imposing Eurocentric standards, leading to enduring discrimination while sparking cultural resilience.

Cultural Traditions
Meaning ❉ Cultural Traditions define the inherited practices and beliefs surrounding textured hair, connecting individuals to their ancestral lineage and collective identity.

African Hair Identity
Meaning ❉ African Hair Identity is the profound meaning of textured hair as a living cultural, historical, and biological legacy for Black and mixed-race communities.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Protective Hairstyles in African Heritage?
Protective hairstyles in African heritage are a profound cultural legacy, symbolizing identity, community, and resistance through their deep connection to textured hair history.

What Does the CROWN Act Mean for Future Textured Hair Heritage?
The CROWN Act safeguards the right to wear natural, textured hair and protective styles, affirming their cultural significance and ancestral heritage.

How Did Colonialism Impact Textured Hair Care?
Colonialism devalued textured hair's ancestral significance, forcing conformity while sparking resilient acts of heritage preservation and reclamation.

Cultural Grooming
Meaning ❉ Cultural Grooming defines the inherited practices and community rituals surrounding textured hair, reflecting identity, social bonds, and ancestral wisdom.

What Historical Biases against Textured Hair Does the CROWN Act Address?
The CROWN Act addresses historical biases that deemed natural textured hair unprofessional, thereby affirming its deep cultural heritage and protecting the right to wear it freely.

Natural Hair Regimens
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Regimens encompass intentional practices and product selections that nurture textured hair in its unaltered state, honoring its heritage and promoting holistic wellness.

Afro Symbolism
Meaning ❉ Afro Symbolism represents the profound, multi-generational meanings, cultural narratives, and inherent spiritual and social significance imbued within Afro-textured hair.

What Is the Historical Connection between Textured Hair and Cultural Identity?
Textured hair is a living archive of cultural identity, its styles and care rituals reflecting millennia of heritage, resilience, and self-expression.
Traditional Styling
Meaning ❉ Traditional Styling encompasses ancestral hair practices and forms of adornment, deeply rooted in the heritage and identity of textured hair communities.

In What Ways Did Protective Styles Act as Resistance for Diasporic Heritage?
Protective styles served as a profound act of resistance by preserving cultural identity and ancestral practices for diasporic heritage.

In What Ways Does the CROWN Act Validate Textured Hair’s Cultural Significance?
The CROWN Act validates textured hair's cultural significance by legally protecting ancestral styles and natural textures, affirming their heritage as valued identity expressions.

In What Ways Does the CROWN Act Honor Black Hair Heritage?
The CROWN Act honors Black hair heritage by legally protecting natural textures and traditional styles, affirming ancestral practices and cultural identity.

In What Ways Does Hair Discrimination Affect Holistic Wellness for Textured Hair?
Hair discrimination disrupts holistic wellness by severing the deep connection between textured hair and its ancestral heritage.


