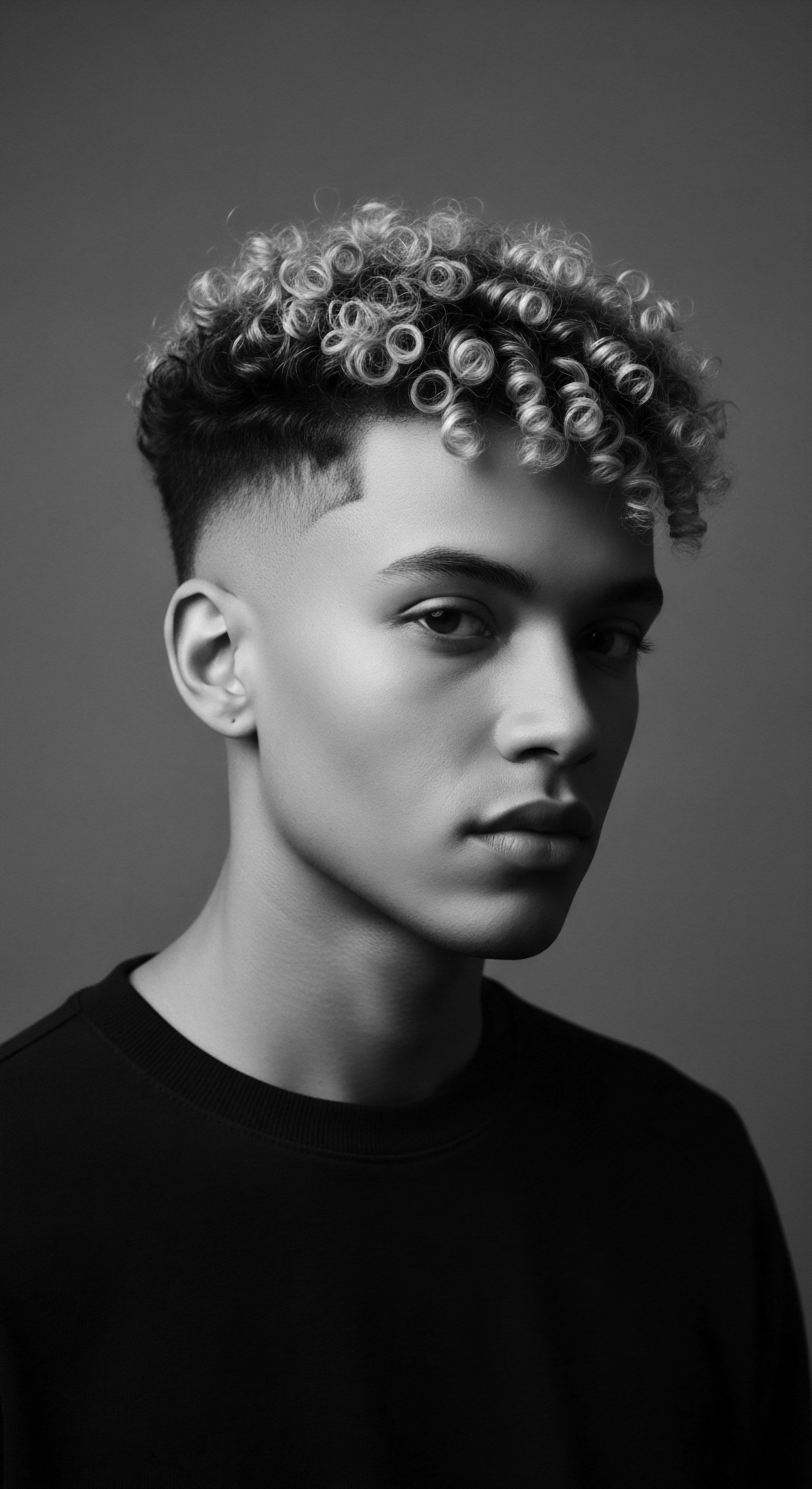

Styling Practices
Meaning ❉ Styling Practices define the deliberate shaping and adornment of hair, reflecting deep cultural heritage and personal identity for textured hair.
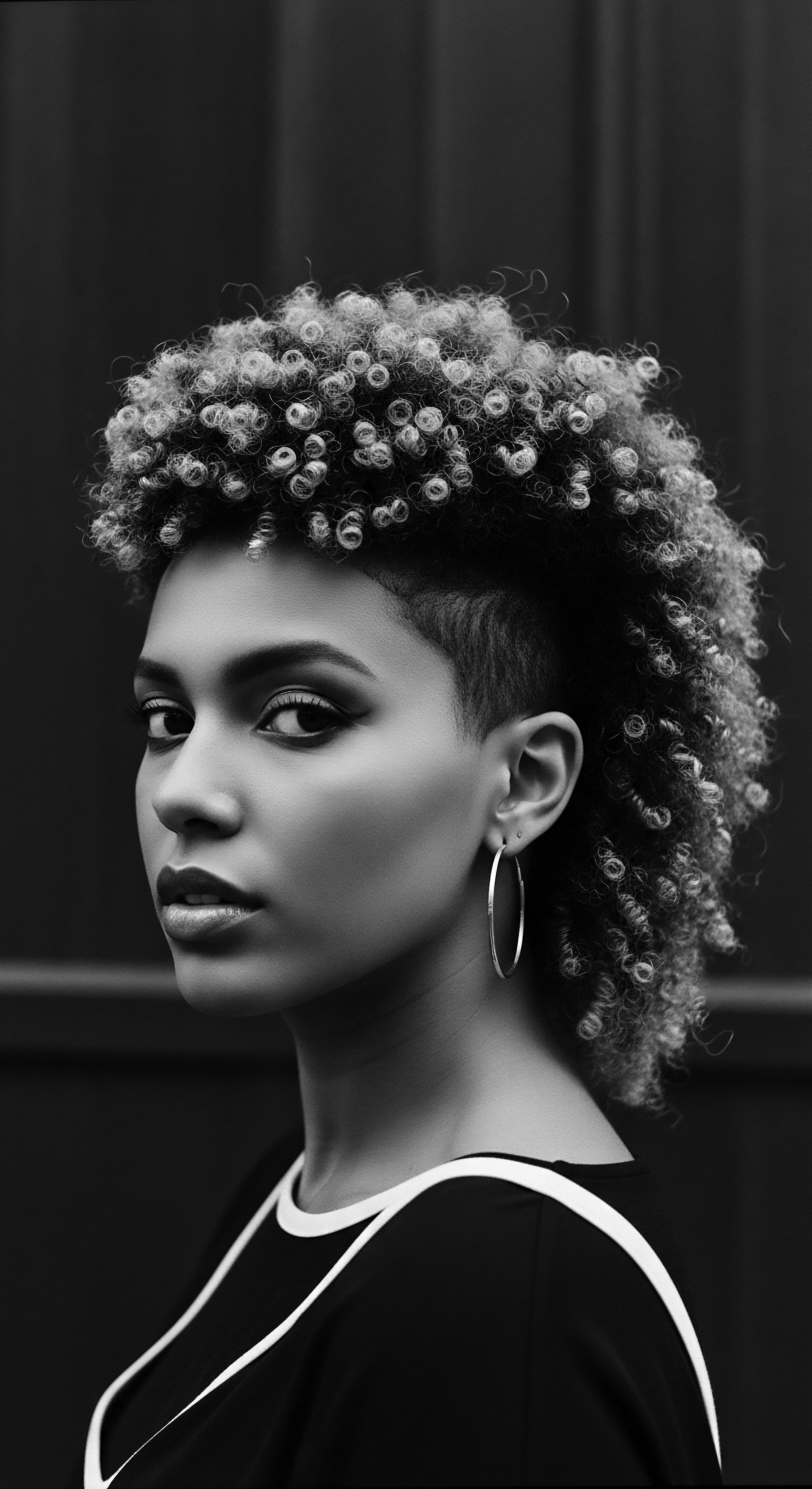

Why Is Hair Care a Significant Part of African Heritage?
Hair care in African heritage is a profound expression of identity, history, and communal bonds, deeply rooted in the unique characteristics of textured hair.
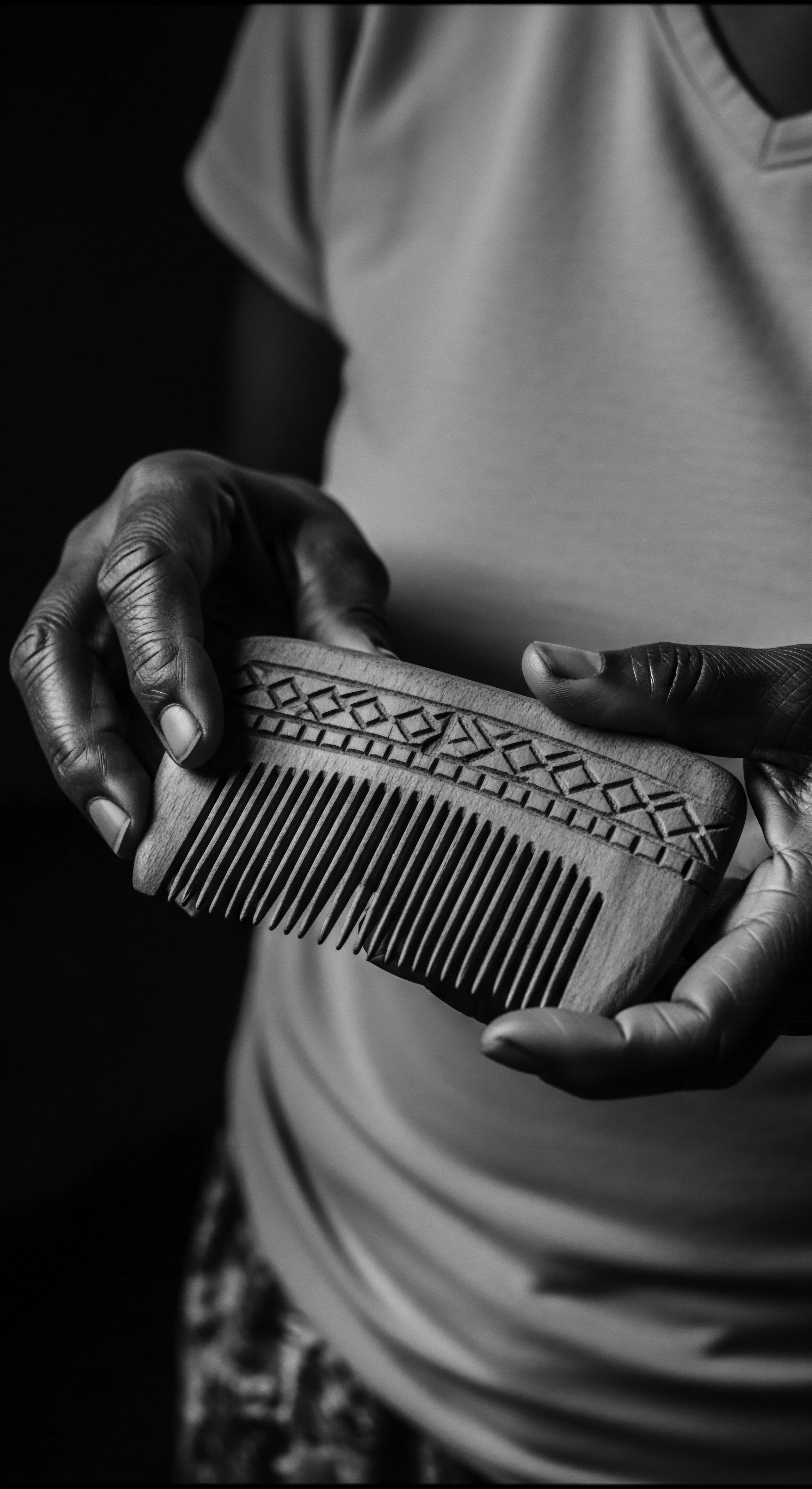

Black Hair Hue
Meaning ❉ The Black Hair Hue denotes the deep, rich coloration of textured hair, a biological trait deeply intertwined with cultural heritage and ancestral practices.

What Historical Significance Do Protective Styles Hold for Textured Hair Identity?
Protective styles for textured hair are historical markers of identity, resistance, and cultural preservation, deeply rooted in ancestral practices.
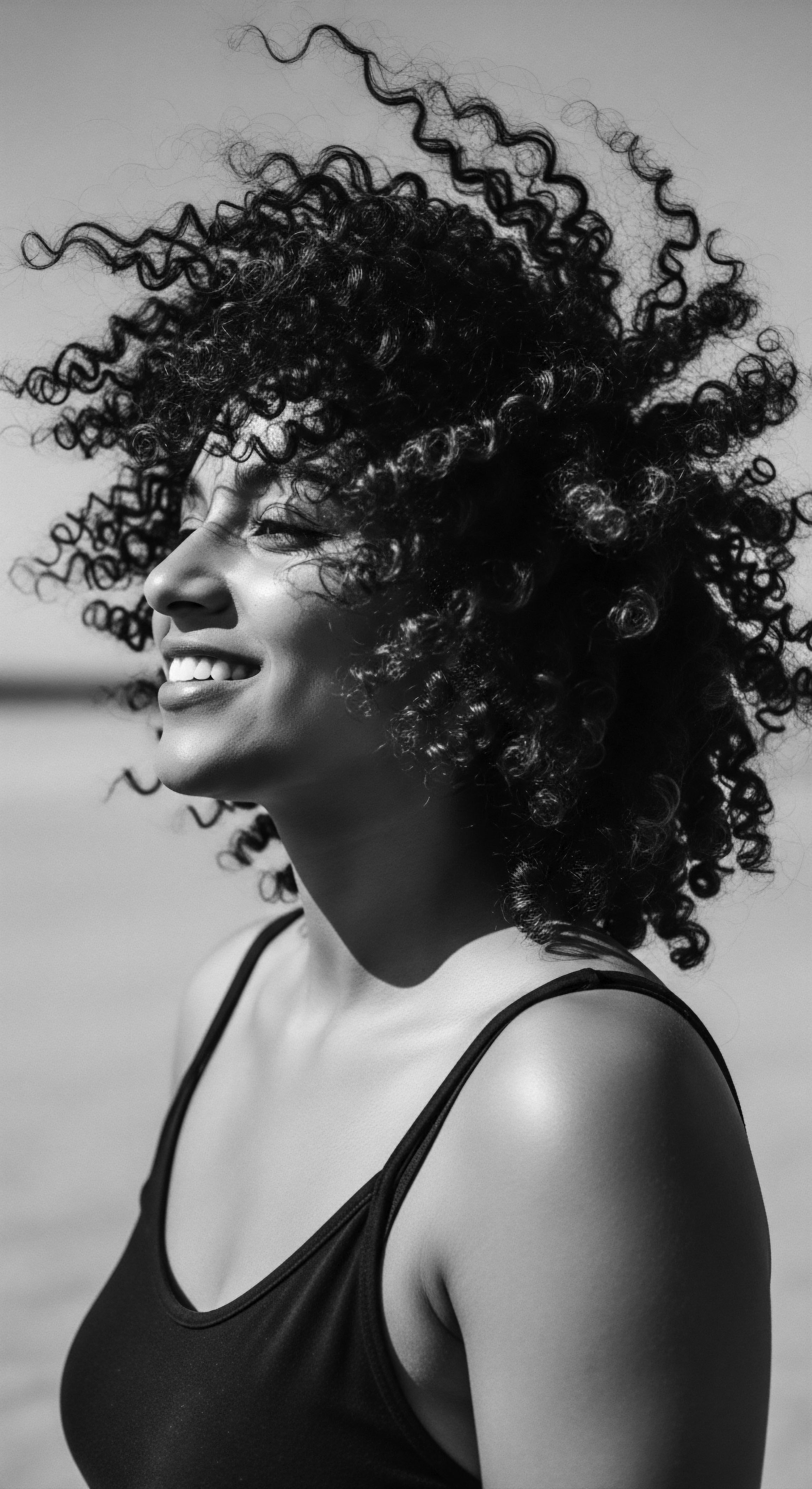

Ancestral Hair Shades
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Shades denote the inherited natural hair colors in textured hair, reflecting deep cultural, historical, and genetic legacies.

Wellness Connection
Meaning ❉ The Wellness Connection defines the profound, interwoven relationship between textured hair health and an individual's holistic well-being, rooted in ancestral practices.

Hair Refiner
Meaning ❉ The Hair Refiner is a conceptual lens for understanding textured hair's intrinsic qualities and historical journey, recognizing its unique structure and cultural significance.

Textured Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Policies encompass the formal and informal norms, expectations, and regulations shaping the perception and experience of textured hair across history and cultures.

Biocultural Significance
Meaning ❉ Biocultural Significance explores how hair's biology and cultural heritage are interwoven, particularly for textured hair experiences.

Hair Protection Methods
Meaning ❉ Hair Protection Methods are practices and styles that shield textured hair from damage, reduce manipulation, and preserve its cultural and historical meaning.

Racialized Beauty Standards
Meaning ❉ Racialized beauty standards are societal frameworks that unequally value physical traits based on race, often devaluing textured hair.

Natural Hair Insulation
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Insulation is the inherent capacity of hair, particularly textured hair, to provide thermal regulation for the scalp and body.

How Did Ancestral Hair Practices Influence Modern Understanding of Textured Hair Health?
Ancestral hair practices, rooted in deep cultural understanding, inform modern textured hair health by emphasizing moisture, protective styling, and natural ingredients.

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Rituals Shape Current Perceptions of Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical hair rituals profoundly shape current perceptions of textured hair heritage by linking ancient symbolism and resistance to modern identity and acceptance.

Follicle Asymmetry
Meaning ❉ Follicle Asymmetry describes the oval shape of hair follicles that determines the unique curl patterns of textured hair.

Afro-Textured Heritage
Meaning ❉ Afro-Textured Heritage signifies the deep cultural, historical, and biological significance of tightly coiled hair in Black and mixed-race communities.

Black Hair Knowledge
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Knowledge is the comprehensive understanding of textured hair's biological, historical, and cultural significance within Black and mixed-race communities.

Navajo Hair Archetype
Meaning ❉ The Navajo Hair Archetype defines hair as a sacred, living extension of identity and wisdom, deeply rooted in Diné cultural heritage.

How Did Early Laws Affect Textured Hair?
Early laws often sought to control textured hair, particularly through mandates like the Tignon Law, directly impacting Black and mixed-race hair heritage.

What Historical Examples Show the Resilience of Textured Hair Heritage?
Textured hair heritage demonstrates resilience through ancient cultural symbolism, resistance during oppression, and contemporary movements for identity and acceptance.

Cultural Hair Vitality
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Vitality is the profound connection between textured hair and ancestral heritage, embodying identity, history, and community resilience.

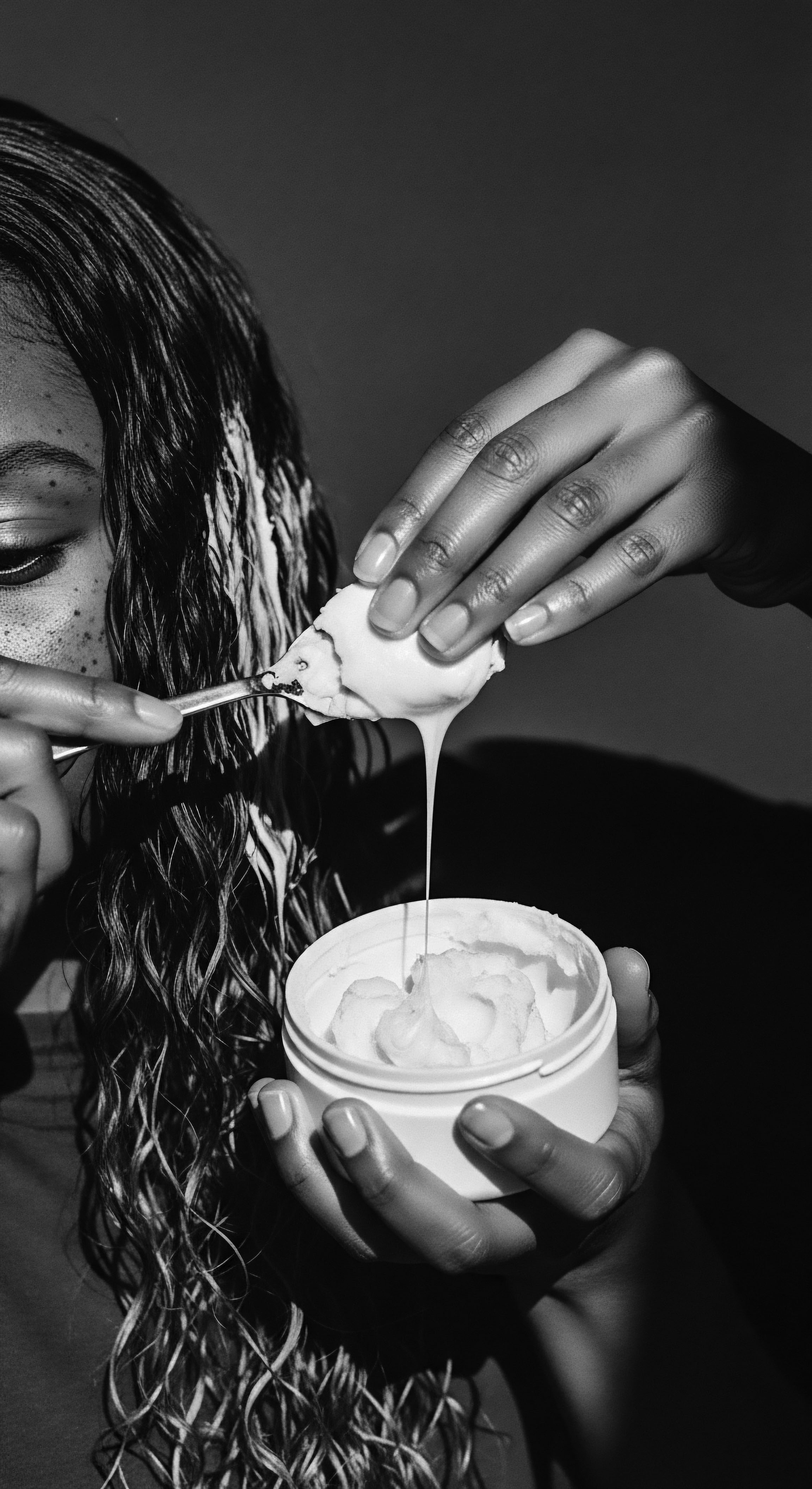
What Ancestral Botanical Ingredients Nourish Textured Hair?
Ancestral botanicals like shea butter, Chebe powder, and castor oil nourish textured hair, deeply rooted in Black and mixed-race heritage.

Hair Miniaturization
Meaning ❉ Hair miniaturization is the progressive shrinking of hair follicles, leading to finer, shorter, and less visible hair strands, deeply impacting textured hair heritage.

Hair Discrimination Jamaica
Meaning ❉ Hair discrimination in Jamaica is the prejudicial treatment of individuals based on their natural textured hair and traditional styles, rooted in colonial legacies.

What Ancestral Practices Continue to Inform Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral practices deeply inform modern textured hair care, connecting contemporary routines to a rich heritage of resilience and wisdom.

Boarding School Policies
Meaning ❉ This entry defines "Boarding School Policies" as the historical, cultural, and societal frameworks that have shaped the experience of textured hair.
Inherited Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Inherited Hair Practices are intergenerational care methods and cultural understandings of hair, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and the biological essence of textured hair.

Ancestral Hair Identity
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Identity is the inherent connection between textured hair and its deep historical, cultural, and biological legacies.

Spiritual Protection
Meaning ❉ Spiritual Protection defines the active safeguarding of textured hair's energetic and cultural integrity as a sacred conduit for ancestral wisdom and identity.

