
Women’s Work
Meaning ❉ "Women's Work" is the enduring, intergenerational practice of textured hair care, embodying cultural preservation and identity for Black and mixed-race communities.

What Historical Struggles and Acts of Resistance Are Tied to Black Hair Practices?
Black hair practices are intrinsically tied to historical struggles and resistance, serving as a powerful emblem of identity and heritage.

How Can Legal Protections Honor Ancestral Textured Hair Practices?
Legal protections honor ancestral textured hair practices by safeguarding cultural identity and ensuring freedom from discrimination.

How Does Hair Bias Affect Black Identity?
Hair bias profoundly affects Black identity by devaluing textured hair, severing ancestral connections, and eroding self-worth, despite its rich heritage.

What Is the Historical Importance of Protective Styles in Black Communities?
Protective styles hold profound historical importance as ancestral practices that preserved textured hair health, conveyed cultural identity, and served as acts of resistance for Black communities.

What Historical Laws Attempted to Control Textured Hair Traditions?
Historical laws, like the Tignon Law, attempted to control textured hair traditions to enforce racial hierarchy and suppress Black heritage.

Black Hair Care Science
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Care Science integrates the unique biology of textured hair with ancestral knowledge and its profound cultural significance.

What Cultural Significance Do Head Wraps Hold for Black Heritage?
Head wraps signify deep cultural heritage for Black communities, reflecting resilience, status, and protection for textured hair across generations.

In What Ways Does the CROWN Act Affirm Textured Hair as Cultural Heritage?
The CROWN Act enshrines textured hair and its protective styles as a vital component of cultural heritage, recognizing centuries of ancestral wisdom and identity.

How Does the CROWN Act Protect Textured Hair as Cultural Heritage Today?
The CROWN Act protects textured hair as cultural heritage by legally prohibiting discrimination against ancestral hairstyles and natural hair textures.

How Do Traditional Hair Practices Preserve Black Identity?
Traditional hair practices preserve Black identity by honoring ancestral knowledge, fostering community, and asserting cultural pride.

Community Hair Significance
Meaning ❉ Community Hair Significance explores the collective identity, shared practices, and historical memory hair embodies within cultural groups, particularly those of Black and mixed-race heritage.

What Historical Discrimination Did the CROWN Act Address regarding Hair?
The CROWN Act legally addresses a long history of systemic discrimination against textured hair and protective styles, affirming their deep connection to racial and cultural heritage.

How Do CROWN Act Provisions Recognize Ancestral Styles?
CROWN Act provisions protect ancestral hair textures and styles, recognizing them as integral to racial and cultural heritage.

Cultural Right
Meaning ❉ The Cultural Right is the inherent entitlement to preserve, express, and celebrate textured hair traditions and associated ancestral knowledge.

What Historical Examples Show the Cultural Power of Black Hair Care?
Black hair care manifests profound cultural power, historically serving as identity, spiritual connection, resistance, and a celebration of heritage.

What Is the Biological Foundation of Textured Hair Patterns?
Textured hair patterns stem from oval follicle shapes and varied keratin bonds, a biological foundation deeply linked to ancestral heritage and cultural identity.

What Is the Historical Meaning of Black Hair Styles?
Black hair styles are a profound historical record, reflecting identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom through textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Do Textured Hair Traditions Reflect Communal Resilience?
Textured hair traditions reflect communal resilience by preserving heritage, facilitating communication, and serving as visible acts of identity and defiance.

How Do Hair Laws Protect Textured Styles?
Hair laws protect textured styles by recognizing them as expressions of racial identity, affirming ancestral practices and challenging historical biases.

Can Traditional Hair Practices Be Legally Protected in Contemporary Society?
Traditional hair practices, central to textured hair heritage, seek legal protection as a vital assertion of cultural identity and human rights.

What Historical Prejudices Did the CROWN Act Address regarding Hair?
The CROWN Act confronts historical prejudices that marginalized textured hair, restoring dignity and protecting Black hair heritage from systemic discrimination.

Societal Meanings
Meaning ❉ The Societal Meanings of textured hair represent its interwoven cultural values, historical narratives, and communal roles within societies.
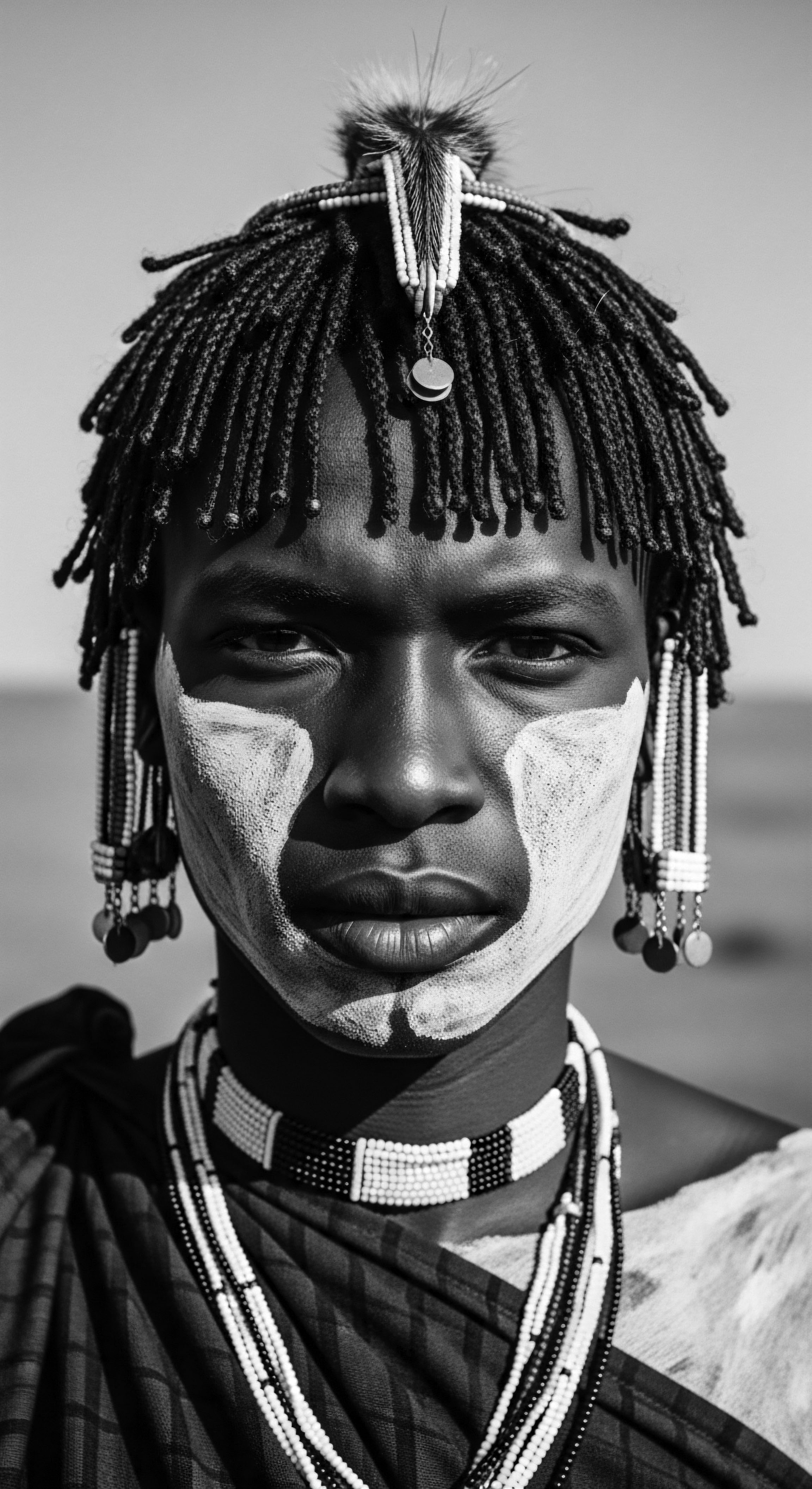

What Cultural Impact Does Hair Heritage Have on Personal Identity and Wellness?
Textured hair heritage profoundly shapes identity and wellness, serving as a powerful link to ancestral wisdom and a site of enduring cultural affirmation.

How Does Modern Legislation Honor Ancestral Hair Traditions and Cultural Practices?
Modern legislation like the CROWN Act honors ancestral hair traditions by legally protecting textured hair styles and cultural practices against discrimination, affirming their heritage.

How Did the Afro Become a Symbol of Black Identity and Political Resistance?
The Afro became a powerful symbol of Black identity and political resistance by visibly asserting self-acceptance and challenging dominant beauty norms, drawing from deep textured hair heritage.

Hair Adversities
Meaning ❉ Hair Adversities describes the multi-layered struggles faced by textured hair, arising from both its biology and socio-historical devaluation.
Dreadlock Politics
Meaning ❉ Dreadlock Politics explores the societal, cultural, and personal dimensions of dreadlocks, highlighting their role in identity, resistance, and heritage.

What Historical Laws Influenced Black Hair Expression and Identity?
Historical laws often sought to control Black hair, driving its expression underground yet fostering resilient forms of heritage-rich identity.

