Why Is Hair Heritage Legally Significant?
Hair heritage is legally significant because it represents an intrinsic part of identity and cultural expression for textured hair communities.

What Cultural Significance Do Ancestral Oils Hold for Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancestral oils symbolize deep heritage for textured hair, representing historical resilience, cultural identity, and intergenerational care practices.

What Historical Struggles Led to Current Hair Discrimination Laws Protecting Black Heritage?
Historical struggles against racial prejudice and Eurocentric beauty standards led to current hair discrimination laws protecting Black heritage.
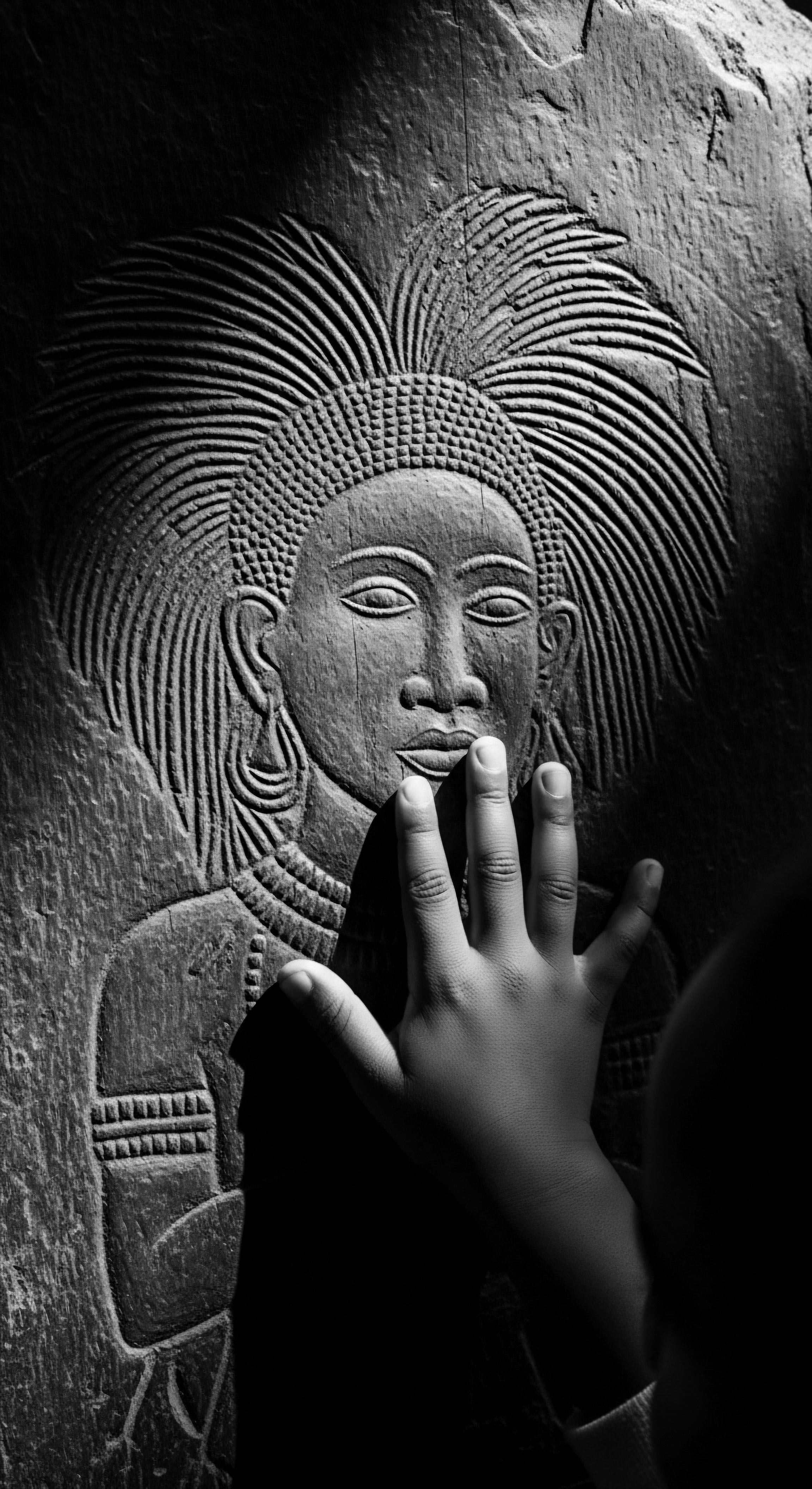

What Is the Cultural Significance of Textured Hair Rituals Throughout History?
Textured hair rituals, deeply rooted in ancestral practices, represent a profound cultural legacy of identity, communication, and resilience.

New Orleans Culture
Meaning ❉ New Orleans culture signifies a dynamic confluence of African, French, Spanish, and Indigenous heritage, deeply expressed through its textured hair traditions.

Self-Acceptance through Hair
Meaning ❉ The profound internal affirmation of one's natural textured hair, celebrating its unique characteristics and ancestral legacy without external conformity.

Indigenous Hair Solutions
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Hair Solutions refer to ancestral, culturally rooted practices and botanicals for textured hair, embodying identity, community, and resilience.

Black Identity Heritage
Meaning ❉ Black Identity Heritage defines the profound cultural, historical, and biological significance of textured hair within Black and mixed-race communities.

African Hair Philosophies
Meaning ❉ African Hair Philosophies delineate hair as a profound cultural archive, intertwining ancestral wisdom, identity, and resilience within textured hair heritage.
Black Hair Autonomy
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Autonomy is the inherent right to define, style, and present one's textured hair free from external constraint or societal prejudice.

Hair Heritage Protection
Meaning ❉ Hair Heritage Protection safeguards the ancestral legacy, cultural identity, and wellbeing intrinsically linked to diverse textured hair, particularly Black and mixed-race hair.

Hair Standards
Meaning ❉ Hair Standards define criteria for hair's appearance and health, historically shaped by cultural heritage and, for textured hair, by legacies of discrimination and resilience.

Hair Bias Laws
Meaning ❉ Hair Bias Laws are legislative measures that prohibit discrimination based on hair texture and styles historically associated with race.

Ori Cosmology
Meaning ❉ Ori Cosmology defines the spiritual and destined connection of the head and hair, revealing a profound heritage of textured hair identity and care.

Holistic Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Holistic Hair Traditions honor textured hair as a sacred extension of self, deeply connected to ancestral wisdom, identity, and community well-being.

Cultural Sovereignty
Meaning ❉ Cultural Sovereignty in textured hair is the inherent right of communities to define, preserve, and celebrate their hair's identity and practices.

In What Ways Did the Black Power Movement Redefine Textured Hair Identity and Cultural Pride?
The Black Power movement redefined textured hair identity by championing natural styles as symbols of cultural pride and resistance against Eurocentric beauty norms.

African Hair Ontology
Meaning ❉ The African Hair Ontology is a framework that understands textured hair as a living archive of ancestral memory, cultural codes, and personal narratives.

What Is the Historical Link between Textured Hair and Communal Well-Being?
Textured hair heritage profoundly links to communal well-being through shared identity, spiritual connection, and collective resistance across generations.

Natural Hair Community
Meaning ❉ The Natural Hair Community is a global movement celebrating and preserving the cultural heritage and diverse textures of Black and mixed-race hair.

Plant-Based Hair Wellness
Meaning ❉ Plant-Based Hair Wellness defines a holistic approach to hair care that honors ancestral botanical practices, particularly for textured hair, promoting health and cultural identity.

Ancestral Hair Respect
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Respect recognizes the deep historical, cultural, and spiritual meaning of textured hair, particularly within Black and mixed-race lineages.

Afro-Diasporic Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Afro-Diasporic Hair Traditions define the collective practices and profound meanings of textured hair among people of African descent, reflecting a rich heritage of resilience and identity.

Diasporic Beauty Rituals
Meaning ❉ Diasporic Beauty Rituals are living traditions of hair and body care from African descendant communities, embodying cultural memory and identity.

What Historical Laws Suppressed Textured Hair Expression?
Historical laws like the Tignon Law suppressed textured hair expression, yet Black communities transformed these mandates into acts of cultural affirmation.

Resistance Symbols
Meaning ❉ Resistance Symbols delineate the profound cultural and historical significance of textured hair as a declaration of identity and enduring defiance.

Professionalism
Meaning ❉ Professionalism, for textured hair, is the skilled, ethical application of care rooted in ancestral wisdom and the courageous affirmation of cultural identity.

What Legal Protections Honor Textured Hair Heritage Today?
Legal protections like the CROWN Act safeguard textured hair heritage by prohibiting discrimination based on hair texture and protective styles.

Hair Health Heritage
Meaning ❉ Hair Health Heritage is the inherited blueprint and cultural wisdom of hair care, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and identity, particularly for textured hair.

